决策树
决策树可以理解为是一颗倒立的树,叶子在下端,根在最上面
一层一层连接的是交内部节点,内部节点主要是一些条件判断表达式,叶子叫叶节点,叶节点其实就是最终的预测结果,那么当输入x进去,一层一层的进行选择,就到最后的叶子节点,就完成整个流程,叶子节点的值就是最终的值。
决策树经常用来做分类任务,下面是基本的决策树的结构
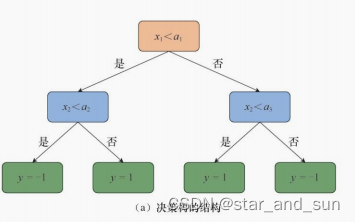
决策树的构造
在构造决策树的时候需要尽可能的减少模型的复杂度,可见决策树的层数和节点数不要过多才最好。
x,y的取值范围是1,。。。,n 则信息熵的公式
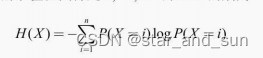
交叉熵
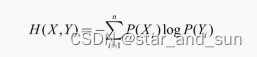
条件熵
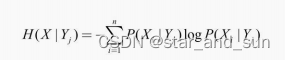
信息增益
**i=h(x)-h(x|y)**
信息增益率
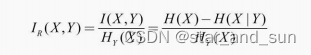
其中
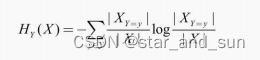
采用信息增益率可以减少模型整体的复杂度。
id3和c4.5
id3算法是基于信息增益来做的,c4.5是结合信息增益率来做的,只能解决分类问题。

cart算法
id3算法,c4.5只能解决分类问题。在回归问题中,采用cart算法,其采用了误差的平方作为标准

此外cart算法可以解决分类问题

import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
# 读取数据
data = pd.read_csv('titanic/train.csv')
# 查看数据集信息和前5行具体内容,其中nan代表数据缺失
print(data.info())
print(data[:5])
# 删去编号、姓名、船票编号3列
data.drop(columns=['passengerid', 'name', 'ticket'], inplace=true)
#%%
feat_ranges = {}
cont_feat = ['age', 'fare'] # 连续特征
bins = 10 # 分类点数
for feat in cont_feat:
# 数据集中存在缺省值nan,需要用np.nanmin和np.nanmax
min_val = np.nanmin(data[feat])
max_val = np.nanmax(data[feat])
feat_ranges[feat] = np.linspace(min_val, max_val, bins).tolist()
print(feat, ':') # 查看分类点
for spt in feat_ranges[feat]:
print(f'{spt:.4f}')
#%%
# 只有有限取值的离散特征
cat_feat = ['sex', 'pclass', 'sibsp', 'parch', 'cabin', 'embarked']
for feat in cat_feat:
data[feat] = data[feat].astype('category') # 数据格式转为分类格式
print(f'{feat}:{data[feat].cat.categories}') # 查看类别
data[feat] = data[feat].cat.codes.to_list() # 将类别按顺序转换为整数
ranges = list(set(data[feat]))
ranges.sort()
feat_ranges[feat] = ranges
#%%
# 将所有缺省值替换为-1
data.fillna(-1, inplace=true)
for feat in feat_ranges.keys():
feat_ranges[feat] = [-1] + feat_ranges[feat]
#%%
# 划分训练集与测试集
np.random.seed(0)
feat_names = data.columns[1:]
label_name = data.columns[0]
# 重排下标之后,按新的下标索引数据
data = data.reindex(np.random.permutation(data.index))
ratio = 0.8
split = int(ratio * len(data))
train_x = data[:split].drop(columns=['survived']).to_numpy()
train_y = data['survived'][:split].to_numpy()
test_x = data[split:].drop(columns=['survived']).to_numpy()
test_y = data['survived'][split:].to_numpy()
print('训练集大小:', len(train_x))
print('测试集大小:', len(test_x))
print('特征数:', train_x.shape[1])
#%%
class node:
def __init__(self):
# 内部结点的feat表示用来分类的特征编号,其数字与数据中的顺序对应
# 叶结点的feat表示该结点对应的分类结果
self.feat = none
# 分类值列表,表示按照其中的值向子结点分类
self.split = none
# 子结点列表,叶结点的child为空
self.child = []
#%%
class decisiontree:
def __init__(self, x, y, feat_ranges, lbd):
self.root = node()
self.x = x
self.y = y
self.feat_ranges = feat_ranges # 特征取值范围
self.lbd = lbd # 正则化系数
self.eps = 1e-8 # 防止数学错误log(0)和除以0
self.t = 0 # 记录叶结点个数
self.id3(self.root, self.x, self.y)
# 工具函数,计算 a * log a
def aloga(self, a):
return a * np.log2(a + self.eps)
# 计算某个子数据集的熵
def entropy(self, y):
cnt = np.unique(y, return_counts=true)[1] # 统计每个类别出现的次数
n = len(y)
ent = -np.sum([self.aloga(ni / n) for ni in cnt])
return ent
# 计算用feat <= val划分数据集的信息增益
def info_gain(self, x, y, feat, val):
# 划分前的熵
n = len(y)
if n == 0:
return 0
hx = self.entropy(y)
hxy = 0 # h(x|y)
# 分别计算h(x|x_f<=val)和h(x|x_f>val)
y_l = y[x[:, feat] <= val]
hxy += len(y_l) / len(y) * self.entropy(y_l)
y_r = y[x[:, feat] > val]
hxy += len(y_r) / len(y) * self.entropy(y_r)
return hx - hxy
# 计算特征feat <= val本身的复杂度h_y(x)
def entropy_yx(self, x, y, feat, val):
hyx = 0
n = len(y)
if n == 0:
return 0
y_l = y[x[:, feat] <= val]
hyx += -self.aloga(len(y_l) / n)
y_r = y[x[:, feat] > val]
hyx += -self.aloga(len(y_r) / n)
return hyx
# 计算用feat <= val划分数据集的信息增益率
def info_gain_ratio(self, x, y, feat, val):
ig = self.info_gain(x, y, feat, val)
hyx = self.entropy_yx(x, y, feat, val)
return ig / hyx
# 用id3算法递归分裂结点,构造决策树
def id3(self, node, x, y):
# 判断是否已经分类完成
if len(np.unique(y)) == 1:
node.feat = y[0]
self.t += 1
return
# 寻找最优分类特征和分类点
best_igr = 0
best_feat = none
best_val = none
for feat in range(len(feat_names)):
for val in self.feat_ranges[feat_names[feat]]:
igr = self.info_gain_ratio(x, y, feat, val)
if igr > best_igr:
best_igr = igr
best_feat = feat
best_val = val
# 计算用best_feat <= best_val分类带来的代价函数变化
# 由于分裂叶结点只涉及该局部,我们只需要计算分裂前后该结点的代价函数
# 当前代价
cur_cost = len(y) * self.entropy(y) + self.lbd
# 分裂后的代价,按best_feat的取值分类统计
# 如果best_feat为none,说明最优的信息增益率为0,
# 再分类也无法增加信息了,因此将new_cost设置为无穷大
if best_feat is none:
new_cost = np.inf
else:
new_cost = 0
x_feat = x[:, best_feat]
# 获取划分后的两部分,计算新的熵
new_y_l = y[x_feat <= best_val]
new_cost += len(new_y_l) * self.entropy(new_y_l)
new_y_r = y[x_feat > best_val]
new_cost += len(new_y_r) * self.entropy(new_y_r)
# 分裂后会有两个叶结点
new_cost += 2 * self.lbd
if new_cost <= cur_cost:
# 如果分裂后代价更小,那么执行分裂
node.feat = best_feat
node.split = best_val
l_child = node()
l_x = x[x_feat <= best_val]
l_y = y[x_feat <= best_val]
self.id3(l_child, l_x, l_y)
r_child = node()
r_x = x[x_feat > best_val]
r_y = y[x_feat > best_val]
self.id3(r_child, r_x, r_y)
node.child = [l_child, r_child]
else:
# 否则将当前结点上最多的类别作为该结点的类别
vals, cnt = np.unique(y, return_counts=true)
node.feat = vals[np.argmax(cnt)]
self.t += 1
# 预测新样本的分类
def predict(self, x):
node = self.root
# 从根结点开始向下寻找,到叶结点结束
while node.split is not none:
# 判断x应该处于哪个子结点
if x[node.feat] <= node.split:
node = node.child[0]
else:
node = node.child[1]
# 到达叶结点,返回类别
return node.feat
# 计算在样本x,标签y上的准确率
def accuracy(self, x, y):
correct = 0
for x, y in zip(x, y):
pred = self.predict(x)
if pred == y:
correct += 1
return correct / len(y)
#%%
dt = decisiontree(train_x, train_y, feat_ranges, lbd=1.0)
print('叶结点数量:', dt.t)
# 计算在训练集和测试集上的准确率
print('训练集准确率:', dt.accuracy(train_x, train_y))
print('测试集准确率:', dt.accuracy(test_x, test_y))
#%%
from sklearn import tree
# criterion表示分类依据,max_depth表示树的最大深度
# entropy生成的是c4.5分类树
c45 = tree.decisiontreeclassifier(criterion='entropy', max_depth=6)
c45.fit(train_x, train_y)
# gini生成的是cart分类树
cart = tree.decisiontreeclassifier(criterion='gini', max_depth=6)
cart.fit(train_x, train_y)
c45_train_pred = c45.predict(train_x)
c45_test_pred = c45.predict(test_x)
cart_train_pred = cart.predict(train_x)
cart_test_pred = cart.predict(test_x)
print(f'训练集准确率:c4.5:{np.mean(c45_train_pred == train_y)},' \
f'cart:{np.mean(cart_train_pred == train_y)}')
print(f'测试集准确率:c4.5:{np.mean(c45_test_pred == test_y)},' \
f'cart:{np.mean(cart_test_pred == test_y)}')
#%%
!pip install pydotplus
from six import stringio
import pydotplus
dot_data = stringio()
tree.export_graphviz( # 导出sklearn的决策树的可视化数据
c45,
out_file=dot_data,
feature_names=feat_names,
class_names=['non-survival', 'survival'],
filled=true,
rounded=true,
impurity=false
)
# 用pydotplus生成图像
graph = pydotplus.graph_from_dot_data(
dot_data.getvalue().replace('\n', ''))
graph.write_png('tree.png')


![常用数据聚类算法总结记录与代码实现[K-means/层次聚类/DBSACN/高斯混合模型(GMM)/密度峰值聚类/均值漂移聚类/谱聚类等]](https://images.3wcode.com/3wcode/20240804/s_0_202408042021086355.png)
发表评论