如何用sql语言查询多个excel表格
没错,之前我也不知道sql语言除了可以查询(本文只讨论查询语句)数据库,还可以查询excel,或者说经过一定处理后,可以像查询数据库一样查询excel。
下面给出一个场景,假如你有几个(个数未知)excel表格,你想在这些表格上实现sql多表查询,该怎么办?
像这样:
| 学号 | 姓名 |
| 1054 | 小姜 |
| 1055 | 小王 |
| 1061 | 小李 |
| 1081 | 王哥 |
| 课程名称 | 任课老师 |
| 人工智能 | 王老师 |
| 数据库 | 李老师 |
| 运筹学 | 张老师 |
| 概率论 | 郝老师 |
| 学号 | 课程名称 | 分数 |
| 1054 | 人工智能 | 90 |
| 1055 | 数据库 | 91 |
| 1061 | 运筹学 | 92 |
| 1081 | 概率论 | 91 |
| 1054 | 运筹学 | 89 |
| 1055 | 概率论 | 91 |
| 1061 | 人工智能 | 95 |
| 1081 | 数据库 | 94 |
大致思路如下:
- 将所有要导入的excel表放入一个.xlsx文件中,将各sheet命名为表名,类似数据库的table名;
- 利用pandas库读取.xlsx文件并创建为一个excelfile类;
- 利用类中名为sheet_names的property获取其所有该文件所有的sheet名;
- 用locals和read_excel函数创建名为各sheet名,值为各sheet内容的局部变量;
- 利用pandasql库中的sqldf来查询一个或多个dataframe,sqldf函数默认查询所有局部变量中的dataframe。
利用pandasql库中的sqldf来查询一个或多个dataframe,sqldf函数默认查询所有局部变量中的dataframe。
代码如下:
import pandas as pd
from pandasql import sqldf
def dealwith_excel(excel_file,sql_query):
xls = pd.excelfile(excel_file)
sheet_names = xls.sheet_names #list type
# print(sheet_names)
for sheet_name in sheet_names:
locals()[sheet_name] = pd.read_excel(excel_file, sheet_name=sheet_name)
df_result = sqldf(sql_query)
return df_result最后返回的就是查询结果!
扩展:
如何使用sql查询excel内容
1. 简介
我们在前面的文章中提到了calcite支持csv和json文件的数据源适配, 其实就是将文件解析成表然后以文件夹为schema, 然后将生成的schema注册到rootsehema(rootschema是所有数据源schema的parent,多个不同数据源schema可以挂在同一个rootschema下)下, 最终使用calcite的特性进行sql的解析查询返回.
但其实我们的数据文件一般使用excel进行存储,流转, 但很可惜, calcite本身没有excel的适配器, 但其实我们可以模仿calcite-file, 自己搞一个calcite-file-excel, 也可以熟悉calcite的工作原理.
2. 实现思路
因为excel有sheet的概念, 所以可以将一个excel解析成schema, 每个sheet解析成table, 实现步骤如下:
- 实现
schemafactory重写create方法: schema工厂 用于创建schema - 继承
abstractschema: schema描述类 用于解析excel, 创建table(解析sheet) - 继承
abstracttable, scannabletable: table描述类 提供字段信息和数据内容等(解析sheet data)
3. excel样例
excel有两个sheet页, 分别是user_info 和 role_info如下:
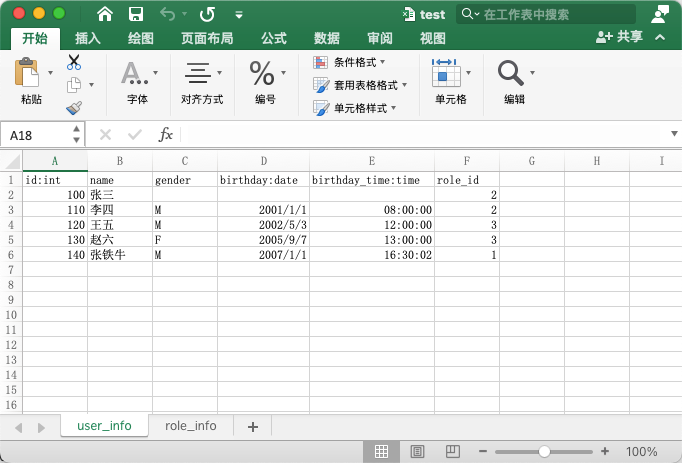
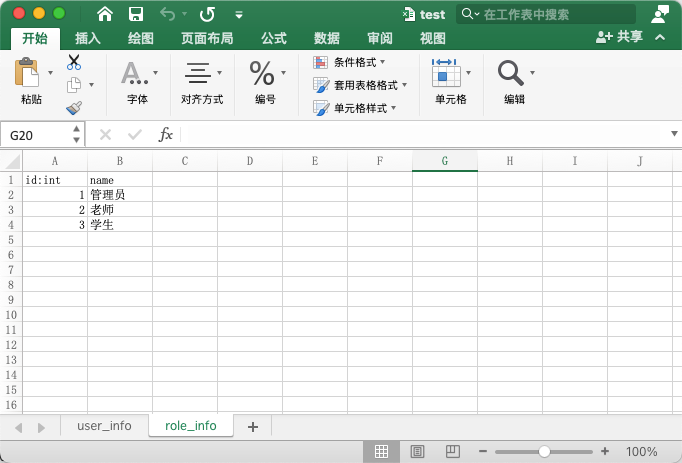
ok, 万事具备.
4. maven
<dependency>
<groupid>org.apache.poi</groupid>
<artifactid>poi-ooxml</artifactid>
<version>5.2.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupid>org.apache.poi</groupid>
<artifactid>poi</artifactid>
<version>5.2.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupid>org.apache.calcite</groupid>
<artifactid>calcite-core</artifactid>
<version>1.37.0</version>
</dependency>5. 核心代码
5.1 schemafactory
package com.ldx.calcite.excel;
import com.google.common.collect.lists;
import org.apache.calcite.schema.schema;
import org.apache.calcite.schema.schemafactory;
import org.apache.calcite.schema.schemaplus;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.objectutils;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.stringutils;
import java.io.file;
import java.util.list;
import java.util.map;
/**
* schema factory
*/
public class excelschemafactory implements schemafactory {
public final static excelschemafactory instance = new excelschemafactory();
private excelschemafactory(){}
@override
public schema create(schemaplus parentschema, string name, map<string, object> operand) {
final object filepath = operand.get("filepath");
if (objectutils.isempty(filepath)) {
throw new nullpointerexception("can not find excel file");
}
return this.create(filepath.tostring());
}
public schema create(string excelfilepath) {
if (stringutils.isblank(excelfilepath)) {
throw new nullpointerexception("can not find excel file");
}
return this.create(new file(excelfilepath));
}
public schema create(file excelfile) {
if (objectutils.isempty(excelfile) || !excelfile.exists()) {
throw new nullpointerexception("can not find excel file");
}
if (!excelfile.isfile() || !isexcelfile(excelfile)) {
throw new runtimeexception("can not find excel file: " + excelfile.getabsolutepath());
}
return new excelschema(excelfile);
}
protected list<string> supportedfilesuffix() {
return lists.newarraylist("xls", "xlsx");
}
private boolean isexcelfile(file excelfile) {
if (objectutils.isempty(excelfile)) {
return false;
}
final string name = excelfile.getname();
return stringutils.endswithany(name, this.supportedfilesuffix().toarray(new string[0]));
}
}schema中有多个重载的create方法用于方便的创建schema, 最终将excel file 交给excelschema创建一个schema对象
5.2 schema
package com.ldx.calcite.excel;
import org.apache.calcite.schema.table;
import org.apache.calcite.schema.impl.abstractschema;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.objectutils;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.sheet;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.workbook;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.workbookfactory;
import org.testng.collections.maps;
import java.io.file;
import java.util.iterator;
import java.util.map;
/**
* schema
*/
public class excelschema extends abstractschema {
private final file excelfile;
private map<string, table> tablemap;
public excelschema(file excelfile) {
this.excelfile = excelfile;
}
@override
protected map<string, table> gettablemap() {
if (objectutils.isempty(tablemap)) {
tablemap = createtablemap();
}
return tablemap;
}
private map<string, table> createtablemap() {
final map<string, table> result = maps.newhashmap();
try (workbook workbook = workbookfactory.create(excelfile)) {
final iterator<sheet> sheetiterator = workbook.sheetiterator();
while (sheetiterator.hasnext()) {
final sheet sheet = sheetiterator.next();
final excelscannabletable excelscannabletable = new excelscannabletable(sheet, null);
result.put(sheet.getsheetname(), excelscannabletable);
}
}
catch (exception ignored) {}
return result;
}
}schema类读取excel file, 并循环读取sheet, 将每个sheet解析成excelscannabletable并存储
5.3 table
package com.ldx.calcite.excel;
import com.google.common.collect.lists;
import com.ldx.calcite.excel.enums.javafiletypeenum;
import org.apache.calcite.datacontext;
import org.apache.calcite.adapter.java.javatypefactory;
import org.apache.calcite.linq4j.enumerable;
import org.apache.calcite.linq4j.linq4j;
import org.apache.calcite.rel.type.reldatatype;
import org.apache.calcite.rel.type.reldatatypefactory;
import org.apache.calcite.rel.type.relprotodatatype;
import org.apache.calcite.schema.scannabletable;
import org.apache.calcite.schema.impl.abstracttable;
import org.apache.calcite.sql.type.sqltypename;
import org.apache.calcite.util.pair;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.objectutils;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.cell;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.row;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.sheet;
import org.checkerframework.checker.nullness.qual.nullable;
import java.util.list;
/**
* table
*/
public class excelscannabletable extends abstracttable implements scannabletable {
private final relprotodatatype protorowtype;
private final sheet sheet;
private reldatatype rowtype;
private list<javafiletypeenum> fieldtypes;
private list<object[]> rowdatalist;
public excelscannabletable(sheet sheet, relprotodatatype protorowtype) {
this.protorowtype = protorowtype;
this.sheet = sheet;
}
@override
public enumerable<@nullable object[]> scan(datacontext root) {
javatypefactory typefactory = root.gettypefactory();
final list<javafiletypeenum> fieldtypes = this.getfieldtypes(typefactory);
if (rowdatalist == null) {
rowdatalist = readexceldata(sheet, fieldtypes);
}
return linq4j.asenumerable(rowdatalist);
}
@override
public reldatatype getrowtype(reldatatypefactory typefactory) {
if (objectutils.isnotempty(protorowtype)) {
return protorowtype.apply(typefactory);
}
if (objectutils.isempty(rowtype)) {
rowtype = deducerowtype((javatypefactory) typefactory, sheet, null);
}
return rowtype;
}
public list<javafiletypeenum> getfieldtypes(reldatatypefactory typefactory) {
if (fieldtypes == null) {
fieldtypes = lists.newarraylist();
deducerowtype((javatypefactory) typefactory, sheet, fieldtypes);
}
return fieldtypes;
}
private list<object[]> readexceldata(sheet sheet, list<javafiletypeenum> fieldtypes) {
list<object[]> rowdatalist = lists.newarraylist();
for (int rowindex = 1; rowindex <= sheet.getlastrownum(); rowindex++) {
row row = sheet.getrow(rowindex);
object[] rowdata = new object[fieldtypes.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < row.getlastcellnum(); i++) {
final javafiletypeenum javafiletypeenum = fieldtypes.get(i);
cell cell = row.getcell(i, row.missingcellpolicy.create_null_as_blank);
final object cellvalue = javafiletypeenum.getcellvalue(cell);
rowdata[i] = cellvalue;
}
rowdatalist.add(rowdata);
}
return rowdatalist;
}
public static reldatatype deducerowtype(javatypefactory typefactory, sheet sheet, list<javafiletypeenum> fieldtypes) {
final list<string> names = lists.newarraylist();
final list<reldatatype> types = lists.newarraylist();
if (sheet != null) {
row headerrow = sheet.getrow(0);
if (headerrow != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < headerrow.getlastcellnum(); i++) {
cell cell = headerrow.getcell(i, row.missingcellpolicy.create_null_as_blank);
string[] columninfo = cell
.getstringcellvalue()
.split(":");
string columnname = columninfo[0].trim();
string columntype = null;
if (columninfo.length == 2) {
columntype = columninfo[1].trim();
}
final javafiletypeenum javafiletype = javafiletypeenum
.of(columntype)
.orelse(javafiletypeenum.unknown);
final reldatatype sqltype = typefactory.createsqltype(javafiletype.getsqltypename());
names.add(columnname);
types.add(sqltype);
if (fieldtypes != null) {
fieldtypes.add(javafiletype);
}
}
}
}
if (names.isempty()) {
names.add("line");
types.add(typefactory.createsqltype(sqltypename.varchar));
}
return typefactory.createstructtype(pair.zip(names, types));
}
}table类中其中有两个比较关键的方法
scan: 扫描表内容, 我们这里将sheet页面的数据内容解析存储最后交给calcite
getrowtype: 获取字段信息, 我们这里默认使用第一条记录作为表头(row[0]) 并解析为字段信息, 字段规则跟csv一样 name:string, 冒号前面的是字段key, 冒号后面的是字段类型, 如果未指定字段类型, 则解析为unknown, 后续javafiletypeenum会进行类型推断, 最终在结果处理时calcite也会进行推断
deducerowtype: 推断字段类型, 方法中使用javafiletypeenum枚举类对java type & sql type & 字段值转化处理方法 进行管理
5.4 columntypeenum
package com.ldx.calcite.excel.enums;
import lombok.getter;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.slf4j;
import org.apache.calcite.avatica.util.datetimeutils;
import org.apache.calcite.sql.type.sqltypename;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.objectutils;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.stringutils;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.time.fastdateformat;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.cell;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.dateutil;
import org.apache.poi.ss.util.cellutil;
import java.text.parseexception;
import java.text.simpledateformat;
import java.util.arrays;
import java.util.date;
import java.util.optional;
import java.util.timezone;
import java.util.function.function;
/**
* type converter
*/
@slf4j
@getter
public enum javafiletypeenum {
string("string", sqltypename.varchar, cell::getstringcellvalue),
boolean("boolean", sqltypename.boolean, cell::getbooleancellvalue),
byte("byte", sqltypename.tinyint, cell::getstringcellvalue),
char("char", sqltypename.char, cell::getstringcellvalue),
short("short", sqltypename.smallint, cell::getnumericcellvalue),
int("int", sqltypename.integer, cell -> (double.valueof(cell.getnumericcellvalue()).intvalue())),
long("long", sqltypename.bigint, cell -> (double.valueof(cell.getnumericcellvalue()).longvalue())),
float("float", sqltypename.real, cell::getnumericcellvalue),
double("double", sqltypename.double, cell::getnumericcellvalue),
date("date", sqltypename.date, getvaluewithdate()),
timestamp("timestamp", sqltypename.timestamp, getvaluewithtimestamp()),
time("time", sqltypename.time, getvaluewithtime()),
unknown("unknown", sqltypename.unknown, getvaluewithunknown()),;
// cell type
private final string typename;
// sql type
private final sqltypename sqltypename;
// value convert func
private final function<cell, object> cellvaluefunc;
private static final fastdateformat time_format_date;
private static final fastdateformat time_format_time;
private static final fastdateformat time_format_timestamp;
static {
final timezone gmt = timezone.gettimezone("gmt");
time_format_date = fastdateformat.getinstance("yyyy-mm-dd", gmt);
time_format_time = fastdateformat.getinstance("hh:mm:ss", gmt);
time_format_timestamp = fastdateformat.getinstance("yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm:ss", gmt);
}
javafiletypeenum(string typename, sqltypename sqltypename, function<cell, object> cellvaluefunc) {
this.typename = typename;
this.sqltypename = sqltypename;
this.cellvaluefunc = cellvaluefunc;
}
public static optional<javafiletypeenum> of(string typename) {
return arrays
.stream(values())
.filter(type -> stringutils.equalsignorecase(typename, type.gettypename()))
.findfirst();
}
public static sqltypename findsqltypename(string typename) {
final optional<javafiletypeenum> javafiletypeoptional = of(typename);
if (javafiletypeoptional.ispresent()) {
return javafiletypeoptional
.get()
.getsqltypename();
}
return sqltypename.unknown;
}
public object getcellvalue(cell cell) {
return cellvaluefunc.apply(cell);
}
public static function<cell, object> getvaluewithunknown() {
return cell -> {
if (objectutils.isempty(cell)) {
return null;
}
switch (cell.getcelltype()) {
case string:
return cell.getstringcellvalue();
case numeric:
if (dateutil.iscelldateformatted(cell)) {
// 如果是日期类型,返回日期对象
return cell.getdatecellvalue();
}
else {
// 否则返回数值
return cell.getnumericcellvalue();
}
case boolean:
return cell.getbooleancellvalue();
case formula:
// 对于公式单元格,先计算公式结果,再获取其值
try {
return cell.getnumericcellvalue();
}
catch (exception e) {
try {
return cell.getstringcellvalue();
}
catch (exception ex) {
log.error("parse unknown data error, cellrowindex:{}, cellcolumnindex:{}", cell.getrowindex(), cell.getcolumnindex(), e);
return null;
}
}
case blank:
return "";
default:
return null;
}
};
}
public static function<cell, object> getvaluewithdate() {
return cell -> {
date date = cell.getdatecellvalue();
if(objectutils.isempty(date)) {
return null;
}
try {
final string formated = new simpledateformat("yyyy-mm-dd").format(date);
date newdate = time_format_date.parse(formated);
return (int) (newdate.gettime() / datetimeutils.millis_per_day);
}
catch (parseexception e) {
log.error("parse date error, date:{}", date, e);
}
return null;
};
}
public static function<cell, object> getvaluewithtimestamp() {
return cell -> {
date date = cell.getdatecellvalue();
if(objectutils.isempty(date)) {
return null;
}
try {
final string formated = new simpledateformat("yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm:ss").format(date);
date newdate = time_format_timestamp.parse(formated);
return (int) newdate.gettime();
}
catch (parseexception e) {
log.error("parse timestamp error, date:{}", date, e);
}
return null;
};
}
public static function<cell, object> getvaluewithtime() {
return cell -> {
date date = cell.getdatecellvalue();
if(objectutils.isempty(date)) {
return null;
}
try {
final string formated = new simpledateformat("hh:mm:ss").format(date);
date newdate = time_format_time.parse(formated);
return newdate.gettime();
}
catch (parseexception e) {
log.error("parse time error, date:{}", date, e);
}
return null;
};
}
}该枚举类主要管理了java type& sql type & cell value convert func, 方便统一管理类型映射及单元格内容提取时的转换方法(这里借用了java8 function函数特性)
注: 这里的日期转换只能这样写, 即使用gmt的时区(抄的
calcite-file), 要不然输出的日期时间一直有时差...
6. 测试查询
package com.ldx.calcite;
import com.ldx.calcite.excel.excelschemafactory;
import lombok.sneakythrows;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.slf4j;
import org.apache.calcite.config.calciteconnectionproperty;
import org.apache.calcite.jdbc.calciteconnection;
import org.apache.calcite.schema.schema;
import org.apache.calcite.schema.schemaplus;
import org.apache.calcite.util.sources;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.afterall;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.beforeall;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.test;
import org.testng.collections.maps;
import java.net.url;
import java.sql.connection;
import java.sql.drivermanager;
import java.sql.resultset;
import java.sql.resultsetmetadata;
import java.sql.sqlexception;
import java.sql.statement;
import java.util.map;
import java.util.properties;
@slf4j
public class calciteexceltest {
private static connection connection;
private static schemaplus rootschema;
private static calciteconnection calciteconnection;
@beforeall
@sneakythrows
public static void beforeall() {
properties info = new properties();
// 不区分sql大小写
info.setproperty(calciteconnectionproperty.case_sensitive.camelname(), "false");
// 创建calcite连接
connection = drivermanager.getconnection("jdbc:calcite:", info);
calciteconnection = connection.unwrap(calciteconnection.class);
// 构建rootschema,在calcite中,rootschema是所有数据源schema的parent,多个不同数据源schema可以挂在同一个rootschema下
rootschema = calciteconnection.getrootschema();
}
@test
@sneakythrows
public void test_execute_query() {
final schema schema = excelschemafactory.instance.create(resourcepath("file/test.xlsx"));
rootschema.add("test", schema);
// 设置默认的schema
calciteconnection.setschema("test");
final statement statement = calciteconnection.createstatement();
resultset resultset = statement.executequery("select * from user_info");
printresultset(resultset);
system.out.println("=========");
resultset resultset2 = statement.executequery("select * from test.user_info where id > 110 and birthday > '2003-01-01'");
printresultset(resultset2);
system.out.println("=========");
resultset resultset3 = statement.executequery("select * from test.user_info ui inner join test.role_info ri on ui.role_id = ri.id");
printresultset(resultset3);
}
@afterall
@sneakythrows
public static void closeresource() {
connection.close();
}
private static string resourcepath(string path) {
final url url = calciteexceltest.class.getresource("/" + path);
return sources.of(url).file().getabsolutepath();
}
public static void printresultset(resultset resultset) throws sqlexception {
// 获取 resultset 元数据
resultsetmetadata metadata = resultset.getmetadata();
// 获取列数
int columncount = metadata.getcolumncount();
log.info("number of columns: {}",columncount);
// 遍历 resultset 并打印结果
while (resultset.next()) {
final map<string, string> item = maps.newhashmap();
// 遍历每一列并打印
for (int i = 1; i <= columncount; i++) {
string columnname = metadata.getcolumnname(i);
string columnvalue = resultset.getstring(i);
item.put(columnname, columnvalue);
}
log.info(item.tostring());
}
}
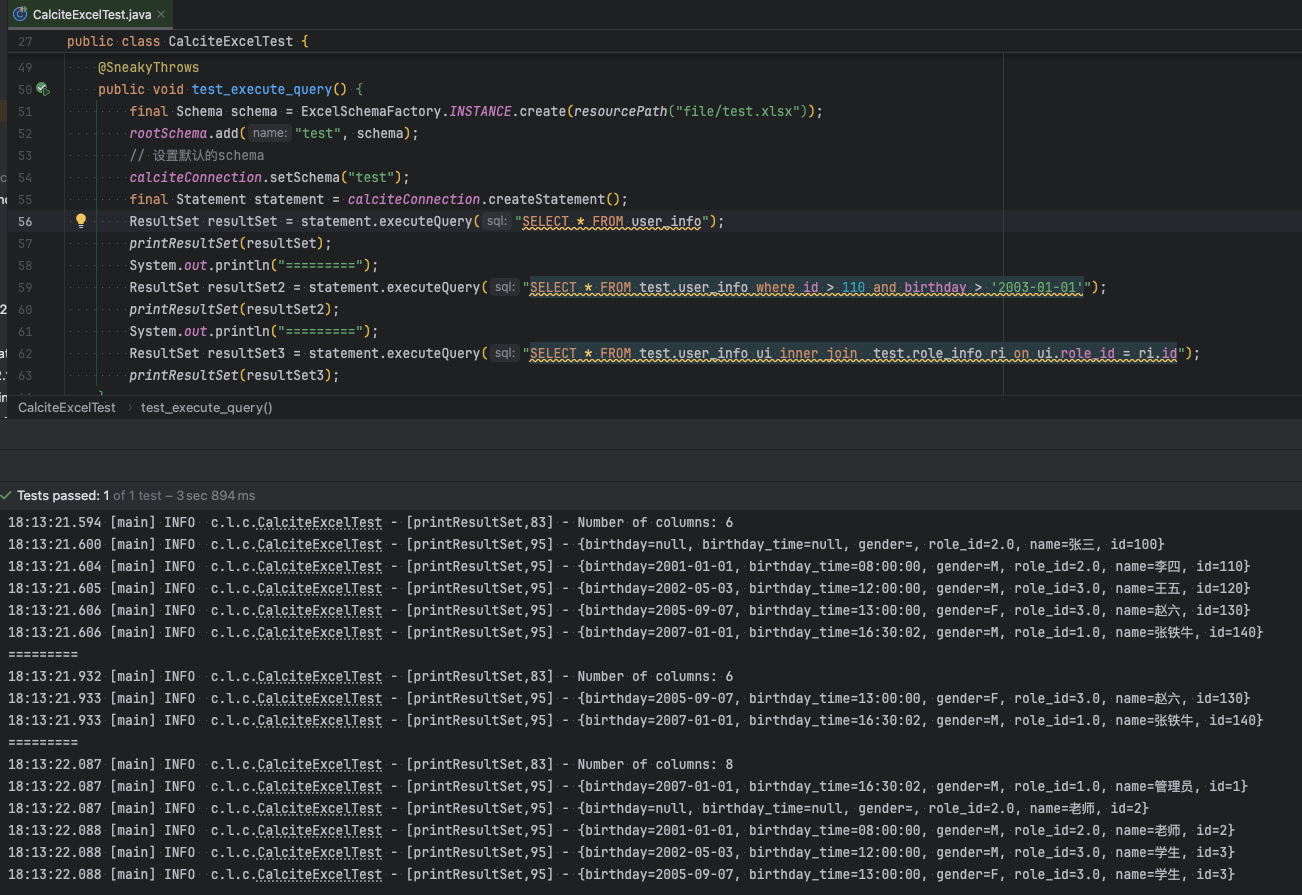
}测试结果如下:
到此这篇关于使用sql语言查询多个excel表格的操作方法的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关sql查询多个excel表格内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!



发表评论