1.栈的概念及结构
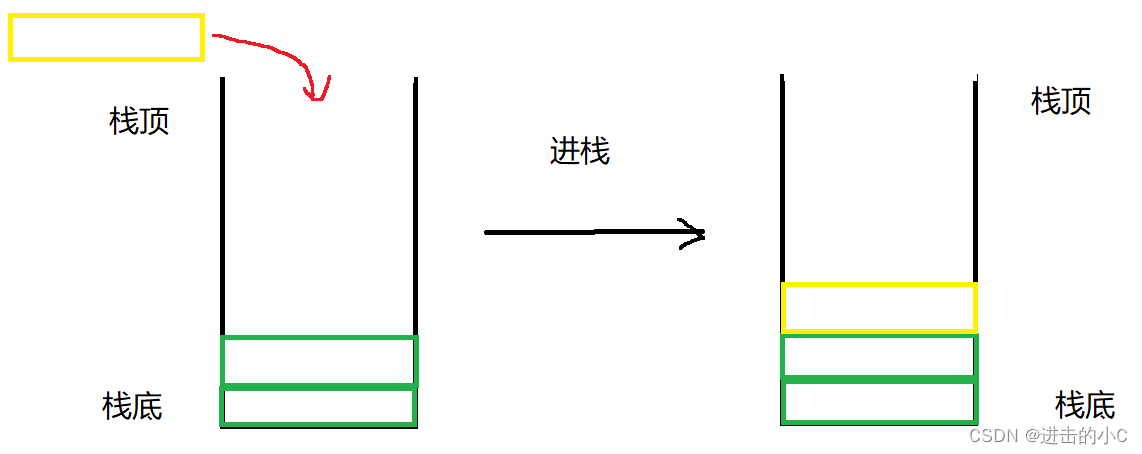
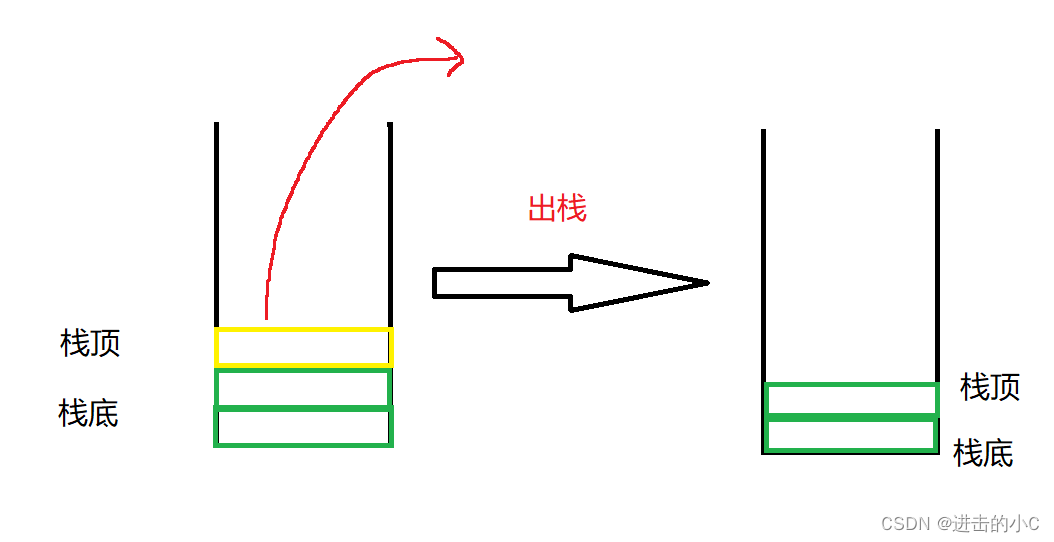 2.栈的实现
2.栈的实现
栈的实现一般可以使用数组或者链表实现,相对而言数组的结构实现更优一些。因为数组在尾上插入数据的代价比较小。
2.1定义一个动态栈
typedef int stdatatype;
typedef struct stack
{
stdatatype* a;
int top;
int capacity;
}st;2.2栈的初始化
void stinit(st* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->a = null;
ps->top = 0;
ps->capacity = 0;
}2.3栈的销毁
void stdestroy(st* ps)
{
assert(ps);
free(ps->a);
ps->a = null;
ps->top = ps->capacity = 0;
}2.4数据进栈
数据进栈的话首先要考虑一下是否需要扩容,所以先判断一下top是否等于capacity,如果满了的话再判断一下capacity是否是第一次扩容,如果是的话则扩容至4,不是的话则扩2倍,再对空间进行扩容,这里巧妙地利用了realloc这个库函数,因为如果需要扩容的这个空间是0,则相当于是malloc,扩容完之后就将数据放进top这个位置,然后再将top++,这样才会使得top一直是栈顶元素的下一个位置。
void stpush(st* ps, stdatatype x)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->top == ps->capacity)
{
int newcapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4:ps->capacity * 2;
stdatatype* tmp = (stdatatype*) realloc(ps->a, sizeof(stdatatype) * newcapacity);
if (tmp == null)
{
perror("realloc fail");
exit(-1);
}
ps->a = tmp;
ps->capacity = newcapacity;
}
ps->a[ps->top] = x;
ps->top++;
}2.5数据出栈
先保证这个栈不是空的,top>0才有数据可以出。出栈直接top--就行了。
void stpop(st* ps, stdatatype x)
{
assert(ps);
//空
assert(ps->top > 0);
--ps->top;
}2.6栈的数据个数
int stsize(st* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top;
}2.7判断栈是否为空
bool stempty(st* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top == 0;
}2.8获取栈顶元素
这里需要注意一下,栈顶元素的位置是top-1.
stdatatype sttop(st* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->top > 0);
return ps->a[ps->top - 1];
}完整代码
stack.h:
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
typedef int stdatatype;
typedef struct stack
{
stdatatype* a;
int top;
int capacity;
}st;
void stinit(st* ps);
void stdestroy(st* ps);
void stpush(st* ps,stdatatype x);
void stpop(st* ps);
int stsize(st* ps);
bool stempty(st* ps);
stdatatype sttop(st* ps);stack.c:
void stinit(st* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->a = null;
ps->top = 0;
ps->capacity = 0;
}
void stdestroy(st* ps)
{
assert(ps);
free(ps->a);
ps->a = null;
ps->top = ps->capacity = 0;
}
void stpush(st* ps, stdatatype x)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->top == ps->capacity)
{
int newcapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4:ps->capacity * 2;
stdatatype* tmp = (stdatatype*) realloc(ps->a, sizeof(stdatatype) * newcapacity);
if (tmp == null)
{
perror("realloc fail");
exit(-1);
}
ps->a = tmp;
ps->capacity = newcapacity;
}
ps->a[ps->top] = x;
ps->top++;
}
void stpop(st* ps, stdatatype x)
{
assert(ps);
//空
assert(ps->top > 0);
--ps->top;
}
int stsize(st* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top;
}
bool stempty(st* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top == 0;
}
stdatatype sttop(st* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->top > 0);
return ps->a[ps->top - 1];
}




发表评论