目录
0. 来点鸡汤
时不时看看自己以前写的博客,感触很多。已经快一年多没有认真写博客了,今天重新开张,希望以此为契机,重拾生活的信心。
去年研究生毕业,去了北京,年薪拿到了30万。但只在山巅呆了四个月,便草草结束,离开北京各中原由无从说起,家庭和事业那时候只能选一个。虽然选了家庭,但现在想起北京的那份工作,也觉得可惜。离开北京之后,“安安心心”拿5000的月薪又快一年了,岗位也从原来的算法工程师变成程序员,这就是上帝给你开了个窗户,你刚看到一丝希望,谁知上帝开窗就给你一个大逼兜,然后关上窗户,留下你在风中凌乱。刚去北京时,我以为命运的齿轮开始转动,我真正的人生正式开始,原来只是去看了一遭那水中花、镜中月,留存脑海中的北京梦,与现在的满地鸡毛,讽刺啊。
哈哈哈,生活还要继续呢!原来京东买东西,现在拼多多、咸鱼也能凑合,玩算法换成写代码就当给自己夯实基础,领导原来是博士、硕士,现在的领导清一色中专,这不工作上更容易忽悠领导了吗?这样想,好多了。 。
。
听我叨逼叨那么多,哈哈,那我顺便说点关于c#的事情吧,也当做我成长的一个记录。这份教程不会每一步都去截图,如果你是小白,建议花个10分钟快速入门一下c#的基本概念,这个链接: c#菜鸟教程 带你快速入门。我写的虽然是wpf入门教程,但是c#遇到的问题我都会记录下来,直到把整个大楼给造好。
1. 概念
c# 怎么读? 读c井?读c星?哈哈
正确读音 c sharp 音标: [ʃɑːrp]
1.1 c#能做什么
上位机软件、桌面显示软件、unity 3d游戏、网页开发等
1.2 为什么要选择c#,而不是qt或者其它?
(1)c# 简单易上手。qt 基本就c++的语法,用起来很复杂。
别扯什么运行速度,内存那些有的没的,那些东西全是扯犊子,对于新手或者绝大多数人,那些东西可能写一辈子代码也不用考虑,现在的计算机不缺算力和存储空间。主要精力应该是保证功能的实现和稳定运行。
(2)c# 是微软创造出来的,背靠宇宙第一强编辑器 visual studio,对于代码的调试,兼容,有着无可比拟的优势。
我举个例子,每台windows电脑都有个事件查看器,它记录了电脑的各种异常事件。我们知道,写代码的时间是远远没有调试的时间长的,而用c#写的程序,通过windows自带的事件查看器就能定位到异常代码是第几行,你就说这点,选不选c#。
(3)学会c# 会的是一类东西。
比如你是用c#写桌面应用程序(winform、wpf),你还可以用c#写网页 (asp.net),现在火热的unity3d脚本也是通过c#来完成的,只要微软不跨,你说为啥不选一劳永逸的语言。
老子就不听傻逼博主的意见,我就要学qt。
宝啊,你看看我写的其他文章,也是鬼话连篇,但是我写博客没有糊弄各位宝,no copy,no paste.(是不是不知道啥意思,哈哈,快去百度翻译一下再和我犟)。如果你还是不选择c#,我只能画个圈诅咒你 —你写的代码如果有bug,永远也找不到。
1.3 winform 和 wpf有什么区别
c#有控制台应用程序console,也有桌面应用程序(图形界面),现在主要就是用来展示数据的。
c#有两种方式写桌面应用程序:wpf、winform。我们来看看它们有什么不同。
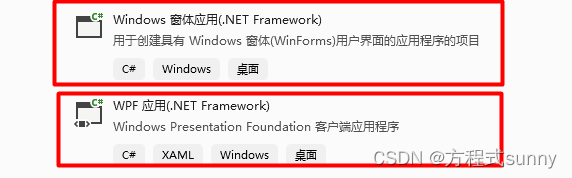
- winform老,wpf新;
- winform窗体的控件属性是在c#里实现的,wpf则是在xaml里面实现的
- winform修改控件复杂,wpf简单
- winform入门简单,wpf入门难
宝啊,你读到此处想说什么?
什么傻逼博主,说了好像又啥都没说,都是些什么鬼啊?
我就想和你说,winform过时了,要学wpf。
1.4 .net framework 和 .net core联系
讲个小插曲,有一次其他部门的一个同事台上发言,原话:“我们这个程序是用 dot net core 开发的”,听到这句话时,我有点懵逼,什么人这是,你就说用c#开发的不就完了么,还tmd左一句dot net core,右一句dot net core,啥也不是。
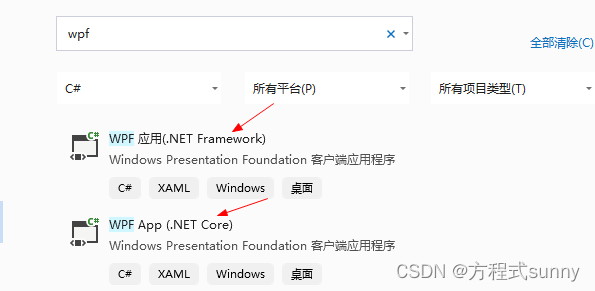
看上面这张图片,我选的都是wpf,但是它们的架构不一样。
- .net framework老, .net core新
- .net framework只针对windows平台,但包含了windows平台的所有特性, .net core 支持多个平台,但没有前者全面.如果要用xp系统,则使用framework是更好的选择
顺便说一嘴:咱可不是喜欢背后说人坏话,我批评甚至是鄙视我那个说dot net core 的同事,原因是他不写任何代码,也不会写,却总是装逼,咱讨厌这样的人。
1.5 wpf各个组成部分

分为xaml文件和cs文件,xaml文件用来处理界面,cs文件处理后台逻辑
app.xaml 指定系统启动界面,资源,引入的程序集
=======现在是 北京时间2023年9月27日 23:13,小傲娇的博主困了,不想写了
2. xaml
wpf有两部分构成,一部分是界面(前端设计),负责界面的设计和数据展示。另一部分是程序逻辑(后端),负责业务流程和数据处理。两部分相互独立,装逼的说法叫前后端分离。前端和后端会存在数据交互,可以通过事件或者绑定等方法来实现。
2.1 xaml中的对象和属性
=======现在是 北京时间2023年10月1日 20:41,小傲娇的博主今天没事,接着写。
xaml是xml的扩展,很多用法和想xml是一致的,如果你学过html,那应该会很快入门xaml,这东西只要入门了,写桌面应用程序布局时很爽,你用了这个,基本不会再用回winform了。
-
- 对象元素
这里的对象和面向对象编程的概念基本一致。面向对象编程的对象是对一类具有相同属性的物体进行抽象,比如有个dog类、cat类,这里的对象是逻辑层面上的。
xaml 中也有对象,比如按钮utton、文本框textbox等都是对象,这里的对象是布局上的概念,更多是文法层面,不是逻辑上的概念。
在wpf中,xmal代码也称作前端代码(控件),而以.cs结尾的代码叫做 “c#代码”(也叫后端代码或者代码隐藏)。
<!--第一种写法--> <button>按钮1</button> <!--第二种写法--> <button content="按钮2"/> - 对象元素
-
- 属性
在c#中(其他编程语言也一样),一个类中往往有各种属性,比如学生类中有姓名属性、年纪属性等等。在xaml中,这个概念有点类似,比如有个按钮控件(按钮类),那它也有自己的属性,比如行高、行宽、背景颜色等等。下面这个示例,grid.row、grid.column都是属性。
<grid grid.row="2" grid.column="0" showgridlines="true"> - 属性
-
- 属性元素
属性元素是对象中的属性的属性,比如button是一个对象,background是一个属性,对属性再设置就叫属性元素: solidcolorbrush
<button> <button.background > <solidcolorbrush color="red"></solidcolorbrush> </button.background> </button> - 属性元素
2.2 xaml页面布局
2.2.1 层级概念
- xaml设计是按照行和列的概念设计的;
- xaml是树形结构,在使用前先对grid进行设计(几行几列);
- 在每个层级下面对界面进行设计
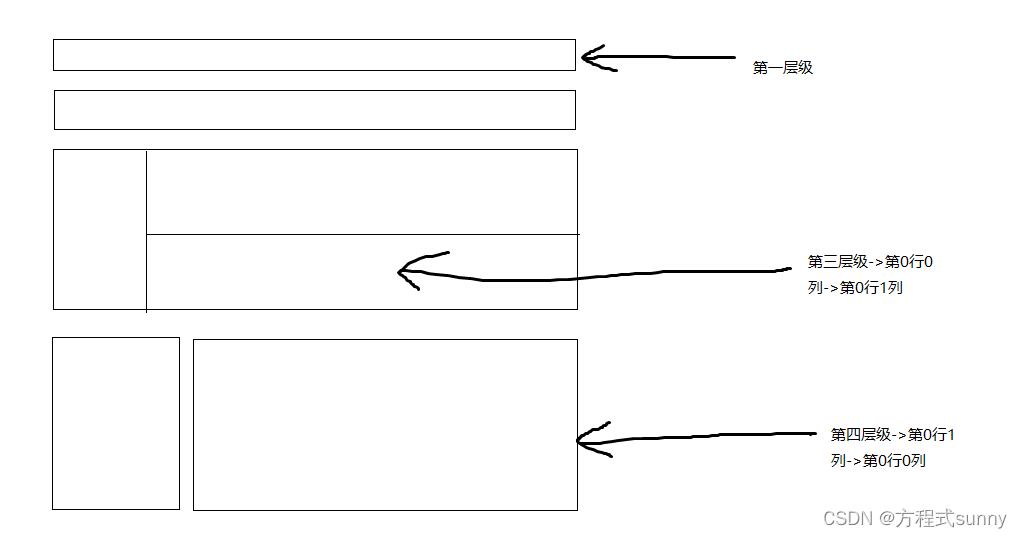
可能看了上面的图片也觉得一头雾水,我们现在从网页上随便截图一张,结合wpf看看到底什么是层级结构
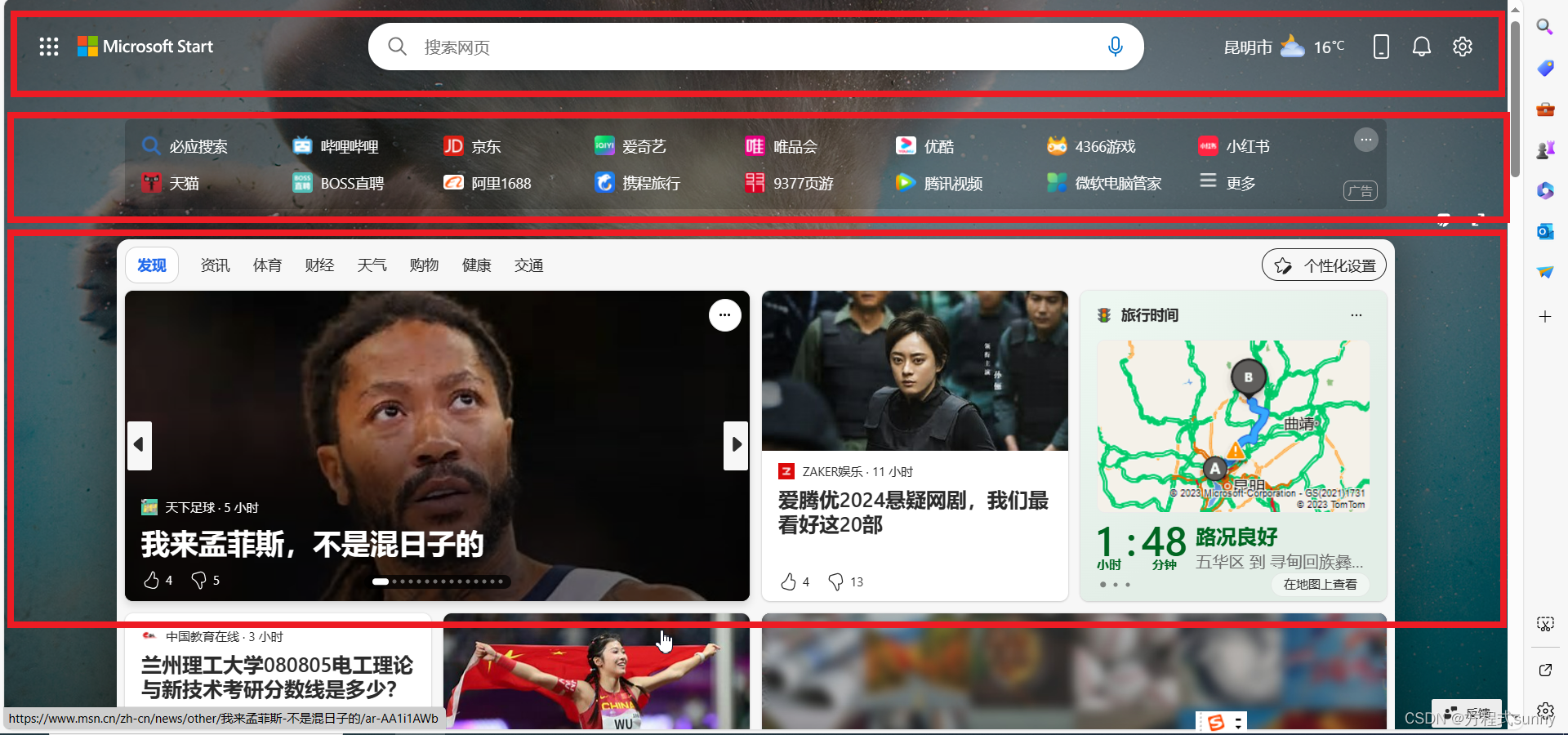
我们把这个界面先整体分成三个区域, 即3行1列
第1行第1列 所有的图标依次用stackpanel放置控件就可以了
在第2行第1列 里面进一步切割,可在分成 2行1列

在第3行第1列 里面进一步切割,可在分成 1行3列
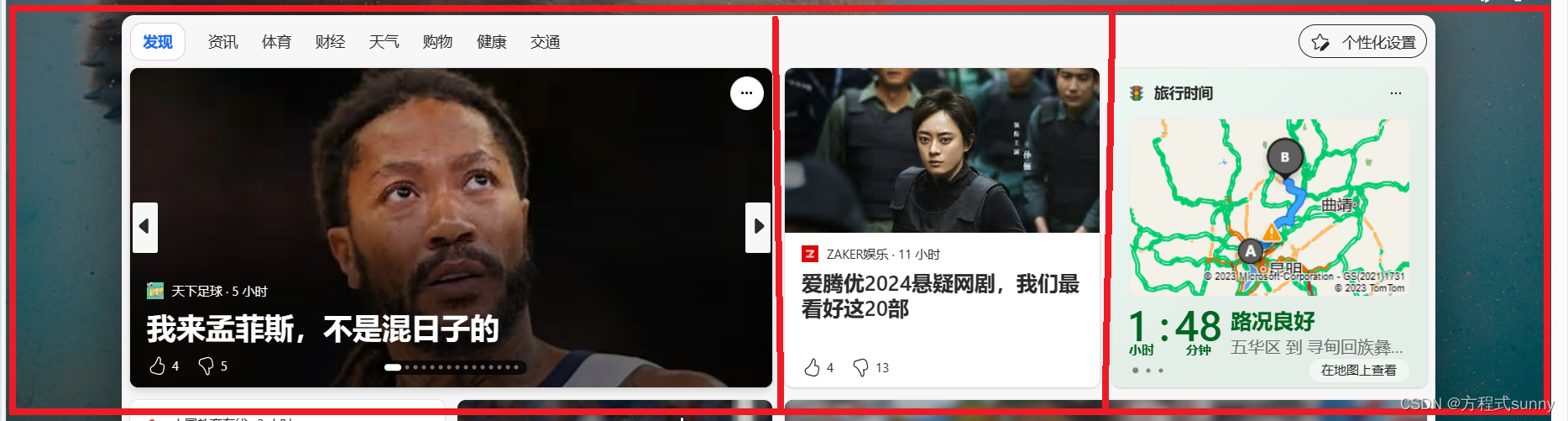
这样一个界面就被切割好了, 理解上面这个例子,应该就知道wpf层级的概念了
2.2.2 使用 grid 定义行和列
根据上面层级的概念,将界面划分区域,接下来就可以用< grid >来实现了. 下面的代码定义2行2列的布局
<grid>
<grid.rowdefinitions>
<rowdefinition height="20"/>
<rowdefinition/>
</grid.rowdefinitions>
<grid.columndefinitions>
<columndefinition/>
<columndefinition/>
</grid.columndefinitions>
</grid>
我们还可以在第2行第2列里再布置2行2列,代码实现如下
<grid>
<grid.rowdefinitions>
<rowdefinition/>
<rowdefinition/>
</grid.rowdefinitions>
<grid.columndefinitions>
<columndefinition/>
<columndefinition/>
</grid.columndefinitions>
<grid grid.row="1" grid.column="1">
<grid.rowdefinitions>
<rowdefinition/>
<rowdefinition/>
</grid.rowdefinitions>
<grid.columndefinitions>
<columndefinition/>
<columndefinition/>
</grid.columndefinitions>
</grid>
</grid>
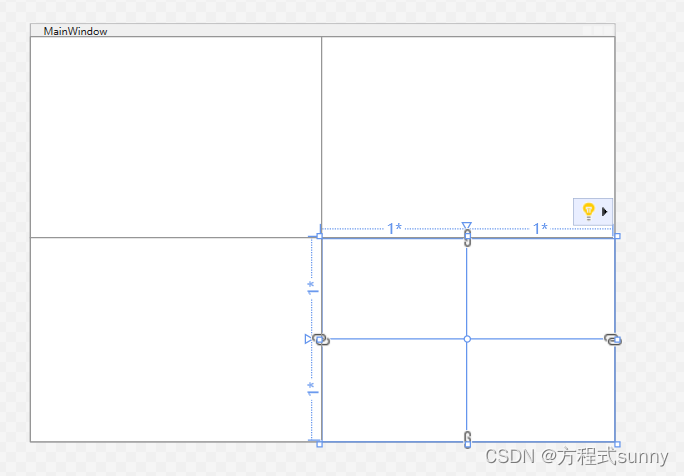
2.2.3 设置行和列
-
绝对值
-
按比例
-
auto
<grid showgridlines="true"> <grid.rowdefinitions> <rowdefinition height="auto"/> <rowdefinition height="80"/> <rowdefinition height="2*"/> </grid.rowdefinitions> <grid.columndefinitions> <columndefinition/> <columndefinition/> <columndefinition/> </grid.columndefinitions> <button grid.row="0" grid.column="0" width="40" height="40"/> <button grid.row="1" grid.column="2"/> </grid>
2.3 xaml样式
2.3.1 方法一:不给样式命名
直接在wpf控件前面写某类控件的样式,该方法不给样式起名字,后面使用该类控件时不需要引用,默认会使用该类样式。如下面代码,当我创建一个按钮是就会使用 <window.resources>里面的样式。
<window x:class="wpf_test.mainwindow"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:wpf_test"
mc:ignorable="d"
title="mainwindow" height="500" width="700">
<window.resources>
<style targettype="button">
<setter property="background" value="#ff20b9e6"/>
<setter property="height" value="50"/>
<setter property="width" value="100"/>
</style>
</window.resources>
<grid>
<grid.rowdefinitions>
<rowdefinition/>
<rowdefinition/>
</grid.rowdefinitions>
<grid.columndefinitions>
<columndefinition/>
<columndefinition/>
</grid.columndefinitions>
<button content="按钮"/>
</grid>
</window>
=======现在是 北京时间2023年10月1日 22:38,小傲娇的博主累了,不想写了
2.3.2 方法二:给样式命名
<window.resources>
<style x:key="login" targettype="button">
<setter property="background" value="#ff06c5f0"/>
<setter property="height" value="50"/>
<setter property="width" value="100"/>
</style>
<style x:key="quit" targettype="button">
<setter property="background" value="#fff1f1f1"/>
<setter property="height" value="50"/>
<setter property="width" value="100"/>
</style>
</window.resources>
2.3.3 给样式命名同时继承基础样式
<window.resources>
<!--基础样式-->
<style targettype="button">
<setter property="fontsize" value="20"/>
</style>
<style x:key="login" targettype="button" basedon="{staticresource {x:type button}}">
<setter property="background" value="#ff06c5f0"/>
</style>
<!--继承基础样式 添加引用-->
<style x:key="quit" targettype="button" basedon="{staticresource {x:type button}}">
<setter property="background" value="#fff1f1f1"/>
</style>
</window.resources>
2.4 在资源字典定义样式
在项目管理文件中添加一个资源字典dictionary,对不同的控件进行样式设计. 在app.xaml中添加一个全局的资源字典, 将dictionary的文件路径添加进去
2.4.1 添加资源字典
//在项目管理文件中添加一个资源字典dictionary
<resourcedictionary xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:wpfapp1">
<!--新建一个全局资源字典-->
<!--基础样式-->
<style targettype="button">
<setter property="fontsize" value="20"/>
</style>
<!--继承基础样式 添加引用-->
<style x:key="login" targettype="button" basedon="{staticresource {x:type button}}">
<setter property="background" value="#ff06c5f0"/>
</style>
<!--继承基础样式 添加引用-->
<style x:key="quit" targettype="button" basedon="{staticresource {x:type button}}">
<setter property="background" value="#fff1f1f1"/>
</style>
</resourcedictionary>
2.4.2 全局引用资源字典
<application x:class="wpfapp1.app"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:wpfapp1"
startupuri="window1.xaml">
<application.resources>
<!--添加一个全局的资源资源字典-->
<resourcedictionary>
<resourcedictionary.mergeddictionaries>
<resourcedictionary source="/basebuttonstyle.xaml"/>
</resourcedictionary.mergeddictionaries>
</resourcedictionary>
</application.resources>
</application>
2.5 控件模板重写
当你创建一个控件时,这个控件有自己的背景、颜色,这都是系统自定义好的,但是这并不是我们需要的,我们不可能每一次创建时都去修改,所以需要对控件模版改造,这个过程就就叫做控件模版重写。
<grid>
<button content="自定义按钮" background="#ff00805d" width="120" height="100" borderbrush="black" borderthickness="4">
<button.template>
<controltemplate targettype="button">
<border name="bbb" background="{templatebinding background}" borderbrush="{templatebinding borderbrush}" borderthickness="{templatebinding borderthickness}" cornerradius="15">
<textblock text="{templatebinding content}" horizontalalignment="center" verticalalignment="center"/>
</border>
<controltemplate.triggers>
<trigger property="ismouseover" value="true">
<setter targetname="bbb" property="background" value="red"/>
</trigger>
<trigger property="ispressed" value="true">
<setter targetname="bbb" property="background" value="#ff10f3ca"/>
</trigger>
</controltemplate.triggers>
</controltemplate>
</button.template>
</button>
</grid>
3. c# 代码语法规则
3.1 变量 、属性、字段分别是什么?
这个概念特别重要,搞不懂不行
类内部的私有变量即为字段,如代码中的变量 a;
属性向外暴露接口(公有部分),使外部能够通过属性访问内部字段, 属性本身不保存数据, 对属性操作实际是对属性对应字段操作; 如代码中对属性b操作,其实是对a操作;
/// <summary>
/// 定义一个变量(字段) a ,同时初始化
/// </summary>
private int a = 1;
/// <summary>
/// 定义属性 b
/// </summary>
public int b
{
get { return a; }
set { a = value; }
}
3.2 属性、变量、字段
在.net中,属性(properties)、字段(fields)和变量(variables)是编程中经常使用的术语,它们各自有不同的含义和用途。以下是这些术语的基本定义和区别:
变量(variables):
- 定义:变量是用来存储数据的标识符,它可以根据程序的需要存储不同类型的数据。
- 访问:通过变量名直接访问。
- 作用域:根据声明的位置(如方法内、类内、命名空间内等),变量的作用域会有所不同。
- 示例:
int number = 10;,这里number是一个整型变量。
字段(fields):
- 定义:字段是类的成员变量,它隶属于类而不是方法。字段通常是私有的,并且可以通过类的属性、方法或其他成员来访问。
- 访问:通常通过类的实例访问,除非它们是静态的,则可以通过类名直接访问。
- 作用域:字段的作用域通常是整个类。
- 示例:
public class myclass { private int myfield; // 这是一个私有字段 public int myproperty // 这是一个属性,下面会详细介绍 { get { return myfield; } set { myfield = value; } } }
属性(properties):
- 定义:属性是类的成员,它提供了一种灵活的方式来读取、写入或计算私有字段的值。属性通常包含get和set访问器。
- 访问:通过类的实例访问,就像访问字段一样,但实际上是在调用方法。
- 作用域:属性的作用域通常是整个类,但可以通过get和set访问器进行更精细的控制。
- 示例:继续上面的
myclass例子,myproperty是一个属性,它有get和set访问器,允许外部代码读取和修改myfield的值。public int myproperty // 属性定义 { get { return myfield; } // get访问器,用于读取属性值 set { myfield = value; } // set访问器,用于设置属性值 }
总结区别:
- 变量是最基本的存储单元,而字段是类的变量成员。
- 属性提供了一种更安全、更灵活的方式来访问类的字段。它们允许在读取或写入字段值之前执行额外的逻辑(例如验证)。
- 通常建议将字段标记为private,并通过公共属性来访问它们,以实现封装和数据隐藏。这样可以确保对象状态的完整性和安全性。
-
易错点
在c#中, 只能在类内定义变量和属性,同时允许对改变量或者属性进行初始化, 但不允许一个变量直接引用另外一个变量,如下所示,这是新人经常犯的一个错误。
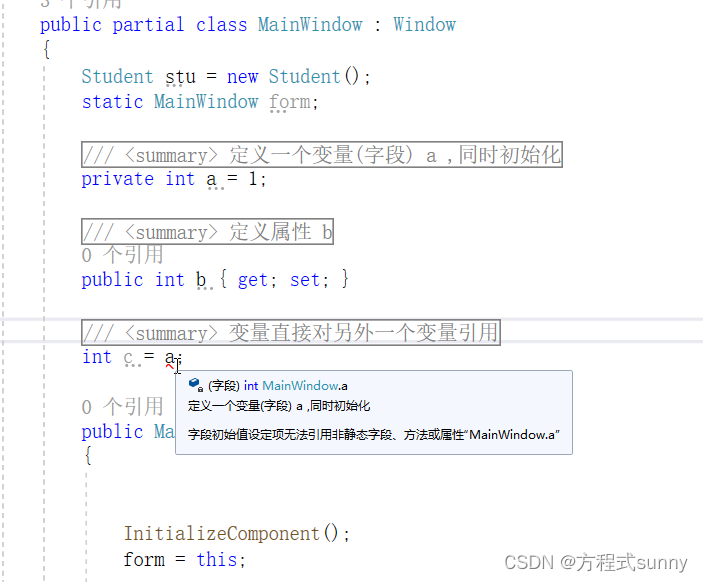
3.3 set{}、get{}用法
在类test中设置一个私有变量name,同时设置一个公有变量,通过公有变量name对私有变量name操作
public class test
{
/// <summary>
/// 字段:一般私有,不对外开放, 首字母一般小写
/// </summary>
private string name;
/// <summary>
/// 属性:一般为共有,作为外部访问对应字段的一个接口, 首字母一般大写
/// </summary>
public string name
{
get { return name; } //通过name返回name的值
set
{
if (value == "keson")
{
console.writeline("hello,keson!");
}
else
{
name = value; //通过name设置name的值
console.writeline("that is not keson,is "+ name);
}
}
}
}
class program
{
static void main()
{
test test = new test();
test.name = "孙悟空";
}
}
3.4 app.config用法
app.config文件是系统默认的配置文件, 使用时需要添加引用 system.configuration.dll, 该配置文件用于修改数据库连接字符串/窗口日志的信息.
app.config代码:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<configuration>
<startup>
<supportedruntime version="v4.0" sku=".netframework,version=v4.7.2" />
</startup>
<appsettings>
<add key="keyname" value="valuename"/>
<add key="keyname2" value="valuename2"/>
<add key="keyname3" value="valuename3"/>
</appsettings>
</configuration>
-
c# 代码
拿到配置文件里的内容
public partial class mainwindow : window { public mainwindow() { initializecomponent(); string settingvalue = system.configuration.configurationmanager.appsettings["keyname"]; } }
3.5 将一个类拆开写在多处
calss1.cs和class2.cs同属于一个类,c#允许一个类拆开写,这样防止写在一处,不方便阅读。
public partial class window1 : window
{
public window1()
{
initializecomponent();
}
}
public partial class window1 : window
{
public window1()
{
fun();
}
}
4. 数据绑定
4.1 原理
通常是指将目标源(具有依赖属性的对象)绑定到 目标数据上(通常是控件)
数据绑定分为4种:
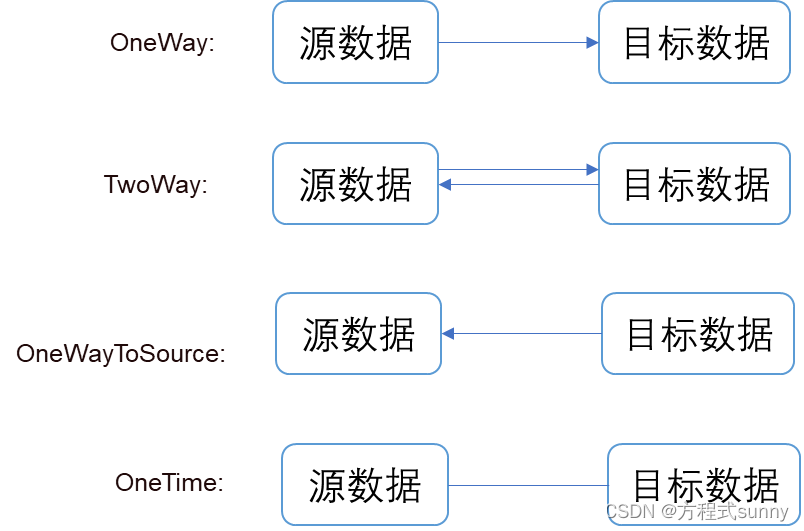
4.2 xaml 实现数据绑定
案例一
绑定源:代码隐藏 绑定目标: textbox
public partial class mainwindow : window
{
public mainwindow()
{
initializecomponent();
//设置窗体上下文对象 这里设置的是myclass
datacontext = new myclass();
}
}
public class myclass
{
public int hight { get; set; } = 100;
public int width { get; set; } = 101;
}
<grid>
<stackpanel>
<wrappanel>
<textblock text="窗口的标题为:"/>
<textbox text="{binding path=title, mode=twoway, updatesourcetrigger=propertychanged}" />
</wrappanel>
<wrappanel>
<textblock text="窗口的高度为:"/>
<!--上面myclass里的hight-->
<textbox text="{binding hight}" width="50" />
</wrappanel>
<wrappanel>
<textblock text="窗口的宽度为:"/>
<textbox text="{binding width}" width="50" />
</wrappanel>
</stackpanel>
</grid>
案例二
绑定源:textbox 绑定目标: textbox
<textbox grid.row="1" name="textbox_receivedata" text={bindingpath=text,elementname=tbx2 }">
</textbox>
4.3 c#代码实现数据绑定
public mainwindow()
{
initializecomponent();
bindingdata();
}
private void bindingdata()
{
//1 创建绑定对象
var binding = new binding("text");
//2 设置绑定源
binding.source = this.keson;
//3 设置绑定目标
keson_copy.setbinding(textblock.textproperty, binding);
}
<stackpanel>
<wrappanel>
<textbox name="keson" text="永远滴神"/>
</wrappanel>
<wrappanel>
<textblock name="keson_copy" />
</wrappanel>
</stackpanel>
namespace wpfapp1
{
/// <summary>
/// window1.xaml 的交互逻辑
/// </summary>
public partial class window1 : window
{
loginmodel loginmodel = new loginmodel();
public window1()
{
initializecomponent();
//数据绑定
this.datacontext = loginmodel;
loginmodel.user_name = "keson";
}
private void button_click(object sender, routedeventargs e)
{
图书馆主界面 lib = new 图书馆主界面();
if(loginmodel.user_name == "张三") //这里的textbox_username就是xaml里的x:name
{
lib.show();
}
else
{
messagebox.show("账号错误");
loginmodel.user_name = ""; //账号不是"张三"时,textbox里的内容会清空
}
}
}
public class loginmodel: inotifypropertychanged
{
private string _user_name;
public string user_name
{
get { return _user_name; }
set
{
_user_name = value;
raisepropertychanged("user_name");
}
}
public event propertychangedeventhandler propertychanged; //1 申明一个事件
private void raisepropertychanged(string propertyname)
{
propertychanged?.invoke(this, new propertychangedeventargs(propertyname));//3 事件绑定一个方法
}
}
}
<grid grid.row="1" grid.column="0">
<stackpanel orientation="horizontal" horizontalalignment="center">
<textblock text="账号:" fontsize="40" foreground="#ff000605" horizontalalignment="center" verticalalignment="center"/>
<textbox text="{binding user_name}" x:name="textbox_username" width="300" background="white" margin="10,10" fontsize="40" foreground="black" horizontalalignment="center" verticalalignment="center"/>
</stackpanel>
</grid>
4.4 propertychanged实现数据绑定
(1)原理
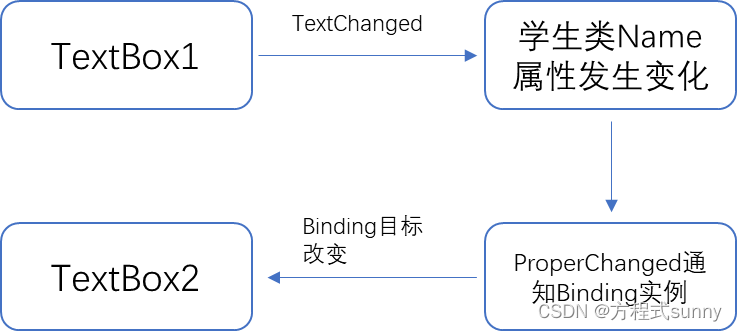
(2) 界面
(3) xaml
<window x:class="wpfapp2.mainwindow"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:wpfapp2"
mc:ignorable="d"
title="mainwindow" height="450" width="800" minheight="40">
<stackpanel >
<textbox name="tbx" height="50" margin="5" text="textbox1"/>
<textbox name="tbx2" height="50" margin="5" text="textbox2" textchanged="tbx2_textchanged"/>
</stackpanel>
</window>
(4) c#
using system;
using system.collections.generic;
using system.componentmodel;
using system.linq;
using system.text;
using system.threading.tasks;
using system.windows;
using system.windows.controls;
using system.windows.data;
using system.windows.documents;
using system.windows.input;
using system.windows.media;
using system.windows.media.imaging;
using system.windows.navigation;
using system.windows.shapes;
namespace wpfapp2
{
/// <summary>
/// mainwindow.xaml 的交互逻辑
/// </summary>
public partial class mainwindow : window
{
student stu;
public mainwindow()
{
initializecomponent();
stu = new student();
// 准备binding
binding binding = new binding();
binding.source = stu;
binding.path = new propertypath("name");
//使用binding连接数据源于binding目标
bindingoperations.setbinding(tbx, textbox.textproperty, binding);
}
private void tbx2_textchanged(object sender, textchangedeventargs e)
{
stu.name = tbx2.text;
}
}
class student : inotifypropertychanged
{
public event propertychangedeventhandler propertychanged;
private string name;
public string name
{
get { return name; }
set
{
name = value;
if(propertychanged != null)
{
propertychanged.invoke(this,new propertychangedeventargs("name"));
}
}
}
}
}
5 c#中的委托
5.1 如何理解委托?
这个名词困惑了了我好久,应该对比c++中的函数指针(一个指向函数的指针),理解了函数指针就理解委托了.
函数指针的就是一个指针变量指向函数,例子如下,定义了一个*pf的函数指针,入参是两个int,返回值也是int,将pf的地址指向max函数,这样pf也能使用max函数.
int max(int a,int b){
return a>b?a;b;
}
int (*pf)(int, int);
pf = max;
不同的是委托可以挂载多个方法。
委托是一个容器,这个容器可以挂载不同的方法。先简单说如何使用:定义一个委托,并给改委托挂载方法,执行委托。
具体步骤:
- 声明委托;
- 创建委托实例;
- 委托绑定方法;
- 调用委托
public delegate int calculate(int a, int b); //委托相当于函数指针
/// <summary>
/// 为委托创建一个加法计算方法
/// </summary>
/// <param name="name"></param>
public static int addmethod(int a, int b)
{
return a + b;
}
/// <summary>
/// 为委托创建一个乘法计算方法
/// </summary>
/// <param name="name"></param>
public static int mutilmethod(int a, int b)
{
return a * b;
}
static void main(string[] args)
{
/// <summary>
/// 将加法计算方法赋值给委托
/// </summary>
calculate cal = addmethod;
cal += mutilmethod;
//调用委托(依次调用)
int a = cal(22, 2);
int b = cal(2, 9);
int c = cal(22, 2);
int d = cal(2, 9);
console.writeline(a);
console.writeline(b);
console.writeline(c);
console.writeline(d);
运行结果:
44
18
44
18
请按任意键继续. . .
5.2 系统自带的两种委托 action<> 和func<>
action<> 用于挂载无返回值的方法
func<> 用于挂载有返回值的方法
static void main(string[] args)
{
delegatefun df = f1;
df();
//内置的委托
//1 指向无返回值方法
action a = f1;
a();
//2 指向有返回值方法
func<int, int, int> func = paremeters_fun;
console.writeline("2 指向有返回值方法,返回值为:" + func(2, 6));
//3 指向无返回值无入参 匿名方法
action a2 = delegate ()
{
console.writeline("3 指向无返回值无入参 匿名方法");
};
a2();
//4 指向无返回值有入参 匿名方法
action<int,string> a3 = delegate (int i,string s)
{
console.writeline($"4 指向无返回值有入参 匿名方法: i = {i},s = {s}");
};
a3(1,"keson");
//5 指向有返回值方法 匿名方法
func<int, int, int> func2 = delegate (int i, int j)
{
return i + j;
};
console.writeline("5 指向有返回值方法 匿名方法: " + func2(50, 6));
//6 指向有返回值lamda表达式
func<int, int, int> func3 =(int i, int j)=>
{
return i + j;
};
console.writeline("6 指向有返回值lamda表达式:" + func3(50, 6));
//7 指向有返回值lamda表达式(省略入参类型)
func<int, int, int> func4 = (i,j) =>
{
return i + j;
};
console.writeline("7 指向有返回值lamda表达式(省略入参类型):" + func3(50, 6));
}
5.3 简写委托的形式
委托经常伴随着lambda表达式, lambda表达式变化很多,有时候看到别人用的时候经常觉得莫名奇妙,我们从基本的开始,看看他们是一步步被简化的.
static void main(string[] args)
{
int[] nums = { 11, 52, 69, 33, 54, 2, 9, 23, 66, 45 };
//ienumerable<int> result = nums.where(a=>a > 10);
//演变顺序
// 1 先写一个匿名方法
action<int> action = delegate (int i) { console.writeline(i); };
// action<int> action2 = delegate (i) { console.writeline(i); }; //匿名方法数据类型不能省略
// action<int> action3 = delegate (int i) console.writeline(i); ; //匿名方法大括号不能省略
// 2 换成lamada表达式
action<int> action4 = (int i) => { console.writeline(i); }; //完整写法
action<int> action5 = (i) => { console.writeline(i); }; //数据类型省略
action<int> action6 = (i) => console.writeline(i); ; //大括号省略
action<int> action7 = (i) => console.writeline(i); //分号省略
action<int> action8 = i => console.writeline(i); //入参只有一个时,入参的小括号省略
//3 如果是有返回值
func<int, bool> func1 = delegate (int i) //先写个匿名方法
{
if (i > 0)
{ return true; }
else
{
return false;
}
};
func<int, bool> func2 = (int i) => //换成lamada表达式
{
if (i > 0)
{ return true; }
else
{
return false;
}
};
func<int, bool> func3 = (i) => //数据类型省略
{
if (i > 0)
{ return true; }
else
{
return false;
}
};
func<int, bool> func4 = (i) => //优化返回代码
{
return i > 0;
};
func<int, bool> func5 = (i) => //返回语句只有一条语句,省略大括号和return关键字
i > 0;
func<int, bool> func6 = i => //入参只有一个,省略入参的括号
i > 0;
}
c#中的事件
- 在类内声明委托
- 在类内声明事件
namespace consoleapp1
{
/// <summary>
/// 事件发布者
/// </summary>
public class greetingmanager
{
/// <summary>
/// 声明一个委托变量
/// </summary>
/// <param name="name"></param>
public delegate void display(string name);
/// <summary>
/// 声明一个事件
/// </summary>
public event display display_event; //相当于对委托类型的变量进行封装
/// <summary>
/// 创建一个处理方法
/// </summary>
/// <param name="name"></param>
public void show(string name)
{
if (display_event != null)
{
display_event(name);
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 订阅者
/// </summary>
public class greetways
{
public void englishgreeting(string name)
{
console.writeline("good moring, " + name);
}
public void chinesegreeting(string name)
{
console.writeline("早上好, " + name);
}
}
class program
{
static void main()
{
greetingmanager greetingmanager = new greetingmanager();
greetways greetways = new greetways();
greetingmanager.display_event += greetways.englishgreeting; //事件绑定方法
greetingmanager.display_event += greetways.chinesegreeting;
greetingmanager.show("keson"); //调用了show就触发了display_event事件
console.readkey();
}
}
}
static void main(string[] args)
{
int[] nums = { 11, 52, 69, 33, 54, 2, 9, 23, 66, 45 };
//ienumerable<int> result = nums.where(a=>a > 10);
//演变顺序
// 1 先写一个匿名方法
action<int> action = delegate (int i) { console.writeline(i); };
// action<int> action2 = delegate (i) { console.writeline(i); }; //匿名方法数据类型不能省略
// action<int> action3 = delegate (int i) console.writeline(i); ; //匿名方法大括号不能省略
// 2 换成lamada表达式
action<int> action4 = (int i) => { console.writeline(i); }; //完整写法
action<int> action5 = (i) => { console.writeline(i); }; //数据类型省略
action<int> action6 = (i) => console.writeline(i); ; //大括号省略
action<int> action7 = (i) => console.writeline(i); //分号省略
action<int> action8 = i => console.writeline(i); //入参只有一个时,入参的小括号省略
//3 如果是有返回值
func<int, bool> func1 = delegate (int i) //先写个匿名方法
{
if (i > 0)
{ return true; }
else
{
return false;
}
};
func<int, bool> func2 = (int i) => //换成lamada表达式
{
if (i > 0)
{ return true; }
else
{
return false;
}
};
func<int, bool> func3 = (i) => //数据类型省略
{
if (i > 0)
{ return true; }
else
{
return false;
}
};
func<int, bool> func4 = (i) => //优化返回代码
{
return i > 0;
};
func<int, bool> func5 = (i) => //返回语句只有一条语句,省略大括号和return关键字
i > 0;
func<int, bool> func6 = i => //入参只有一个,省略入参的括号
i > 0;
}
```
# c#不同界面之间互相操作控件
- 主界面可以操作子界面,子界面不可以操作主界面
```csharp
//主界面窗口
public partial class form1 : form
{
public delegate void del_main();
static public form1 form1 = new form1();
public form1()
{
form1 = this;
initializecomponent();
}
private void button_ok_click(object sender, eventargs e)
{
form2.form2.show();
}
private void form1_formclosing(object sender, formclosingeventargs e)
{
form2.form2.close();
environment.exit(0);
}
}
public partial class form2 : form
{
static public form2 form2 = new form2();
public form2()
{
form2 = this;
initializecomponent();
}
private void form2_button_click(object sender, eventargs e)
{
update_textbox_rcvcandata("测试");
}
private void update_textbox_rcvcandata(string text)
{
if (form1.form1.textbox.invokerequired)
{
//确保是在ui线程调用控件
form1.form1.textbox.invoke(new action<string>(update_textbox_rcvcandata), text);
return;
}
form1.form1.textbox.appendtext(text);
}
}
lambda表达式
在.net core中,lambda表达式是一种简洁的代码块表示形式,通常用于创建匿名方法。lambda表达式可以包含表达式和语句,并且可用于创建委托或表达式树类型。lambda表达式在linq查询、集合操作、排序、事件处理等方面非常有用。
lambda表达式的基本语法如下:
(parameter list) => expression
其中,(parameter list) 是参数列表,expression 是lambda主体表达式。
以下是一些在.net core中使用lambda表达式的常见用法示例:
list<int> numbers = new list<int> { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 }; //数据源
- 作为参数传递给方法:
list<int> numbers = new list<int> { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
int evencount = numbers.count(n => n % 2 == 0); // 使用lambda表达式作为count方法的参数来计算偶数数量
- 用于linq查询:
var filterednumbers = numbers.where(n => n > 3); // 使用lambda表达式过滤大于3的数字
- 用于排序集合:
var sortednumbers = numbers.orderby(n => n); // 使用lambda表达式按升序对数字进行排序
- 作为事件处理程序:
button.click += (sender, e) => { /* 处理点击事件的代码 */ }; // 使用lambda表达式作为事件处理程序订阅按钮的click事件
- 创建委托实例:
func<int, int> square = x => x * x; // 使用lambda表达式创建委托实例,该委托接受一个int参数并返回其平方
int result = square(4); // 调用委托实例计算4的平方并获取结果
- 在并行编程中使用:
parallel.for(0, numbers.count, i => { /* 并行处理的代码 */ }); // 使用lambda表达式定义并行循环中的操作逻辑
这些是.net core中lambda表达式的常见用法示例。通过使用lambda表达式,你可以以简洁、可读性强且功能强大的方式表示代码块,并在各种场景中应用它们。
mvvm
-
m model 数据模型
-
v view 界面
-
vm viewmodel 整合业务
wpf 定时器
(system.threading.timer)的使用
using system;
using system.collections.generic;
using system.componentmodel;
using system.linq;
using system.text;
using system.threading.tasks;
using system.windows;
using system.windows.controls;
using system.windows.data;
using system.windows.documents;
using system.windows.input;
using system.windows.media;
using system.windows.media.imaging;
using system.windows.navigation;
using system.windows.shapes;
using system.windows.threading;
//using system.timers;
using system.threading;
namespace wpfapp2
{
private timer timer;
public partial class mainwindow : window
{
public mainwindow()
{
initializecomponent();
timer = new timer(new timercallback(timercall), null, 0, 5000);
}
private void timercall(object state)
{
this.dispatcher.begininvoke(new action(() =>
{
tbx3.appendtext("定时器时间到 ");
}));
}
}
}
配置文件读取
public partial class mainwindow : window
{
public string path;
public mainwindow()
{
initializecomponent();
path = system.appdomain.currentdomain.basedirectory + "config.ini";
createfile(path);
readconfigfile(path);
}
dictionary<string, string> dictinitdata = new dictionary<string, string>();
public void readconfigfile(string path)
{
//读取配置文件并保存到字典中
streamreader sr = new streamreader(path);
string line;
while ((line = sr.readline()) != null)
{
line = line.trim();
if (line.startswith("#"))
{
continue;
}
if (!string.isnullorempty(line) && line.contains("="))
{
int equalsindex = line.indexof('=');
if (equalsindex > 0)
{
string key = line.substring(0, equalsindex).trim();
string value = line.substring(equalsindex + 1).trim();
dictinitdata.add(key, value);
}
}
}
sr.close();
if (dictinitdata.count != 3)
{
file.delete(path);
createfile(path);
}
}
private void createfile(string path)
{
//判断配置文件是否存在,不存在创建一个
if (!file.exists(path))
{
streamwriter sw = file.createtext(path);
sw.writeline("ip=192.168.0.1");
sw.writeline("port=80");
sw.flush();
sw.close();
}
}
}
ui线程
private void update_textbox_rcvguidedata(string text)
{
if (this.ishandlecreated)
textbox_rcvguidedata.begininvoke(new action(() =>
{
textbox_rcvguidedata.appendtext(text + "\r\n");
if (textbox_rcvguidedata.lines.length > 500)
{
textbox_rcvguidedata.clear();
}
}));
}
辨识attribute和property
- property
property针对类和对象来说(c#代码),下面这个类中的name,fun2都叫property
class person()
{
string name;
int age;
void fun1(){
//吃饭
}
void fun2(){
//睡觉
}
}
- attribute
attribute是编程语言文法层面的东西(针对xaml来说),比如button按钮的宽度/高度
链接: link
单例:加深理解静态成员和方法
宝啊,你有没有想过什么是单例?类似单身狗吗?茕茕孑立,形影相吊,这好像不太正确,还有影子陪着单身汪的呀!
一个类只能创建一个实例(有啥用?鬼知道哩,反正我没用过)我写这个主要是帮着我理解c#的关键字 ”static“。
internal class singleton
{
private static singleton uniqueinstance;
private static readonly object lockobject = new object();
private string? name;
private int age;
private singleton(string name,int age)
{
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public static singleton getinstance()
{
if (uniqueinstance == null)
{
lock (lockobject)
{
if(uniqueinstance == null)
{
uniqueinstance = new singleton(name, age);
}
}
}
return uniqueinstance;
}
}
为啥上面的代码无论你实例化多少个对象,实际上只有一个对象,这是为什么?原因就是“static”,无论成员还是方法,加上这个关键字,在实例化的时候,都不属于实例本身,他们都属于类本身,换句话说,类中的静态成员和方法被所有类共享。
上面的uniqueinstance是一个静态变量,无论创建多少个实例,最后这些实例都是共享一个静态成员变量。
linq的用法
这部分内容借鉴了杨中科老师的很多东西,大家可以去b站找他的视频学习真的值得一看. 链接: 杨中科老师视频链接
linq中where用法和原理
static void main(string[] args)
{
int[] nums = { 11, 52, 69, 33, 54, 2, 9, 23, 66, 45 };
// 1. 调用系统的方法
ienumerable<int> result = nums.where<int>(a => a > 20 && a < 40); //where后面的是lamada表达式的简写形式
foreach(var i in result)
{
console.writeline(i);
}
console.writeline(" ");
// 2. 调用自己写的方法1
ienumerable<int> result2 = selectnums(nums, a => a > 20);
foreach (var i in result2)
{
console.writeline(i);
}
console.writeline(" ");
// 3. 调用自己写的方法2
ienumerable<int> result3 = selectnums2(nums, a => a > 30);
foreach (var i in result3) //foreach (var i in selectnums2(nums, a => a > 20))
{
console.writeline(i);
}
}
static ienumerable<int> selectnums(ienumerable<int> items, func<int, bool> func)
{
list<int> list = new list<int>();
foreach(int item in items)
{
if(func(item) == true)
{
list.add(item);
}
}
return list;
}
static ienumerable<int> selectnums2(ienumerable<int> items, func<int, bool> func)
{
foreach (int item in items)
{
if (func(item) == true)
{
yield return item;
}
}
}
linq常用扩展方法
static void main(string[] args)
{
list<employee> list = new list<employee>();
list.add(new employee { id = 1, name = "张三", age = 50, gender = true, salary = 50000 });
list.add(new employee { id = 2, name = "李四", age = 40, gender = false, salary = 90000 });
list.add(new employee { id = 3, name = "赵六", age = 30, gender = false, salary = 30000 });
ienumerable<employee> employee = list.where((e) => { return e.age > 30; }); // employees.where(e => return e.age > 30 );
foreach(var i in employee)
{
console.writeline(i);
}
console.writeline(list.count(e => e.salary > 50000));
console.writeline(list.any(e => e.gender == true));
// 防御性编程
console.writeline(list.single(e => e.name == "张三"));
// console.writeline(list.single(e => e.name == "孙悟空"));//没有该条信息,会报异常
console.writeline(list.singleordefault(e => e.name == "孙悟空"));
}
class employee
{
public long id { get; set; }
public string name { get; set; }
public int age { get; set; }
public bool gender { get; set; }
public int salary{ get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// c#所有的class和struct都会继承object,而每一个object都会有一个tostring的方法,这里重写该方法
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public override string tostring()
{
return $"id={id},name={name},age={age},gender={gender},salary={salary}";
}
}
class dog
{
public string nickname { get; set; }
public int age { get; set; }
public override string tostring()
{
return $"nickname = {nickname},age={age}";
}
}
static void main(string[] args)
{
list<employee> list = new list<employee>();
list.add(new employee { id = 1, name = "张三", age = 50, gender = true, salary = 50000 });
list.add(new employee { id = 2, name = "李四", age = 40, gender = false, salary = 90000 });
list.add(new employee { id = 3, name = "赵六", age = 30, gender = false, salary = 30000 });
list.add(new employee { id = 4, name = "gati", age = 34, gender = true, salary = 6000 });
list.add(new employee { id = 5, name = "jim", age = 40, gender = false, salary = 7000 });
list.add(new employee { id = 6, name = "ancle", age = 24, gender = false, salary = 2000 });
console.writeline("where:");
ienumerable<employee> employee = list.where((e) => { return e.age > 30; }); // employees.where(e => e.age > 30 );
foreach(var i in employee)
{
console.writeline(i);
}
console.writeline("count:");
console.writeline(list.count(e => e.salary > 50000));
console.writeline(list.any(e => e.gender == true));
// 防御性编程
console.writeline("single:");
console.writeline(list.single(e => e.name == "张三"));
// console.writeline(list.single(e => e.name == "孙悟空"));//没有该条信息,会报异常
console.writeline(list.singleordefault(e => e.name == "孙悟空"));
//排序
console.writeline("order:");
foreach (var i in list.orderby(e => e.salary))
{
console.writeline(i);
}
//跳过和取
console.writeline("skip and take:");
foreach (var i in list.skip(2).take(30))
{
console.writeline(i);
}
//分组
console.writeline("\r\n groupby:");
var groupitem = list.groupby(e => e.age);
foreach(var i in groupitem)
{
console.writeline(i.key);
foreach(var j in i)
{
console.writeline(j);
}
console.writeline("");
}
//投影 类似数据库的select
ienumerable<int> age_select = list.select(e => e.age); //把所有的年龄取出来
ienumerable<string> name_select = list.select(e => e.name);
console.writeline("\r\n 投影:");
foreach (var i in age_select)
{
console.writeline(i);
}
ienumerable<dog> dogs = list.select(e => new dog { nickname = e.name, age = e.age });
console.writeline("\r\n 投影dog类:");
foreach (var i in dogs)
{
console.writeline(i);
}
console.writeline("\r\n 匿名类型:");
var items = list.select(e => new{ 姓名 = e.name,性别 = e.gender?"男":"女"});
foreach (var i in items)
{
console.writeline(i.姓名+" "+i.性别);
}
//综合语法
console.writeline("\r\n 综合语法:");
var items2 = list.groupby(e => e.age).select(g => new { 年龄 = g.key, maxsalary = g.max(e => e.salary), minsalary = g.min(e => e.salary),人数 = g.count()});
foreach (var i in items2)
{
console.writeline(i. 年龄 + " " + i.maxsalary+ " " + i.minsalary + " " + i.人数);
}
}
//类型转化
ienumerable<employee> items = list.where(e => e.salary > 6000);
list<employee> l1 = items.tolist();
employee[] arry = items.toarray();
//链式语法
console.writeline("\r\n 链式语法:");
var list2 = list.where(e => e.id > 2).groupby(e => e.age).orderby(g => g.key).take(3).
select(g => new { 年龄 = g.key, 平均工资 = g.average(e => e.salary) });
foreach(var i in list2)
{
console.writeline(i.年龄 + " " + i.平均工资);
}
split方法可能会掉入的陷阱
split会按照特定字符进行分割,同时返回分割后的字符数组.分割后一定要注意字符前后端是否存在空格,不然会掉入大坑.
通过linq读取配置文件
//配置文件接口类
public interface iconfigservice
{
string getvalue(string name);
}
//配置文件实现类
public class inifileconfig : iconfigservice
{
public string filepath { get; set; }
public string getvalue(string name)
{
var kv = file.readalllines(filepath).select(s => s.split('=')).select(strs => new { name = strs[0].trim(), value = strs[1].trim() }).singleordefault(keyvalue => keyvalue.name == name);
//var kv2 = kv.select(s => s.split('='));
if (kv != null)
{
return kv.value;
}
else
{
return null;
}
}
}
//调用配置文件
inifileconfig config = new inifileconfig();
string smtpserver = config.getvalue("smtpserver");
string username = config.getvalue("username");
string password = config.getvalue("password");
linq常见问题
//linq解决面试问题
int i = 4;
int j = 5;
int k = 6;
int[] nums = new int[] { i,j,k };
//linq求解
int max = nums.max();
//math处理
int max2 = math.max(i, math.max(j, k));
//三元运算法
int max3 = (i = i > j ? i : j) > k ? i : k;
int max4 = i > j ? i > k ? i : k : j > k ? j : k;
console.writeline(max4);
//求解平均值
string s = "1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9";
string[] str = s.split(',');
ienumerable<int> arry = str.select(e => convert.toint32(e));
console.writeline(arry.average());
var avg = s.split(',').select(p => convert.toint32(p));
//统计字符串字母出现的频率
console.writeline("\r\n 统计字符串字母出现的频率:");
string s1 = "hello world,keson,hgongnoring";
var items4 = s1.where(c => char.isletter(c)).select(c => char.tolower(c)).groupby(c => c).select(g => new { g.key, count = g.count() })
.orderbydescending(g=>g.count).where(g=>g.count>2);
foreach(var item in items4)
{
console.writeline(item);
}
依赖注入
将一个类放到一个容器中,使用这个类时不需要实例化,直接从从容器中取出来
using system;
using system.collections.generic;
using system.threading.tasks;
using system.linq;
using microsoft.extensions.dependencyinjection;
namespace consoleapp1
{
class program
{
delegate void delegatefun();
static void main(string[] args)
{
/*
* 1 servicecollection是内置的反转控制容器;services.buildserviceprovider是使用容器中服务
* 2 使用步骤:创建控制容器;向容器中注册方法;使用容器的buildserviceprovider向容器中获取服务
*/
//注册服务
servicecollection services = new servicecollection();
//services.addtransient<testserviceimpl>();
//services.addsingleton<testserviceimpl>();
services.addscoped<testserviceimpl>(); //同一个scope里拿到的对象是一致的
using (serviceprovider sp = services.buildserviceprovider())
{
testserviceimpl testservice = sp.getrequiredservice<testserviceimpl>();
testservice.name = "keson";
testservice.sayhello();
testserviceimpl testservice2 = sp.getrequiredservice<testserviceimpl>();
//console.writeline("testservice, testservice2:" + object.referenceequals(testservice, testservice2));
using (iservicescope scope1 = sp.createscope())
{
testserviceimpl t = scope1.serviceprovider.getservice<testserviceimpl>();
t.name = "张三";
t.sayhello();
testserviceimpl t1 = scope1.serviceprovider.getservice<testserviceimpl>();
//console.writeline("t, t1:" + object.referenceequals(t, t1));
//console.writeline("t, testservice:" + object.referenceequals(t, testservice));
}
using (iservicescope scope2 = sp.createscope())
{
testserviceimpl t = scope2.serviceprovider.getservice<testserviceimpl>();
t.name = "李四";
t.sayhello();
}
}
}
}
public interface itestservic
{
string name { get; set; }
void sayhello();
}
public class testserviceimpl : itestservic,idisposable
{
public string name { get; set; }
public void dispose()
{
console.writeline("disposable..........");
}
public void sayhello()
{
console.writeline($"hi,my {name}");
}
}
public class testserviceimpl2 : itestservic
{
public string name { get; set; }
public void sayhello()
{
console.writeline($"你好,我是{name}");
}
}
}
依赖注入 : 接口 + 实现
直接从类中注入
在一个a类中使用另外一个b类,不需要new 一个新的b类对象,只需要在被注入对象a实例化时传入b类的接口即可。
//program.cs
static void main(string[] args)
{
notificationservice notificationservice = new notificationservice(new emailsender());
notificationservice.usesendmessage();
}
//--------------------------------------------
public interface imessagesender
{
void sendmessage(string message);
}
//--------------------------------------------
public class emailsender : imessagesender
{
public void sendmessage(string message)
{
console.writeline(message);
}
}
//--------------------------------------------
public class notificationservice
{
private readonly imessagesender messagesender;
public notificationservice(imessagesender messagesender)
{
this.messagesender = messagesender;
}
public void usesendmessage()
{
messagesender.sendmessage("hello,keson");
}
}
通过服务容器依赖注入
using system;
using system.collections.generic;
using system.threading.tasks;
using system.linq;
using microsoft.extensions.dependencyinjection;
namespace consoleapp1
{
class program
{
delegate void delegatefun();
static void main(string[] args)
{
/*
* 1 servicecollection是内置的反转控制容器;services.buildserviceprovider是使用容器中服务
* 2 使用步骤:创建控制容器;向容器中注册方法;使用容器的buildserviceprovider向容器中获取服务
*/
//注册服务
servicecollection services = new servicecollection();
services.addscoped<itestservice, testserviceimpl>(); // 接口 + 实现
services.addscoped<itestservice, testserviceimpl2>();
using (serviceprovider sp = services.buildserviceprovider()) //当然,你也可以用services.buildserviceprovider(),这里用变量接一下方便用
{
//services.buildserviceprovider().getservice<itestservic>();
itestservice itest = sp.getservice<itestservice>();
itest.name = "孙悟空";
itest.sayhello();
//console.writeline(itest.gettype());
itestservice itest1 = sp.getrequiredservice<itestservice>(); //确定一定有这个服务
ienumerable<itestservice> itest2 = sp.getservices<itestservice>(); //获取多个服务
foreach(var i in itest2)
{
console.writeline(itest2.gettype());
}
}
}
}
public interface itestservice
{
string name { get; set; }
void sayhello();
}
public class testserviceimpl : itestservice,idisposable
{
public string name { get; set; }
public void dispose()
{
console.writeline("disposable..........");
}
public void sayhello()
{
console.writeline($"hi,i am {name}");
}
}
public class testserviceimpl2 : itestservice
{
public string name { get; set; }
public void sayhello()
{
console.writeline($"你好,我是{name}");
}
}
}
依赖注入:通过构造函数
这里有一个小细节,所有实现的接口的实现必须是公有的
using system;
using system.collections.generic;
using system.threading.tasks;
using system.linq;
using microsoft.extensions.dependencyinjection;
namespace consoleapp1
{
class program
{
delegate void delegatefun();
static void main(string[] args)
{
servicecollection services = new servicecollection();
services.addscoped<controller>();
services.addscoped<ilog, logimpl>();
services.addscoped<istorage, storageimpl>();
services.addscoped<iconfig, configimpl>();
services.addscoped<ilog, logimpl>();
using(var sp = services.buildserviceprovider())
{
var c = sp.getrequiredservice<controller>();
c.test();
}
console.readkey();
}
}
class controller
{
private readonly ilog log;
private readonly istorage storage;
public controller(ilog log,istorage storage)
{
this.log = log;
this.storage = storage;
}
public void test()
{
log.log("开始上传");
storage.save(" 名字 ", " 上传的内容 ");
log.log("上传完毕");
}
}
interface ilog
{
void log(string msg);
}
class logimpl : ilog
{
public void log(string msg)
{
console.writeline($"日志: {msg}");
}
}
interface iconfig
{
string getvalue(string name);
}
class configimpl:iconfig
{
public string getvalue(string name)
{
return "config file";
}
}
interface istorage
{
void save(string name,string content);
}
class storageimpl:istorage
{
private readonly iconfig config;
public storageimpl(iconfig config)
{
this.config = config;
}
public void save(string name,string content)
{
string server = config.getvalue("server");
console.writeline($"向服务器为: {server}的文件名为: {name}上传:{content}");
}
}
}
配置读取
配置容器
可能年纪大了,对于那种不讲人话的人,特别反感,包括但不限于:领导、同同事、同学、长辈、博主、水军、我自己。他们就一个特点,很简单的事情他们包装的面目全非,听得新人云里雾里,以彰显在别人眼里不值一提的优越感。
什么是配置容器?他就是一种管理配置文件的东西。什么是配置文件,举个例子,你想连接数据库,你得有账户名、密码、端口号等等,这些东西不可能每次登录都自己手动输入,也不可能都会提供输入这些信息的界面,那就得从文件中读取,我们把它叫做配置文件。
*本章的核心就是configrution这个命名空间,*搞懂这个就ok了,主要包括两个点:怎么创建配置容器?如何通过配置容器读取配置文件。
步骤
-
构建配置容器;
-
向配置容器中添加配置文件(json,xml,txt);
-
通过build()读取配置文件;
configurationbuilder builder = new();
builder.addjsonfile("config.json",optional:true,reloadonchange:true);
iconfigurationroot configroot = builder.build();
json文件作为绑定源, 配置类作为绑定目标. 将配置类绑定到配置文件. 配置文件肯定得拿出来才能用, 如果一致放在json文件中,无法用,所以用一个和json配置文件相同的类来接受数据
//选项类被绑定到 icconfigurationroot 接口
config config = new config();
configurationroot.bind(config);
//选项类被绑定到 icconfigurationroot 接口 子类
service service = new service();
configurationroot.getsection("service").bind(service);
实例:数据源绑定单个类
该方式将类单个单个的配置,配置起来简单,但不利于集中管理
//json file
{
"key1": "iamstring",
"key2": 10,
"key3": true
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------
using microsoft.extensions.configuration;
using microsoft.extensions.configuration.json;
class program
{
static void main(string[] args)
{
iconfigurationbuilder builder = new configurationbuilder();
builder.addjsonfile("appsetting.json", optional: true, reloadonchange: true);
var configurationroot = builder.build();
//选项类被绑定到 icconfigurationroot 接口
config config = new config();
configurationroot.bind(config);
console.writeline($"key1:{config.key1}");
console.writeline($"key2:{config.key2}");
console.writeline($"key3:{config.key3}");
//选项类被绑定到 icconfigurationroot 接口 子类
service service = new service();
configurationroot.getsection("service").bind(service);
console.writeline($"service.host {service.host}");
console.writeline($"service.host {service.port}");
//
console.readkey();
}
}
class config
{
public string key1 { get; set; }
public int key2 { get; set; }
public bool key3 { get; set; }
}
class service
{
public string host { get; set; }
public string port { get; set; }
//不能注入私有属性
//public string port { get; private set; } = "999";
}
注册服务
步骤
-
创建一个服务容器;
-
容器对配置类进行注册服务;
services.configurede<ttype>{lamda表达式}; -
获取服务
serviceprovider.getrequiredservice<ioptions<myoption>>();
//或者
serviceprovider.getrequiredservice<ioptionssnapshot<config>>();
实例:直接通过lambda表达式对类配置
using microsoft.extensions.configuration;
//using microsoft.extensions.configuration.json;
using microsoft.extensions.dependencyinjection;
using microsoft.extensions.options;
using system;
var services = new servicecollection();
// 通过.configure 对选项类进行配置(注册服务)
services.configure<myoption>(n =>
{
n.a = "keson";
n.b = "";
});
var serviceprovider = services.buildserviceprovider();
//通过<ioptions<myoption>>()获取服务
var myoption = serviceprovider.getrequiredservice<ioptions<myoption>>();
myoption myoptionvalue = myoption.value;
console.writeline(myoptionvalue.a);
console.writeline(myoptionvalue.b);
public class myoption
{
public string a { get; set; }
public string b { get; set; }
}
实例:通过addoption配置
这种方法配置起来也很简单,且可以链式编程(集中配置,再一个地方对多个类绑定数据源)
addoption和ioptionssnapshot区别:前者是刚运行时就保存在缓存中,后者是每次处理请求时都会重新从ioptionssnapshot中读取,以便能够获取到最新的配置信息。
//--------------------------json文件-------------------------------
{
"name": "keson",
"age": "28",
"proxy": {"address": "192.168.1.0","port": "80"}
}
//--------------------------main()-------------------------------
namespace 配置文件
{
internal class program
{
static void main(string[] args)
{
servicecollection services = new();
services.addscoped<controller>();
configurationbuilder builder = new();
/*
//通过json读取配置文件
builder.addjsonfile("config.json",optional:true,reloadonchange:true);
*/
//通过命令行读取配置文件 可以在调试中设置 不同参数用空格分开,不能有多余的空格
builder.addcommandline(args);
iconfigurationroot configroot = builder.build();
services.addoptions().configure<config>(e => configroot.bind(e));
using (var sp= services.buildserviceprovider())
{
//通过一个controller类来操控config
var c2 = sp.getrequiredservice<controller>();
c2.test();
//直接操控
var c = sp.getrequiredservice<ioptionssnapshot<config>>();
c.value.name = "孙悟空";
c.value.age = "500";
console.writeline(c.value.name);
console.writeline("--------------");
console.writeline(c.value.age);
}
}
}
class config
{
public string name { get; set; }
public string age { get; set; }
public proxy proxy { get; set; }
}
class proxy
{
public string address { get; set; }
public int port { get; set; }
}
}
//--------------------------controller-------------------------------
internal class controller
{
//用于访问请求生存期的 toptions 的值
private readonly ioptionssnapshot<config> optconfig;
public controller(ioptionssnapshot<config> optconfig)
{
this.optconfig = optconfig;
}
public void test()
{
console.writeline(optconfig.value.name);
console.writeline("--------------");
console.writeline(optconfig.value.age);
}
}
扁平化配置
name=如来 age=10000 proxy:address=1.1.1.1 proxy:port=9999 proxy:ids:0=69 proxy:ids:1=69
日志系统
日志级别
trace -> debug -> informatio -> warning -> error -> critical
日志记录到控制台
核心代码:
-
引用扩展包
-
将日志记录到控制台
-
设置记录到控制台代码log level
using microsoft.extensions.logging; //记录日志用的扩展包
loggingbuilder.addconsole(); //将日志记录到控制台
loggingbuilder.setminimumlevel(loglevel.trace); //设置最低输出级别信息
完整代码
//----------------test()类-------------------------
using microsoft.extensions.logging;
using system;
using system.collections.generic;
using system.linq;
using system.text;
using system.threading.tasks;
namespace 日志系统
{
internal class testlogging
{
private readonly ilogger<testlogging> logger;
public testlogging(ilogger<testlogging> logger)
{
this.logger = logger;
}
public void test()
{
logger.logdebug("开始执行logging");
logger.logwarning("程序警告");
logger.logerror("程序失败");
try
{
file.readalltext("a://");
logger.logdebug("读取文件成功");
}
catch (exception e)
{
logger.logerror(e, "读取文件失败"); //将捕获的异常也打印出来
}
}
}
}
//----------------main()-------------------------
using microsoft.extensions.dependencyinjection;
using microsoft.extensions.logging;
using microsoft.extensions.logging.console;
using 日志系统;
servicecollection services = new servicecollection();
services.addlogging(loggingbuilder =>
{
loggingbuilder.addconsole(); //将日志记录到控制台
//loggingbuilder.addeventlog(); //将日志记录到windows日志事件中
loggingbuilder.setminimumlevel(loglevel.trace); //设置最低输出级别信息
});
services.addscoped<testlogging>();
using(var sp = services.buildserviceprovider())
{
testlogging testlogging = sp.getrequiredservice<testlogging>();
testlogging.test();
}
日志记录到文本: nlog
官网查看例程
很多时候我们不仅需要从控制台查看日志, 还需要从日志文件上查看, microsoft.extensions.logging不满足需求, 需要引用 nlog.extensions.logging . 下面的例图是访问nlog.extensions.logging扩展包的方法

复制config代码,注意名字一定要是nlog.config , 存储位置也要修改,直接改为程序的根目录.

nlog核心代码
nlog是通过xml实现配置的, 主要有两部分组成: target 和 rules, 先定义目标,通过规则匹配
target:
- type: 输出到文件还是控制台
- name: target的名字,就像你声明一个变量 int a = 5, 引用它的时候,就可以通过name引用.
- filename: 输出文件名字
rules:
- name: 匹配的名字,允许使用正则表达式,例如匹配命名空间的名字
- minlevel: 需要记录的最低日志权限
- wirteto: 需要输出到的匹配的 target name
<targets>
<target xsi:type="file" name="allfile" filename="test.log"/>
<target xsi:type="console" name="lifetimeconsole" />
</targets>
<rules>
<logger name="*" minlevel="trace" writeto="allfile" />
<logger name="systemservices.*" minlevel="warn" writeto="lifetimeconsole" />
</rules>
实例
- main()
using microsoft.extensions.dependencyinjection;
using microsoft.extensions.logging;
//using microsoft.extensions.logging.console;
using nlog.extensions.logging;
using systemservices;
using 日志系统;
servicecollection services = new servicecollection();
services.addlogging(loggingbuilder =>
{
//loggingbuilder.addconsole();
//loggingbuilder.addeventlog(); //将日志记录到windows日志事件中
loggingbuilder.addnlog(); //日志记录到文本文件
//loggingbuilder.setminimumlevel(loglevel.trace); //设置最低输出级别信息
});
services.addscoped<test1>();
services.addscoped<test2>();
using(var sp = services.buildserviceprovider())
{
test1 test1 = sp.getrequiredservice<test1>();
test1.test();
test2 test2 = sp.getrequiredservice<test2>();
test2.test();
}
- nlog.config
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<nlog xmlns="http://www.nlog-project.org/schemas/nlog.xsd"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/xmlschema-instance"
autoreload="true"
internalloglevel="info"
internallogfile="internal-nlog-aspnetcore.txt">
<!-- enable asp.net core layout renderers -->
<extensions>
<add assembly="nlog.web.aspnetcore"/>
</extensions>
<!-- the targets to write to -->
<targets>
<!-- file target for all log messages with basic details -->
<target xsi:type="file" archiveabovesize="100" maxarchivefiles="10" name="allfile" filename="logs/nlog-aspnetcore-all-${shortdate}.log"
layout="${longdate}|${event-properties:item=eventid_id:whenempty=0}|
${level:uppercase=true}|${logger}|${message} ${exception:format=tostring}" />
<!-- file target for own log messages with extra web details using some asp.net core renderers -->
<target xsi:type="file" name="ownfile-web" archiveabovesize="1000" filename="logs/nlog-aspnetcore-own-${shortdate}.log"
layout="${longdate}|${event-properties:item=eventid_id:whenempty=0}|
${level:uppercase=true}|${logger}|${message} ${exception:format=tostring}|url: ${aspnet-request-url}|action: ${aspnet-mvc-action}" />
<!--console target for hosting lifetime messages to improve docker / visual studio startup detection -->
<target xsi:type="console" name="lifetimeconsole" layout="${microsoftconsolelayout}" />
</targets>
<!-- rules to map from logger name to target -->
<rules>
<!--all logs, including from microsoft-->
<logger name="*" minlevel="trace" writeto="allfile" />
<logger name="日志系统.*" minlevel="debug" writeto="lifetimeconsole" />
<logger name="systemservices.*" minlevel="warn" maxlevel="warn" writeto="lifetimeconsole" />
<!--output hosting lifetime messages to console target for faster startup detection -->
<logger name="microsoft.hosting.lifetime" minlevel="info" writeto="lifetimeconsole, ownfile-web" final="true" />
<!--skip non-critical microsoft logs and so log only own logs (blackhole) -->
<logger name="microsoft.*" maxlevel="info" final="true" />
<logger name="system.net.http.*" maxlevel="info" final="true" />
<logger name="*" minlevel="trace" writeto="ownfile-web" />
</rules>
</nlog>
-
两个test类
//------------------test1------------------ using microsoft.extensions.logging; using system; using system.collections.generic; using system.linq; using system.text; using system.threading.tasks; namespace 日志系统 { internal class test1 { private readonly ilogger<test1> logger; public test1(ilogger<test1> logger) { this.logger = logger; } public void test() { logger.logdebug("test1开始执行"); logger.logwarning("test1程序警告"); logger.logerror("test1程序失败"); } } } //------------------test2------------------ using microsoft.extensions.logging; using system; using system.collections.generic; using system.linq; using system.text; using system.threading.tasks; using 日志系统; namespace systemservices { internal class test2 { private readonly ilogger<test2> logger; public test2(ilogger<test2> logger) { this.logger = logger; } public void test() { logger.logdebug("test2开始执行"); logger.logwarning("test2开始执行程序警告"); logger.logerror("test2开始执行程序失败"); } } }
serilog: 结构化日志
以键值对的形式传保存日志
主要代码和nlog基本一致,只要把 serilog添加到容器中就好
using serilog;
using serilog.formatting.json;
servicecollection services = new servicecollection();
services.addlogging(loggingbuilder =>
{
//loggingbuilder.addconsole();
//loggingbuilder.addeventlog(); //将日志记录到windows日志事件中
//loggingbuilder.addnlog(); //日志记录到文本文件
//loggingbuilder.setminimumlevel(loglevel.trace); //设置最低输出级别信息
//使用serilog
serilog.log.logger = new loggerconfiguration()
.minimumlevel.debug()
.writeto.console(new jsonformatter())
.writeto.file(new jsonformatter(), "logs/serilog.log")
.createlogger();
loggingbuilder.addserilog();
});
entity framework core
通过c#代码创建表
假设我们要设计这样一张表,我们是不是得一句一句的去写sql语句

操作步骤:
-
先建实体类, 再建实体配置类, 再建数据库配置
-
控制台迁移数据: add-migration init
-
将数据写入数据库: update-database
// 1.建立实体类 internal class person { public int id { get; set; } public string name { get; set; } public int age { get; set; } public datetime birthday { get; set;} public string birthplace { get; set; } } //2.配置实体类 internal class personentityconfig:ientitytypeconfiguration<person> { public void configure(entitytypebuilder<person> builder) //configure继承自ientitytypeconfiguration { builder.totable("t_persons"); } } //3.也可以只定义实体类,但不配置,系统会默认配置 internal class dog { public int id { get; set; } public string name { get; set; } } //4.写个数据库配置类 将要写入数据库的类用dbset<type>在这里声明,同时该类继承自dbcontext.类里重写两个方法,onconfiguring用啦配置数据的连接 onmodelcreating组装数据模型 internal class mydbcontext:dbcontext { public dbset<book> books { get; set; } public dbset<person> persons { get; set; } public dbset<dog> dog { get; set; } protected override void onconfiguring(dbcontextoptionsbuilder optionsbuilder) { string connstr = "server=.;database=demo1;trusted_connection=true;encrypt=false;"; optionsbuilder.usesqlserver(connstr); optionsbuilder.logto(console.writeline); } protected override void onmodelcreating(modelbuilder modelbuilder) { base.onmodelcreating(modelbuilder); modelbuilder.applyconfigurationsfromassembly(this.gettype().assembly); } } //5. 控制台迁移数据: add-migration init; 将数据写入数据库: update-database
通过c#对表进行怎删改查
上面的内容是对数据库的表进行设计, 怎么实现对设计好的表进行增删改查
插入数据/查询数据
-------------------------main()-----------------------------
using ef_core;
using (mydbcontext ctx = new mydbcontext())
{
//ctx相当于逻辑上的数据库
dog d = new dog();
d.name = "旺财";
ctx.dog.add(d); //把d对象加入dog这个逻辑上的表里
//ctx.savechanges();
await ctx.savechangesasync();
book b1 = new book { name = "三体", authorname = "刘慈欣", price = 15 };
book b2 = new book { name = "西游记", authorname = "罗贯中", price = 20 };
book b3 = new book { name = "水浒传", authorname = "施耐庵", price = 18 };
book b4 = new book { name = "红楼梦", authorname = "曹雪芹", price = 19 };
ctx.books.add(b1);
ctx.books.add(b2);
ctx.books.add(b3);
ctx.books.add(b4);
var books = ctx.books.select(b => b.price ==15).tolist(); //查询数据
iqueryable<book> books = ctx.books.where(b => b.price > 18);
foreach (book book in books)
{
console.writeline(book.name);
console.writeline("**********");
}
}
删除数据/更新数据
//删除内容: 1.先查出实体 2.从内存中删除数据
var b = ctx.books.where(b=>b.name == "西游记");
foreach(var i in b)
{
//ctx.books.remove(i); //删除数据
i.authorname = "guanzhong luo"; //跟新数据
}
fluenapi和dataannotation区别
fluenapi复杂不耦合, dataannotation简单但是存在耦合
# fluenapi: 单独写个配置类
internal class personentityconfig:ientitytypeconfiguration<person>
{
public void configure(entitytypebuilder<person> builder)
{
builder.totable("t_persons");
}
}
# dataannotation: 直接通过注解的方式配置
[table("t_cat")]
internal class cat
{
public int id { get; set; }
[required]
[maxlength(69)]
public string name { get; set; }
public int catid1 { get; set; }
[notmapped] //不将该属性映射到数据库,尽量不要用
public int catid2 { get; set; }
}
guid用法
---------------实体类---------------------
internal class rabbit
{
public guid id { get; set; }
public string name { get; set; }
}
---------------main()---------------------
rabbit r1 = new rabbit();
r1.name = "红兔";
ctx.rabbits.add(r1);
await ctx.savechangesasync();
hi/lo算法
migration的常用命令
-
把数据库升级或者回滚到某个状态: update-database migrationstate
-
删除最后一次的迁移脚本: remov-migration
-
生成sql迁移脚本: script-migration
-
add-migration 取一个名字
-
updat-database
反向工程
scaffold-dbcontext "server=.;database=student;trusted_connection=true;multipleactiveresultsets=true;encrypt=false;" microsoft.entityframeworkcore.sqlserver
ef core查询执行sql语句
- 标准日志: optionsbuilder.useloggerfactory(loggerfactory)
- 简单日志: optionsbuilder.logto(console.writeline)
- toquerystring()方法: var books = ctx.books.where(b => b.price ==15); string sql = books.toquerystring();
怎么记录c#代码对数据库的操作步骤,可以有标准日志和简单日志的方法
--------------book类----------------
internal class book
{
public long id { get; set; }
public string name { get; set; }
public string title { get; set; }
public string authorname { get; set; }
public float price { get; set; }
}
--------------book配置类------------------
using ef_core;
using static system.reflection.metadata.blobbuilder;
using (mydbcontext ctx = new mydbcontext())
{
book b1 = new book { name = "三体", authorname = "刘慈欣", price = 15 };
ctx.books.add(b1);
await ctx.savechangesasync();
var books = ctx.books.where(b => b.price ==15);
string sql = books.toquerystring();
console.writeline(sql);
}
-------------main()------------------
internal class mydbcontext:dbcontext
{
private static iloggerfactory loggerfactory =
loggerfactory.create(b => b.addconsole());
public dbset<book> books { get; set; }
protected override void onconfiguring(dbcontextoptionsbuilder optionsbuilder)
{
string connstr = "server=.;database=student;trusted_connection=true;encrypt=false;";
optionsbuilder.usesqlserver(connstr);
optionsbuilder.useloggerfactory(loggerfactory); //标准日志
optionsbuilder.logto(console.writeline); //简单日志
}
protected override void onmodelcreating(modelbuilder modelbuilder)
{
base.onmodelcreating(modelbuilder);
modelbuilder.applyconfigurationsfromassembly(this.gettype().assembly);
}
}
ef core映射mysql
所有代码都和上面的sqlserver一样,只是在dbcontext上修改, 在onconfiguring上进行配置
string mysqlconnestr = "server=localhost;user=root;password=123456;database=demo1";
//特别注意:此处使用的是:pomelo.entityframework.mysql包.
var serverversion = new mysqlserverversion(new version(8, 0, 34));
optionsbuilder.usemysql(mysqlconnestr, serverversion);
对应关系: 关系配置在任何一方
一个artcle对应多个comment
四种关系: 弄清楚谁是主语,谁是宾语
| one | many | |
|---|---|---|
| has | hasone | hasmany |
| with | withone | withmany |
一对多: 关系配置在多端
comment类和配置
internal class comment
{
public long id { get; set; }
public string? message { get; set; }
public artcle? artcle1 { get; set; }
}
internal class commentconfig : ientitytypeconfiguration<comment>
{
public void configure(entitytypebuilder<comment> builder)
{
builder.totable("t_commnet");
builder.hasone(c => c.artcle1).withmany(a=>a.comments);
}
}
artcle类和配置类
internal class artcle
{
public long id { get; set; }
public string? title { get; set; }
public string? message { get; set; }
public list<comment> comments { get; set; } = new list<comment>();
}
internal class artcleconfig : ientitytypeconfiguration<artcle>
{
public void configure(entitytypebuilder<artcle> builder)
{
builder.totable("t_artcle");
}
}
mydbcontext
internal class mydbcontext:dbcontext
{
public dbset<artcle> artcles { get; set; }
public dbset<comment> comments { get; set; }
protected override void onconfiguring(dbcontextoptionsbuilder optionsbuilder)
{
string connstr = "server=.;database=demo1;trusted_connection=true;encrypt=false;";
optionsbuilder.usesqlserver(connstr);
//optionsbuilder.logto(console.writeline);
}
protected override void onmodelcreating(modelbuilder modelbuilder)
{
base.onmodelcreating(modelbuilder);
modelbuilder.applyconfigurationsfromassembly(this.gettype().assembly);
}
}
main()
using ef_core;
using microsoft.entityframeworkcore;
using 一对多;
using (mydbcontext ctx = new mydbcontext())
{
/*
artcle artcle = new();
artcle.title = "keson is the best";
artcle.message = "据说,他是当代扫地僧";
//comment c1 = new() { message = "太牛了" };
comment c2 = new() { message = "也太搞笑了" };
//artcle.comments.add(c1);
artcle.comments.add(c2);
ctx.artcles.add(artcle);
ctx.savechanges();
*/
/*
//iqueryable<artcle> artcles = ctx.artcles.where(a => a.id == 1); //不查询关联表
iqueryable<artcle> artcles = ctx.artcles.include(a=>a.comments). where(a => a.id == 1); //关联表也查询出来
foreach (var artcle in artcles)
{
console.writeline(artcle.id);
console.writeline(artcle.title);
foreach(var c in artcle.comments)
{
}
}
*/
/*
var comments = ctx.comments.include(c=>c.artcle1).where(c => c.id == 1);
foreach(var c in comments)
{
console.writeline(c.id);
console.writeline(c.artcle1.id);
console.writeline(c.artcle1.message);
}
*/
//上面的取法会取出所有的字段,通过匿名方法可以只获取需要的字段,提高数据库性能
var a1 = ctx.artcles.select(a => new { a.id, a.title }).first();
console.writeline(a1.id + a1.title);
}
一对多:关系配置在一端
所有的代码都一样,只是配置在一端
internal class artcleconfig : ientitytypeconfiguration<artcle>
{
public void configure(entitytypebuilder<artcle> builder)
{
builder.totable("t_artcle");
builder.hasmany(a => a.comments).withone(c => c.artcle1);
}
}
efcore性能
ef core绝大部分的性能超过绝大多数程序员
单向导航
-
withmany()不带参数
-
有主从表的用一对多
-
只是基础处关系的用单向导航
internal class user
{
public long id { get; set; }
public string name { get; set; }
}
internal class userconfig : ientitytypeconfiguration<user>
{
public void configure(entitytypebuilder<user> builder)
{
builder.totable("t_user");
}
}
*******************************
internal class leave
{
public long id { get; set; }
public user requester { get; set; }
public user? approver { get; set; }
public string? remake { get; set; }
}
internal class leaveconfig : ientitytypeconfiguration<leave>
{
public void configure(entitytypebuilder<leave> builder)
{
builder.totable("t_leaves");
builder.hasone<user>(l => l.requester).withmany();
builder.hasone<user>(l => l.approver).withmany();
}
}
*******************************
internal class mydbcontext:dbcontext
{
public dbset<user> users { get; set; }
public dbset<leave> leaves { get; set; }
protected override void onconfiguring(dbcontextoptionsbuilder optionsbuilder)
{
string connstr = "server=.;database=demo1;trusted_connection=true;encrypt=false;";
optionsbuilder.usesqlserver(connstr);
optionsbuilder.logto(console.writeline);
}
protected override void onmodelcreating(modelbuilder modelbuilder)
{
base.onmodelcreating(modelbuilder);
modelbuilder.applyconfigurationsfromassembly(this.gettype().assembly);
}
}
--------------------main()----------------------
using ef_core;
using 单向导航;
console.writeline("hello, world!");
using (mydbcontext ctx = new mydbcontext())
{
/*
var l = ctx.leaves.firstordefault();
if (l != null)
{
console.writeline(l);
}
*/
user u1 = new user { name = "孙悟空" };
leave leave = new leave { requester = u1, remake = "回家结婚" };
ctx.leaves.add(leave);
ctx.savechanges();
}




发表评论