网上学习资料一大堆,但如果学到的知识不成体系,遇到问题时只是浅尝辄止,不再深入研究,那么很难做到真正的技术提升。
一个人可以走的很快,但一群人才能走的更远!不论你是正从事it行业的老鸟或是对it行业感兴趣的新人,都欢迎加入我们的的圈子(技术交流、学习资源、职场吐槽、大厂内推、面试辅导),让我们一起学习成长!
{
cloud_segments_array[1]->points.push\_back(current_point);
}
else if (origin_distance < clustering_ranges_[2])
{
cloud_segments_array[2]->points.push\_back(current_point);
}
else if (origin_distance < clustering_ranges_[3])
{
cloud_segments_array[3]->points.push\_back(current_point);
}
else
{
cloud_segments_array[4]->points.push\_back(current_point);
}
}
std::vector<std::thread> thread\_vec(cloud_segments_array.size());
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < cloud_segments_array.size(); i++)
{
std::promise<std::vector<pcl::pointindices>> promiseobj;
std::shared_future<std::vector<pcl::pointindices>> futureobj = promiseobj.get\_future();
thread_vec[i] = std::thread(&euclideancluster::clusterindicesmultithread, this, cloud_segments_array[i], std::ref(clustering_distances_[i]), std::ref(promiseobj));
clusterindices = futureobj.get();
for (int j = 0; j < clusterindices.size(); j++)
{
//每次聚类得出的indices为输入点云对应的索引
pcl::pointcloud<pcl::pointxyzi>::ptr temp\_cluster(new pcl::pointcloud<pcl::pointxyzi>);
pcl::copypointcloud(\*cloud_segments_array[i], clusterindices[j], \*temp_cluster);
\*outcloudptr += \*temp_cluster;
points_vector.push\_back(temp_cluster);
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < thread_vec.size(); i++)
{
thread_vec[i].join();
}
}
}
## 计算包围框
先介绍下包围框
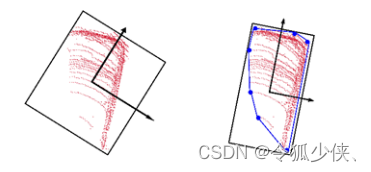
包围框的定义:
* 包围框指一个简单几何空间,在三维点云中,里面包含一系列点集,为点集构建包围框能够有效提取障碍物几何属性给跟踪模块作为观测值。
包围框分类:
* 轴对齐包围框:包围框的三条边与坐标轴平行,无方向,目标有旋转时会增大间隙
* 方向包围框:根据目标几何形状来决定包围框大小和方向,也就是计算最小外接斜矩形,常用方法:pca算法和l-shape拟合
* 点云凸包:最小凸多边形也叫凸包,就是将最外层点链接起来,包含所有的点集,常用算法granham扫描法
此代码流程:
1. 聚类并计算障碍物中心,和bounding box
五个点云分别使用不同的半径阈值进行欧几里德聚类,对聚类完以后的一个个点云簇,我们计算其形心作为该障碍物的中心,同时计算点云簇的长宽高,从而确定一个能够将点云簇包裹的三维bounding box
2. 凸多边形拟合,优化bounding box的中心和长宽
3. 计算bounding box朝向
采用拟合出的凸多边型的顶点计算点云轮廓最小外界矩形,是一个box2d结构,包含最小外接矩形的中心、宽高、旋转角度(水平轴(x轴)逆时针旋转,与碰到的矩形的第一条边的夹角)
void boundingbox::setcloud(std_msgs::header header, const pcl::pointcloudpcl::pointxyzi::ptr in, bool in_estimate_pose)
{
// extract pointcloud using the indices
// calculate min and max points
pcl::pointcloudpcl::pointxyzrgb::ptr currentcluster(new pcl::pointcloudpcl::pointxyzrgb);
float min_x = std::numeric_limits::max();
float max_x = -std::numeric_limits::max();
float min_y = std::numeric_limits::max();
float max_y = -std::numeric_limits::max();
float min_z = std::numeric_limits::max();
float max_z = -std::numeric_limits::max();
float average_x = 0, average_y = 0, average_z = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < in->points.size(); i++)
{
// fill new colored cluster point by point
pcl::pointxyzrgb p;
p.x = in->points[i].x;
p.y = in->points[i].y;
p.z = in->points[i].z;
average_x += p.x;
average_y += p.y;
average_z += p.z;
centroid_.x += p.x;
centroid_.y += p.y;
centroid_.z += p.z;
currentcluster->points.push\_back(p);
if (p.x < min_x)
min_x = p.x;
if (p.y < min_y)
min_y = p.y;
if (p.z < min_z)
min_z = p.z;
if (p.x > max_x)
max_x = p.x;
if (p.y > max_y)
max_y = p.y;
if (p.z > max_z)
max_z = p.z;
}
// min, max points
minpoint_.x = min_x;
minpoint_.y = min_y;
minpoint_.z = min_z;
maxpoint_.x = max_x;
maxpoint_.y = max_y;
maxpoint_.z = max_z;
// calculate centroid, average
if (in->points.size() > 0)
{
centroid_.x /= in->points.size();
centroid_.y /= in->points.size();
centroid_.z /= in->points.size();
average_x /= in->points.size();
average_y /= in->points.size();
average_z /= in->points.size();
}
averagepoint_.x = average_x;
averagepoint_.y = average_y;
averagepoint_.z = average_z;
// calculate bounding box
float length_ = maxpoint_.x - minpoint_.x;
float width_ = maxpoint_.y - minpoint_.y;
float height_ = maxpoint_.z - minpoint_.z;
boundingbox_.header = header;
boundingbox_.pose.position.x = minpoint_.x + length_ / 2;
boundingbox_.pose.position.y = minpoint_.y + width_ / 2;
boundingbox_.pose.position.z = minpoint_.z + height_ / 2;
boundingbox_.dimensions.x = ((length_ < 0) ? -1 * length_ : length_);
boundingbox_.dimensions.y = ((width_ < 0) ? -1 * width_ : width_);
boundingbox_.dimensions.z = ((height_ < 0) ? -1 * height_ : height_);
// pose estimation
double rz = 0;
std::vectorcv::point2f points;
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < currentcluster->points.size(); i++)
{
cv::point2f pt;
pt.x = currentcluster->points[i].x;
pt.y = currentcluster->points[i].y;
points.push_back(pt);
}
std::vectorcv::point2f hull;
cv::convexhull(points, hull);
polygon_.header = header;
for (size_t i = 0; i < hull.size() + 1; i++)
{
geometry_msgs::point32 point;
point.x = hull[i % hull.size()].x;
point.y = hull[i % hull.size()].y;
point.z = minpoint_.z;
polygon_.polygon.points.push_back(point);
}
if (in_estimate_pose)
{
cv::rotatedrect box = minarearect(hull);
rz = box.angle * 3.14 / 180;
boundingbox_.pose.position.x = box.center.x;
boundingbox_.pose.position.y = box.center.y;
boundingbox_.dimensions.x = box.size.width;
boundingbox_.dimensions.y = box.size.height;
}
// set bounding box direction
tf::quaternion quat = tf::createquaternionfromrpy(0.0, 0.0, rz);
/** \brief convert quaternion to quaternion msg*/
tf::quaterniontftomsg(quat, boundingbox_.pose.orientation);
currentcluster->width = currentcluster->points.size();
currentcluster->height = 1;
currentcluster->is_dense = true;
// get eigenvalues, eigenvectors
if (currentcluster->points.size() > 3)
{
pcl::pcapcl::pointxyz currentclusterpca;
pcl::pointcloudpcl::pointxyz::ptr current_cluster_mono(new pcl::pointcloudpcl::pointxyz);
pcl::copypointcloud(\*currentcluster, \*current_cluster_mono);
currentclusterpca.setinputcloud(current_cluster_mono);
eigenvectors_ = currentclusterpca.geteigenvectors();
eigenvalues_ = currentclusterpca.geteigenvalues();
}
validcluster_ = true;
pointcloud_ = currentcluster;
}
4.对可能的bounding\_box进行合并
void boundingbox::getboundingbox(std_msgs::header header,
std::vector<pcl::pointcloudpcl::pointxyzi::ptr> &points_vector,
autoware_msgs::cloudclusterarray &inoutclusters)
{
std::vector clusters;
for (int i = 0; i < points_vector.size(); i++)
{
// pcl::pointcloudpcl::pointxyzi::ptr temp_cluster(new pcl::pointcloudpcl::pointxyzi);
// pcl::copypointcloud(*in, it->indices, *temp_cluster);
// *outcloudptr += *temp_cluster;
boundingboxptr cluster(new boundingbox());
cluster->setcloud(header, points_vector[i], inestimatepose_);
clusters.push\_back(cluster);
}
// clusters can be merged or checked in here
// check for mergable clusters
std::vector midclusters;
std::vector finalclusters;
if (clusters.size() > 0)
checkallformerge(header, clusters, midclusters, clustermergethreshold_, inestimatepose_);
else
midclusters = clusters;
if (midclusters.size() > 0)
checkallformerge(header, midclusters, finalclusters, clustermergethreshold_, inestimatepose_);
else
finalclusters = midclusters;
// get final pointcloud to be published
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < clusters.size(); i++)
{
if (clusters[i]->validcluster_)
{
autoware_msgs::cloudcluster cloudcluster;
clusters[i]->torosmessage(header, cloudcluster);
inoutclusters.clusters.push_back(cloudcluster);
}
}
inoutclusters.header = header;
}
**网上学习资料一大堆,但如果学到的知识不成体系,遇到问题时只是浅尝辄止,不再深入研究,那么很难做到真正的技术提升。**
**[需要这份系统化的资料的朋友,可以添加戳这里获取](https://bbs.csdn.net/topics/618668825)**
**一个人可以走的很快,但一群人才能走的更远!不论你是正从事it行业的老鸟或是对it行业感兴趣的新人,都欢迎加入我们的的圈子(技术交流、学习资源、职场吐槽、大厂内推、面试辅导),让我们一起学习成长!**
181)]
[外链图片转存中...(img-oq9amwjk-1715884623181)]
**网上学习资料一大堆,但如果学到的知识不成体系,遇到问题时只是浅尝辄止,不再深入研究,那么很难做到真正的技术提升。**
**[需要这份系统化的资料的朋友,可以添加戳这里获取](https://bbs.csdn.net/topics/618668825)**
**一个人可以走的很快,但一群人才能走的更远!不论你是正从事it行业的老鸟或是对it行业感兴趣的新人,都欢迎加入我们的的圈子(技术交流、学习资源、职场吐槽、大厂内推、面试辅导),让我们一起学习成长!**


发表评论