一、disruptor的简介
disruptor是基于事件异步驱动模型实现的,采用了ringbuffer数据结构,支持高并发、低延时、高吞吐量的高性能工作队列,它是由英国外汇交易公司lmax开发的,研发的初衷是解决内存队列的延迟问题,不同于我们常用的分布式消息中间件rocketmq、kafaka,而disruptor是单机的、本地内存队列,类似jdk的arrayblockingqueue等队列。
disruptor的使用场景
- 加密货币交易撮合引擎
- log4j2基于disruptor实现的异步日志处理
- canal+disruptor实现高效的数据同步
- 知名开源框架apache strom
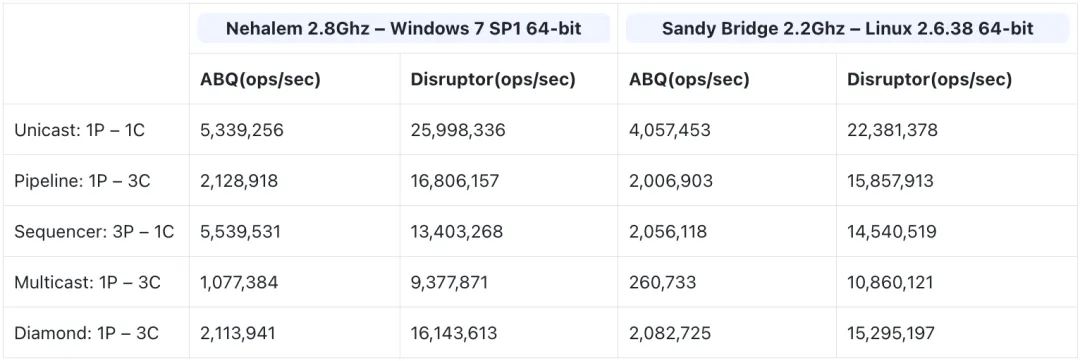
disruptor和arrayblockingqueue性能对比
- arrayblockingqueue是基于数组arraylist实现的,通过reentrantlock独占锁保证线程安全;
- disruptor是基于环形数组队列ringbuffer实现的,通过cas乐观锁保证线程安全。在多种生产者-消费者模式下的性能对比。

figure 1. unicast: 1p--1c

figure 2. three step pipeline: 1p--3c
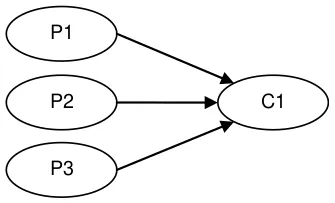
figure 3. sequencer: 3p--1c

figure 4. multicast: 1p--3c
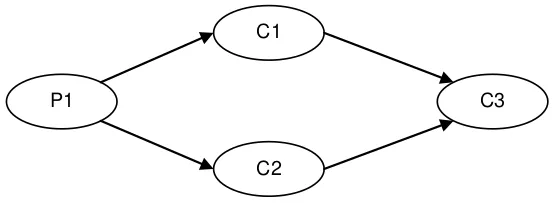
figure 5. diamond: 1p--3c
disruptor快速接入指南
引入maven依赖
<dependency>
<groupld>com.lmax</groupld>
<artifactld>disruptor</artifactld>
<version>4.0.0</version>
</dependency>
自定义事件和事件工厂
public class longevent {
private long value;
public void set(long value) {
this.value = value;
}
[@override](https://my.oschina.net/u/1162528)
public string tostring() {
return "longevent{" + "value=" + value + '}';
}
}
public class longeventfactory implements eventfactory<longevent> {
[@override](https://my.oschina.net/u/1162528)
public longevent newinstance() {
return new longevent();
}
}
定义事件处理器,即消费者
public class longeventhandler implements eventhandler<longevent> {
[@override](https://my.oschina.net/u/1162528)
public void onevent(longevent event, long sequence, boolean endofbatch) {
system.out.println("event: " + event);
}
}
定义事件生产者
import com.lmax.disruptor.ringbuffer;
import com.lmax.disruptor.examples.longevent.longevent;
import java.nio.bytebuffer;
public class longeventproducer {
private final ringbuffer<longevent> ringbuffer;
public longeventproducer(ringbuffer<longevent> ringbuffer) {
this.ringbuffer = ringbuffer;
}
public void ondata(bytebuffer bb) {
long sequence = ringbuffer.next();
try {
longevent event = ringbuffer.get(sequence);
event.set(bb.getlong(0));
}
finally {
ringbuffer.publish(sequence);
}
}
}
编写启动类
public class longeventmain {
public static void main(string[] args) throws interruptedexception {
// 消费者线程池
executor executor = executors.newcachedthreadpool();
// 事件工厂
longeventfactory eventfactory = new longeventfactory();
// 指定ringbuffer大小
int buffersize = 1024;
// 构造事件分发器
disruptor<longevent> disruptor = new disruptor<>(eventfactory
, buffersize
, executor
, producertype.single // 1.producertype.single 单生产者模式 2.producertype.multi 多生产者模式
, new yieldingwaitstrategy());//消费者等待策略
// 注册消费者
disruptor.handleeventswith(new longeventhandler());
// 启动事件分发
disruptor.start();
// 获取ringbuffer 用于生产事件
ringbuffer<longevent> ringbuffer = disruptor.getringbuffer();
longeventproducer producer = new longeventproducer(ringbuffer);
bytebuffer bb = bytebuffer.allocate(8);
for (long i=0;true; i++) {
bb.putlong(0, i);
// 发送事件
producer.ondata(bb);
thread.sleep(1000);
}
}
}
disruptor消费者等待策略
等待策略waitstrategy是一种决定一个消费者如何等待生产者将event对象放入disruptor的方式/策略。
下面是常见的4种消费者等待策略:

disruptor灵活的消费者模式
支持单生产者和多生产者
构造disruptor时指定生产者类型即可:producertype.single 和 producertype.multi 单消费者
单消费者
//注册单个消费者
disruptor.handleeventswith(new longeventhandler());
多消费者:并行的、广播模式
同一个事件会同时被所有消费者处理,同组内消费者之间不存在竞争关系。
//注册多个消费者
disruptor.handleeventswith(new longeventhandler()
, new longeventhandler1()
, new longeventhandler2());
多消费者:并行的、消费者组模式
同组内消费者之间互斥,一个事件只会被同组内单个消费者处理,但可以支持多个消费者组,消费者组之间完全隔离,互不影响,代码实现方式有两点不同之处:
- 消费者需要实现workhandler接口,而不是 eventhandler 接口;
- 使用handleeventswithworkerpool设置disruptor的消费者,而不是handleeventswith方法
public class longworkhandler implements workhandler<longevent> {
[@override](https://my.oschina.net/u/1162528)
public void onevent(longevent longevent) throws exception {
system.out.println("event: " + logevent);
}
}
public class otherworkhandler implements workhandler<longevent> {
[@override](https://my.oschina.net/u/1162528)
public void onevent(longevent longevent) throws exception {
system.out.println("event: " + logevent);
}
}
//注册消费者组
disruptor.handleeventswithworkerpool(new longworkhandler()
, new longworkhandler()
, new longworkhandler());
- 多个消费者组之间并行模式
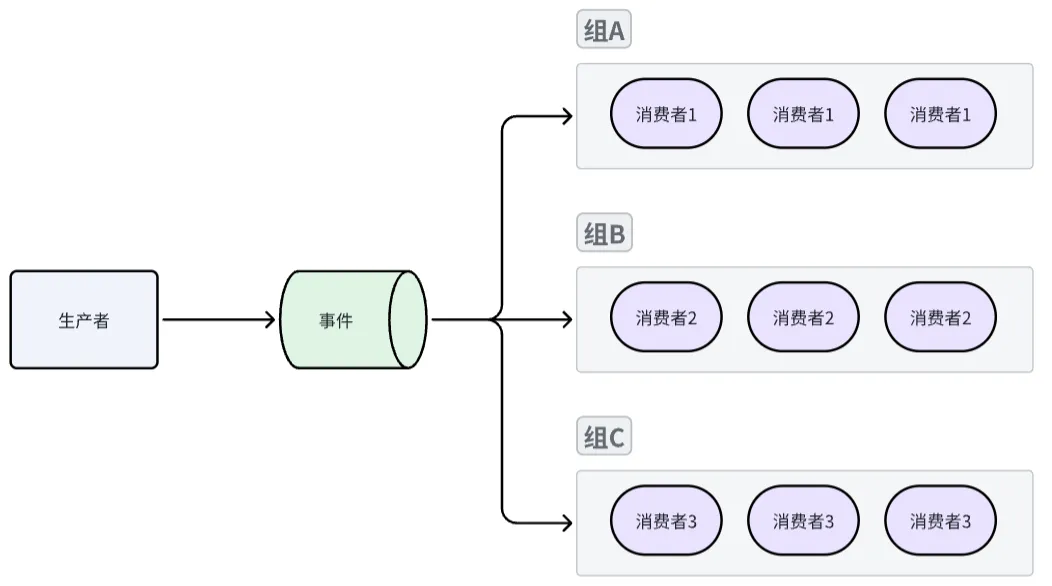
//注册消费者组1
disruptor.handleeventswithworkerpool(new longworkhandler()
, new longworkhandler()
, new longworkhandler());
//注册消费者组2
disruptor.handleeventswithworkerpool(new otherworkhandler()
, new otherworkhandler()
, new otherworkhandler());
- 多个消费者组之间航道执行模式
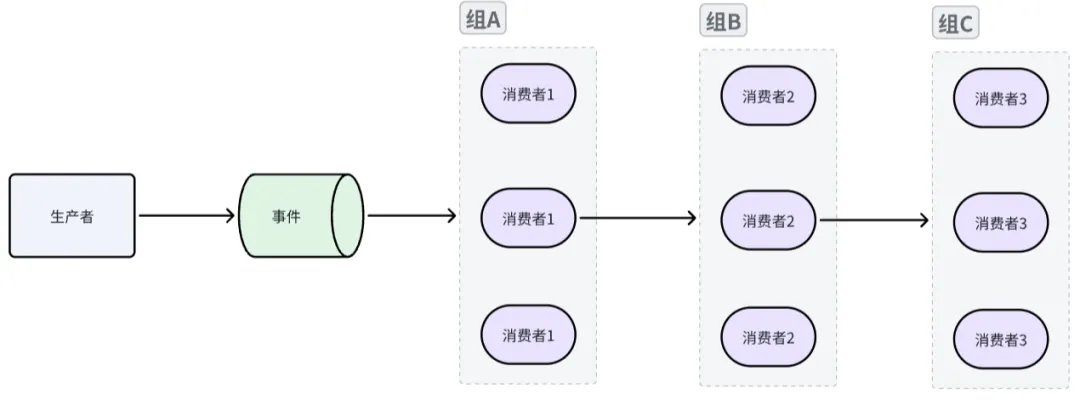
//注册消费者
disruptor.handleeventswithworkerpool(new longworkhandler(), new longworkhandler(), new longworkhandler())
.thenhandleeventswithworkerpool(new otherworkhandler(), new otherworkhandler(), new otherworkhandler());
多消费者:链式、菱形、六边形执行模式
通过多种组合方式,可实现灵活的消费者执行顺序,如下:
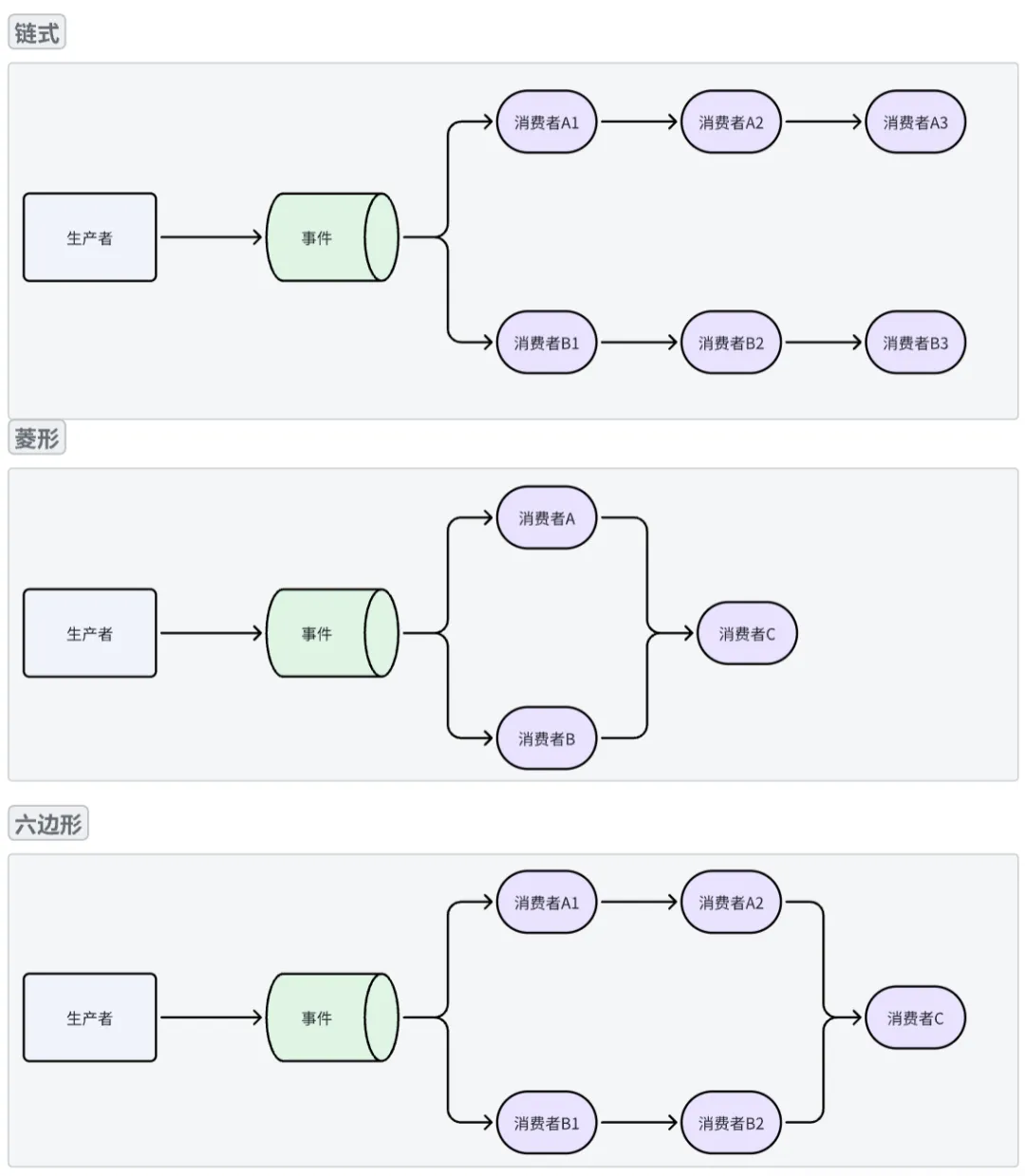
//链式
disruptor.handleeventswith(new longeventhandler11()).then(new longeventhandler12());
disruptor.handleeventswith(new longeventhandler21()).then(new longeventhandler22());
//菱形
disruptor.handleeventswith(new longeventhandler1(), new longeventhandler2())
.then(new longeventhandler3());
//六边形
longeventhandler handler11 = new longeventhandler();
longeventhandler handler12 = new longeventhandler();
longeventhandler handler21 = new longeventhandler();
longeventhandler handler22 = new longeventhandler();
longeventhandler handler3 = new longeventhandler();
disruptor.handleeventswith(handler11, handler21);
disruptor.after(handler11).handleeventswith(handler12);
disruptor.after(handler21).handleeventswith(handler22);
disruptor.after(handler12, handler22).handleeventswith(handler3);
二、disruptor的核心概念
disruptor内部组件交互图

核心概念
有些概念前面已经介绍过,在此不再赘述,说一说还未介绍的几个概念:
sequence
sequence本身就是一个序号管理器,它是严格顺序增长的,disruptor通过它标识和定位ringbuffer中的每一个事件,每个consumer都维护一个sequence,通过sequence可以跟踪consumer事件处理进度,它有atomiclong的大多数功能特性,而且它消除了cpu伪共享的问题。
sequencer
sequencer是一个接口,它有两个实现类:singleproducersequencer(单生产者实现)、multiproducersequencer(多生产者实现),它主要作用是实现生产者和消费者之间快速、正确传递数据的并发算法。
sequencer是生产者与缓冲区ringbuffer之间的桥梁。生产者可以通过sequencer向ringbuffer申请数据的存放空间,并使用publish()方法通过waitestrategy通知消费者。
sequencebarrier(序列屏障)
sequencebarrier用于保证事件的有序性。它通过维护一组sequence来跟踪消费者的进度,当生产者发布新的事件时,序列屏障会检查是否所有消费者都已处理完前面的事件,如果是,则通知生产者可以发布新的事件。
sequencebarrier是消费者与ringbuffer之间的桥梁。在disruptor中,消费者直接访问的是sequencebarrier,而不是ringbuffer,因此sequencebarrier能减少ringbuffer上的并发冲突,当消费者的消费速度大于生产者的生产速度时,消费者就可以通过waitfor()方法给予生产者一定的缓冲时间,从而协调了生产者和消费者的速度问题。
sequencebarrier同时也是消费者与消费者之间消费依赖的抽象,sequencebarrier只有一个实现类,即processingsequencebarrier。processingsequencebarrier由生产者sequencer、消费定位cursorsequence、等待策略waitstrategy、还有一组依赖sequence(dependentsequence)组成。
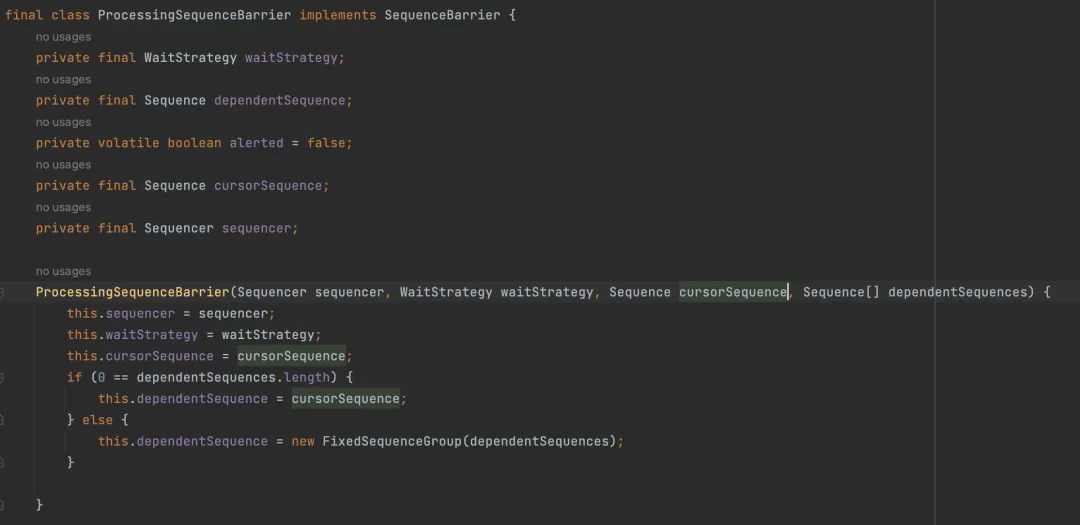
三、disruptor的特点
环形数组结构
- 采用首尾相接的数组而非链表,无需担心index溢出问题,且数组对处理器的缓存机制更加友好;
- 在ringbuffer数组长度设置为2^n时,通过sequence & (buffersize-1)加速定位元素实际下标索引,通过结合左移(<<)操作实现乘法;
- 结合sequencebarrier机制,实现线程与线程之间高效的数据交互。
无锁化设计
每个生产者或者消费者线程,会先申请可以操作的元素在数组中的位置,申请到之后,直接在该位置写入或者读取数据,整个过程通过原子变量cas,保证操作的线程安全,即disruptor的sequence的自增就是cas的自旋自增,对应的arrayblockqueue的数组索引index是互斥自增。
独占缓存行的方式消除伪共享
什么是伪共享
出现伪共享问题(false sharing)的原因:
- 一个缓存行可以存储多个变量(存满当前缓存行的字节数);64个字节可以放8个long,16个int;
- 而cpu对缓存的修改又是以缓存行为最小单位的;不是以long 、byte这样的数据类型为单位的;
- 在多线程情况下,如果需要修改"共享同一个缓存行的其中一个变量",该行中其他变量的状态就会失效,甚至进行一致性保护。
所以,伪共享问题(false sharing)的本质是:
cpu针对缓存的操作是以cache line为基本单位,对缓存行中的单个变量进行修改,会导致整个缓存行其他不相关的数据也都失效了,需要从主存重新加载,这个过程会带来性能损耗。
disruptor是如何解决伪共享的
sequence是标识ringbuffer环形数组的下标,同时生产者和消费者也会维护各自的sequence,最重要的是,sequence通过填充cpu缓存行避免了伪共享带来的性能损耗,来看下其填充缓存行源码:
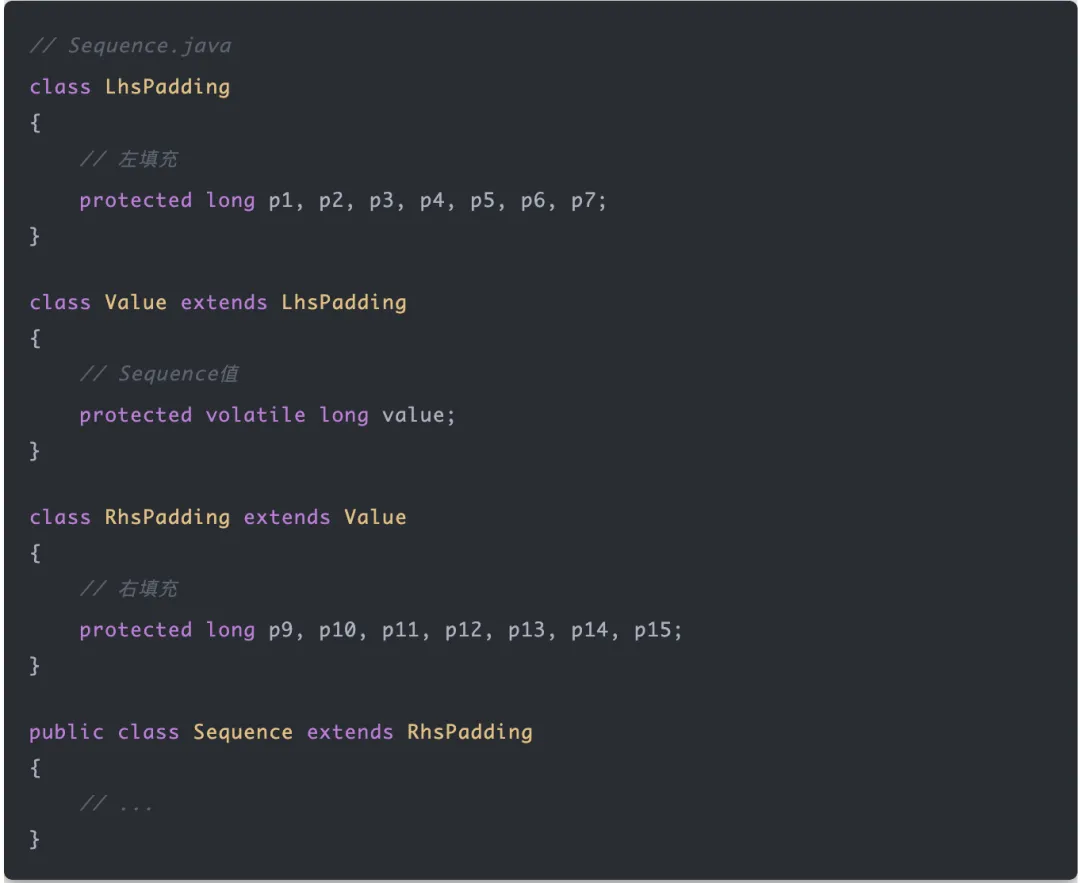
预分配内存
环形队列存放的是event对象,而且是在disruptor创建的时候调用eventfactory创建并一次将队列填满。event保存生产者生产的数据,消费者也是通过event获取数据,后续生产者只需要替换掉event中的属性值。这种方式避免了重复创建对象,降低jvm的gc频率,带来系统性能的提升。后续我们在做编码的时候其实也可以借鉴这种实现思路。

四、disruptor在撮合引擎中的应用
数字货币交易系统的简介
背景&价值
为用户提供数字虚拟货币的实时在线交易平台,实现盈亏。
c端核心界面
交易系统简化交互图
为了便于理解,简单列举交易系统的核心服务和数据流向,见下图:

撮合应用的特点
- 纯内存的、cpu密集型的
应用启动时加载数据库未处理订单、写日志、撮合成功发送消息到mq会涉及io操作。
- 有状态的
正因为应用是有状态的,所以需要通过disruptor提升单机的性能和吞吐量。
为什么撮合应用不设计成无状态的?
在学习或者实际做架构设计时,一般大多数情况都建议将应用设计为无状态的,可以通过水平扩展,实现应用的高可用、高性能。而有状态的应用一般有单点故障问题,难以通过水平扩展提升应用的性能,但是做架构设计的时候,还是需要从实际的场景出发,而撮合应用场景很显然更适合设计成有状态的。在数字加密货币交易平台,每一种数字加密货币都是由唯一的"交易对"去标识的,类似股票交易中的股票代码,针对不同交易对的买卖交易单是天然隔离的,而同种交易对的买卖交易单必须是在同一个应用去处理的,否则匹配撮合的时候是有问题的。如果使用无状态的设计,那么所有的交易对都必须在一个集群内处理,而且每个应用都必须要有全量交易对的订单数据,这样就会存在两个问题:多个应用撮合匹配结果不一致,以哪个为准、热点交易对如何做隔离,所以解决方案就是根据交易对维度对订单做分片,同一个交易对的订单消息路由到同一个撮合应用进行处理,这样其实就是将撮合应用设计成有状态的。每一种交易对每个时刻有且只有一个应用能处理,然后再通过k8s的liveness和readiness探针做自动故障转移和恢复来解决单点故障的问题,最后通过本地缓存caffeine+高性能队列disruptor提升单pod的吞吐量。16c64g的配置在实际业务场景压测的结果是,单机最大tps在200w/s左右,对于整个交易系统而言性能瓶颈已经不在撮合应用,因为极端情况下可以配置成一个pod处理一个交易对。
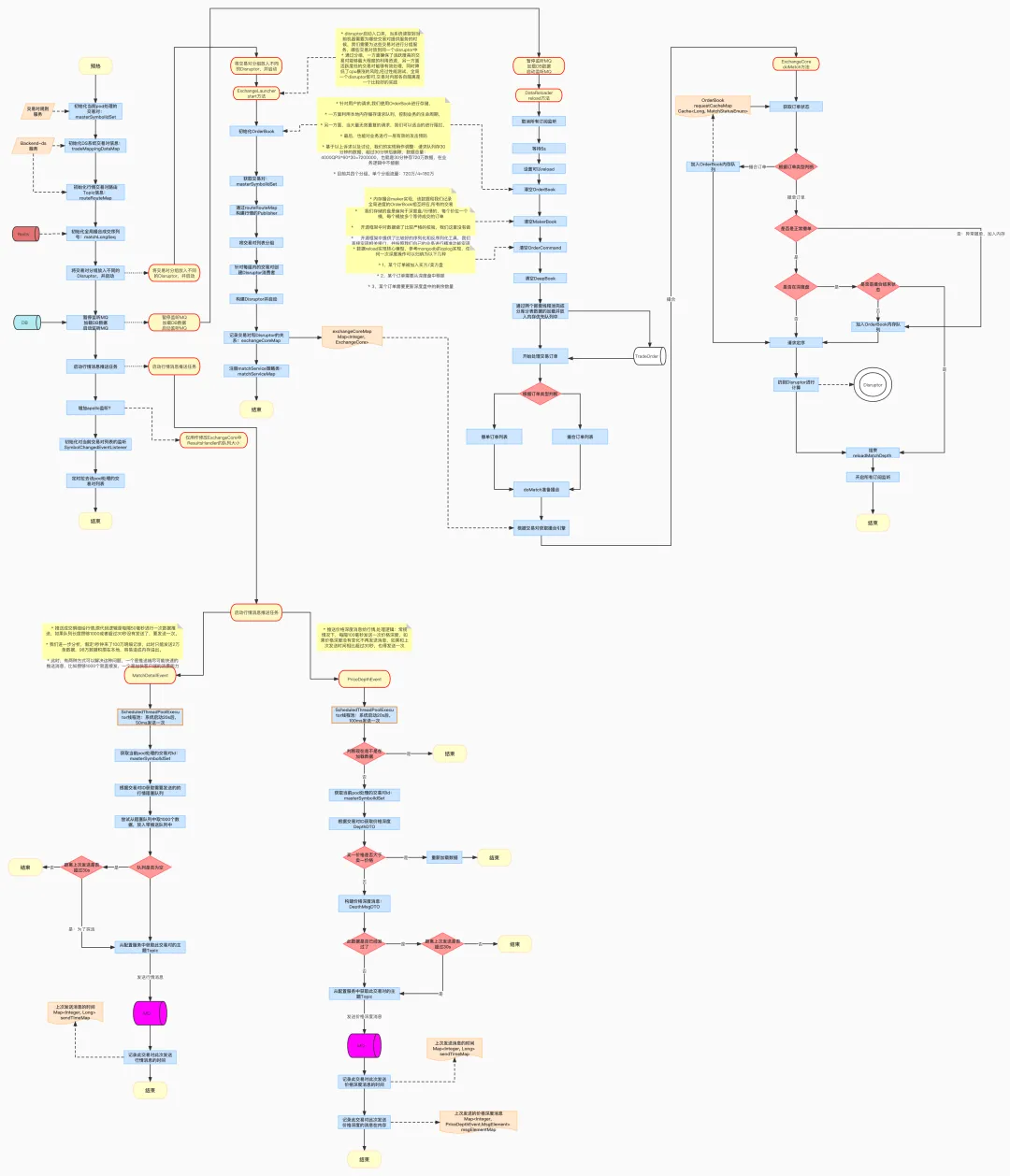
撮合引擎流程图
撮合引擎服务核心链路流程图:
撮合引擎之disruptor代码
为了便于理解,删除了和disruptor无关的代码,只列举和disruptor相关联的代码。
定义事件:用户交易单
@data
@builder
@noargsconstructor
@allargsconstructor
public class disruptorevent implements serializable {
private static final long serialversionuid = -5886259612924517631l;
//成交单
private entrustorder entrustorder;
}
定义事件处理器:对用户买单和卖单进行撮合匹配
//撮合事件处理器
public class resultshandler implements eventhandler<disruptorevent> {
private final set<integer> symbolidset = new hashset<>();
private int workerqueuesize;
public resultshandler(set<integer> symbolidset, int queuesize) {
this.symbolidset.addall(symbolidset);
this.workerqueuesize = queuesize;
}
@override
public void onevent(disruptorevent disruptorevent, long sequence, boolean endofbatch) {
try {
//获取订单
entrustorder entrustorder = disruptorevent.getentrustorder();
//常规的撮合,正常撤单,异常撤单
if (operationtypeenum.match.getcode() == entrustorder.getoperationtype() ||
operationtypeenum.cancel.getcode() == entrustorder.getoperationtype()) {
// 取消订单需要在引擎内处理
if (objects.equals(entrustorder.getoperationtype(), operationtypeenum.match.getcode())) {
//更新为处理中
orderbook.addtoorderbook(entrustorder.getorderid(), matchstatusenum.match_ing);
} else if (objects.equals(entrustorder.getoperationtype(), operationtypeenum.cancel.getcode())) {
//更新为处理中
if (orderbook.getbyorderid(entrustorder.getorderid()) != null) {
orderbook.addtoorderbook(entrustorder.getorderid(), matchstatusenum.cancel_ing);
}
}
// 执行撮合
this.domatch(entrustorder);
}
} catch (exception e) {
log.error("match disruptor event handler error:{}", e.getmessage(), e);
}
}
/**
* 根据规则选择不同的撮合策略算法,进行撮合处理
* @param takerorder
*/
public void domatch(entrustorder takerorder) {
sideenum sideenum = sideenum.getsideenum(takerorder.getside());
ordertypeenum ordertypeenum = ordertypeenum.getordertypeenum(takerorder.getordertype());
//选择撮合策略
matchservice matchservice = matchstrategy.router(ordertypeenum, sideenum);
matchcontext matchcontext = matchcontext.getcontext();
matchcontext.settakerorder(takerorder);
//执行撮合
matchservice.start(matchcontext);
//撮合完成
matchservice.stop(matchcontext);
}
}
事件生产者:构建disruptor、生产事件
/**
* disruptor启动入口类,当系统读取到当前机器需要为哪些交易对提供服务的时候,
* 我们需要为这些交易对进行分组服务,哪些交易对放到同一个disruptor中
* 通过分组,一方面确保了活跃度高的交易对能够最大程度的利用资源,另一方面活跃度低的交易对能够有效处理,
* 同时降低了cpu暴涨的风险
*/
@service
@slf4j
public class exchangelauncher {
private static int buffer_size = 1024 * 16;
@resource
private limitbuymatchservice limitbuymatchservice;
@resource
private limitsellmatchservice limitsellmatchservice;
@resource
private marketbuymatchservice marketbuymatchservice;
@resource
private marketsellmatchservice marketsellmatchservice;
@resource
private matchclusterconfiguration matchclusterconfiguration;
@value("${match.worker-queue-size:5}")
private int worksize;
//一个交易对对应一个disruptor
private map<integer, exchangecore> exchangecoremap = new concurrenthashmap<>();
private list<exchangecore> exchangecorelist = new copyonwritearraylist<>();
public void start() {
try {
//init order book
orderbook.init();
set<integer> symbolidlistset = matchclusterconfiguration.getmastersymbolidset();
if (collectionutils.isnotempty(symbolidlistset)) {
list<integer> allsymbolids = new arraylist<>(symbolidlistset);
list<list<integer>> pagelist = listutils.partition(allsymbolids, worksize);
pagelist.foreach(symbolids -> {
resultshandler handler = new resultshandler(new hashset<>(symbolids), worksize);
exchangecore exchangecore = new exchangecore(handler, buffer_size, new namedthreadfactory("match", false));
exchangecore.start();
exchangecorelist.add(exchangecore);
symbolids.foreach(symbolid -> exchangecoremap.put(symbolid, exchangecore));
});
}
// 注册matchservice子类
registermatchservices();
} catch (exception e) {
log.error("exchangelauncher start error:{}", e.getmessage(), e);
}
}
private void registermatchservices() {
matchstrategy.register(ordertypeenum.limit, sideenum.buy, limitbuymatchservice);
matchstrategy.register(ordertypeenum.limit, sideenum.sell, limitsellmatchservice);
matchstrategy.register(ordertypeenum.market, sideenum.buy, marketbuymatchservice);
matchstrategy.register(ordertypeenum.market, sideenum.sell, marketsellmatchservice);
}
}
public class exchangecore extends abstractlifecycle {
private final disruptor<disruptorevent> disruptor;
private matcheventpublisher publisher;
private resultshandler eventhandler;
public exchangecore(resultshandler matchhandler, int ringbuffersize, threadfactory threadfactory) {
eventfactory eventfactory = () -> new disruptorevent();
this.disruptor = new disruptor<>(eventfactory, ringbuffersize, threadfactory);
publisher = new matcheventpublisher(this.disruptor);
disruptor.setdefaultexceptionhandler(new disruptorexceptionhandler());
this.eventhandler = matchhandler;
disruptor.handleeventswith(eventhandler);
disruptor.start();
}
@override
public void start() {
super.start();
}
@override
public void stop() {
super.stop();
disruptor.shutdown();
}
public baseresponse domatch(entrustorder taker) {
// 前置处理----start
if (ordertypeenum.getordertypeenum(taker.getordertype()) == null || sideenum.getsideenum(taker.getside()) == null) {
log.error("{} - parameter error:{} or {}", taker.gettraceid(), "ordertype", "side");
return baseresponse.error(tradingmatchcodeenum.parameter_error);
}
matchstatusenum matchstatusenum = orderbook.getbyorderid(taker.getorderid());
metricservice metricservice = springcontextutil.getbean(metricservice.class);
matchclusterconfiguration configuration = springcontextutil.getbean(matchclusterconfiguration.class);
// 撮合防重校验,并发存在问题。但是消费的时候,是单线程,做了校验,不存在重复撮合的问题。
if (operationtypeenum.match.getcode() == taker.getoperationtype()) {
if (matchstatusenum != null) {
//短时间内重复撮合
log.error("{} - match repeat ,orderid :{}", taker.gettraceid(), taker.getorderid());
return baseresponse.error(tradingmatchcodeenum.repeat_request);
}
//构造对象进入等待队列
orderbook.addtoorderbook(taker.getorderid(), matchstatusenum.wait_ing);
metricservice.count(metricnames.order_type_num, "type", "match", "group", configuration.getclustername());
} else if (operationtypeenum.cancel.getcode() == taker.getoperationtype()) {
int canceltype = taker.getcanceltype();
/**
异常单-产生情况:收单服务 调用撮合 出现异常,不知道成功没,没有明确响应 开始进行异常撤单
*/
if (canceltypeenum.normal_cancel.getcode() == canceltype) {
if (matchstatusenum == null) {
// 数据有可能在请求队列中被逐出,需要继续走逻辑
//
} else {
if (matchstatusenum.match_end == matchstatusenum) {
//重复撤销,深度盘已经没有数据,没必要继续往下,不走disruptor 和撮合直接返回
log.error("{} - cancel failed, match end ,orderid :{}", taker.gettraceid(), taker.getorderid());
return baseresponse.error(tradingmatchcodeenum.repeat_request);
}
orderbook.addtoorderbook(taker.getorderid(), matchstatusenum.wait_cancel);
}
} else {
// reload异常撤单,要加入内存
orderbook.addtoorderbook(taker.getorderid(), matchstatusenum.wait_cancel);
}
} else {
log.warn("--------can not find the operationtype[{}]", taker.getoperationtype());
throw new tradingmatchexception("can not find the operationtype[" + taker.getoperationtype() + "]");
}
// 前置处理----end
//disruptor开始发布事件
publisher.publish(taker);
return baseresponse.success();
}
public disruptor<disruptorevent> getdisruptor() {
return disruptor;
}
}
public class matcheventpublisher {
private disruptor<disruptorevent> disruptor;
public matcheventpublisher(disruptor<disruptorevent> disruptor) {
this.disruptor = disruptor;
}
private static final eventtranslatoronearg<disruptorevent, entrustorder> translator =
(event, sequence, entrustorder) -> {
event.setentrustorder(entrustorder);
};
public void publish(entrustorder taker) {
ringbuffer<disruptorevent> ringbuffer = disruptor.getringbuffer();
taker.setsequence(ringbuffer.getcursor());
taker.setarrivetime(system.currenttimemillis());
ringbuffer.publishevent(translator, taker);
// ...
}
}
五、总结
disruptor作为一个以高性能著称的队列,它有很多优秀的设计思想值得我们学习,比如环形数组队列ringbuffer、sequencebarrier机制、无锁化设计、预分配内存、消除伪共享、以及灵活丰富的生产者和消费者模式。本文只是介绍了一些对disruptor的基本功能和实际使用场景,后续大家有兴趣可以结合源码去做更加深入的理解。由于本人文笔和经验有限,若有不足之处,还请及时指正,共同学习和进步。
引用: https://lmax-exchange.github.io/disruptor/user-guide/#_advanced_techniques
*文/ 天佑
本文属得物技术原创,更多精彩文章请看:得物技术
未经得物技术许可严禁转载,否则依法追究法律责任!







发表评论