本文为该系列第一篇:入门篇。
笔者不才,有任何错误纰漏,欢迎大家指正。

▐ 功能分类
一般来说,数据开发包括了以下几个类型:
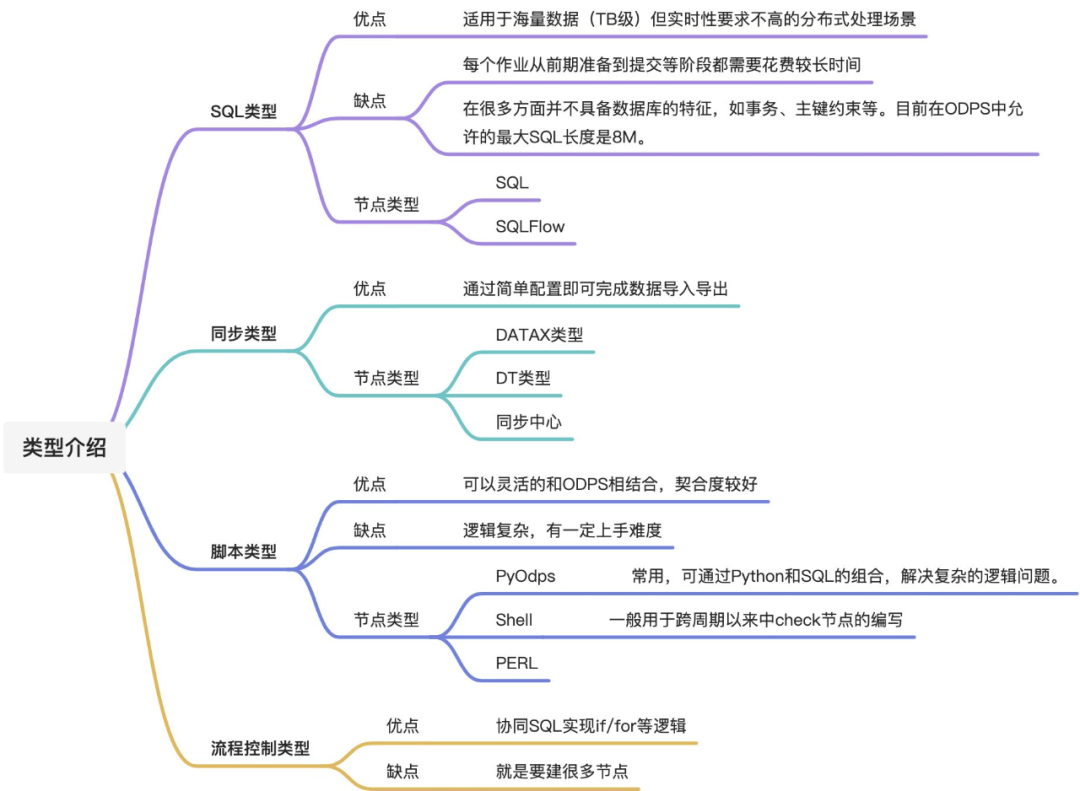
▐ maxcompute功能
在此,我们重点介绍一下其中maxcompute模块(maxcompute是适用于数据分析场景的企业级saas模式云数据仓库)的功能:


基础sql
▐ ddl
具体语句1:
--创建新表。create [external] table [if not exists] <table_name>[primary key (<pk_col_name>, <pk_col_name2>),(<col_name> <data_type>[not null] [default <default_value>] [comment <col_comment>], ...)][comment <table_comment>][partitioned by (<col_name> <data_type> [comment <col_comment>], ...)]--用于创建聚簇表时设置表的shuffle和sort属性。[clustered by | range clustered by (<col_name> [, <col_name>, ...])[sorted by (<col_name> [asc | desc] [, <col_name> [asc | desc] ...])] into <number_of_buckets> buckets]--仅限外部表。[stored by storagehandler]--仅限外部表。[with serdeproperties (options)]--仅限外部表。[location <osslocation>]--指定表为transactional1.0表,后续可以对该表执行更新或删除表数据操作,但是transactional表有部分使用限制,请根据需求创建。[tblproperties("transactional"="true")]--指定表为transactional2.0表,后续可以做upsert,增量查询,time-travel等操作[tblproperties ("transactional"="true" [, "write.bucket.num" = "n", "acid.data.retain.hours"="hours"...])] [lifecycle <days>];---------------------------------------------------------------------例子:create table if not exists xxx.xxxx_xxxx_xxxx_hh(xxxxx string comment '商品',xxxxx string comment '名字')comment 'xxx表'partitioned by(ds string comment 'yyyymmddhh')lifecycle 7;
参数说明:
external:可选。表示创建的表为外部表。
if not exists:可选。如果不指定if not exists选项而存在同名表,会报错。
table_name:必填。表名。
primary key(pk):可选。表的主键。
col_name:可选,表的列名。
col_comment:可选。列的注释内容。
data_type:可选。列的数据类型。
not null:可选。禁止该列的值为null。default_value:可选。指定列的默认值。
table_comment:可选。表注释内容。
lifecycle:可选。表的生命周期。
partitioned by (<col_name> <data_type> [comment <col_comment>], ...:可选。指定分区表的分区字段。
具体语句2:修改表的所有人
alter table <table_name> changeowner to <new_owner>;----------------------------------------------------------例子--将表test1的所有人修改为aliyun$xxx@aliyun.comalter table test1 changeowner to 'aliyun$xxx@aliyun.com';--将表test1的所有人修改为名称为ram_test的ram用户alter table test1 changeowner to 'ram$13xxxxxxxxxxx:ram_test';
参数说明:
table_name:必填。待修改owner的表名。
new_owner:必填。修改后的owner账号。如果要修改owner为ram用户,格式为:ram$<uid>:<ram_name>,其中uid为阿里云账号的账号id,ram_name为ram用户显示名称。
具体语句3:修改表的注释
alter table <table_name> set comment '<new_comment>';----------------------------------------------------------例子alter table sale_detail set comment 'new coments for table sale_detail';
参数说明:
table_name:必填。待修改注释的表的名称。
new_comment:必填。修改后的注释名称。
具体语句4:修改表的修改时间
alter table <table_name> touch;----------------------------------------------------------例子alter table sale_detail touch;
alter table <table_name> rename to <new_table_name>;----------------------------------------------------------例子alter table sale_detail rename to sale_detail_rename;
table_name:必填。待修改名称的表。
new_table_name:必填。修改后的表名称。如果已存在与new_table_name同名的表,会返回报错。
具体语句6:删除表
drop table [if exists] <table_name>;----------------------------------------------------------例子drop table if exists sale_detail;
--查看表或视图信息。desc <table_name|view_name> [partition (<pt_spec>)];--查看外部表、聚簇表或transactional表信息。也可以查看内部表的扩展信息。desc extended <table_name>;----------------------------------------------------------例子desc test1;
desc <table_name> partition (<pt_spec>);----------------------------------------------------------例子--查询分区表sale_detail的分区信息。desc sale_detail partition (xxxx_date='201310',region='beijing');
show create table <table_name>;----------------------------------------------------------例子--查看表sale_detail的建表语句。show create table sale_detail;
show partitions <table_name>;----------------------------------------------------------例子--列出sale_detail中的所有分区。show partitions sale_detail;
alter table <table_name>[partition ( <pt_spec>[, <pt_spec>....] )]clear column column1[, column2, column3, ...][without touch];
clone table <[<src_project_name>.]<src_table_name>> [partition(<pt_spec>), ...]to <[<dest_project_name>.]<dest_table_name>> [if exists [overwrite | ignore]] ;------------------------------------------------------------------------------例子--复制表数据。clone table xxxx_detail partition (xxxx_date='2013', region='china') to xxxx_detail_clone if exists overwrite;
参数说明:
src_project_name:可选。源表所属maxcompute项目名称。
src_table_name:必填。源表名称。
pt_spec:可选。源表的分区信息。
dest_project_name:可选。
dest_table_name:必填。目标表名称。
▐ dml
具体语句1:插入或覆写数据
--插入:直接向表或静态分区中插入数据,可以在insert语句中直接指定分区值,将数据插入指定的分区。如果您需要插入少量测试数据,可以配合values使用。--覆写:先清空表或静态分区中的原有数据,再向表或静态分区中插入数据。insert {into|overwrite} table <table_name> [partition (<pt_spec>)] [(<col_name> [,<col_name> ...)]]<select_statement>from <from_statement>[zorder by <zcol_name> [, <zcol_name> ...]];------------------------------------------------------------------------------例子--向源表追加数据。其中:insert into table table_name可以简写为insert into table_name,但insert overwrite table table_name不可以省略table关键字。insert into xxxx_detail partition (xxxx_date='2013', region='china') values ('s1','c1',100.1),('s2','c2',100.2),('s3','c3',100.3);--执行insert overwrite命令向表xxxx_detail_insert中覆写数据,调整select子句中列的顺序。insert overwrite table xxxx_detail_insert partition (xxxx_date='2013', region='china')select xxxx_id, xxxx_name, xxxx_price from xxxx_detail;
--在使用maxcompute sql处理数据时,分区列的值在select子句中提供,系统自动根据分区列的值将数据插入到相应分区。insert {into|overwrite} table <table_name> partition (<ptcol_name>[, <ptcol_name> ...])<select_statement> from <from_statement>;------------------------------------------------------------------------------例子--指定一级分区,将数据插入目标表。insert overwrite table sale_detail_dypart partition (sale_date='2013', region)select shop_name,customer_id,total_price,region from sale_detail;--将源表sale_detail中的数据插入到目标表sale_detail_dypart。insert overwrite table sale_detail_dypart partition (sale_date, region)select shop_name,customer_id,total_price,sale_date,region from sale_detail;
参数说明:
table_name:必填。需要插入数据的目标表名。
ptcol_name:必填。目标表分区列的名称。
select_statement:必填。select子句,从源表中查询需要插入目标表的数据。
from_statement:必填。from子句,表示数据来源。例如,源表名称。
具体语句3:更新或删除数据
--删除操作:用于删除transactional或delta table表中满足指定条件的单行或多行数据。delete from <table_name> [where <where_condition>];--清空列数据:将不再使用的列数据从磁盘删除并置null,从而达到降低存储成本的目的。alter table <table_name>[partition ( <pt_spec>[, <pt_spec>....] )]clear column column1[, column2, column3, ...][without touch];--更新操作:用于将transactional表或delta table表中行对应的单列或多列数据更新为新值。--方式1update <table_name> set <col1_name> = <value1> [, <col2_name> = <value2> ...] [where <where_condition>];--方式2update <table_name> set (<col1_name> [, <col2_name> ...]) = (<value1> [, <value2> ...])[where <where_condition>];--方式3update <table_name>set <col1_name> = <value1> [ , <col2_name> = <value2> , ... ][ from <additional_tables> ][ where <where_condition> ]
参数说明:
table_name:必填。
where_condition:可选。where子句,用于筛选满足条件的数据。
partition:指定分区,若未指定,则表示操作所有分区。
pt_spec:分区描述。
without touch:表示不更新lastdatamodifiedtime。
col1_name、col2_name:待修改行对应的列名称。
value1、value2:至少更新一个列值。修改后的新值。
where_condition:可选。where子句,用于筛选满足条件的数据。
additional_tables:可选,from子句。
具体语句4:merge into
merge into <target_table> as <alias_name_t> using <source expression|table_name> as <alias_name_s>--从on开始对源表和目标表的数据进行关联判断。on <boolean expression1>--when matched…then指定on的结果为true的行为。多个when matched…then之间的数据无交集。when matched [and <boolean expression2>] then update set <set_clause_list>when matched [and <boolean expression3>] then delete--when not matched…then指定on的结果为false的行为。when not matched [and <boolean expression4>] then insert values <value_list>------------------------------------------------------------------------------例子--执行merge into操作,对符合on条件的数据用源表的数据对目标表进行更新操作,对不符合on条件并且源表中满足event_type为i的数据插入目标表。命令示例如下:merge into acid_address_book_base1 as t using tmp_table1 as son s.id = t.id and t.year='2020' and t.month='08' and t.day='20' and t.hour='16'when matched then update set t.first_name = s.first_name, t.last_name = s.last_name, t.phone = s.phonewhen not matched and (s._event_type_='i') then insert values(s.id, s.first_name, s.last_name,s.phone,'2020','08','20','16');
参数说明:
target_table:必填。目标表名称,必须是实际存在的表。
alias_name_t:必填。目标表的别名。
source expression|table_name:必填。关联的源表名称、视图或子查询。
alias_name_s:必填。关联的源表、视图或子查询的别名。
boolean expression1:必填。boolean类型判断条件,判断结果必须为true或false。
boolean expression2:可选。update、delete、insert操作相应的boolean类型判断条件。
set_clause_list:当出现update操作时必填。
value_list:当出现insert操作时必填。
具体语句5:values
--insert … valuesinsert into table <table_name>[partition (<pt_spec>)][(<col1_name> ,<col2_name>,...)]values (<col1_value>,<col2_value>,...),(<col1_value>,<col2_value>,...),...--values tablevalues (<col1_value>,<col2_value>,...),(<col1_value>,<col2_value>,...),<table_name> (<col1_name> ,<col2_name>,...)...
--将hologres、oss、amazon redshift、bigquery外部存储的csv格式或其他开源格式数据导入maxcompute的表或表的分区。{load overwrite|into} table <table_name> [partition (<pt_spec>)]from location <external_location>stored by <storagehandler>[with serdeproperties (<options>)];------------------------------------------------------------------------------例子load overwrite table xxxx_data_csv_loadfromlocation 'oss://oss-cn-hangzhou-internal.aliyuncs.com/mc-test/data_location/'stored by 'com.aliyun.odps.csvstoragehandler'with serdeproperties ('odps.properties.rolearn'='acs:ram::xxxxx:role/aliyunodpsdefaultrole', --aliyunodpsdefaultrole的arn信息,可通过ram角色管理页面获取。'odps.text.option.delimiter'=',');
table_name:必填。需要插入数据的目标表名称。
pt_spec:可选。需要插入数据的目标表分区信息。
external_location:必填。指定读取外部存储数据的oss目录。
storagehandler:必填。指定内置的storagehandler名称。
options:可选。指定外部表相关参数。
--将maxcompute的数据导出至oss、hologres外部存储,oss支持以csv格式或其他开源格式存储数据。unload from {<select_statement>|<table_name> [partition (<pt_spec>)]}intolocation <external_location>stored by <storagehandler>[with serdeproperties ('<property_name>'='<property_value>',...)];------------------------------------------------------------------------------例子--控制导出文件个数:设置单个worker读取maxcompute表数据的大小,单位为mb。由于maxcompute表有压缩,导出到oss的数据一般会膨胀4倍左右。set odps.stage.mapper.split.size=256;--导出数据。unload from sale_detail partition (sale_date='2013',region='china')intolocation 'oss://oss-cn-hangzhou-internal.aliyuncs.com/mc-unload/data_location'stored by 'com.aliyun.odps.tsvstoragehandler'with serdeproperties ('odps.properties.rolearn'='acs:ram::139699392458****:role/aliyunodpsdefaultrole', 'odps.text.option.gzip.output.enabled'='true');
select_statement:select查询子句,
table_name、pt_spec:使用表名称或表名称加分区名称的方式指定需要导出的数据。
external_location:必填。
storagehandler:必填。指定内置的storagehandler名称。
<property_name>'='<property_value>':可选。property_name为属性名称,property_value为属性值。
--分析查询语句或表结构来分析性能瓶颈explain <dml query>;------------------------------------------------------------------------------例子explainselect a.customer_id as ashop, sum(a.total_price) as ap,count(b.total_price) as bpfrom (select * from sale_detail_jt where sale_date='2013' and region='china') ainner join (select * from sale_detail where sale_date='2013' and region='china') bon a.customer_id=b.customer_idgroup by a.customer_idorder by a.customer_idlimit 10;
dml query:必填。select语句。
具体语句9:公用表表达式
--临时命名结果集,用于简化sql,可以更好地提高sql语句的可读性与执行效率with<cte_name> as(<cte_query>)[,<cte_name2> as(<cte_query2>),……]------------------------------------------------------------------------------例子witha as (select * from src where key is not null),b as (select * from src2 where value > 0),c as (select * from src3 where value > 0),d as (select a.key, b.value from a join b on a.key=b.key),e as (select a.key,c.value from a left outer join c on a.key=c.key and c.key is not null)insert overwrite table srcp partition (p='abc')select * from d union all select * from e;
参数说明:
cte_name:必填。cte的名称,不能与当前with子句中的其他cte的名称相同。查询中任何使用到cte_name标识符的地方,均指cte。
cte_query:必填。一个select语句。select的结果集用于填充cte。
▐ dql
select语句
1. select语法
[with <cte>[, ...] ]select [all | distinct] <select_expr>[, <except_expr>][, <replace_expr>] ...from <table_reference>[where <where_condition>][group by {<col_list>|rollup(<col_list>)}][having <having_condition>][window <window_clause>][order by <order_condition>][distribute by <distribute_condition> [sort by <sort_condition>]|[ cluster by <cluster_condition>] ][limit <number>]
下面将介绍select命令格式及如何实现嵌套查询、分组查询、排序等操作。
2. select语序
--语法顺序from <table_reference>[where <where_condition>][group by <col_list>][having <having_condition>][window <window_name> as (<window_definition>)][qualify <expression>]select [all | distinct] <select_expr>, <select_expr>, ...[order by <order_condition>][distribute by <distribute_condition> [sort by <sort_condition>] ][limit <number>]
场景1:from->where->group by->having->select->order by->limit
场景2:from->where->select->distribute by->sort by
3. with子句
witha as (select 1 as c),b as (select * from a)select * from b;
在同一with子句中的cte必须具有唯一的名字。
在with子句中定义的cte仅对在同一with子句中的其他cte可以使用。
4. 列表达式
------------------------------------------------------------------------------例子--读取表xxxx_detail的列shop_nameselect xxxx_name from xxxx_detail;--查询表xxxx_detail中region列数据,如果有重复值时仅显示一条。select distinct region from xxxx_detail;--选出xxxx_detail表中列名不为xxxx_name的所有列select `(xxxx_name)?+.+` from xxxx_detail;--去重多列时,distinct的作用域是select的列集合,不是单个列。select distinct region, xxxx_date from xxxx_detail;
用列名指定要读取的列。
用星号(*)代表查询所有的列。
可以使用正则表达式。
在选取的列名前可以使用distinct去掉重复字段,只返回去重后的值。
5. 排除列
--读取xxxx_detail表的数据,并排除region列的数据。------------------------------------------------------------------------------例子select * except(region) from xxxx_detail;
当希望读取表内大多数列的数据,同时要排除表中少数列的数据时。
表示读取表数据时会排除指定列(col1、col2)的数据。
6. where
--配合关系运算符,筛选满足指定条件的数据。关系运算符包含:>、<、=、>=、<=、<>like、rlikein、not inbetween…and------------------------------------------------------------------------------例子select *from xxxx_detailwhere xxxx_date >= '2008' and xxxx_date <= '2014';--等价于如下语句。select *from xxxx_detailwhere xxxx_date between '2008' and '2014';
where子句为过滤条件。如果表是分区表,可以实现列裁剪。
7. group by
------------------------------------------------------------------------------例子--直接使用输入表列名region作为group by的列,即以region值分组select region from xxxx_detail group by region;--以region值分组,返回每一组的销售额总量。select sum(xxxx_price) from xxxx_detail group by region;--以region值分组,返回每一组的region值(组内唯一)及销售额总量。select region, sum (xxxx_price) from xxxx_detail group by region;
group by操作优先级高于select操作,因此group by的取值是select输入表的列名或由输入表的列构成的表达式。需要注意的是:
group by取值为正则表达式时,必须使用列的完整表达式。
select语句中没有使用聚合函数的列必须出现在group by中。
8. having
------------------------------------------------------------------------------例子--为直观展示数据呈现效果,向sale_detail表中追加数据。insert into sale_detail partition (sale_date='2014', region='shanghai')values ('null','c5',null),('s6','c6',100.4),('s7','c7',100.5);--使用having子句配合聚合函数实现过滤。select region,sum(total_price) from sale_detailgroup by regionhaving sum(total_price)<305;
通常having子句与聚合函数一起使用,实现过滤。
9. order by
------------------------------------------------------------------------------例子--查询表xxxx_detail的信息,并按照xxxx_price升序排列前2条。select * from xxxx_detail order by xxxx_price limit 2;--将表xxx_detail按照xxxx_price升序排序后,输出从第3行开始的3行数据。select xxxx_id,xxxx_price from xxxx_detail order by xxxx_price limit 3 offset 2;
默认对数据进行升序排序,如果降序排序,需要使用desc关键字。
order by默认要求带limit数据行数限制,没有limit会返回报错。
------------------------------------------------------------------------------例子--查询表xxxx_detail中的列region值并按照region值进行哈希分片。select region from xxxx_detail distribute by region;--等价于如下语句。select region as r from xxxx_detail distribute by region;select region as r from xxxx_detail distribute by r;
distribute by控制map(读数据)的输出在reducer中是如何划分的,如果不希望reducer的内容存在重叠,或需要对同一分组的数据一起处理,可以使用distribute by来保证同组数据分发到同一个reducer中。
11. sort by局部排序
------------------------------------------------------------------------------例子--查询表xxxx_detail中的列region和xxxx_price的值并按照region值进行哈希分片,然后按照xxxx_price对哈希分片结果进行局部升序排序。select region,xxxx_price from xxxx_detail distribute by region sort by xxxx_price;--查询表xxxx_detail中的列region和xxxx_price的值并按照region值进行哈希分片,然后按照xxxx_price对哈希分片结果进行局部降序排序。select region,xxxx_price from xxxx_detail distribute by region sort by xxxx_price desc;--如果sort by语句前没有distribute by,sort by会对每个reduce中的数据进行局部排序。select region,xxxx_price from xxxx_detail sort by xxxx_price desc;
sort by默认对数据进行升序排序,如果降序排序,需要使用desc关键字。
如果sort by语句前有distribute by,sort by会对distribute by的结果按照指定的列进行排序。
12. limit限制输出行数
select * from xxxxx.xxxx_xxxx_xxxxwhere ds = 20240520limit 100;
limit <number>中的number是常数,用于限制输出行数,取值范围为int32位取值范围。
子查询
1. 基础子查询
--格式1select <select_expr> from (<select_statement>) [<sq_alias_name>];--格式2select (<select_statement>) from <table_name>;
普通查询操作的对象是目标表,但是查询的对象也可以是另一个select语句,这种查询为子查询。在from子句中,子查询可以被当作一张表,与其他表或子查询进行join操作。
2. in subquery
--in subquery与left semi join用法类似--格式一select<select_expr1>from<table_name1>where<select_expr2>in(select<select_expr3>from<table_name2>);--等效于leftsemijoin如下语句。select<select_expr1>from<table_name1><alias_name1>leftsemijoin<table_name2><alias_name2>on<alias_name1>.<select_expr2>=<alias_name2>.<select_expr3>;--格式二select<select_expr1>from<table_name1>where<select_expr2>in(select<select_expr3>from<table_name2>where<table_name1>.<col_name>=<table_name2>.<col_name>);------------------------------------------------------------------------------例子set odps.sql.allow.fullscan=true;select * from xxxx_detail where xxxx_price in (select xxxx_price from shop);set odps.sql.allow.fullscan=true;select * from xxxx_detail where xxxx_pricein (select xxxx_price from shop where xxxx_id = shop.xxxx_id);
select_expr1:必填。格式为col1_name, col2_name, 正则表达式,...,表示待查询的普通列、分区列或正则表达式。
table_name1、table_name2:必填。表的名称。
select_expr2、select_expr3:必填。表示table_name1和table_name2互相映射的列名。
col_name:必填。表的列名。
3. not in subquery
--如果查询目标表的指定列名中有任意一行为null,则not in表达式值为null,导致where条件不成立,无数据返回select <select_expr1> from <table_name1> where <select_expr2> not in (select <select_expr2> from <table_name2>);--等效于left anti join如下语句。select <select_expr1> from <table_name1> <alias_name1>left anti join <table_name2> <alias_name2> on <alias_name1>.<select_expr1> = <alias_name2>.<select_expr2>;------------------------------------------------------------------------------例子--创建一张新表shop1并追加数据。create table shop1 as select xxxx_name,xxxx_id,xxxx_price from xxxx_detail;insert into shop1 values ('s8','c1',100.1);select * from shop1 where xxxx_name not in (select xxxx_name from xxxx_detail);set odps.sql.allow.fullscan=true;select * from shop1 where xxxx_name not in (select xxxx_name from xxxx_detail where xxxx_id = shop1.xxxx_id);
select_expr1:必填。格式为col1_name, col2_name, 正则表达式,...,表示待查询的普通列、分区列或正则表达式。
table_name1、table_name2:必填。表的名称。
select_expr2、select_expr3:必填。表示table_name1和table_name2互相映射的列名。
col_name:必填。表的列名。
4. exists subquery
--使用exists subquery时,当子查询中有至少一行数据时,返回true,否则返回false。select <select_expr> from <table_name1> where exists(select <select_expr> from <table_name2>where <table_name2_colname> = <table_name1>.<colname>);------------------------------------------------------------------------------例子set odps.sql.allow.fullscan=true;select * from xxxx_detail where exists(select * from shop where customer_id = xxxx_detail.xxxx_id);--等效于以下语句。select * from xxxx_detail a left semi join shop b on a.xxxx_id = b.xxxx_id;
select_expr:必填。格式为col1_name, col2_name, 正则表达式,...,表示待查询的普通列、分区列或正则表达式。
table_name1、table_name2:必填。表的名称。
col_name:必填。表的列名。
5. not exists subquery
--当子查询中无数据时,返回true,否则返回falseselect <select_expr> from <table_name1> where not exists(select <select_expr> from <table_name2> where <table_name2_colname> = <table_name1>.<colname>);------------------------------------------------------------------------------例子set odps.sql.allow.fullscan=true;select * from xxxx_detail where not exists (select * from shop where xxxx_name = xxxx_detail.xxxx_name);--等效于以下语句。select * from xxxx_detail a left anti join shop b on a.shop_name = b.xxxx_name;
select_expr:必填。格式为col1_name, col2_name, 正则表达式,...,表示待查询的普通列、分区列或正则表达式。
table_name1、table_name2:必填。表的名称。
col_name:必填。表的列名。
6. scalar subquery
--当子查询的输出结果为单行单列时,可以做为标量使用,即可以参与标量运算。select <select_expr> from <table_name1> where(<select count(*) from <table_name2> where <table_name2_colname> = <table_name1>.<colname>)<标量运算符> <scalar_value>;------------------------------------------------------------------------------例子set odps.sql.allow.fullscan=true;select * from shop where(select count(*) from xxxx_detail where xxxx_detail.xxxx_name = shop.xxxx_name) >= 1;
select_expr:必填。格式为col1_name, col2_name, 正则表达式。
table_name1、table_name2:必填。表的名称。
col_name:必填。表的列名。
标量运算符:必填。例如大于(>)、小于(<)、等于(=)。
scalar_value:必填。标量值
交集,并集和补集
1. 交集
--取交集不去重。<select_statement1> intersect all <select_statement2>;--取交集并去重。intersect效果等同于intersect distinct。<select_statement1> intersect [distinct] <select_statement2>;------------------------------------------------------------------------------例子select * from values (1, 2), (1, 2), (3, 4), (5, 6) t(a, b)intersect allselect * from values (1, 2), (1, 2), (3, 4), (5, 7) t(a, b);--结果+------------+------------+| a | b |+------------+------------+| 1 | 2 || 3 | 4 |+------------+------------+
select_statement1、select_statement2:必填。
distinct:可选。对两个数据集取交集的结果去重。
2. 并集
--取并集不去重。<select_statement1> union all <select_statement2>;--取并集并去重。<select_statement1> union [distinct] <select_statement2>;------------------------------------------------------------------------------例子select * from values (1, 2), (1, 2), (3, 4) t(a, b)union allselect * from values (1, 2), (1, 4) t(a, b);--结果+------------+------------+| a | b |+------------+------------+| 1 | 2 || 1 | 2 || 3 | 4 || 1 | 2 || 1 | 4 |+------------+------------+
select_statement1、select_statement2:必填。select语句。
distinct:可选。对两个数据集取并集的结果去重。
3. 补集
--取补集不去重。<select_statement1> except all <select_statement2>;<select_statement1> minus all <select_statement2>;--取补集并去重。<select_statement1> except [distinct] <select_statement2>;<select_statement1> minus [distinct] <select_statement2>;------------------------------------------------------------------------------例子select * from values (1, 2), (1, 2), (3, 4), (3, 4), (5, 6), (7, 8) t(a, b)except allselect * from values (3, 4), (5, 6), (5, 6), (9, 10) t(a, b);--结果+------------+------------+| a | b |+------------+------------+| 1 | 2 || 1 | 2 || 3 | 4 || 7 | 8 |+------------+------------+
select_statement1、select_statement2:必填。select语句。
distinct:可选。对取补集的结果去重。
join语句
这里先放一张示意图:
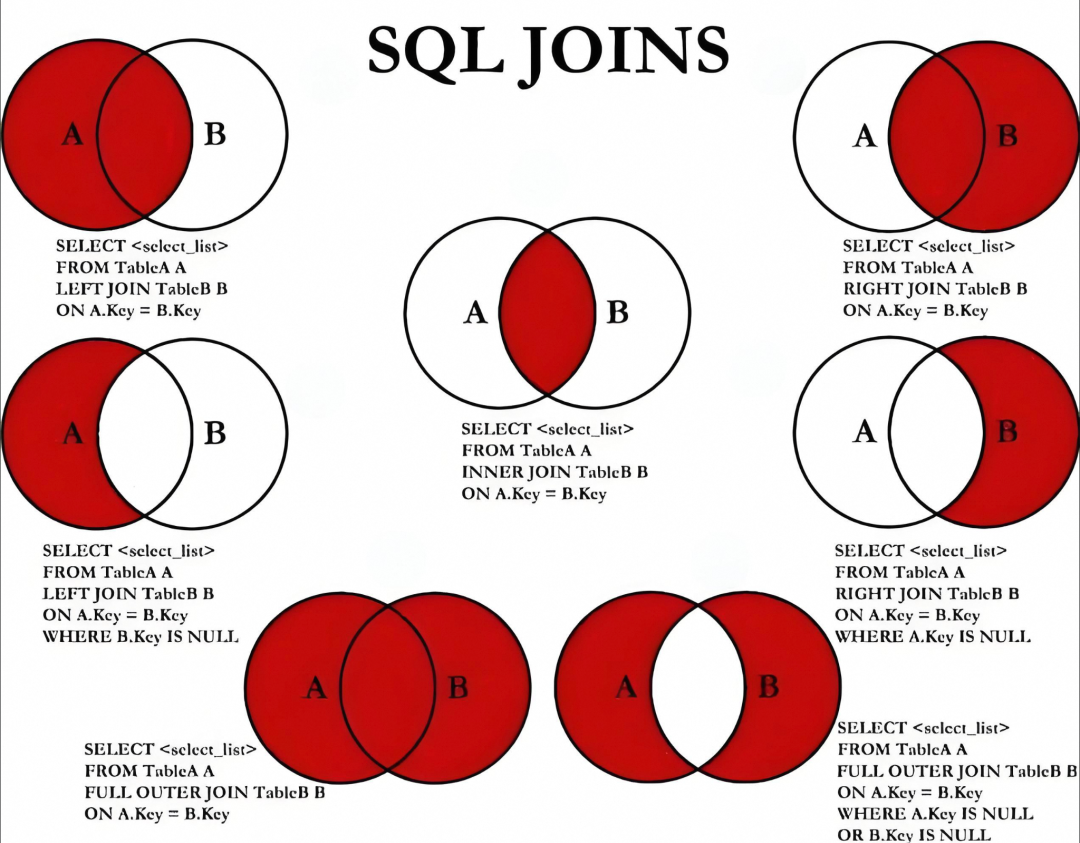
--基本格式select column1, column2, ...from table1{left outer|right outer|full outer|inner|natural}join table2on condition;
参数说明:
column1, column2, ...:要选择的字段名称,可以为多个字段。如果不指定字段名称,则会选择所有字段。
table1:要连接的第一个表。
table2:要连接的第二个表。
condition:连接条件,用于指定连接方式。
左连接(left outer join) 可简写为left join |
返回左表中的所有记录,即使右表中没有与之匹配的记录。 |
右连接(right outer join) 可简写为right join |
返回右表中的所有记录,即使左表中没有与之匹配的记录。 |
全连接(full outer join) 可简写为full join |
返回左右表中的所有记录。 |
内连接(inner join) 关键字inner可以省略 |
左右表中至少存在一个匹配行时,inner join返回数据行。 |
自然连接(natural join) |
参与join的两张表根据字段名称自动决定连接字段。 支持outer natural join,支持使用using子句执行join,输出字段中公共字段只出现一次。 |
隐式连接 |
即不指定join关键字执行连接。 |
多路连接 |
多路join连接。支持通过括号指定join的优先级,括号内的join优先级较高。 |
半连接和mapjoin
|
maxcompute支持半连接操作,通过右表过滤左表的数据,使右表的数据不出现在结果集中,可以提高查询性能。 |
2. left semi join |
当join条件成立时,返回左表中的数据。如果左表中满足指定条件的某行数据在右表中出现过,则此行保留在结果集中。 |
3. left anti join |
当join条件不成立时,返回左表中的数据。如果左表中满足指定条件的某行数据没有在右表中出现过,则此行保留在结果集中。 |
4. mapjoin hint |
当对一个大表和一个或多个小表执行join操作时,可以在select语句中显式指定mapjoin hint提示以提升查询性能。 |
|
5. 在select语句中,使用hint提示/*+ mapjoin(<table_name>) */才会执行mapjoin |
引用小表或子查询时,需要引用别名。 mapjoin支持小表为子查询。 在mapjoin中,可以使用不等值连接或or连接多个条件。您可以通过不写on语句而通过mapjoin on 1 = 1的形式,实现笛卡尔乘积的计算。 mapjoin中多个小表用英文逗号(,)分隔,例如/*+ mapjoin(a,b,c)*/。 |
--允许分区表的全表扫描set odps.sql.allow.fullscan=true;-- 使用mapjoin查询select /*+ mapjoin(a) */a.xxxx_name,a.xxxx_price,b.xxxx_pricefrom xxxx_detail_sj a join xxxx_detail bon a.xxxx_price < b.xxxx_price or a.xxxx_price + b.xxxx_price < 500;
skewjoin hint
其原理图:
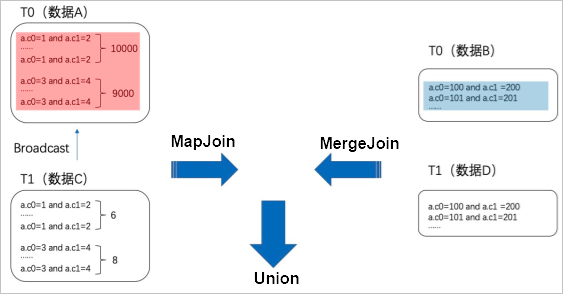
--方法1:hint表名(注意hint的是表的alias)。select /*+ skewjoin(a) */ * from t0 a join t1 b on a.c0 = b.c0 and a.c1 = b.c1;--方法2:hint表名和认为可能产生倾斜的列,例如表a的c0和c1列存在数据倾斜。select /*+ skewjoin(a(c0, c1)) */ * from t0 a join t1 b on a.c0 = b.c0 and a.c1 = b.c1 and a.c2 = b.c2;--方法3:hint表名和列,并提供发生倾斜的key值。如果是string类型,需要加上引号。例如(a.c0=1 and a.c1="2")和(a.c0=3 and a.c1="4")的值都存在数据倾斜。select /*+ skewjoin(a(c0, c1)((1, "2"), (3, "4"))) */ * from t0 a join t1 b on a.c0 = b.c0 and a.c1 = b.c1 and a.c2 = b.c2;
当两张表join存在热点,导致出现长尾问题时:
可以通过取出热点key,将数据分为热点数据和非热点数据两部分处理,最后合并的方式,提高join效率。
having子句
--格式select column_name, aggregate_function(column_name)from table_namewhere column_name operator valuegroup by column_namehaving aggregate_function(column_name) operator value--例子select customer,sum(orderprice) from ordersgroup by customerhaving sum(orderprice)<2000
maxcompute sql的where关键字无法与聚合函数一起使用。
此时可以使用having子句来实现。

表同步
▐ 在线表同步odps
这里以mysql同步odps为例子,其他表同步过程也类似。
首先介绍一下步骤:
step1:进入dataworks,选择:数据开发(datastudio) ——> 数据集成 ——> di数据同步 节点:
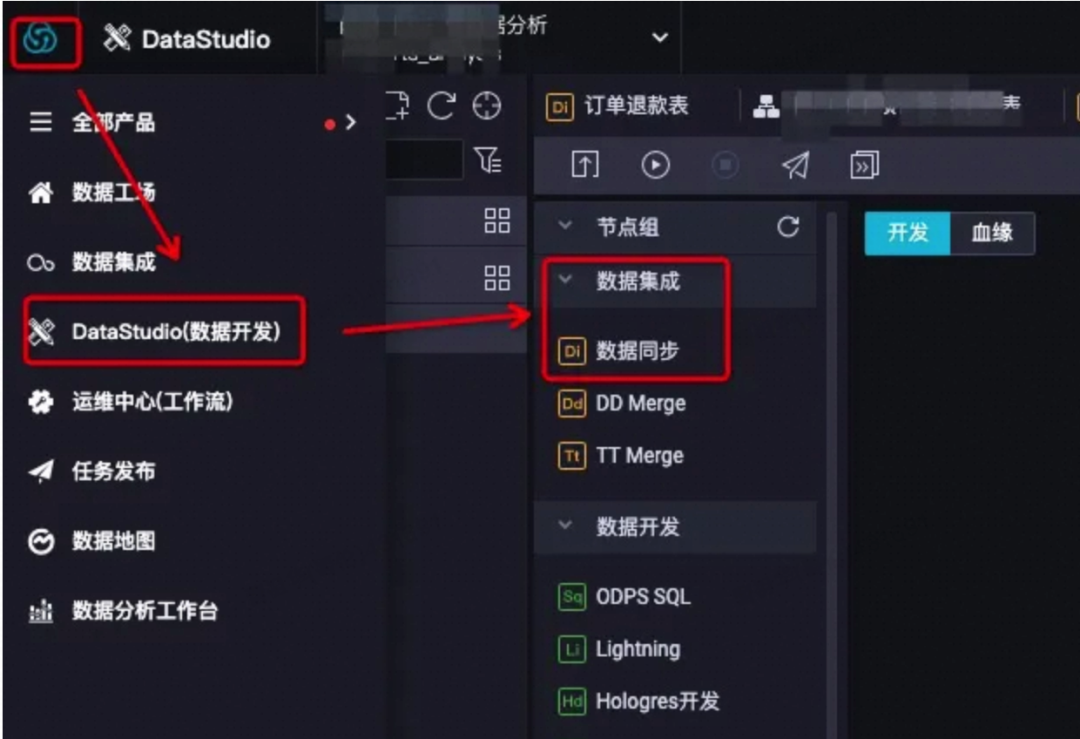
-
数据来源:数据源选择 “mysql” ,填入要同步的mysql的数据表名,会自动搜索到对应的物理表;
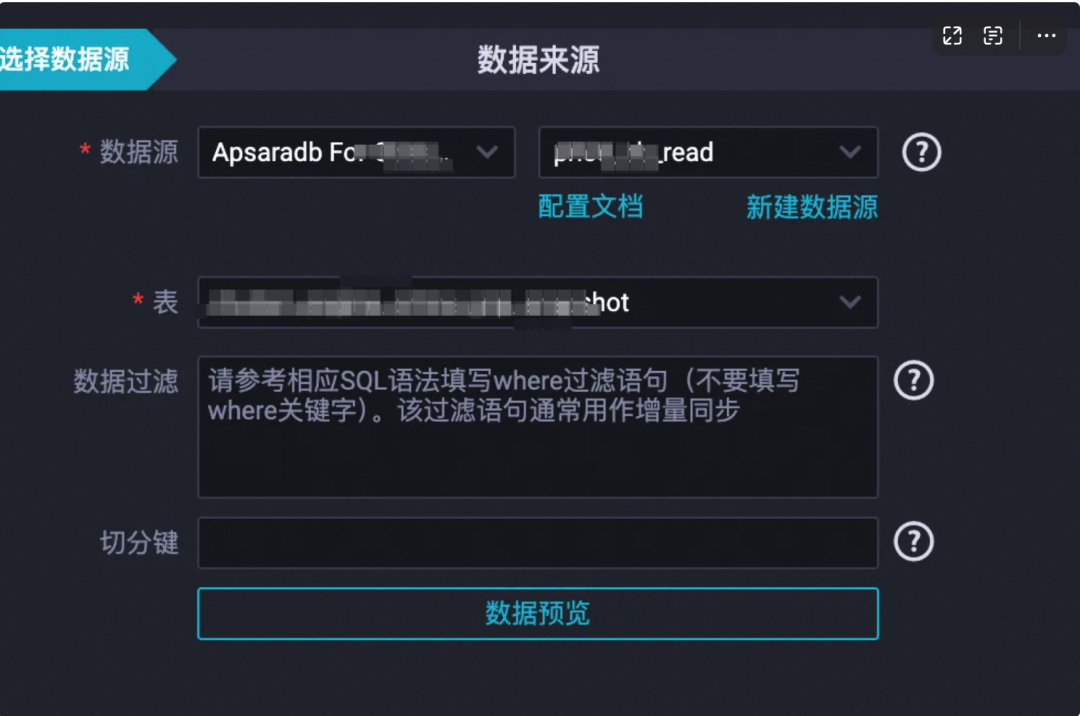
数据去向:数据源选择“odps”,odps的目标表可以先建好,也可以使用“一键生成目标表” 的功能(推荐,简单高效);
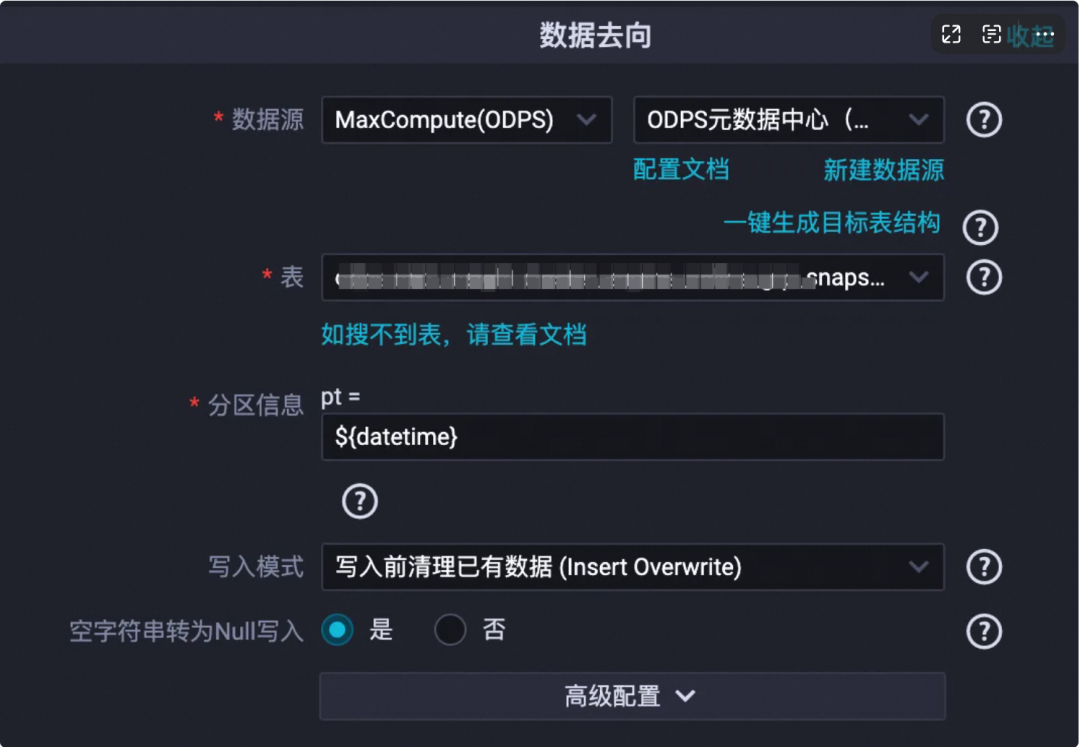
配置好来源去向后,源头表字段和目标表字段会自动映射匹配;

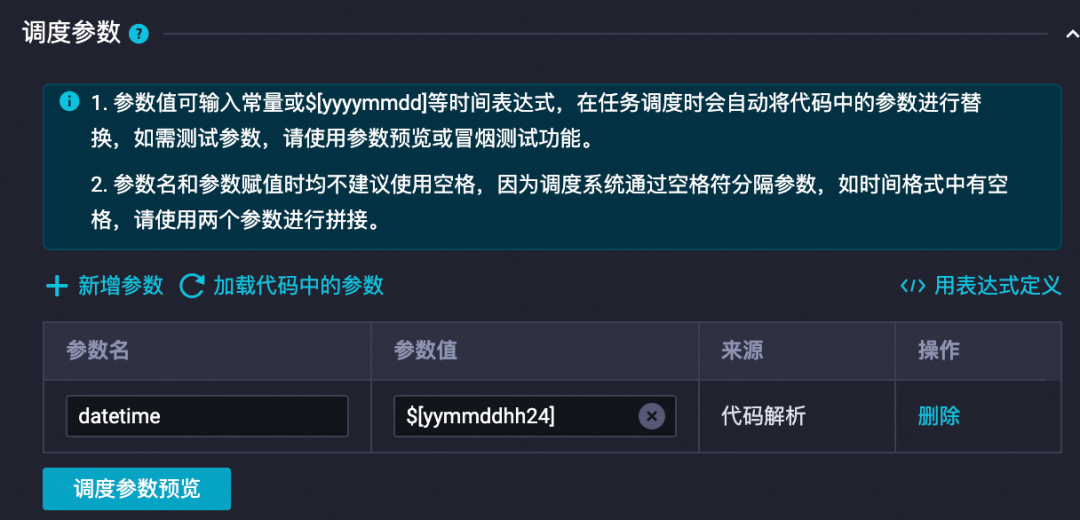
step3: 填好调度配置
调度参数,注意参数值不同,展示的时间也不同
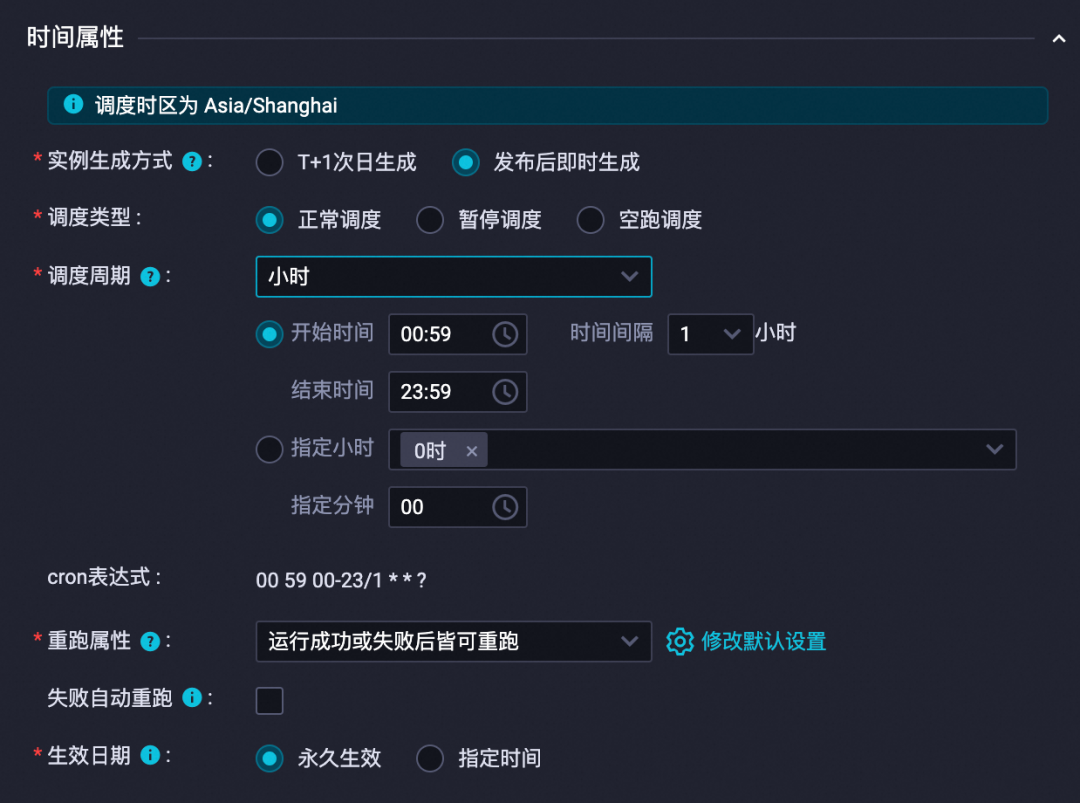
注意调度周期,天级,小时级或其他周期
设置好调度依赖,即依赖哪些上级文件的产出,若无可填根节点:

step4:同步信息填写完成后,在调度配置里配置好调度信息,保存——>发布——>补数据 即可:
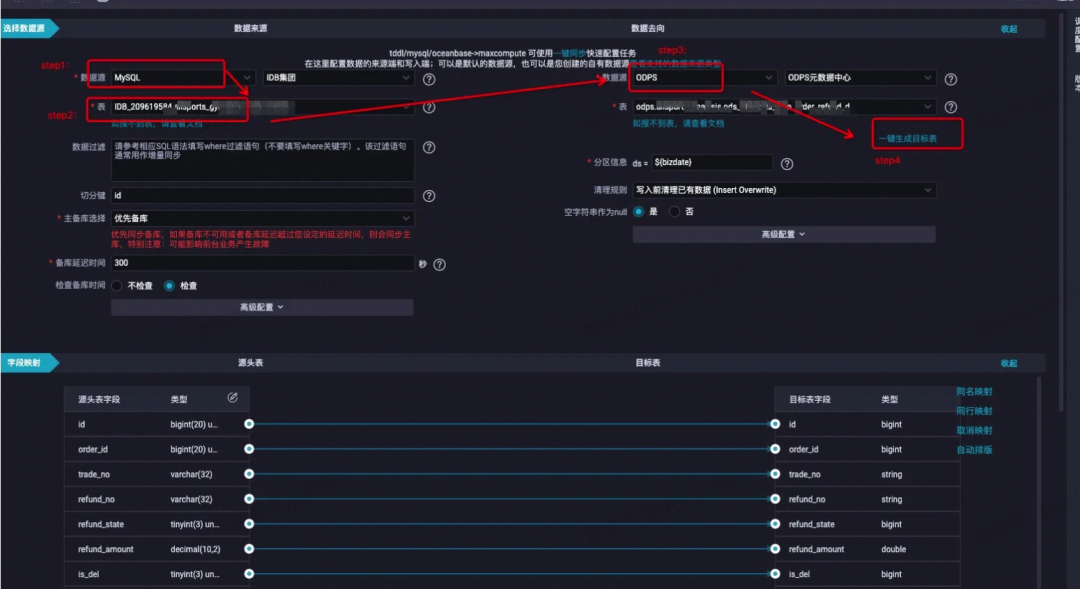
1、“数据来源”的“数据过滤”,不填表示全量同步mysql的数据;也可以使用类似(gmt_create='${bizdate}')条件来过滤,每次增量同步mysql的数据 |
2、“数据去向”的“一键生成目标表”功能,建表ddl语句需要人工检查下:
|
3、“数据去向”的“分区信息”,当建的是分区表时,会自动出现该处的分区信息配置;若建的是非分区表,则不必配置 |
4、调度配置中,可以按需选择天、小时或其他时间粒度调度任务 |
5、非该odps项目空间的表不能在该odps项目空间做同步任务 |
6、odps个别字段内容太长,超出mysql表的该字段存储限制,也会导致写入idb失败,报脏数据(修改idb表字段类型,可将对应字段类型修改为 longtext) |
7、idb表字段设为非null,但odps对应字段存在 null值,会导致写入idb失败,报脏数据(修改idb表定义,将对应字段改默认为null) |
8、odps字段和idb字段不必非得一对一保持应,可以手动选择相关字段 连线 ,odps和idb字段可各有未参与同步的字段(注意:idb字段的剩余字段必须是可以自动填充或默认为null类型的) |
▐ odps导入hologres
目前对于需要周期性导入odps分区表数据到hologres, holo提供了两种导入方式:
方式一:一键可视化导入并且周期性导入,详情见datastudio一键导入
方式二:使用sql导入,详情见hologres sql
一键可视化导入
新建任务,在数据开发单击一键数据同步,并填写节点信息。

2. 配置信息,填写同步信息。
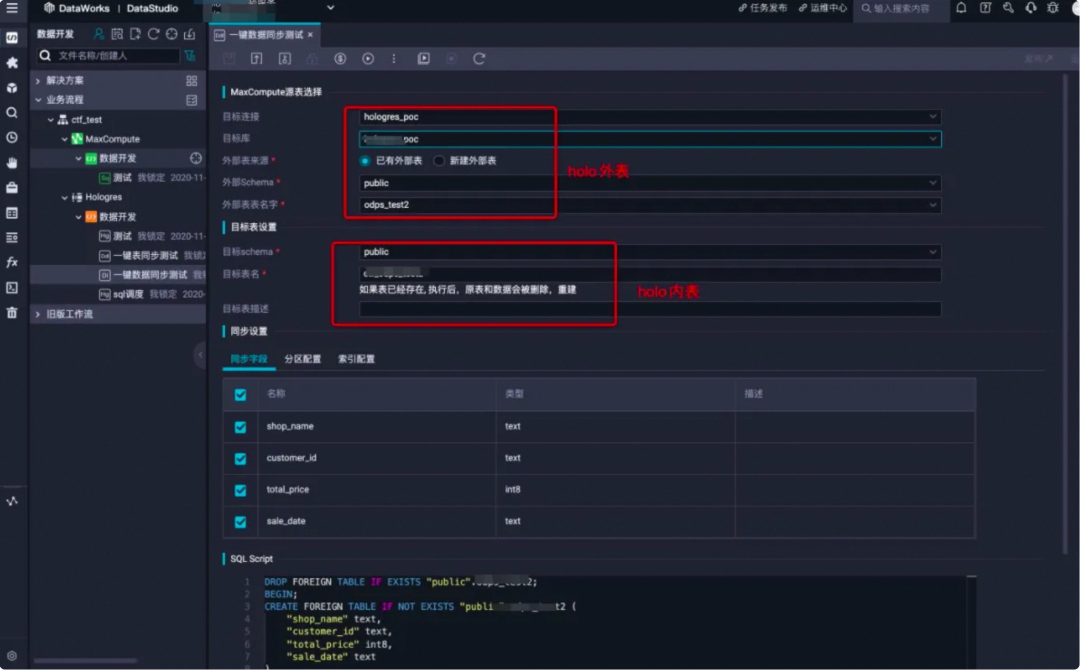
3. 参数说明
参数 |
配置项 |
说明 |
备注 |
maxcompute源表选择 |
目标连接 |
hologres的实例名 |
无 |
目标库 |
hologres的db名 |
无 |
|
外部表来源 |
|
|
|
外部表表名字 |
已有的外部表表名 |
外部表用于映射maxcompute数据,需要与同步数据的maxcompute表对应 |
|
目标表设置 |
目标schema |
当前db下的schema名 |
默认为public,也可以选择新建schema并使用 |
目标表名 |
要导入数据的表名 |
需要同步表数据的内表名称,如已有表,执行后原表和数据将被删除重建 |
|
目标表描述 |
为目标表添加comment |
无 |
|
同步设置 |
同步字段 |
选择需要同步的maxcompute表字段 |
可以选择全部字段,也可以选择部分字段 |
分区配置 |
选择需要同步的分区字段 |
当前hologres仅支持一级分区 |
|
索引配置 |
为目标表构建索引 |
索引的创建可以参见文档设置表属性 |
|
sql script |
sql script |
自动解析出当前运行的sql,方便参照 |
无 |
保持并运行,执行同步任务。任务执行完成之后,可以使用hologres sql查看数据。
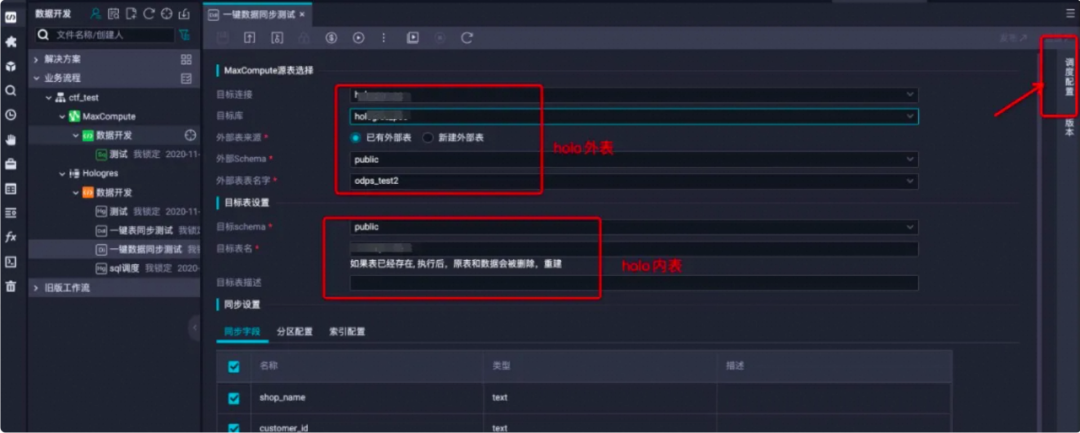
周期性调度
若是您需要周期性导数据,需要单机右侧调度配置进行任务配置,并且保存作业,然后点击右上角发布,将作业发布至生产环境进行周期性调度。
4. 总结
方式一优点:可视化操作,简单快捷,方便小白用户使用,能满足一般场景的使用。
方式一缺点:不支持修改sql逻辑,若是需要修改,需将sql copy再新建一个hologres sql节点,根据业务逻辑修改sql即可。
自写sql导入
先介绍一下操作步骤,基本和方式一相同。
新建业务流程:选择左侧菜单栏数据开发--新建--业务流程,即可创建一个属于自己的业务流程。

2. 输入业务流程名称
3. 新建hologres sql
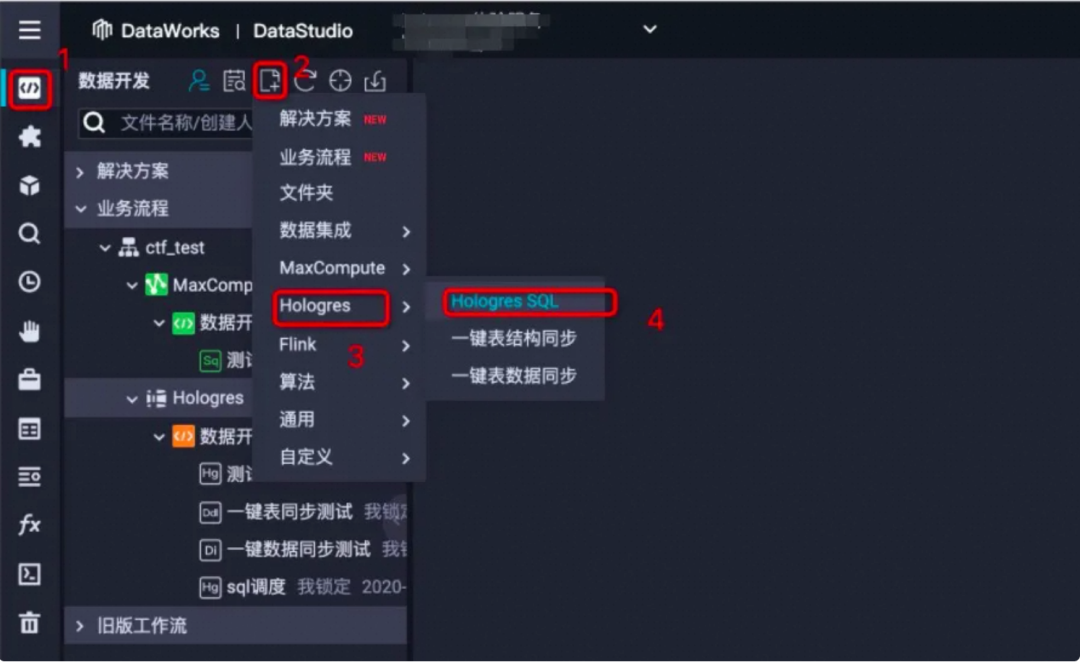
4. hologres开发:打开新建的hologres sql选择对应hologres实例,既可使用标准的postgresql语言开发。
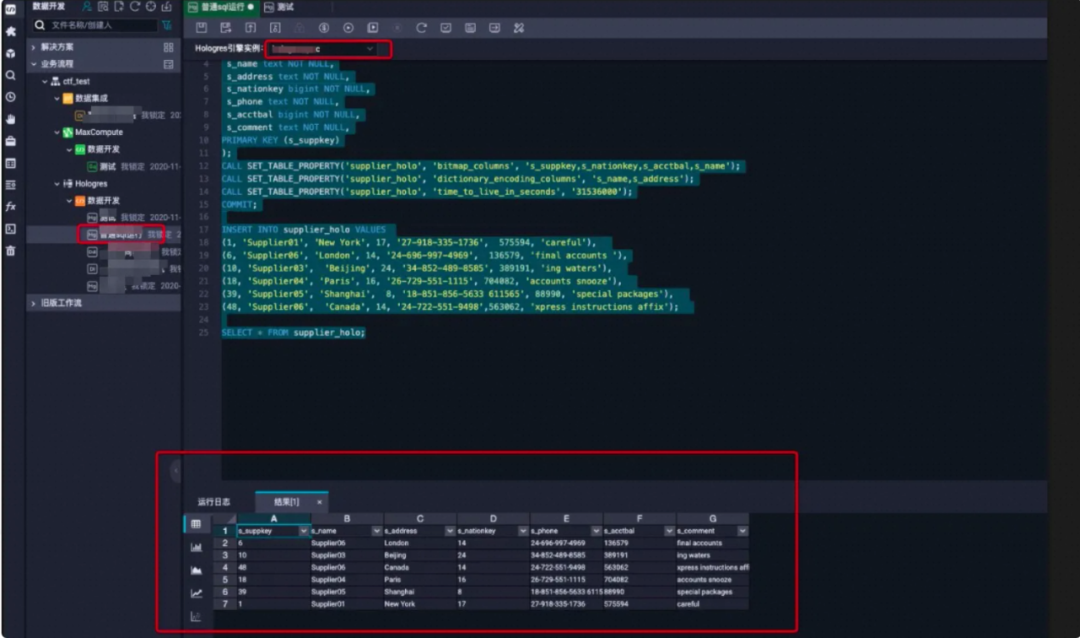
步骤1:准备maxcompute表数据
--maxcompute分区表ddlcreate table if not exists public_data.dwd_product_movie_basic_info(movie_name string comment '电影名称',dirctor string comment '导演',scriptwriter string comment '编剧',area string comment '制片地区/国家',actors string comment '主演',`type` string comment '类型',movie_length string comment '电影长度',movie_date string comment '上映日期',movie_language string comment '语言',imdb_url string comment 'imdb号')partitioned by (ds string) stored as aliorc;--查看分区表的某个分区数据select * from public_data.xxxx_movie_basic_info where ds = '20170112';
import foreign schema public_data limit to (dwd_product_movie_basic_info)from server odps_server into public options(if_table_exist 'update');
begin;create table "public"."holo_dwd_product_movie_basic_info" ("movie_name" text,"dirctor" text,"scriptwriter" text,"area" text,"actors" text,"type" text,"movie_length" text,"movie_date" text,"movie_language" text,"imdb_url" text,"ds" text)partition by list (ds);call set_table_property('"public"."holo_dwd_product_movie_basic_info"', 'orientation', 'column');call set_table_property('"public"."holo_dwd_product_movie_basic_info"', 'bitmap_columns', '"movie_name","dirctor","scriptwriter","area","actors","type","movie_length","movie_date","movie_language","imdb_url","ds"');call set_table_property('"public"."holo_dwd_product_movie_basic_info"', 'dictionary_encoding_columns', '"movie_name:auto","dirctor:auto","scriptwriter:auto","area:auto","actors:auto","type:auto","movie_length:auto","movie_date:auto","movie_language:auto","imdb_url:auto","ds:auto"');call set_table_property('"public"."holo_dwd_product_movie_basic_info"', 'time_to_live_in_seconds', '3153600000');comment on column "public"."holo_dwd_product_movie_basic_info"."movie_name" is '电影名称';comment on column "public"."holo_dwd_product_movie_basic_info"."dirctor" is '导演';comment on column "public"."holo_dwd_product_movie_basic_info"."scriptwriter" is '编剧';comment on column "public"."holo_dwd_product_movie_basic_info"."area" is '制片地区/国家';comment on column "public"."holo_dwd_product_movie_basic_info"."actors" is '主演';comment on column "public"."holo_dwd_product_movie_basic_info"."type" is '类型';comment on column "public"."holo_dwd_product_movie_basic_info"."movie_length" is '电影长度';comment on column "public"."holo_dwd_product_movie_basic_info"."movie_date" is '上映日期';comment on column "public"."holo_dwd_product_movie_basic_info"."movie_language" is '语言';comment on column "public"."holo_dwd_product_movie_basic_info"."imdb_url" is 'imdb号';commit;
步骤4:新建分区子表数据开发
在hologres sql中另开一个作业,用于分区表跑调度。
--创建临时分区子表begin;create table if not exists "public".tmp_holo_dwd_product_movie_basic_info_${bizdate} ("movie_name" text,"dirctor" text,"scriptwriter" text,"area" text,"actors" text,"type" text,"movie_length" text,"movie_date" text,"movie_language" text,"imdb_url" text,"ds" text);commit;--更新外表数据import foreign schema public_data limit to (dwd_product_movie_basic_info) from server odps_server into public options(if_table_exist 'update');--等待30s再导入hologres,以防hologres meta信息更新缓存慢导致的数据不一致而同步不成功select pg_sleep(30);--将maxcompute数据导入临时分区子表insert into "public".tmp_holo_dwd_product_movie_basic_info_${bizdate}select"movie_name","dirctor","scriptwriter","area","actors","type","movie_length","movie_date","movie_language","imdb_url","ds"from "public".dwd_product_movie_basic_infowhere ds='${bizdate}';--导入的场景逻辑比较多,下面有两个场景供参考,可以根据业务逻辑二选一即可--场景1:导入新的分区数据可以参考以下逻辑,begin;alter table "public".tmp_holo_dwd_product_movie_basic_info_${bizdate} rename to holo_dwd_product_movie_basic_info_${bizdate};--将临时分区子表绑定在分区父表上alter table "public".holo_dwd_product_movie_basic_info attach partition "public".holo_dwd_product_movie_basic_info_${bizdate} for values in ('${bizdate}');commit;--场景2:重新对历史分区数据刷新可以参考该逻辑begin;alter table if exists "public".holo_dwd_product_movie_basic_info detach partition "public".holo_dwd_product_movie_basic_info_${bizdate};drop table if exists "public".holo_dwd_product_movie_basic_info_${bizdate};alter table "public".tmp_holo_dwd_product_movie_basic_info_${bizdate} rename to holo_dwd_product_movie_basic_info_${bizdate};--将分区子表绑定在分区父表上alter table "public".holo_dwd_product_movie_basic_info attach partition "public".holo_dwd_product_movie_basic_info_${bizdate} for values in ('${bizdate}');commit;
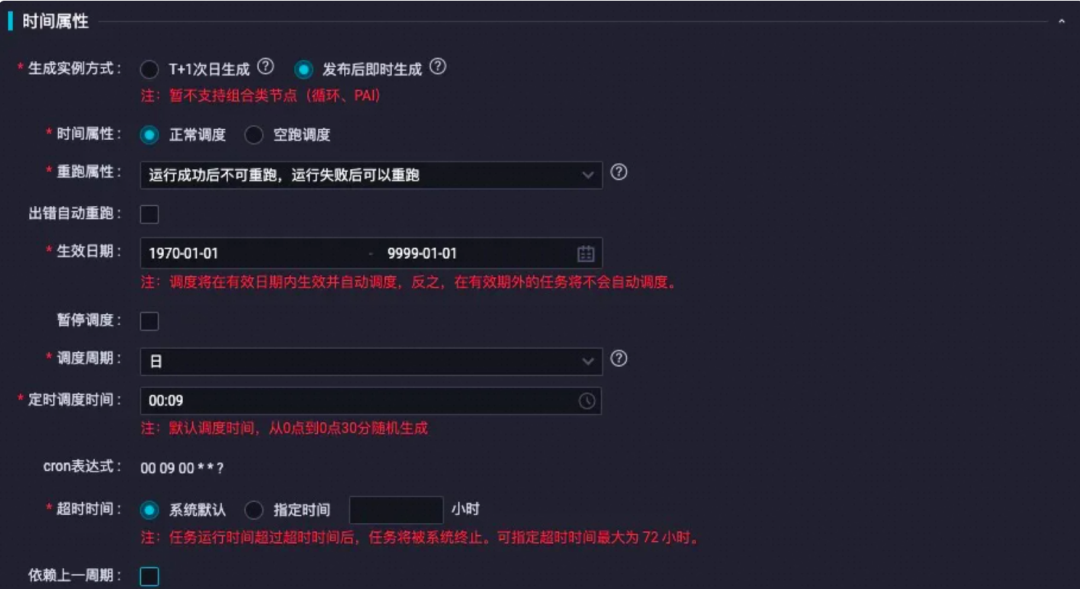
2)时间属性设置
主要设置时间的重跑属性,其余参数可以根据业务情况自行设置。
3)调度依赖设置
调度依赖为root节点即可(也可以根据业务逻辑选择已有的父节点)请先单击自动解析为是,然后单击使用工作空间根节点,会自动解析出root节点,然后将自动解析设置为否。
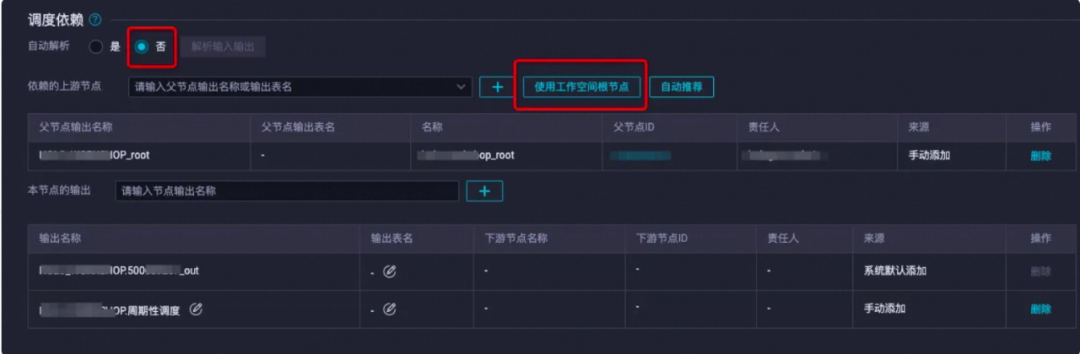
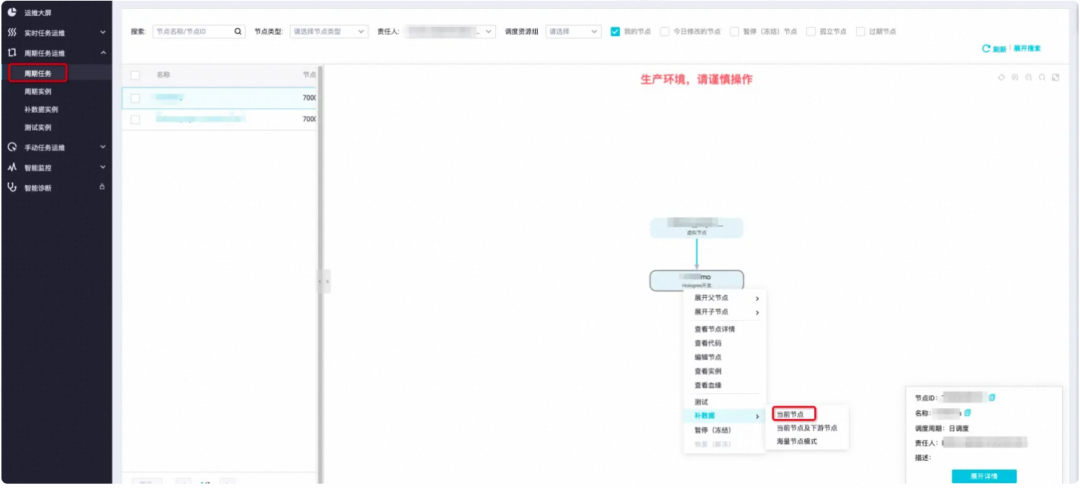
补完数据之后,在补数据实例可以看到正在运行的任务,以及任务运行状态。

--查看分区子表数据select * from holo_dwd_product_movie_basic_info_20170112;--查看分区父表总数据select count (*) from holo_dwd_product_movie_basic_info;
总结:
方式二优点:可按业务需求进行定制,对sql进行修改,满足复杂特定场景的需求,包括历史数据格式转换、数据清理等;通过sql导入性能更优。
方式二缺点:有一定学习成本,初学者不太适合,可先通过方式一了解其数据同步的流程和原理,再切换到方式二。
流程梳理
-- 1.创建外表create foreign table if not exists ${odps_table_name} ("user_id" bigint,"user_name" text,"ds" text)server odps_serveroptions (project_name 'onetag', table_name '${odps_table_name}');commit;-- 2.刷新外表的schemaimport foreign schema ${odps_project} limit to(${odps_table_name})from server odps_server into publicoptions(if_table_exist 'update',if_unsupported_type 'error');-- 3.清理潜在的临时表begin ;drop table if exists ${holo_table_name}_tmp_${bizhour};commit ;-- 4.创建临时表begin ;create table if not exists "public".${holo_table_name}_tmp_${bizhour} ("user_id" bigint,"user_name" text,"ds" text,primary key (user_id,ds));commit;-- 5.通过查询外表,向临时表插入数据insert into ${holo_table_name}_tmp_${bizhour}select *from public.${odps_table_name}where ds='${bizhour}';-- 6.替换子表begin ;-- 6.1删除已经存在的子表drop table if exists ${holo_table_name}_${bizhour};-- 6.2将临时表改名alter table ${holo_table_name}_tmp_${bizhour} rename to ${holo_table_name}_${bizhour};-- 6.3将临时表绑定至指定分区表alter table ${holo_table_name} attach partition ${holo_table_name}_${bizhour}for values in ('${bizhour}');commit ;-- 7. 大量数据导入后执行analyze分区表父表操作analyze ${holo_table_name};
注意点:
使用临时表的原因是为了保证原子性,只有在导入完成后才绑定至分区表,为了避免导入任务失败时还需要重新删除表等操作。
对于更新子表分区数据场景,需要删除子表和重新绑定临时表放入一个事务过程中,保证该过程的事务性。
maxcompute的表数据更新之后,在hologres存在缓存延迟(一般为10分钟内),建议在导入数据前使用import foreign schema语法更新外部表以获取最新数据。
导入maxcompute数据至hologres时,建议使用sql导入,不建议使用数据集成导入,因为使用sql导入性能表现更优。

注意事项
▐ 调度配置
这里强调一下调度参数:
调度参数通常会被用于指代某些动态时间的场景,此场景下,可基于业务日期和定时时间进行调度参数的取值设置。配置调度参数前,您可先了解这两个时间概念,便于后续设置调度参数取值。
取值方式 |
参数格式 |
参数示例 |
相关参考 |
基于业务日期获取时间数据 |
通常,使用大括号${...},结合yyyy、yy、mm及dd自定义组合生成时间参数,获取业务日期前后多少年、月、天。 |
可通过${yyyymmdd}、${yyyy-mm-dd}等${...}自定义时间格式获取,例如:
|
更多赋值示例,请参见自定义参数${...} |
基于定时时间获取时间数据 |
通常,使用中括号$[...],结合yyyy、yy、mm、dd、hh24、mi及ss自定义组合生成时间参数,获取定时时间前后多少年、月、天、小时、分钟、秒。 |
可通过$[yyyymmddhh24miss]等$[...]自定义时间格式获取。例如,取前一天的前一小时,参数表达式为$[yyyymmdd-1-1/24]。 |
|
内置参数:
内置参数 |
定义 |
$bizdate |
业务日期,格式为yyyymmdd,与自定义参数${yyyymmdd}取值一致。 该参数的应用较为广泛,日常调度中默认任务预期运行时间的前一天为业务日期。 |
$cyctime |
任务的定时时间,格式为yyyymmddhh24miss,与自定义参数$[yyyymmddhh24miss]取值一致。 |
$gmtdate |
当前日期,格式为yyyymmdd。 该参数默认取当天日期,执行补数据操作时输入的日期为业务日期+1。 |
$bizmonth |
业务月份,格式为yyyymm。
|
$jobid |
任务所属的业务流程id。 |
$nodeid |
节点id。 |
$taskid |
节点产生的实例id。 |
调度配置的各板块:
配置基础属性 |
名称,节点id,节点类型,责任人,描述 |
配置调度参数 |
调度参数支持的格式 配置并使用调度参数 |
配置时间属性 |
时间属性配置说明 实例生成方式:发布后即时生成实例 调度周期:分钟/小时/天/月调度 |
配置资源属性 |
默认配置为公共调度资源组。 |
配置调度依赖 |
调度依赖配置 配置同周期调度依赖 配置依赖上一周期(跨周期依赖) 复杂依赖场景调度配置原则 |
配置节点上下文 |
在节点上下文配置本节点输入参数和本节点输出参数 输出参数的取值分为常量和变量两种类型 配置输入参数,在调度依赖中添加依赖的上游节点 |
更多内容请期待下一篇:进阶篇。






发表评论