mysql - 一文搞懂主键与外键:设计原则 + 实战案例
在关系型数据库的设计中,主键(primary key)和外键(foreign key)是两个基石般的核心概念。它们不仅是数据完整性的保障,更是实现数据关联、维护数据一致性的关键。无论是初学者还是经验丰富的开发者,深入理解主键与外键的工作原理、设计原则以及实际应用场景,对于构建高效、可靠的数据库系统至关重要。本文将带你从零开始,全面解析主键与外键,结合丰富的实战案例和 java 代码示例,让你彻底掌握这一核心技能。
一、什么是主键(primary key)?
1.1 基本定义
主键(primary key)是数据库表中用来唯一标识每一行记录的列或列的组合。它是表中最重要的约束之一,确保了表内数据的唯一性和不可重复性。想象一下,你有一个学生名单,每个学生的学号就是主键,它独一无二,不允许重复,也不能为 null。
1.2 主键的核心特性
- 唯一性 (uniqueness): 主键的值在表中必须是唯一的,不能出现重复。
- 非空性 (not null): 主键列的值不能为空(null)。这确保了每一条记录都有一个明确的身份标识。
- 不可变性 (immutability): 一旦主键值被设定,通常不应更改。这是为了保证数据引用的稳定性。
- 唯一标识 (unique identifier): 主键是表中每一行的唯一标识符。
1.3 主键的类型
- 单列主键 (single column primary key): 由表中的一个单独列构成主键。这是最常见的形式。
- 示例:
user_id列作为主键。
- 示例:
- 复合主键 (composite primary key): 由表中的多个列组合构成主键。这些列的组合必须唯一。
- 示例:
order_id和product_id组成的复合主键,表示某订单中特定产品的记录。
- 示例:
1.4 主键的创建方式
在 mysql 中,可以通过以下几种方式定义主键:
在创建表时定义:
create table users (
user_id int primary key,
username varchar(50) not null,
email varchar(100) unique
);
在定义列之后定义:
create table orders (
order_id int,
user_id int,
order_date date,
primary key (order_id) -- 定义主键
);
使用复合主键:
create table order_items (
order_id int,
product_id int,
quantity int,
primary key (order_id, product_id) -- 复合主键
);
1.5 自增主键 (auto-increment primary key)
最常用的主键类型是自增主键。通过 auto_increment 关键字,mysql 会自动为新插入的记录分配一个唯一的递增值。
create table products (
product_id int auto_increment primary key,
product_name varchar(100) not null,
price decimal(10, 2)
);
二、什么是外键(foreign key)?
2.1 基本定义
外键(foreign key)是表中的一列或列的组合,它引用另一个表的主键。外键的作用是建立和加强两个表数据之间的链接关系,确保数据的引用完整性。外键的存在使得我们可以轻松地通过一个表关联到另一个表,从而实现数据的关联查询。
2.2 外键的核心特性
- 引用完整性 (referential integrity): 外键值必须是被引用表(父表)主键中存在的值,或者为 null(如果允许)。
- 级联操作 (cascade operations): 可以定义当父表中的记录被修改或删除时,子表中的相关记录应该如何处理(如级联删除、级联更新等)。
- 关联关系 (relationship): 外键定义了两个表之间的关系,通常是“一对多”或“一对一”的关系。
2.3 外键的关系类型
- 一对多 (one-to-many): 这是最常见的关系。一个父表的记录可以对应多个子表的记录。例如,一个用户可以有多个订单。
- 一对一 (one-to-one): 一个父表的记录只能对应一个子表的记录。例如,一个用户可能有一个对应的详细信息表。
- 多对多 (many-to-many): 通常通过中间表(关联表)来实现。例如,一个学生可以选修多门课程,一门课程也可以被多个学生选修。
2.4 外键的创建方式
在 mysql 中,外键约束需要在创建表时或之后通过 add constraint 语句添加。
-- 创建父表
create table categories (
category_id int primary key,
category_name varchar(100) not null
);
-- 创建子表并定义外键
create table products (
product_id int auto_increment primary key,
product_name varchar(100) not null,
category_id int,
foreign key (category_id) references categories(category_id)
);或者,先创建表,再添加外键约束:
create table products (
product_id int auto_increment primary key,
product_name varchar(100) not null,
category_id int
);
alter table products
add constraint fk_category
foreign key (category_id) references categories(category_id);2.5 外键的级联操作
在定义外键时,可以指定级联操作,以控制当父表记录发生变化时,子表记录的行为。
- cascade: 当父表记录被更新或删除时,相关的子表记录也会被自动更新或删除。
- set null: 当父表记录被删除时,子表中对应的外键字段会被设置为 null(前提是该字段允许为 null)。
- restrict / no action: 拒绝执行会导致违反外键约束的操作(默认行为)。
- set default: 设置外键字段为默认值(mysql 5.7+ 支持)。
-- 定义带有级联删除的外键
create table orders (
order_id int auto_increment primary key,
user_id int,
order_date date,
foreign key (user_id) references users(user_id) on delete cascade
);
三、主键与外键的核心区别
| 特性 | 主键 (primary key) | 外键 (foreign key) |
|---|---|---|
| 作用 | 唯一标识表中的每一行记录 | 建立表之间的关联关系 |
| 唯一性 | 值必须唯一 | 值可以重复(引用父表的主键值) |
| 非空性 | 必须非空 | 可以为 null(除非定义为 not null) |
| 数量 | 每张表只能有一个主键 | 每张表可以有多个外键 |
| 来源 | 通常由自身表定义 | 引用其他表的主键 |
| 索引 | 自动创建唯一索引 | 通常创建非唯一索引(除非是唯一外键) |
| 数据一致性 | 确保表内数据唯一 | 确保表间数据引用一致 |
四、主键与外键的设计原则
4.1 主键设计原则
- 选择合适的列:
- 自然键: 如果存在天然的唯一标识符(如身份证号、学号),可以考虑使用。
- 代理键: 更推荐使用自增主键或 uuid。自增主键简单、高效,uuid 更适合分布式环境。
- 避免使用业务逻辑字段: 如用户名、邮箱等,因为它们可能变更或重复。
- 保证唯一性:
- 主键值必须在整个表中唯一,这是其核心属性。
- 保证非空性:
- 主键列必须设置为
not null。
- 主键列必须设置为
- 保持不变性:
- 一旦主键值确定,应尽量避免修改,以维持数据引用的稳定性。
- 考虑性能:
- 尽量选择较小的数据类型(如
int而不是varchar)以提高索引效率。 - 对于复合主键,将最常用于查询的列放在前面。
- 尽量选择较小的数据类型(如
4.2 外键设计原则
- 明确关联关系:
- 清楚地定义父表和子表之间的关系类型(一对多、一对一等)。
- 选择合适的列:
- 外键列的数据类型必须与被引用的主键列的数据类型完全一致。
- 外键列的长度也必须匹配(如果适用)。
- 考虑约束类型:
- 根据业务需求决定是否启用外键约束,以及是否需要级联操作。
- 外键约束虽然保证了数据一致性,但也可能影响插入和更新的性能。
- 维护数据完整性:
- 外键确保了引用完整性,防止出现孤立记录(即子表中有指向不存在的父表记录)。
- 性能考量:
- 外键会创建索引(通常是非唯一索引),这有助于加速关联查询,但也增加了插入和更新的成本。
- 如果不需要强制引用完整性,可以考虑不使用外键,而通过应用层逻辑来保证。
4.3 设计时的注意事项
- 避免循环引用: 确保表之间的外键关系不会形成循环依赖,这会导致数据库设计混乱和维护困难。
- 合理使用复合主键: 虽然复合主键很强大,但过于复杂的复合主键可能降低查询效率。
- 考虑未来扩展性: 设计时要预留一定的灵活性,以便未来业务变化时能够方便地调整表结构。
- 文档化: 详细记录数据库的结构、主键和外键的定义及它们之间的关系,这对于后续的维护至关重要。
五、实战案例:电商系统的数据库设计
让我们通过一个真实的电商系统案例来深入理解主键与外键的应用。
5.1 需求分析
假设我们要设计一个简单的电商系统,主要功能包括:
- 管理用户(user)
- 管理商品类别(category)
- 管理商品(product)
- 管理订单(order)
- 管理订单项(orderitem)
我们需要确保:
- 每个用户、商品、类别都有唯一标识。
- 商品必须属于某个类别。
- 订单必须关联到一个用户。
- 订单项必须关联到一个订单和一个商品。
5.2 数据库表结构设计
我们将创建以下表:
- users (用户表): 存储用户基本信息。
- categories (类别表): 存储商品类别信息。
- products (商品表): 存储商品信息,关联到类别。
- orders (订单表): 存储订单信息,关联到用户。
- order_items (订单项表): 存储订单中包含的商品项,关联到订单和商品。
5.2.1 创建用户表 (users)
create table users (
user_id int auto_increment primary key,
username varchar(50) not null unique,
email varchar(100) not null unique,
password_hash varchar(255) not null,
created_at timestamp default current_timestamp
);
- user_id: 自增主键,唯一标识每个用户。
- username: 用户名,非空且唯一。
- email: 邮箱,非空且唯一。
- password_hash: 密码哈希值,非空。
- created_at: 创建时间戳,默认为当前时间。
5.2.2 创建类别表 (categories)
create table categories (
category_id int auto_increment primary key,
category_name varchar(100) not null unique,
description text,
created_at timestamp default current_timestamp
);
- category_id: 自增主键,唯一标识每个类别。
- category_name: 类别名称,非空且唯一。
- description: 类别描述。
- created_at: 创建时间戳。
5.2.3 创建商品表 (products)
create table products (
product_id int auto_increment primary key,
product_name varchar(200) not null,
description text,
price decimal(10, 2) not null,
stock_quantity int default 0,
category_id int,
created_at timestamp default current_timestamp,
foreign key (category_id) references categories(category_id) on delete set null
);
- product_id: 自增主键,唯一标识每个商品。
- product_name: 商品名称,非空。
- description: 商品描述。
- price: 商品价格,非空。
- stock_quantity: 库存数量,默认为 0。
- category_id: 外键,引用
categories.category_id。 - created_at: 创建时间戳。
- foreign key: 定义外键约束,当
categories中的记录被删除时,products中的category_id会被设置为 null(如果category_id允许为 null)。
5.2.4 创建订单表 (orders)
create table orders (
order_id int auto_increment primary key,
user_id int not null,
order_date timestamp default current_timestamp,
total_amount decimal(10, 2) not null,
status enum('pending', 'processing', 'shipped', 'delivered', 'cancelled') default 'pending',
foreign key (user_id) references users(user_id) on delete cascade
);
- order_id: 自增主键,唯一标识每个订单。
- user_id: 外键,引用
users.user_id。 - order_date: 订单日期,默认为当前时间。
- total_amount: 订单总金额,非空。
- status: 订单状态,默认为 ‘pending’。
- foreign key: 定义外键约束,当
users中的记录被删除时,所有相关的orders记录也会被自动删除(级联删除)。
5.2.5 创建订单项表 (order_items)
create table order_items (
order_item_id int auto_increment primary key,
order_id int not null,
product_id int not null,
quantity int not null default 1,
unit_price decimal(10, 2) not null,
foreign key (order_id) references orders(order_id) on delete cascade,
foreign key (product_id) references products(product_id) on delete cascade
);
- order_item_id: 自增主键,唯一标识每个订单项。
- order_id: 外键,引用
orders.order_id。 - product_id: 外键,引用
products.product_id。 - quantity: 购买数量,默认为 1。
- unit_price: 单价,非空。
- foreign key: 定义两个外键约束,分别关联到
orders和products表。当订单或商品被删除时,相关的订单项也会被自动删除。
5.3 表关系图解
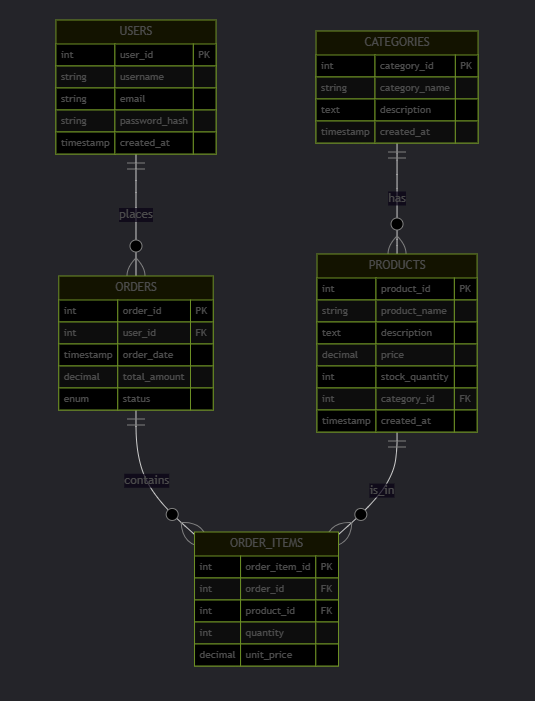
5.4 数据插入示例
-- 插入用户数据
insert into users (username, email, password_hash) values
('alice', 'alice@example.com', 'hashed_password_1'),
('bob', 'bob@example.com', 'hashed_password_2');
-- 插入类别数据
insert into categories (category_name, description) values
('electronics', 'electronic devices and gadgets'),
('books', 'books and literature');
-- 插入商品数据
insert into products (product_name, description, price, stock_quantity, category_id) values
('smartphone', 'latest model smartphone', 699.99, 50, 1),
('laptop', 'high-performance laptop', 1299.99, 20, 1),
('novel', 'popular fiction novel', 12.99, 100, 2);
-- 插入订单数据
insert into orders (user_id, total_amount, status) values
(1, 712.98, 'delivered'), -- alice's order for 1 smartphone (699.99) + 1 novel (12.99)
(2, 1312.98, 'processing'); -- bob's order for 1 laptop (1299.99) + 1 novel (12.99)
-- 插入订单项数据
insert into order_items (order_id, product_id, quantity, unit_price) values
(1, 1, 1, 699.99), -- alice ordered 1 smartphone
(1, 3, 1, 12.99), -- alice ordered 1 novel
(2, 2, 1, 1299.99), -- bob ordered 1 laptop
(2, 3, 1, 12.99); -- bob ordered 1 novel六、java 代码示例:spring boot + jpa 实现
我们将使用 spring boot 和 jpa 来实现上述电商系统的实体类和 repository,以展示如何在 java 应用中处理主键与外键。
6.1 项目结构
src/ ├── main/ │ ├── java/ │ │ └── com/ │ │ └── example/ │ │ └── ecommerce/ │ │ ├── ecommerceapplication.java │ │ ├── config/ │ │ │ └── databaseconfig.java (可选) │ │ ├── entity/ │ │ │ ├── user.java │ │ │ ├── category.java │ │ │ ├── product.java │ │ │ ├── order.java │ │ │ └── orderitem.java │ │ ├── repository/ │ │ │ ├── userrepository.java │ │ │ ├── categoryrepository.java │ │ │ ├── productrepository.java │ │ │ ├── orderrepository.java │ │ │ └── orderitemrepository.java │ │ ├── service/ │ │ │ ├── userservice.java │ │ │ ├── productservice.java │ │ │ ├── orderservice.java │ │ │ └── orderitemservice.java │ │ └── controller/ │ │ ├── usercontroller.java │ │ ├── productcontroller.java │ │ └── ordercontroller.java │ └── resources/ │ ├── application.properties │ └── data.sql (可选,用于初始化数据) └── pom.xml
6.2 maven 依赖 (pom.xml)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/pom/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/xmlschema-instance"
xsi:schemalocation="http://maven.apache.org/pom/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelversion>4.0.0</modelversion>
<groupid>com.example</groupid>
<artifactid>ecommerce</artifactid>
<version>0.0.1-snapshot</version>
<name>ecommerce</name>
<description>e-commerce system example</description>
<parent>
<groupid>org.springframework.boot</groupid>
<artifactid>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactid>
<version>2.7.0</version> <!-- 使用兼容的版本 -->
<relativepath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<properties>
<java.version>11</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupid>org.springframework.boot</groupid>
<artifactid>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactid>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupid>org.springframework.boot</groupid>
<artifactid>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactid>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupid>mysql</groupid>
<artifactid>mysql-connector-java</artifactid>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupid>org.springframework.boot</groupid>
<artifactid>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactid>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- 添加 lombok 依赖以简化实体类代码 -->
<dependency>
<groupid>org.projectlombok</groupid>
<artifactid>lombok</artifactid>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupid>org.springframework.boot</groupid>
<artifactid>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactid>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>6.3 配置文件 (application.properties)
# database configuration spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ecommerce_db?usessl=false&servertimezone=utc&allowpublickeyretrieval=true spring.datasource.username=your_username spring.datasource.password=your_password spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.driver # jpa configuration spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=update # 仅用于演示,生产环境应谨慎使用 spring.jpa.show-sql=true spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect=org.hibernate.dialect.mysql8dialect spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.format_sql=true # lombok configuration (if using) # lombok.mapstruct.default-component-model=spring
6.4 实体类 (entity)
user.java
package com.example.ecommerce.entity;
import javax.persistence.*;
import java.time.localdatetime;
import java.util.list;
@entity
@table(name = "users")
public class user {
@id
@generatedvalue(strategy = generationtype.identity)
@column(name = "user_id")
private long userid; // 主键,自增
@column(name = "username", nullable = false, unique = true)
private string username; // 用户名
@column(name = "email", nullable = false, unique = true)
private string email; // 邮箱
@column(name = "password_hash", nullable = false)
private string passwordhash; // 密码哈希
@column(name = "created_at", updatable = false)
private localdatetime createdat; // 创建时间
// 与 order 的一对多关系 (一个用户可以有多个订单)
@onetomany(mappedby = "user", cascade = cascadetype.all, fetch = fetchtype.lazy)
private list<order> orders;
// 构造函数
public user() {}
public user(string username, string email, string passwordhash) {
this.username = username;
this.email = email;
this.passwordhash = passwordhash;
this.createdat = localdatetime.now(); // 自动设置创建时间
}
// getter 和 setter 方法
public long getuserid() {
return userid;
}
public void setuserid(long userid) {
this.userid = userid;
}
public string getusername() {
return username;
}
public void setusername(string username) {
this.username = username;
}
public string getemail() {
return email;
}
public void setemail(string email) {
this.email = email;
}
public string getpasswordhash() {
return passwordhash;
}
public void setpasswordhash(string passwordhash) {
this.passwordhash = passwordhash;
}
public localdatetime getcreatedat() {
return createdat;
}
public void setcreatedat(localdatetime createdat) {
this.createdat = createdat;
}
public list<order> getorders() {
return orders;
}
public void setorders(list<order> orders) {
this.orders = orders;
}
@override
public string tostring() {
return "user{" +
"userid=" + userid +
", username='" + username + '\'' +
", email='" + email + '\'' +
", createdat=" + createdat +
'}';
}
}category.java
package com.example.ecommerce.entity;
import javax.persistence.*;
import java.time.localdatetime;
import java.util.list;
@entity
@table(name = "categories")
public class category {
@id
@generatedvalue(strategy = generationtype.identity)
@column(name = "category_id")
private long categoryid; // 主键,自增
@column(name = "category_name", nullable = false, unique = true)
private string categoryname; // 类别名称
@column(name = "description", columndefinition = "text")
private string description; // 类别描述
@column(name = "created_at", updatable = false)
private localdatetime createdat; // 创建时间
// 与 product 的一对多关系 (一个类别可以有多个商品)
@onetomany(mappedby = "category", cascade = cascadetype.all, fetch = fetchtype.lazy)
private list<product> products;
// 构造函数
public category() {}
public category(string categoryname, string description) {
this.categoryname = categoryname;
this.description = description;
this.createdat = localdatetime.now(); // 自动设置创建时间
}
// getter 和 setter 方法
public long getcategoryid() {
return categoryid;
}
public void setcategoryid(long categoryid) {
this.categoryid = categoryid;
}
public string getcategoryname() {
return categoryname;
}
public void setcategoryname(string categoryname) {
this.categoryname = categoryname;
}
public string getdescription() {
return description;
}
public void setdescription(string description) {
this.description = description;
}
public localdatetime getcreatedat() {
return createdat;
}
public void setcreatedat(localdatetime createdat) {
this.createdat = createdat;
}
public list<product> getproducts() {
return products;
}
public void setproducts(list<product> products) {
this.products = products;
}
@override
public string tostring() {
return "category{" +
"categoryid=" + categoryid +
", categoryname='" + categoryname + '\'' +
", description='" + description + '\'' +
", createdat=" + createdat +
'}';
}
}product.java
package com.example.ecommerce.entity;
import javax.persistence.*;
import java.math.bigdecimal;
import java.time.localdatetime;
@entity
@table(name = "products")
public class product {
@id
@generatedvalue(strategy = generationtype.identity)
@column(name = "product_id")
private long productid; // 主键,自增
@column(name = "product_name", nullable = false)
private string productname; // 商品名称
@column(name = "description", columndefinition = "text")
private string description; // 商品描述
@column(name = "price", nullable = false, precision = 10, scale = 2)
private bigdecimal price; // 商品价格
@column(name = "stock_quantity", nullable = false, defaultvalue = "0")
private integer stockquantity; // 库存数量
@column(name = "created_at", updatable = false)
private localdatetime createdat; // 创建时间
// 与 category 的多对一关系 (一个商品属于一个类别)
@manytoone(fetch = fetchtype.lazy)
@joincolumn(name = "category_id") // 外键,引用 category.category_id
private category category;
// 与 orderitem 的一对多关系 (一个商品可以出现在多个订单项中)
@onetomany(mappedby = "product", cascade = cascadetype.all, fetch = fetchtype.lazy)
private java.util.list<orderitem> orderitems;
// 构造函数
public product() {}
public product(string productname, string description, bigdecimal price, integer stockquantity, category category) {
this.productname = productname;
this.description = description;
this.price = price;
this.stockquantity = stockquantity;
this.category = category;
this.createdat = localdatetime.now(); // 自动设置创建时间
}
// getter 和 setter 方法
public long getproductid() {
return productid;
}
public void setproductid(long productid) {
this.productid = productid;
}
public string getproductname() {
return productname;
}
public void setproductname(string productname) {
this.productname = productname;
}
public string getdescription() {
return description;
}
public void setdescription(string description) {
this.description = description;
}
public bigdecimal getprice() {
return price;
}
public void setprice(bigdecimal price) {
this.price = price;
}
public integer getstockquantity() {
return stockquantity;
}
public void setstockquantity(integer stockquantity) {
this.stockquantity = stockquantity;
}
public localdatetime getcreatedat() {
return createdat;
}
public void setcreatedat(localdatetime createdat) {
this.createdat = createdat;
}
public category getcategory() {
return category;
}
public void setcategory(category category) {
this.category = category;
}
public java.util.list<orderitem> getorderitems() {
return orderitems;
}
public void setorderitems(java.util.list<orderitem> orderitems) {
this.orderitems = orderitems;
}
@override
public string tostring() {
return "product{" +
"productid=" + productid +
", productname='" + productname + '\'' +
", description='" + description + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
", stockquantity=" + stockquantity +
", createdat=" + createdat +
", category=" + (category != null ? category.getcategoryname() : "null") +
'}';
}
}order.java
package com.example.ecommerce.entity;
import javax.persistence.*;
import java.math.bigdecimal;
import java.time.localdatetime;
import java.util.list;
@entity
@table(name = "orders")
public class order {
@id
@generatedvalue(strategy = generationtype.identity)
@column(name = "order_id")
private long orderid; // 主键,自增
@column(name = "order_date", nullable = false)
private localdatetime orderdate; // 订单日期
@column(name = "total_amount", nullable = false, precision = 10, scale = 2)
private bigdecimal totalamount; // 订单总金额
@column(name = "status", nullable = false, columndefinition = "enum('pending', 'processing', 'shipped', 'delivered', 'cancelled')")
private string status; // 订单状态
// 与 user 的多对一关系 (一个订单属于一个用户)
@manytoone(fetch = fetchtype.lazy)
@joincolumn(name = "user_id", nullable = false) // 外键,引用 user.user_id
private user user;
// 与 orderitem 的一对多关系 (一个订单包含多个订单项)
@onetomany(mappedby = "order", cascade = cascadetype.all, fetch = fetchtype.lazy)
private list<orderitem> orderitems;
// 构造函数
public order() {}
public order(user user, bigdecimal totalamount, string status) {
this.user = user;
this.totalamount = totalamount;
this.status = status;
this.orderdate = localdatetime.now(); // 自动设置订单日期
}
// getter 和 setter 方法
public long getorderid() {
return orderid;
}
public void setorderid(long orderid) {
this.orderid = orderid;
}
public localdatetime getorderdate() {
return orderdate;
}
public void setorderdate(localdatetime orderdate) {
this.orderdate = orderdate;
}
public bigdecimal gettotalamount() {
return totalamount;
}
public void settotalamount(bigdecimal totalamount) {
this.totalamount = totalamount;
}
public string getstatus() {
return status;
}
public void setstatus(string status) {
this.status = status;
}
public user getuser() {
return user;
}
public void setuser(user user) {
this.user = user;
}
public list<orderitem> getorderitems() {
return orderitems;
}
public void setorderitems(list<orderitem> orderitems) {
this.orderitems = orderitems;
}
@override
public string tostring() {
return "order{" +
"orderid=" + orderid +
", orderdate=" + orderdate +
", totalamount=" + totalamount +
", status='" + status + '\'' +
", user=" + (user != null ? user.getusername() : "null") +
'}';
}
}orderitem.java
package com.example.ecommerce.entity;
import javax.persistence.*;
import java.math.bigdecimal;
@entity
@table(name = "order_items")
public class orderitem {
@id
@generatedvalue(strategy = generationtype.identity)
@column(name = "order_item_id")
private long orderitemid; // 主键,自增
@column(name = "quantity", nullable = false, defaultvalue = "1")
private integer quantity; // 购买数量
@column(name = "unit_price", nullable = false, precision = 10, scale = 2)
private bigdecimal unitprice; // 单价
// 与 order 的多对一关系 (一个订单项属于一个订单)
@manytoone(fetch = fetchtype.lazy)
@joincolumn(name = "order_id", nullable = false) // 外键,引用 order.order_id
private order order;
// 与 product 的多对一关系 (一个订单项包含一个商品)
@manytoone(fetch = fetchtype.lazy)
@joincolumn(name = "product_id", nullable = false) // 外键,引用 product.product_id
private product product;
// 构造函数
public orderitem() {}
public orderitem(order order, product product, integer quantity, bigdecimal unitprice) {
this.order = order;
this.product = product;
this.quantity = quantity;
this.unitprice = unitprice;
}
// getter 和 setter 方法
public long getorderitemid() {
return orderitemid;
}
public void setorderitemid(long orderitemid) {
this.orderitemid = orderitemid;
}
public integer getquantity() {
return quantity;
}
public void setquantity(integer quantity) {
this.quantity = quantity;
}
public bigdecimal getunitprice() {
return unitprice;
}
public void setunitprice(bigdecimal unitprice) {
this.unitprice = unitprice;
}
public order getorder() {
return order;
}
public void setorder(order order) {
this.order = order;
}
public product getproduct() {
return product;
}
public void setproduct(product product) {
this.product = product;
}
@override
public string tostring() {
return "orderitem{" +
"orderitemid=" + orderitemid +
", quantity=" + quantity +
", unitprice=" + unitprice +
", order=" + (order != null ? order.getorderid() : "null") +
", product=" + (product != null ? product.getproductname() : "null") +
'}';
}
}6.5 repository 接口
userrepository.java
package com.example.ecommerce.repository;
import com.example.ecommerce.entity.user;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.jparepository;
import org.springframework.stereotype.repository;
import java.util.optional;
@repository
public interface userrepository extends jparepository<user, long> {
optional<user> findbyusername(string username);
optional<user> findbyemail(string email);
}categoryrepository.java
package com.example.ecommerce.repository;
import com.example.ecommerce.entity.category;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.jparepository;
import org.springframework.stereotype.repository;
import java.util.optional;
@repository
public interface categoryrepository extends jparepository<category, long> {
optional<category> findbycategoryname(string categoryname);
}productrepository.java
package com.example.ecommerce.repository;
import com.example.ecommerce.entity.product;
import com.example.ecommerce.entity.category;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.jparepository;
import org.springframework.stereotype.repository;
import java.util.list;
@repository
public interface productrepository extends jparepository<product, long> {
list<product> findbycategory(category category);
}orderrepository.java
package com.example.ecommerce.repository;
import com.example.ecommerce.entity.order;
import com.example.ecommerce.entity.user;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.jparepository;
import org.springframework.stereotype.repository;
import java.util.list;
@repository
public interface orderrepository extends jparepository<order, long> {
list<order> findbyuser(user user);
}orderitemrepository.java
package com.example.ecommerce.repository;
import com.example.ecommerce.entity.orderitem;
import com.example.ecommerce.entity.order;
import com.example.ecommerce.entity.product;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.jparepository;
import org.springframework.stereotype.repository;
import java.util.list;
@repository
public interface orderitemrepository extends jparepository<orderitem, long> {
list<orderitem> findbyorder(order order);
list<orderitem> findbyproduct(product product);
}6.6 service 层 (部分示例)
orderservice.java
package com.example.ecommerce.service;
import com.example.ecommerce.entity.*;
import com.example.ecommerce.repository.orderitemrepository;
import com.example.ecommerce.repository.orderrepository;
import com.example.ecommerce.repository.productrepository;
import com.example.ecommerce.repository.userrepository;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.transactional;
import java.math.bigdecimal;
import java.util.arraylist;
import java.util.list;
@service
@transactional // 确保事务管理
public class orderservice {
@autowired
private orderrepository orderrepository;
@autowired
private userrepository userrepository;
@autowired
private productrepository productrepository;
@autowired
private orderitemrepository orderitemrepository;
// 创建订单的示例方法
public order createorder(long userid, list<long> productidsandquantities) {
// 1. 获取用户
user user = userrepository.findbyid(userid)
.orelsethrow(() -> new runtimeexception("user not found with id: " + userid));
// 2. 创建订单对象
order order = new order(user, bigdecimal.zero, "pending");
order = orderrepository.save(order); // 保存订单以获取自动生成的 orderid
// 3. 计算总价并创建订单项
bigdecimal totalamount = bigdecimal.zero;
list<orderitem> orderitems = new arraylist<>();
for (long[] item : productidsandquantities) {
long productid = item[0];
integer quantity = item[1].intvalue();
product product = productrepository.findbyid(productid)
.orelsethrow(() -> new runtimeexception("product not found with id: " + productid));
if (product.getstockquantity() < quantity) {
throw new runtimeexception("insufficient stock for product: " + product.getproductname());
}
bigdecimal itemtotal = product.getprice().multiply(bigdecimal.valueof(quantity));
totalamount = totalamount.add(itemtotal);
orderitem orderitem = new orderitem(order, product, quantity, product.getprice());
orderitems.add(orderitem);
}
// 4. 保存订单项
orderitemrepository.saveall(orderitems);
// 5. 更新订单总价
order.settotalamount(totalamount);
order = orderrepository.save(order);
// 6. (可选) 更新商品库存
// 这里可以添加逻辑来减少商品库存
// 为简单起见,这里省略
return order;
}
// 获取用户的所有订单
public list<order> getordersbyuser(long userid) {
user user = userrepository.findbyid(userid)
.orelsethrow(() -> new runtimeexception("user not found with id: " + userid));
return orderrepository.findbyuser(user);
}
// 获取订单详情(包括订单项)
public order getorderdetails(long orderid) {
return orderrepository.findbyid(orderid)
.orelsethrow(() -> new runtimeexception("order not found with id: " + orderid));
}
}6.7 controller 层 (部分示例)
ordercontroller.java
package com.example.ecommerce.controller;
import com.example.ecommerce.entity.order;
import com.example.ecommerce.service.orderservice;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.autowired;
import org.springframework.http.responseentity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import java.math.bigdecimal;
import java.util.list;
@restcontroller
@requestmapping("/api/orders")
public class ordercontroller {
@autowired
private orderservice orderservice;
// 创建订单
@postmapping("/create")
public responseentity<order> createorder(
@requestparam long userid,
@requestbody list<long[]> productidsandquantities) { // 使用 long[] 数组传递 [productid, quantity]
try {
// 注意:这里简化了参数传递。在实际应用中,通常会使用 dto。
// 例如,定义一个 orderrequestdto 包含 userid 和 list<orderitemrequestdto>
// 这里直接使用 long[] 数组模拟 [productid, quantity] 对
list<long[]> items = new java.util.arraylist<>();
for (long[] item : productidsandquantities) {
items.add(new long[]{item[0], item[1]}); // 转换为 long[]
}
order order = orderservice.createorder(userid, items);
return responseentity.ok(order);
} catch (exception e) {
return responseentity.badrequest().build(); // 或者返回具体错误信息
}
}
// 获取用户的所有订单
@getmapping("/user/{userid}")
public responseentity<list<order>> getordersbyuser(@pathvariable long userid) {
list<order> orders = orderservice.getordersbyuser(userid);
return responseentity.ok(orders);
}
// 获取订单详情
@getmapping("/{orderid}")
public responseentity<order> getorderdetails(@pathvariable long orderid) {
order order = orderservice.getorderdetails(orderid);
return responseentity.ok(order);
}
}6.8 启动类与主程序
ecommerceapplication.java
package com.example.ecommerce;
import org.springframework.boot.springapplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.springbootapplication;
@springbootapplication
public class ecommerceapplication {
public static void main(string[] args) {
springapplication.run(ecommerceapplication.class, args);
}
}6.9 运行与测试
- 配置数据库: 确保你的 mysql 数据库已运行,并且在
application.properties中正确配置了数据库连接信息。 - 运行项目: 使用 maven (
mvn spring-boot:run) 或 ide 启动 spring boot 应用。 - 测试 api:
- 创建用户:
curl -x post http://localhost:8080/api/users \ -h "content-type: application/json" \ -d '{"username":"alice","email":"alice@example.com","passwordhash":"hashed_password_1"}' - 创建类别:
curl -x post http://localhost:8080/api/categories \ -h "content-type: application/json" \ -d '{"categoryname":"electronics","description":"electronic devices and gadgets"}' - 创建商品:
curl -x post http://localhost:8080/api/products \ -h "content-type: application/json" \ -d '{"productname":"smartphone","description":"latest model smartphone","price":699.99,"stockquantity":50,"category":{"categoryid":1}}' - 创建订单:
curl -x post http://localhost:8080/api/orders/create?userid=1 \ -h "content-type: application/json" \ -d '[ [1, 1] ]' # [productid, quantity] - 获取订单详情:
curl -x get http://localhost:8080/api/orders/1
- 创建用户:
通过这种方式,jpa 会自动处理主键的自动生成(@generatedvalue(strategy = generationtype.identity)),以及外键的关联(@manytoone, @onetomany 注解)。java 对象之间的关联关系映射到了数据库中的主键和外键约束上,实现了 orm(对象关系映射)。
七、主键与外键的性能影响
7.1 索引与查询性能
- 主键索引: 每个表的主键都会自动创建一个唯一索引(primary key index)。这个索引是聚簇索引(clustered index)在 innodb 存储引擎中,它决定了数据在磁盘上的物理存储顺序。查询主键的性能非常高,因为它直接定位到数据页。
- 外键索引: 外键列通常也会被创建索引(除非显式指定不创建)。这有助于加速 join 查询和外键约束检查。但请注意,外键索引会增加插入和更新操作的开销。
7.2 插入性能
- 主键: 插入新记录时,主键值需要满足唯一性约束。对于自增主键,这个过程非常高效。
- 外键: 插入记录时,数据库需要检查外键约束。如果外键引用的表中有大量的数据,这个检查可能会花费一些时间。此外,如果外键列上有索引,插入操作还需要维护索引。
7.3 更新与删除性能
- 主键: 更新主键(如果允许)通常代价很高,因为它需要重新组织数据以适应新的主键值。因此,一般不建议修改主键。
- 外键: 删除父表中的记录时,如果设置了级联删除(
on delete cascade),那么相关的子表记录也会被删除。这可能会影响性能,特别是当子表记录很多时。同样,更新外键值也需要检查约束并可能更新索引。
7.4 内存与缓存
- 索引内存: 主键和外键索引都会占用内存。在内存充足的环境中,这通常不是问题,但需要考虑索引对内存的消耗。
- 缓存效率: 由于主键索引是聚簇索引,它在缓存中通常表现更好。外键索引也可能提升查询缓存的效果。
八、主键与外键的高级话题
8.1 外键约束的管理
- 启用/禁用约束: 在某些情况下,可能需要临时禁用外键约束以进行批量操作。mysql 提供了
set foreign_key_checks语句来控制。set foreign_key_checks = 0; -- 禁用外键检查 -- 执行批量操作 set foreign_key_checks = 1; -- 启用外键检查
- 检查约束: 可以使用
show create table table_name;查看表的结构,包括主键和外键约束的定义。
8.2 复合主键与复合外键
- 复合主键: 如前面示例所示,由多个列组成的主键。
- 复合外键: 在某些情况下,外键也可能由多个列组成,以确保引用的唯一性。
8.3 外键与事务
- 事务一致性: 外键约束在事务中工作良好,确保了事务内的数据一致性。如果在事务中违反了外键约束,整个事务将回滚。
- 死锁: 在并发环境中,不当的外键操作可能导致死锁。需要合理设计索引和事务隔离级别。
8.4 无主键表 (myisam)
- myisam 存储引擎: 在 myisam 存储引擎中,表可以没有主键。在这种情况下,表中的每一行通过行号(row number)来标识。然而,myisam 已经被 innodb 取代,不推荐在新项目中使用。
8.5 uuid 作为主键
- 优点: uuid 是全球唯一的,非常适合分布式系统,避免了主键冲突的问题。
- 缺点: uuid 是字符串类型,比整数类型占用更多空间,且可能导致索引碎片,影响性能。如果需要使用 uuid,通常会使用
char(36)或binary(16)类型。
九、常见陷阱与注意事项
9.1 主键陷阱
- 使用业务字段作为主键: 如果业务字段(如用户名、邮箱)在未来可能会变更,将其用作主键会导致严重问题。
- 复合主键设计不当: 如果复合主键中的列顺序不合理,或者包含经常变动的列,可能会影响查询性能和维护性。
- 不使用自增主键: 虽然 uuid 等代理键是好的选择,但在性能要求极高的场景下,自增主键仍然是首选。
9.2 外键陷阱
- 忘记创建外键索引: 外键列如果没有索引,会导致查询性能急剧下降。虽然外键约束会自动创建索引,但有时可能需要手动优化。
- 级联操作滥用: 过度使用
on delete cascade可能导致意外的数据删除。应谨慎使用,确保业务逻辑清晰。 - 循环外键: 设计时应避免表之间的循环引用,这会使数据库结构复杂化,难以维护。
- 外键与存储引擎: 外键约束在 myisam 存储引擎中是不支持的,只能在 innodb 中使用。确保使用正确的存储引擎。
9.3 数据完整性与业务逻辑
- 外键不是万能的: 外键约束可以保证数据库层面的引用完整性,但不能替代业务逻辑验证。例如,一个订单状态的变更需要符合业务规则,这需要在应用层实现。
- 空值处理: 外键列可以为 null(如果允许),但需要明确其含义。通常,null 表示“没有关联”或“未指定”。
- 数据一致性: 在应用层处理数据时,务必确保数据的一致性。例如,在删除用户时,确保所有相关的订单也被正确处理。
十、总结与展望
主键与外键是关系型数据库设计的核心支柱。它们不仅确保了数据的唯一性和完整性,还为我们提供了强大的数据关联能力。通过本文的讲解和示例,你应该对主键和外键有了深刻的理解。
- 主键: 是表的唯一标识符,保证了行的唯一性。选择合适的主键类型(自增、uuid 等)对性能和扩展性至关重要。
- 外键: 是表间关联的桥梁,维护了数据的引用完整性。合理设计外键关系,可以简化复杂的查询和数据操作。
- 设计原则: 在设计数据库时,遵循明确的主键和外键设计原则,有助于构建稳定、高效的系统。
- 实践应用: 通过 spring boot 和 jpa 的实践,我们看到了如何在 java 应用中优雅地处理主键和外键关系。
随着数据库技术的发展,新的存储引擎和优化策略不断涌现。但主键和外键的基本原理和设计思想依然不变。掌握这些知识,不仅能帮助你构建更可靠的数据库应用,也为学习更高级的数据库技术和架构打下了坚实的基础。
记住,好的数据库设计是一个持续的过程。随着业务的发展和需求的变化,定期回顾和优化你的数据库结构是非常必要的。希望这篇文章能成为你数据库设计之旅中的一个重要里程碑!
附录:相关资源链接
- mysql 8.0 官方文档 - primary keys
- mysql 8.0 官方文档 - foreign keys
- mysql 8.0 官方文档 - creating tables
- spring boot 官方文档 - using jpa with spring boot
- hibernate 官方文档 - mapping basic types
- w3schools - sql primary key
- w3schools - sql foreign key
图表:主键与外键关系图
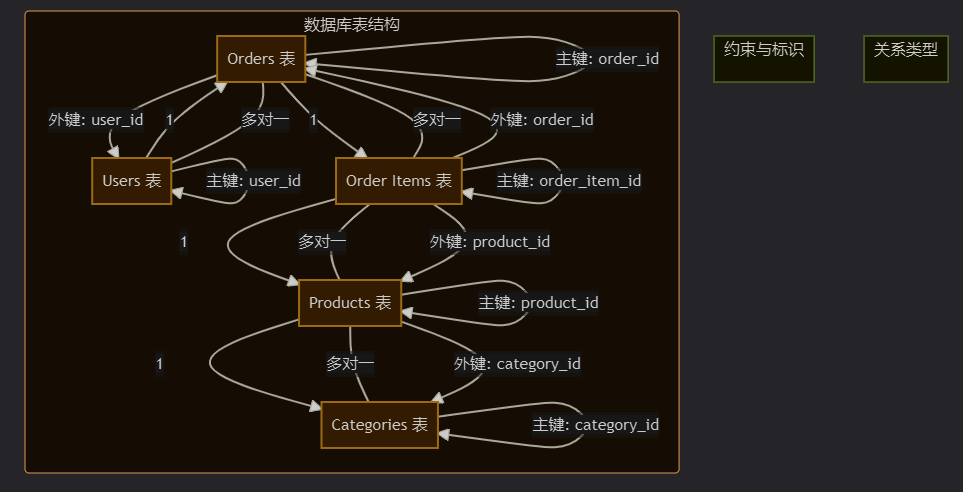
希望这篇全面的指南能帮助你彻底掌握主键与外键的概念、设计原则和实战应用。记住,实践是最好的老师,多动手练习,你就能在数据库设计的道路上越走越远!
到此这篇关于mysql - 一文搞懂主键与外键:设计原则 + 实战案例的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关mysql主键与外键内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!





发表评论