rpc通信模式
概述
在rabbitmq中,rpc模式通过消息队列实现远程调用功能。客户端(生产者)发送消息到消费队列,服务端(消费者)进行消息消费并执行相应的程序,然后将结果发送到回调队列供客户端使用。这是一种双向的生产消费模式,其中客户端既是生产者又是消费者,服务端则专注于处理消息并生成响应。
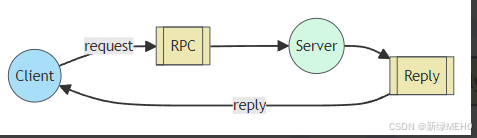
在rpc通信的过程中, 没有⽣产者和消费者, ⽐较像咱们rpc远程调⽤, ⼤概就是通过两个队列实现了⼀个可回调的过程.
工作流程
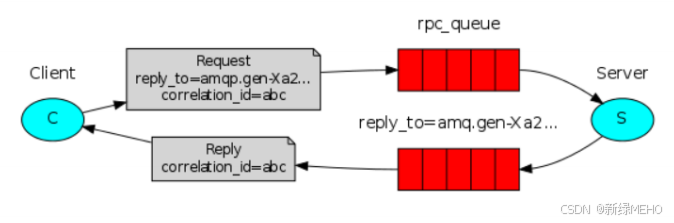
1.客户端发送请求:
客户端连接到rabbitmq服务器。
客户端声明一个用于发送rpc请求的队列(通常是固定的,如rpc_queue)。
客户端创建一个临时的回调队列,并在发送请求时,将回调队列的名称作为消息属性(reply_to)发送给交换机。
客户端为每个请求生成一个唯一的correlation_id,并将其作为消息属性发送,以便在接收响应时能够匹配请求与响应。
2.交换机路由请求:
交换机接收到rpc请求后,根据路由键将请求路由到服务端监听的队列。
3.服务端处理请求:
服务端(消费者)从队列中接收请求。
服务端处理请求,并生成响应。
服务端将响应发送到客户端指定的回调队列,并在消息属性中设置相同的correlation_id。
4.客户端接收响应:
客户端监听其回调队列以接收响应。
当接收到响应时,客户端检查correlation_id以确定响应是否与之前的请求匹配。
如果匹配,客户端处理响应;如果不匹配,客户端可能丢弃该响应。
特点
1.解耦:客户端和服务端之间不需要直接通信,降低了系统间的耦合度。
2.灵活性:支持多种语言和平台之间的远程调用。
3.可扩展性:通过增加服务端(消费者)的数量,可以轻松扩展rpc服务。
4.性能开销:由于涉及到网络传输和消息队列的处理,rpc调用的性能通常低于本地调用。
5.复杂性:需要处理消息队列的可靠性、持久性、消息确认等复杂问题。
6.安全性:远程调用可能面临更多的安全风险,如消息篡改、中间人攻击等。
应用场景
rabbitmq的rpc通信模式适用于需要远程调用服务的场景,如分布式系统中的服务调用、微服务架构中的服务通信等。通过rabbitmq的消息队列机制,可以实现跨系统、跨语言的远程调用,提高系统的灵活性和可扩展性。
代码案例
引入依赖
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.rabbitmq/amqp-client -->
<dependency>
<groupid>com.rabbitmq</groupid>
<artifactid>amqp-client</artifactid>
<version>5.21.0</version>
</dependency>常量类
public class constants {
public static final string host = "47.98.109.138";
public static final int port = 5672;
public static final string user_name = "study";
public static final string password = "study";
public static final string virtual_host = "aaa";
//rpc 模式
public static final string rpc_request_queue = "rpc.request.queue";
public static final string rpc_response_queue = "rpc.response.queue";
}编写客户端代码
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import rabbitmq.constant.constants;
import java.io.ioexception;
import java.util.uuid;
import java.util.concurrent.arrayblockingqueue;
import java.util.concurrent.blockingqueue;
import java.util.concurrent.timeoutexception;
/**
* rpc 客户端
* 1. 发送请求
* 2. 接收响应
*/
public class rpcclient {
public static void main(string[] args) throws ioexception, timeoutexception, interruptedexception {
//1. 建立连接
connectionfactory connectionfactory = new connectionfactory();
connectionfactory.sethost(constants.host);
connectionfactory.setport(constants.port); //需要提前开放端口号
connectionfactory.setusername(constants.user_name);//账号
connectionfactory.setpassword(constants.password); //密码
connectionfactory.setvirtualhost(constants.virtual_host); //虚拟主机
connection connection = connectionfactory.newconnection();
//2. 开启信道
channel channel = connection.createchannel();
channel.queuedeclare(constants.rpc_request_queue, true, false, false, null);
channel.queuedeclare(constants.rpc_response_queue, true, false, false, null);
//3. 发送请求
string msg = "hello rpc...";
//设置请求的唯一标识
string correlationid = uuid.randomuuid().tostring();
//设置请求的相关属性
amqp.basicproperties props = new amqp.basicproperties().builder()
.correlationid(correlationid)
.replyto(constants.rpc_response_queue)
.build();
channel.basicpublish("", constants.rpc_request_queue, props, msg.getbytes());
//4. 接收响应
//使用阻塞队列, 来存储响应信息
final blockingqueue<string> response = new arrayblockingqueue<>(1);
defaultconsumer consumer = new defaultconsumer(channel){
@override
public void handledelivery(string consumertag, envelope envelope, amqp.basicproperties properties, byte[] body) throws ioexception {
string respmsg = new string(body);
system.out.println("接收到回调消息: "+ respmsg);
if (correlationid.equals(properties.getcorrelationid())){
//如果correlationid校验一致
response.offer(respmsg);
}
}
};
channel.basicconsume(constants.rpc_response_queue, true, consumer);
string result = response.take();
system.out.println("[rpc client 响应结果]:"+ result);
}
}编写服务端代码
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import rabbitmq.constant.constants;
import java.io.ioexception;
import java.util.concurrent.timeoutexception;
/**
* rpc server
* 1. 接收请求
* 2. 发送响应
*/
public class rpcserver {
public static void main(string[] args) throws ioexception, timeoutexception {
//1. 建立连接
connectionfactory connectionfactory = new connectionfactory();
connectionfactory.sethost(constants.host);
connectionfactory.setport(constants.port); //需要提前开放端口号
connectionfactory.setusername(constants.user_name);//账号
connectionfactory.setpassword(constants.password); //密码
connectionfactory.setvirtualhost(constants.virtual_host); //虚拟主机
connection connection = connectionfactory.newconnection();
//2. 开启信道
channel channel = connection.createchannel();
//3. 接收请求
channel.basicqos(1);
defaultconsumer consumer = new defaultconsumer(channel){
@override
public void handledelivery(string consumertag, envelope envelope, amqp.basicproperties properties, byte[] body) throws ioexception {
string request = new string(body,"utf-8");
system.out.println("接收到请求:"+ request);
string response = "针对request:"+ request +", 响应成功";
amqp.basicproperties basicproperties = new amqp.basicproperties().builder()
.correlationid(properties.getcorrelationid())
.build();
channel.basicpublish("", constants.rpc_response_queue, basicproperties, response.getbytes());
channel.basicack(envelope.getdeliverytag(), false);
}
};
channel.basicconsume(constants.rpc_request_queue, false, consumer);
}
}运行程序(先运行客户端,再运行服务端)
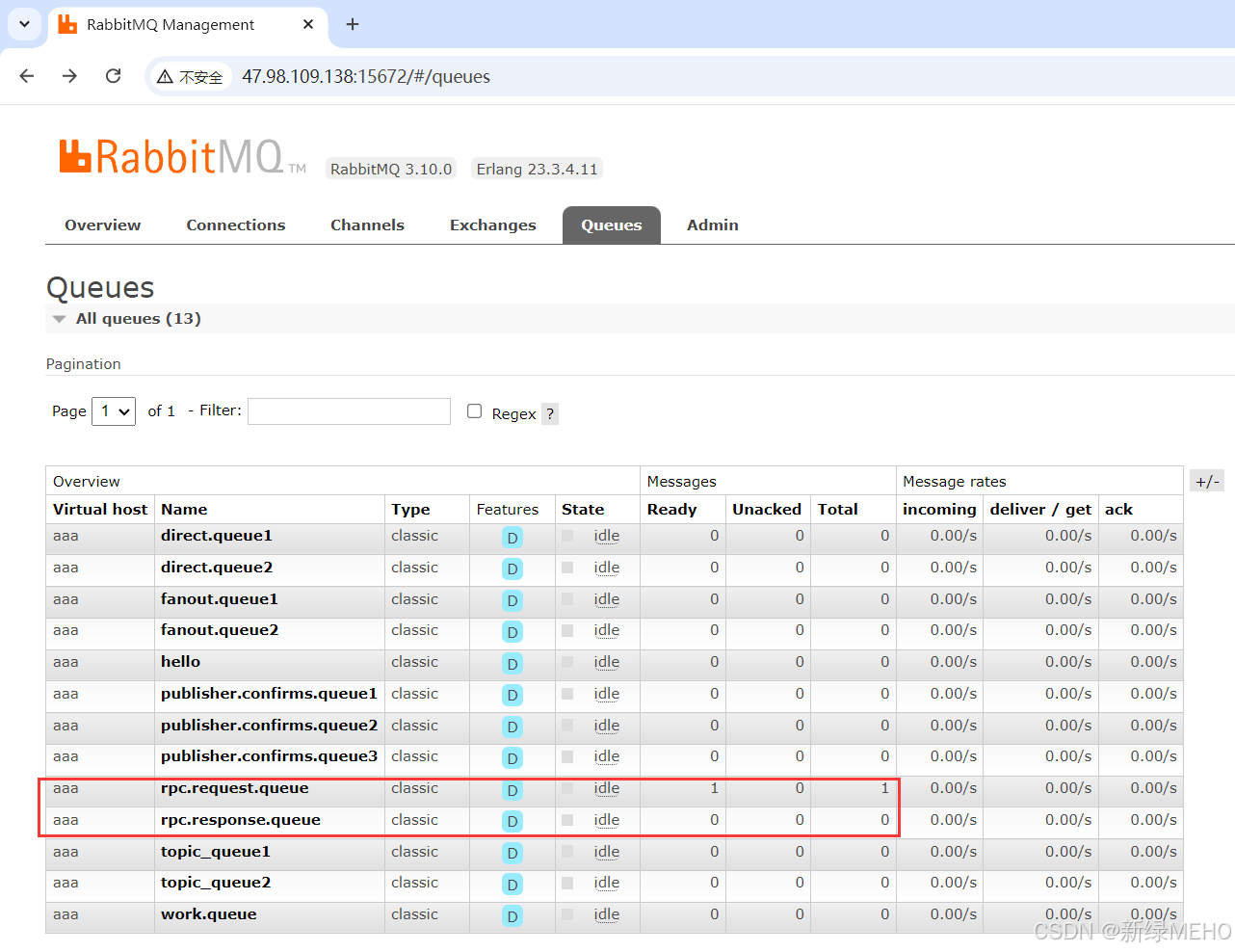
可以在管理界面看到其中一个队列中有1条消息
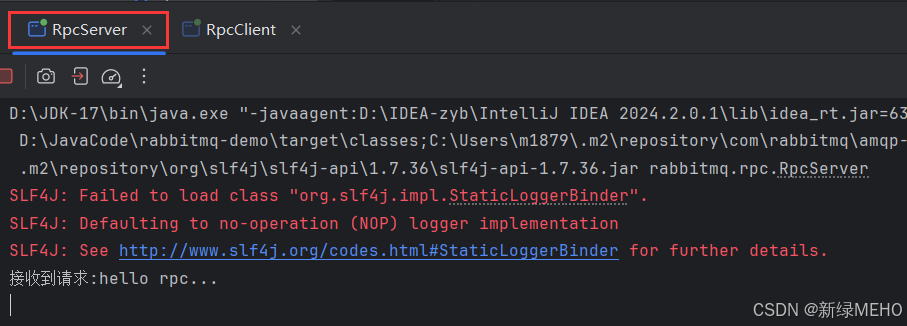
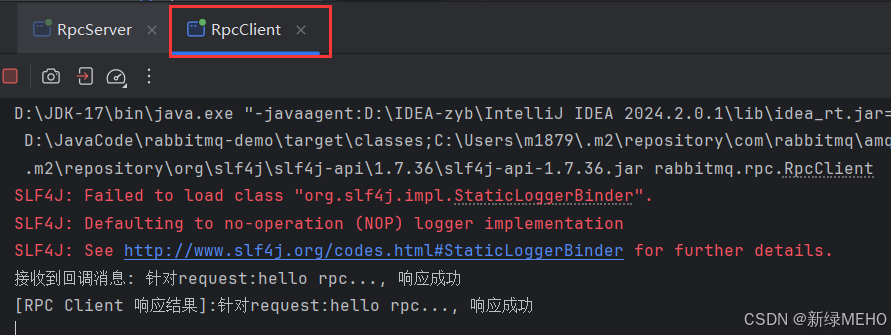
我们可以看到,服务端接收到了消息并给客户端发送了响应,与预期符合。
到此这篇关于rabbitmq工作模式之rpc通信模式的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关rabbitmq rpc通信模式内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!






发表评论