在 java 多线程编程中,线程池(threadpoolexecutor)是一个常用的工具,用于管理线程的生命周期并提升应用程序的性能。然而,在使用线程池时,异常处理可能会被忽略,从而导致潜在的程序问题甚至崩溃。如果任务出现了异常,会发生什么呢?该怎么处理呢?怎么获取到异常信息来解决异常?想要知道如何解决,就需要了解了解线程池提交任务的两个方法execute与submit
一.execute与submit
package demo1;
import java.util.concurrent.executionexception;
import java.util.concurrent.executorservice;
import java.util.concurrent.executors;
import java.util.concurrent.future;
public class test2 {
public static void main(string[] args) {
//只有一个线程的线程池
executorservice threadpool = executors.newfixedthreadpool(1);
threadpool.execute(()->{
system.out.println("execute: current thread is " + thread.currentthread().getname());
method_1();
});
future<?> submit = threadpool.submit(() -> {
system.out.println("execute: current thread is " + thread.currentthread().getname());
method_1();
});
future<?> submit2 = threadpool.submit(() -> {
system.out.println("execute: current thread is " + thread.currentthread().getname());
method_1();
});
}
public static string method_1(){
system.out.println("starting.....");
int i = 1/0;
system.out.println("ending.....");
return "ok";
}
}
这里我execute与submit 分别执行两个有异常的任务,同时打印了当前线程,以下是运行结果
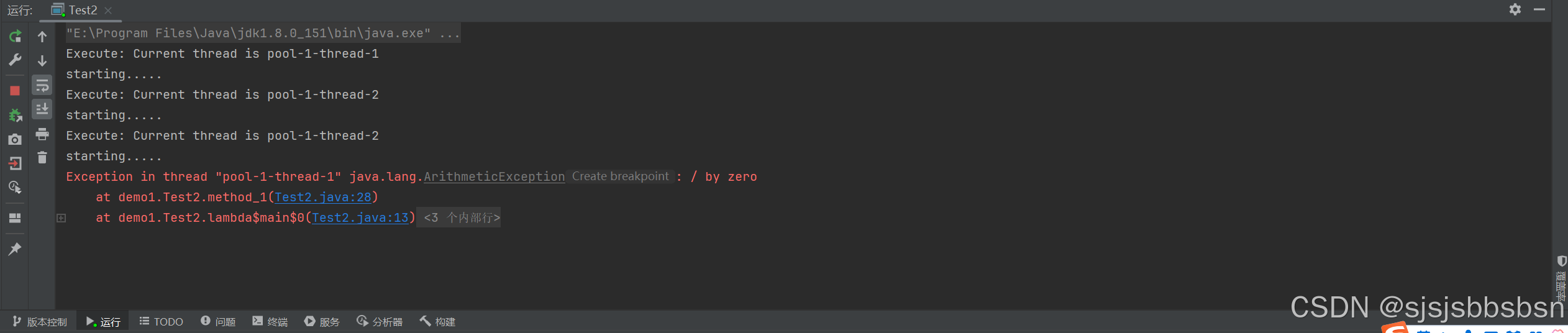
可见execute方法在遇到异常之后会抛出异常,并且线程池中的线程终止
submit方法遇到异常不会抛出异常
| 特性 | execute | submit |
|---|---|---|
| 方法定义 | void execute(runnable command) | future<?> submit(runnable task)future<t> submit(callable<t> task) |
| 返回值 | 无返回值,不关心任务的执行结果 | 返回 future 对象,可用于获取任务结果或状态 |
| 支持任务类型 | 仅支持 runnable | 支持 runnable 和 callable |
| 异常处理 | 任务抛出的异常不会被捕获,直接传播到线程池的工作线程 | 任务抛出的异常会被封装在 future 中,需通过 future.get() 获取 |
| 使用场景 | 适用于无需获取任务结果的场景 | 适用于需要获取任务执行结果或捕获异常的场景 |
| 示例 | threadpool.execute(() -> method_1()); | future<?> future = threadpool.submit(() -> method_1()); |
| 任务执行方式 | 直接提交给线程池执行 | 包装为 futuretask 后交由线程池执行 |
| 线程池依赖 | 线程池的 execute 方法是基础实现 | submit 方法内部调用 execute 执行任务 |
| 异常传播位置 | 通过默认的 uncaughtexceptionhandler 处理 | 通过 future.get() 抛出异常 |
二.如何处理异常
2.1使用try-catch
这里不多赘述,这是最简单明了的方法,直接用try-catch捕获就行
2.2 使用 threadpoolexecutor 的 afterexecute 方法
threadpoolexecutor 提供了一个 afterexecute 钩子方法,可以在任务完成后检查是否有异常。
通过覆盖此方法,可以捕获所有任务中未被捕获的异常。
package demo1;
import java.io.ioexception;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class test3 {
public static void main(string[] args) {
executorservice threadpool = new /**
* @author 方
*/
threadpoolexecutor(1, 1, 60, timeunit.seconds, new linkedblockingqueue<>()) {
@override
protected void afterexecute(runnable r, throwable t) {
super.afterexecute(r, t);
if (t != null) {
system.out.println("task threw an exception: " + t.getmessage());
}
// 针对 future 的异常处理
if (r instanceof future<?>) {
try {
((future<?>) r).get(); // 调用 get 检查任务是否抛出异常
} catch (exception e) {
system.out.println("exception in future: " + e.getcause());
}
}
}
};
threadpool.execute(() -> {
system.out.println("execute: current thread is " + thread.currentthread().getname());
throw new runtimeexception("test1 exception in execute");
});
threadpool.submit(() -> {
system.out.println("execute: current thread is " + thread.currentthread().getname());
throw new runtimeexception("test2 exception in submit");
});
threadpool.submit(() -> {
system.out.println("execute: current thread is " + thread.currentthread().getname());
throw new runtimeexception("test3 exception in submit");
});
threadpool.shutdown();
}
}
运行结果:
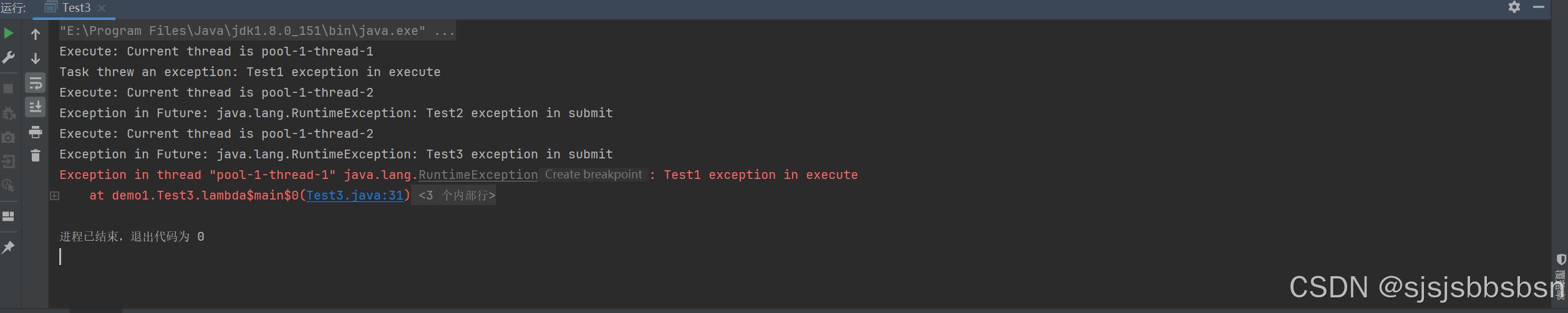
可见execute方法在遇到异常之后会抛出异常,并且线程池中的线程终止,submit没有抛出异常
但是他们两个**都记录了异常信息**
2.3设置 uncaughtexceptionhandler
package demo1;
import java.io.ioexception;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class test3 {
public static void main(string[] args) {
//1.实现一个自己的线程池工厂
threadfactory factory = (runnable r) -> {
//创建一个线程
thread t = new thread(r);
//给创建的线程设置uncaughtexceptionhandler对象 里面实现异常的默认逻辑
t.setdefaultuncaughtexceptionhandler((thread thread1, throwable e) -> {
//出现异常
if (e != null){
system.out.println(thread.currentthread().getname()+e.getmessage());
e.printstacktrace();
}
});
return t;
};
//2.创建一个自己定义的线程池,使用自己定义的线程工厂
executorservice threadpool = new threadpoolexecutor(
1,
1,
0,
timeunit.milliseconds,
new linkedblockingqueue(10),
factory);
threadpool.execute(() -> {
system.out.println("execute: current thread is " + thread.currentthread().getname());
throw new runtimeexception("test1 exception in execute");
});
threadpool.submit(() -> {
system.out.println("execute: current thread is " + thread.currentthread().getname());
throw new runtimeexception("test2 exception in submit");
});
threadpool.submit(() -> {
system.out.println("execute: current thread is " + thread.currentthread().getname());
throw new runtimeexception("test3 exception in submit");
});
threadpool.shutdown();
}
}
运行结果:
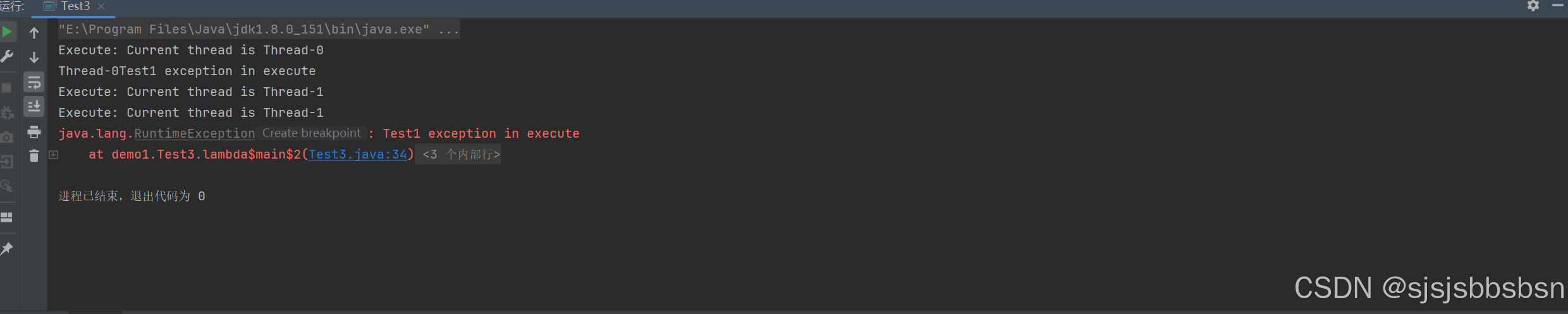
可见execute方法在遇到异常之后会抛出异常,并且线程池中的线程终止,submit没有抛出异常
三.springboot中的线程池异常处理
@bean(mallchat_executor)
@primary
public threadpooltaskexecutor mallchatexecutor() {
//spring的线程池
threadpooltaskexecutor executor = new threadpooltaskexecutor();
//线程池优雅停机的关键
executor.setwaitfortaskstocompleteonshutdown(true);
executor.setcorepoolsize(10);
executor.setmaxpoolsize(10);
executor.setqueuecapacity(200);
executor.setthreadnameprefix("mallchat-executor-");
//拒绝策略->满了调用线程执行,认为重要任务
executor.setrejectedexecutionhandler(new threadpoolexecutor.callerrunspolicy());
//自己就是一个线程工程
executor.setthreadfactory(new mythreadfactory(executor));
executor.initialize();
return executor;
}
package org.fth.mallchat.common.common.thread;
import lombok.allargsconstructor;
import java.util.concurrent.threadfactory;
/**
* @author 方
*/
@allargsconstructor
public class mythreadfactory implements threadfactory {
private static final myuncaughtexceptionhandler myuncaughtexceptionhandler = new myuncaughtexceptionhandler();
private threadfactory original;
@override
public thread newthread(runnable r) {
//执行spring线程自己的创建逻辑
thread thread = original.newthread(r);
//我们自己额外的逻辑
thread.setuncaughtexceptionhandler(myuncaughtexceptionhandler);
return thread;
}
}
package org.fth.mallchat.common.common.thread;
import org.slf4j.logger;
import org.slf4j.loggerfactory;
/**
* @author 方
*/
public class myuncaughtexceptionhandler implements thread.uncaughtexceptionhandler {
private static final logger log = loggerfactory.getlogger(myuncaughtexceptionhandler.class);
@override
public void uncaughtexception(thread t, throwable e) {
log.error("exception in thread",e);
}
}
1. 线程池配置 (threadpooltaskexecutor)
在 spring boot 中,threadpooltaskexecutor 用于管理线程池的执行,允许我们设置线程池的核心大小、最大线程数、队列容量等。通过这种配置,我们可以控制线程池的资源使用情况,确保任务的执行效率与可靠性。在你的代码中,线程池的配置包括:
corepoolsize和maxpoolsize:指定线程池的最小和最大线程数。这里设置为 10,意味着线程池最多同时运行 10 个线程。queuecapacity:指定任务队列的容量。任务超过这个容量会被拒绝执行,进入拒绝策略处理。setrejectedexecutionhandler:设置任务队列满时的拒绝策略。在这个配置中,使用callerrunspolicy,意味着如果队列已满,任务会直接在调用线程中执行,而不是抛出异常。setwaitfortaskstocompleteonshutdown(true):设置线程池在关闭时等待所有任务完成再退出,确保优雅停机。
2. 自定义线程工厂 (threadfactory)
通过 threadfactory,你可以自定义线程的创建过程。在你的代码中,你为每个线程设置了一个异常处理器。这意味着,如果线程内发生未捕获的异常,这些异常会被专门的异常处理器捕获并记录,而不是导致线程崩溃或丢失异常信息。
- 自定义异常处理器:
thread.setdefaultuncaughtexceptionhandler会设置线程的默认异常处理器,确保在任何线程中出现未捕获的异常时,异常都能被记录。这个处理器的作用是将异常信息输出到日志中,避免错误被忽略或导致线程不可控。
3. 线程销毁与异常
线程池的行为与异常处理相关:
- 如果线程发生未捕获的异常,
uncaughtexceptionhandler会记录异常,但不会销毁线程。线程池中的其他线程仍然会继续工作。 - 线程池会自动重用空闲线程。即使某个线程发生异常,线程池仍然会创建新的线程来执行其他任务,只要线程池的资源没有完全用尽。
因此,线程池不会因单个线程的异常而销毁整个线程池,它会继续运行,并且通过异常处理机制记录异常,确保系统的稳定性。
现未捕获的异常时,异常都能被记录。这个处理器的作用是将异常信息输出到日志中,避免错误被忽略或导致线程不可控。
不过sumbit还是必须要get才能拿到异常信息,我们还是可以通过重写threadpoolexecutor 的 afterexecute 方法 不过这样的话就有点麻烦
到此这篇关于springboot线程池异常处理的实现示例的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关springboot线程池异常处理内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!





发表评论