背景
在现代 web 应用开发中,数据库性能是影响系统响应时间和用户体验的关键因素之一。随着业务需求的不断增长,单表查询和联表查询的效率问题日益凸显。特别是在 spring boot 项目中,结合 mysql 数据库进行复杂查询时,如何优化查询性能已成为开发者必须面对的重要问题。
在本实验中,我们使用了 spring boot 框架结合 mysql 数据库,进行了两种常见查询方式的性能对比:多线程查询 和 联表查询。通过对比这两种查询方式的响应时间,本文旨在探讨在实际业务场景中,选择哪种方式能带来更高的查询效率,尤其是在面对大数据量和复杂查询时的性能表现。
实验目的
本实验的主要目的是通过对比以下两种查询方式的性能,帮助开发者选择在不同业务场景下的查询方式:
- 联表查询(使用 sql 语句中的 left join 等连接操作)
- 多线程查询(通过 spring boot 异步处理,分批查询不同表的数据)
实验环境
开发框架:spring boot
数据库:mysql
数据库表结构:
test_a:主表,包含与其他表(test_b、test_c、test_d、test_e)的关联字段。test_b、test_c、test_d、test_e:附表,分别包含不同的数据字段。
这些表通过外键(逻辑)关联,
test_a表中的test_b_id、test_c_id、test_d_id和test_e_id字段指向各自的附表。数据量:约 100,000 条数据,分别在主表和附表中填充数据。
一.建表语句
主表a
create table `test_a` ( `id` int not null auto_increment, `name` varchar(255) not null, `description` varchar(255) default null, `test_b_id` int default null, `test_c_id` int default null, `test_d_id` int default null, `test_e_id` int default null, `created_at` timestamp null default current_timestamp, `updated_at` timestamp null default current_timestamp on update current_timestamp, primary key (`id`) ) engine=innodb auto_increment=6 default charset=utf8mb4 collate=utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci;
附表b,c,d,e
create table `test_b` ( `id` int not null auto_increment, `field_b1` varchar(255) default null, `field_b2` int default null, `created_at` timestamp null default current_timestamp, primary key (`id`) ) engine=innodb auto_increment=792843462 default charset=utf8mb4 collate=utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci; create table `test_c` ( `id` int not null auto_increment, `field_c1` varchar(255) default null, `field_c2` datetime default null, `created_at` timestamp null default current_timestamp, primary key (`id`) ) engine=innodb auto_increment=100096 default charset=utf8mb4 collate=utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci; create table `test_d` ( `id` int not null auto_increment, `field_d1` text, `field_d2` tinyint(1) default null, `created_at` timestamp null default current_timestamp, primary key (`id`) ) engine=innodb auto_increment=100300 default charset=utf8mb4 collate=utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci; create table `test_e` ( `id` int not null auto_increment, `field_e1` int default null, `field_e2` varchar(255) default null, `created_at` timestamp null default current_timestamp, primary key (`id`) ) engine=innodb auto_increment=100444 default charset=utf8mb4 collate=utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci;
二.填充数据
@springboottest
class demotestqueryspringbootapplicationtests {
@autowired
private testamapper testamapper;
@autowired
private testbmapper testbmapper;
@autowired
private testcmapper testcmapper;
@autowired
private testdmapper testdmapper;
@autowired
private testemapper testemapper;
@test
void contextloads() {
// 随机数生成器
random random = new random();
for (int i = 1; i <= 100000; i++) {
// 插入 test_b 数据
int testbid = inserttestb(random);
// 插入 test_c 数据
int testcid = inserttestc(random);
// 插入 test_d 数据
int testdid = inserttestd(random);
// 插入 test_e 数据
int testeid = insertteste(random);
// 插入 test_a 数据
inserttesta(testbid, testcid, testdid, testeid, random);
}
}
private int inserttestb(random random) {
testb testb = new testb();
testb.setfieldb1("b field " + random.nextint(1000));
testb.setfieldb2(random.nextint(1000));
testbmapper.insert(testb); // 插入数据
return testb.getid();
}
private int inserttestc(random random) {
testc testc = new testc();
testc.setfieldc1("c field " + random.nextint(1000));
testc.setfieldc2(new java.sql.timestamp(system.currenttimemillis()));
testcmapper.insert(testc); // 插入数据
return testc.getid();
}
private int inserttestd(random random) {
testd testd = new testd();
testd.setfieldd1("d field " + random.nextint(1000));
testd.setfieldd2(random.nextboolean());
testdmapper.insert(testd); // 插入数据
return testd.getid();
}
private int insertteste(random random) {
teste teste = new teste();
teste.setfielde1(random.nextint(1000));
teste.setfielde2("e field " + random.nextint(1000));
testemapper.insert(teste); // 插入数据
return teste.getid();
}
private void inserttesta(int testbid, int testcid, int testdid, int testeid, random random) {
testa testa = new testa();
testa.setname("test a name " + random.nextint(1000));
testa.setdescription("test a description " + random.nextint(1000));
testa.settestbid(testbid);
testa.settestcid(testcid);
testa.settestdid(testdid);
testa.settesteid(testeid);
testamapper.insert(testa); // 插入数据
}
}
三.配置线程池
3.1配置
/**
* 实现asyncconfigurer接口
* 并重写了 getasyncexecutor方法,
* 这个方法返回 myexecutor(),
* spring 默认会将 myexecutor 作为 @async 方法的线程池。
*/
@configuration
@enableasync
public class threadpoolconfig implements asyncconfigurer {
/**
* 项目共用线程池
*/
public static final string test_query = "testquery";
@override
public executor getasyncexecutor() {
return myexecutor();
}
@bean(test_query)
@primary
public threadpooltaskexecutor myexecutor() {
//spring的线程池
threadpooltaskexecutor executor = new threadpooltaskexecutor();
//线程池优雅停机的关键
executor.setwaitfortaskstocompleteonshutdown(true);
executor.setcorepoolsize(10);
executor.setmaxpoolsize(10);
executor.setqueuecapacity(200);
executor.setthreadnameprefix("my-executor-");
//拒绝策略->满了调用线程执行,认为重要任务
executor.setrejectedexecutionhandler(new threadpoolexecutor.callerrunspolicy());
//自己就是一个线程工程
executor.setthreadfactory(new mythreadfactory(executor));
executor.initialize();
return executor;
}
}
3.2异常处理
public class myuncaughtexceptionhandler implements thread.uncaughtexceptionhandler {
private static final logger log = loggerfactory.getlogger(myuncaughtexceptionhandler.class);
@override
public void uncaughtexception(thread t, throwable e) {
log.error("exception in thread",e);
}
}
3.3线程工厂
@allargsconstructor
public class mythreadfactory implements threadfactory {
private static final myuncaughtexceptionhandler myuncaughtexceptionhandler = new myuncaughtexceptionhandler();
private threadfactory original;
@override
public thread newthread(runnable r) {
//执行spring线程自己的创建逻辑
thread thread = original.newthread(r);
//我们自己额外的逻辑
thread.setuncaughtexceptionhandler(myuncaughtexceptionhandler);
return thread;
}
}
四.service查询方法
4.1left join连接查询
@override
public ipage<testall> gettestallpage_1(int current, int size) {
// 创建 page 对象,current 为当前页,size 为每页大小
page<testall> page = new page<>(current, size);
return testamapper.selectallwithpage(page);
}
对应的xml 的sql语句
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!doctype mapper public "-//mybatis.org//dtd mapper 3.0//en" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="org.fth.demotestqueryspringboot.com.test.mapper.testamapper">
<!-- 基本的 resultmap 映射 -->
<resultmap id="baseresultmap" type="org.fth.demotestqueryspringboot.com.test.entity.vo.testall">
<id column="test_a_id" jdbctype="integer" property="testaid" />
<result column="name" jdbctype="varchar" property="name" />
<result column="description" jdbctype="varchar" property="description" />
<result column="test_b_id" jdbctype="integer" property="testbid" />
<result column="test_c_id" jdbctype="integer" property="testcid" />
<result column="test_d_id" jdbctype="integer" property="testdid" />
<result column="test_e_id" jdbctype="integer" property="testeid" />
<result column="created_at" jdbctype="timestamp" property="createdat" />
<result column="updated_at" jdbctype="timestamp" property="updatedat" />
<!-- testb -->
<result column="field_b1" jdbctype="varchar" property="fieldb1" />
<result column="field_b2" jdbctype="integer" property="fieldb2" />
<result column="test_b_created_at" jdbctype="timestamp" property="testbcreatedat" />
<!-- testc -->
<result column="field_c1" jdbctype="varchar" property="fieldc1" />
<result column="field_c2" jdbctype="timestamp" property="fieldc2" />
<result column="test_c_created_at" jdbctype="timestamp" property="testccreatedat" />
<!-- testd -->
<result column="field_d1" jdbctype="varchar" property="fieldd1" />
<result column="field_d2" jdbctype="boolean" property="fieldd2" />
<result column="test_d_created_at" jdbctype="timestamp" property="testdcreatedat" />
<!-- teste -->
<result column="field_e1" jdbctype="integer" property="fielde1" />
<result column="field_e2" jdbctype="varchar" property="fielde2" />
<result column="test_e_created_at" jdbctype="timestamp" property="testecreatedat" />
</resultmap>
<!-- 分页查询 testa 和其他表的数据 -->
<select id="selectallwithpage" resultmap="baseresultmap">
select
a.id as test_a_id,
a.name,
a.description,
a.test_b_id,
a.test_c_id,
a.test_d_id,
a.test_e_id,
a.created_at,
a.updated_at,
-- testb
b.field_b1,
b.field_b2,
b.created_at as test_b_created_at,
-- testc
c.field_c1,
c.field_c2,
c.created_at as test_c_created_at,
-- testd
d.field_d1,
d.field_d2,
d.created_at as test_d_created_at,
-- teste
e.field_e1,
e.field_e2,
e.created_at as test_e_created_at
from test_a a
left join test_b b on a.test_b_id = b.id
left join test_c c on a.test_c_id = c.id
left join test_d d on a.test_d_id = d.id
left join test_e e on a.test_e_id = e.id
</select>
</mapper>
4.2多线程查询
@override
public ipage<testall> gettestallpage_2(int current, int size) {
ipage<testa> testapage = testamapper.selectpage(new page<>(current, size), null);
list<testa> testas = testapage.getrecords();
completablefuture<list<testb>> futurebs = selecttestbids(testas.stream().map(testa::gettestbid).collect(collectors.toset()));
completablefuture<list<testc>> futurecs = selecttestcids(testas.stream().map(testa::gettestcid).collect(collectors.toset()));
completablefuture<list<testd>> futureds = selecttestdids(testas.stream().map(testa::gettestdid).collect(collectors.toset()));
completablefuture<list<teste>> futurees = selecttesteids(testas.stream().map(testa::gettesteid).collect(collectors.toset()));
// 等待所有异步任务完成并收集结果
completablefuture<void> allfutures = completablefuture.allof(futurebs, futurecs, futureds, futurees);
try {
// 等待所有异步任务完成
allfutures.get();
} catch (interruptedexception | executionexception e) {
e.printstacktrace();
throw new runtimeexception("failed to fetch data", e);
}
// 获取异步查询的结果
list<testb> bs = futurebs.join();
list<testc> cs = futurecs.join();
list<testd> ds = futureds.join();
list<teste> es = futurees.join();
// 将结果映射到map以便快速查找
map<integer, testb> bmap = bs.stream().collect(collectors.tomap(testb::getid, b -> b));
map<integer, testc> cmap = cs.stream().collect(collectors.tomap(testc::getid, c -> c));
map<integer, testd> dmap = ds.stream().collect(collectors.tomap(testd::getid, d -> d));
map<integer, teste> emap = es.stream().collect(collectors.tomap(teste::getid, e -> e));
list<testall> testalllist = testas.stream().map(testa -> {
testall testall = new testall();
testall.settestaid(testa.getid());
testall.setname(testa.getname());
testall.setdescription(testa.getdescription());
testall.setcreatedat(testa.getcreatedat());
// 根据 testbid 填充 testb 的字段
if (testa.gettestbid() != null) {
testb testb = bmap.get(testa.gettestbid());
if (testb != null) {
testall.setfieldb1(testb.getfieldb1());
testall.setfieldb2(testb.getfieldb2());
testall.settestbcreatedat(testb.getcreatedat());
}
}
// 根据 testcid 填充 testc 的字段
if (testa.gettestcid() != null) {
testc testc = cmap.get(testa.gettestcid());
if (testc != null) {
testall.setfieldc1(testc.getfieldc1());
testall.setfieldc2(testc.getfieldc2());
testall.settestccreatedat(testc.getcreatedat());
}
}
// 根据 testdid 填充 testd 的字段
if (testa.gettestdid() != null) {
testd testd = dmap.get(testa.gettestdid());
if (testd != null) {
testall.setfieldd1(testd.getfieldd1());
testall.setfieldd2(testd.getfieldd2());
testall.settestdcreatedat(testd.getcreatedat());
}
}
// 根据 testeid 填充 teste 的字段
if (testa.gettesteid() != null) {
teste teste = emap.get(testa.gettesteid());
if (teste != null) {
testall.setfielde1(teste.getfielde1());
testall.setfielde2(teste.getfielde2());
testall.settestecreatedat(teste.getcreatedat());
}
}
return testall;
}).collect(collectors.tolist());
// 创建并返回新的分页对象
ipage<testall> page = new page<>(testapage.getcurrent(), testapage.getsize(), testapage.gettotal());
page.setrecords(testalllist);
return page;
}
@async
public completablefuture<list<testb>> selecttestbids(set<integer> bids) {
return completablefuture.supplyasync(() -> testbmapper.selectbatchids(bids));
}
@async
public completablefuture<list<testc>> selecttestcids(set<integer> cids) {
return completablefuture.supplyasync(() -> testcmapper.selectbatchids(cids));
}
@async
public completablefuture<list<testd>> selecttestdids(set<integer> dids) {
return completablefuture.supplyasync(() -> testdmapper.selectbatchids(dids));
}
@async
public completablefuture<list<teste>> selecttesteids(set<integer> eids) {
return completablefuture.supplyasync(() -> testemapper.selectbatchids(eids));
}
五.结果测试
5.1连接查询
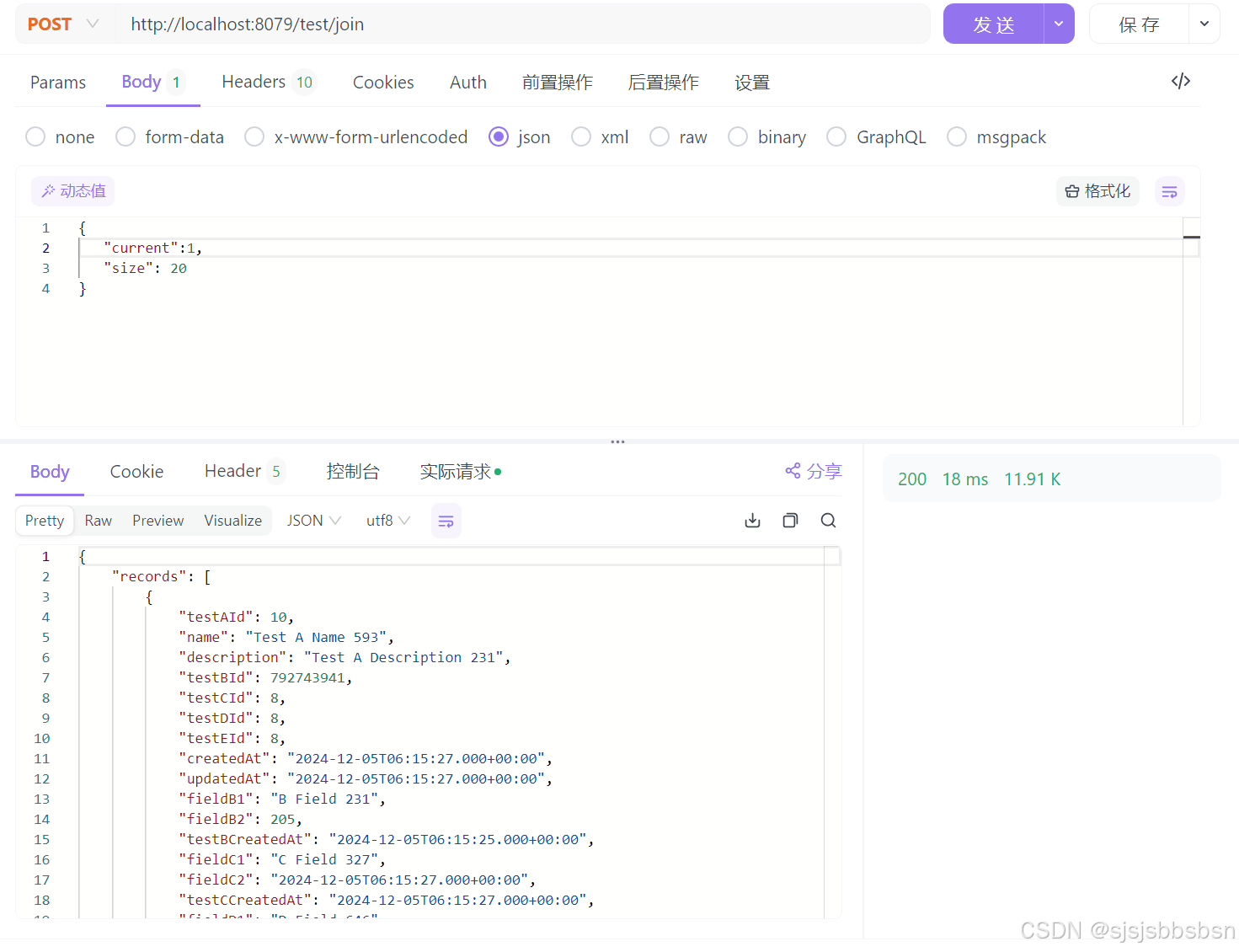
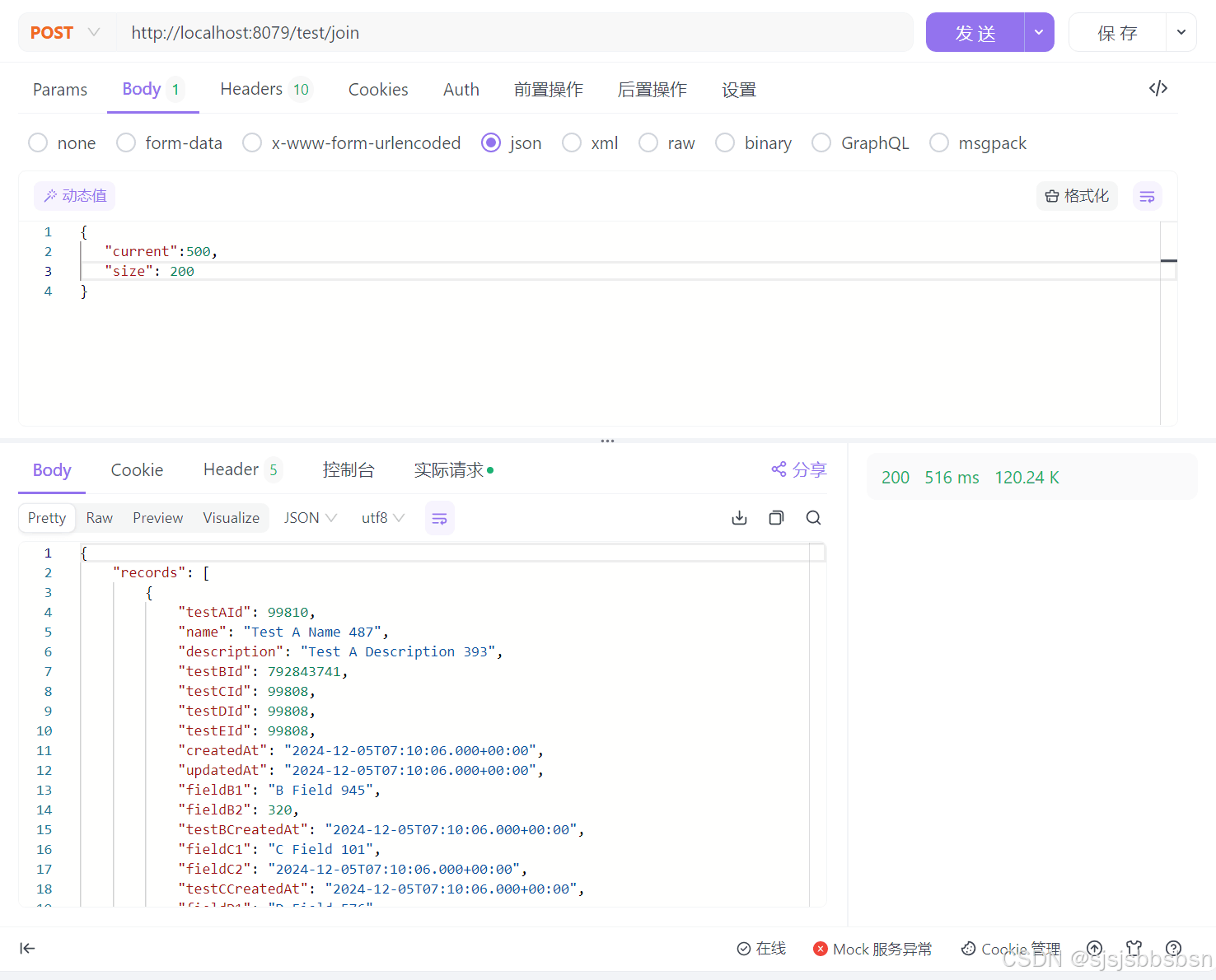
查询结果表格
| current | size | 响应时间 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 20 | 16ms |
| 50 | 20 | 23ms |
| 100 | 20 | 22ms |
| 500 | 20 | 52ms |
| 200 | 200 | 213ms |
| 500 | 200 | 517ms |
5.2多线程查询
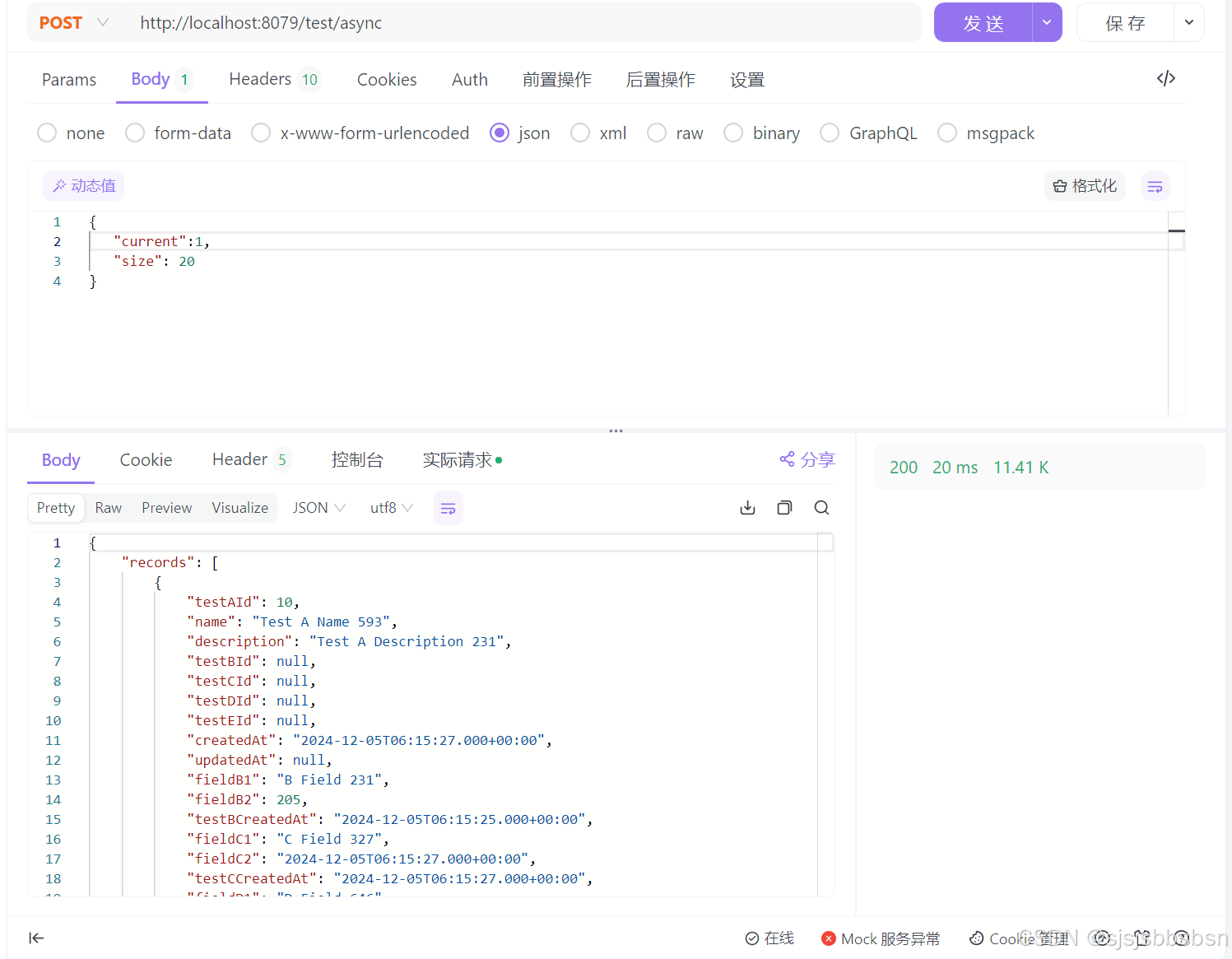
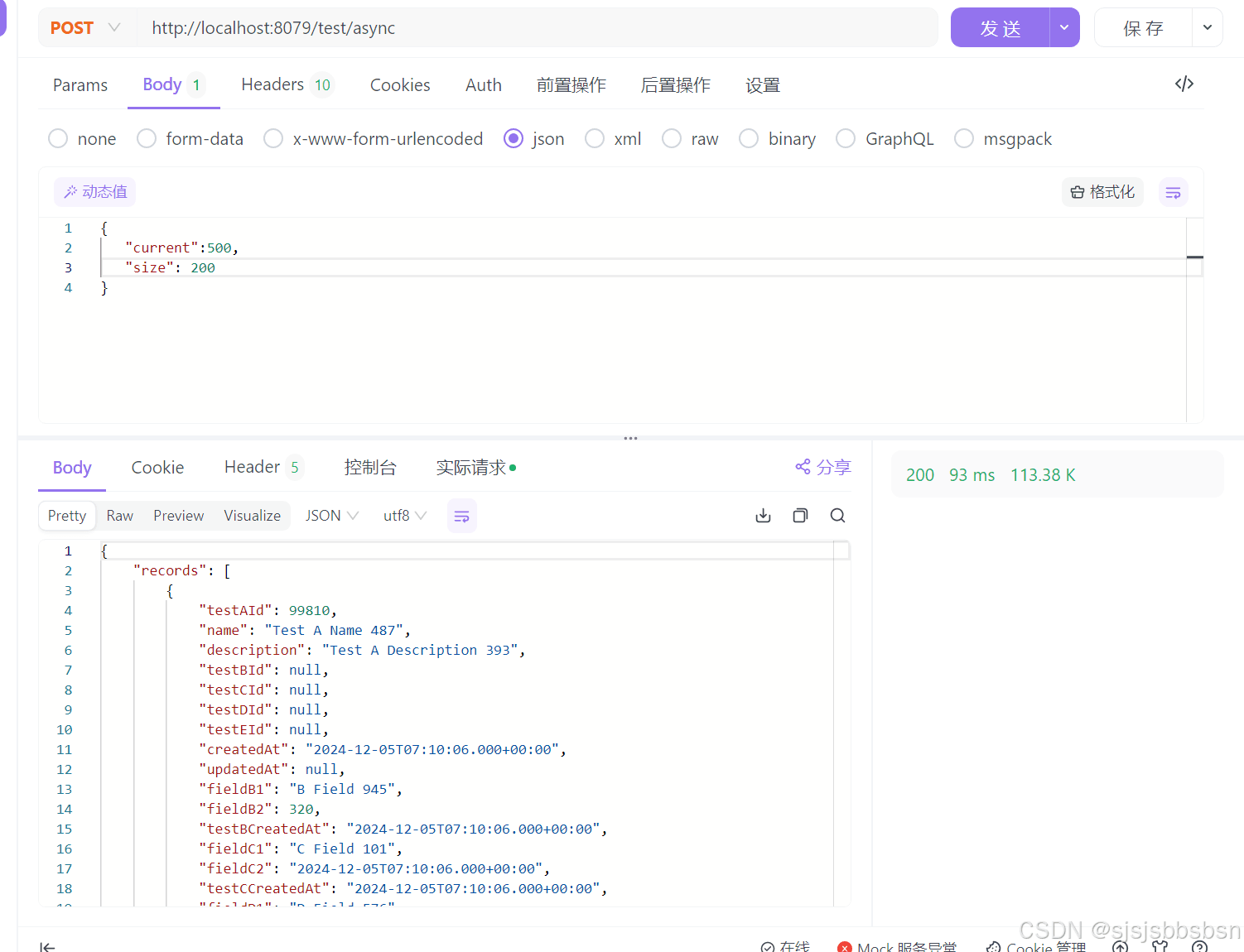
查询结果表格
| current | size | 响应时间 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 20 | 18ms |
| 50 | 20 | 17ms |
| 100 | 20 | 17ms |
| 500 | 20 | 21ms |
| 200 | 200 | 56ms |
| 500 | 200 | 80ms |
总结与建议
- 选择联表查询:当数据量较小,或者查询逻辑较为简单时,使用联表查询可以更简单直接,查询性能也较为优秀。
- 选择多线程查询:当面对大数据量或者复杂查询时,采用多线程查询将带来更显著的性能提升。通过异步并行查询,可以有效缩短响应时间,提升系统的整体性能。
在实际开发中,可以根据具体的业务需求和数据库的规模,合理选择查询方式,从而提高数据库查询效率,优化系统性能
到此这篇关于springboot+ mysql多线程查询与联表查询性能对比的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关springboot+ mysql多线程查询与联表查询内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!





发表评论