前言
在数据库操作中,group by分组查询和联合查询是非常强大且常用的功能,它们能够帮助我们从大量数据中提取有价值的信息。本文将深入探讨这两种查询方式,并结合具体示例进行详细讲解。
1. group by分组查询
1.1 语句格式
group by语句的基本格式如下:
select
分组列的列名,
除分组列的列名之外只能使用聚合函数
from
查询表的表名
group by
分组列的列名
having
having子句:对group by的结果进行过滤(只能和group by一起使用)
在这个语句中,select关键字用于指定要查询的列,其中除了分组列之外,其他列必须使用聚合函数(如sum、avg、count等)。from关键字指定要查询的表。group by关键字用于指定按照哪一列进行分组。having子句则用于对分组后的结果进行进一步的筛选。
1.2 示例说明
假设有如下所示的exam表:
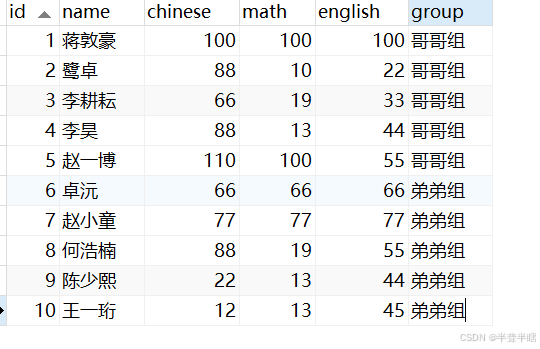
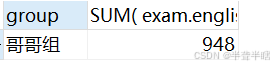
1.2.1 分别查询哥哥组和弟弟组的英语成绩总和
select
exam.`group`,
sum(exam.english)
from
exam as exam
group by
exam.`group`
在这个查询中,我们使用group by将数据按照group列进行分组,然后使用sum聚合函数计算每个组的英语成绩总和。执行结果如下:

1.2.2 查询哥哥组的所有成绩总和
select
exam.`group`,
sum( exam.english +exam.chinese+exam.math)
from
exam as exam
group by
exam.`group`
having
exam.`group` ='哥哥组'
这里同样使用group by进行分组,不过在sum函数中计算了每个学生的所有科目成绩总和。having子句用于筛选出group为哥哥组的记录。执行结果如下:
通过这两个示例,我们可以看到group by分组查询在对数据进行分类统计时的强大功能。它能够根据指定的列将数据分组,并对每个组的数据进行聚合计算,从而得到我们需要的统计信息。
2. 联合查询
联合查询用于将多个查询结果合并在一起,常见的联合查询包括内连接、外连接、自连接、子查询和合并查询等。下面我们将逐一介绍这些联合查询的用法。
2.1 内连接
内连接是一种最常用的连接方式,它返回两个表中满足连接条件的所有行。
2.1.1 语法格式
select * from table1,table2 where table1.xx=table2.xx;
这是一种基于逗号分隔的表名和where子句指定连接条件的写法。更标准的写法是使用join关键字:
select * from table1 join table2 on table1.xx = table2.xx;
2.1.2 执行过程
内连接的执行过程可以分为以下几个步骤:
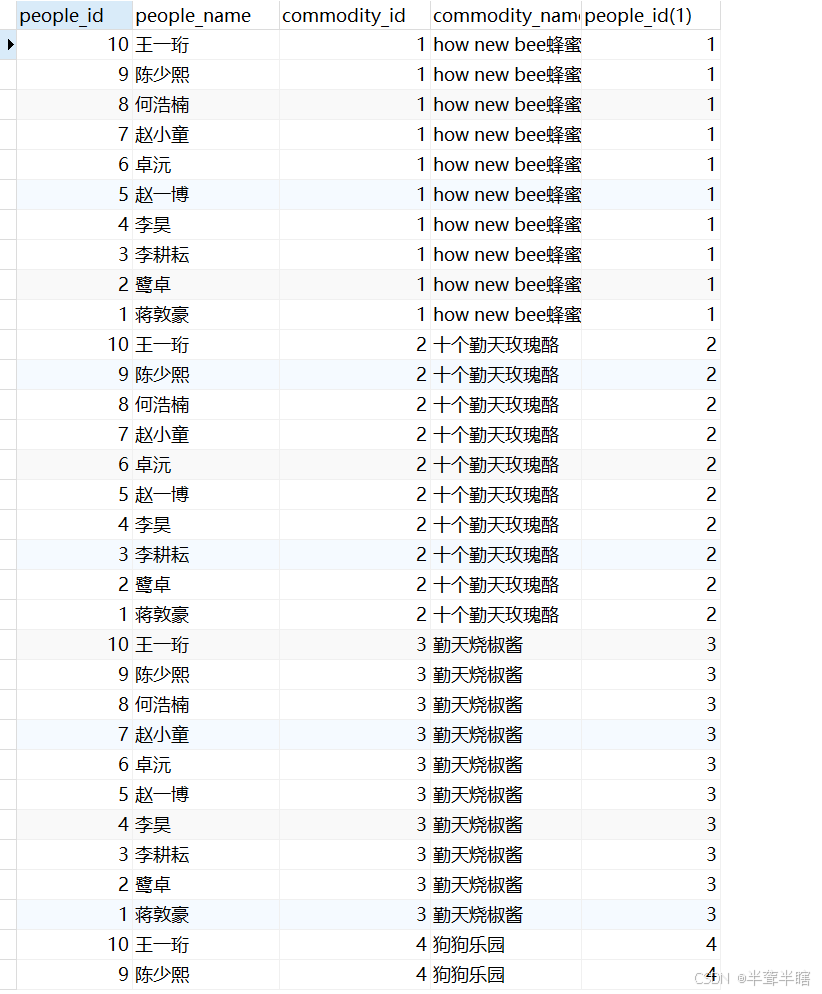
- 计算笛卡尔积:首先计算参加表连接的两个表的笛卡尔积。例如,假设有
qintianpeople表和qintiancommodity表,执行以下查询:
select
*
from
qintianpeople,
qintiancommodity
结果会得到两个表的笛卡尔积,即qintianpeople表中的每一行与qintiancommodity表中的每一行进行组合,结果集的行数为两个表行数的乘积。执行结果如下:
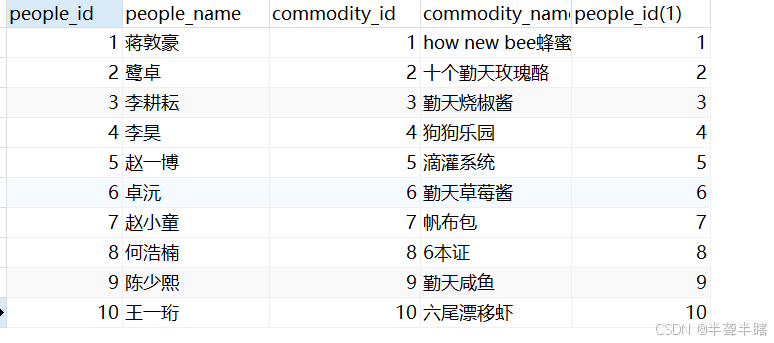
- 通过连接条件过滤无效数据:在笛卡尔积的基础上,通过连接条件过滤掉不满足条件的数据。例如:
select
*
from
qintianpeople,
qintiancommodity
where
qintianpeople.people_id = qintiancommodity.people_id
这里使用where子句指定了连接条件,只有people_id相等的行才会被保留。执行结果如下:
- 加入查询条件得到想要的结果行:可以进一步添加查询条件来筛选出符合特定要求的行。例如:
select
*
from
qintianpeople,
qintiancommodity
where
qintianpeople.people_id = qintiancommodity.people_id and
qintianpeople.people_id>5
这里在连接条件的基础上,添加了qintianpeople.people_id>5的条件,进一步筛选出符合条件的行。执行结果如下:
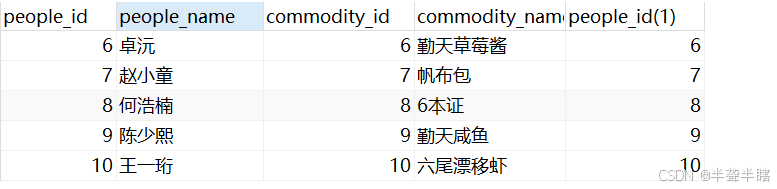
- 精简列名得到最终想要查询的列:最后,可以根据需求选择需要显示的列,精简结果集。例如:
select
qintianpeople.people_id,
people_name,
commodity_name
from
qintianpeople,
qintiancommodity
where
qintianpeople.people_id = qintiancommodity.people_id and
qintianpeople.people_id>5
这个查询只选择了people_id、people_name和commodity_name这几列,得到了更精简的结果。执行结果如下:
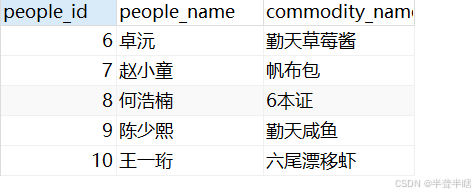
2.2 外连接
外连接分为左外连接和右外连接,它们的区别在于以哪个表为基准进行连接。
2.2.1 左外连接
语法格式:
select * from table1 left join table2 on table1.xx=table2.xx;
左外连接以左表为基准,左边的数据全部显示,右边的数据没有对应记录的显示为null。例如:
select
qintianpeople.people_id,
people_name,
commodity_name
from
qintiancommodity
left join
qintianpeople
on
qintiancommodity.people_id = qintianpeople.people_id
执行结果如下:
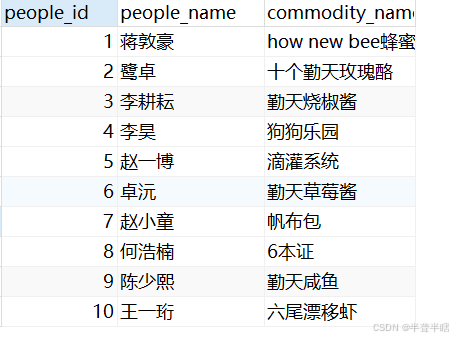
2.2.2 右外连接
语法格式:
select * from table1 right join table2 on table1.xx=table2.xx;
右外连接以右表为基准,右边的数据全部显示,左边的数据没有对应记录的显示为null。例如:
select
qintianpeople.people_id,
people_name,
commodity_name
from
qintiancommodity
right join
qintianpeople
on
qintiancommodity.people_id = qintianpeople.people_id
执行结果如下:
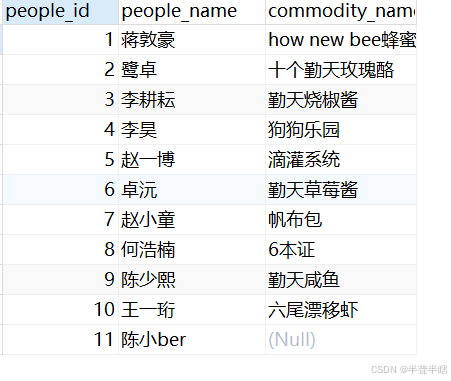
2.3 自连接
自连接是指在同一个表上进行连接操作,它可以把行比较转化为列比较,在查询时可以使用where进行过滤。
语法格式:
select * from table1 t1,table1 t2 where t1.xx=t2.xx;
2.4 子查询
子查询是指在一个查询中嵌套另一个查询,将内层查询的结果作为外层查询的条件。子查询可以分为单行子查询和多行子查询。
2.4.1 单行子查询
语法格式:
select * from table1 where id=(select id from table2 where...);
例如,假设有customers表和orders表,我们想要查询下了订单的客户信息,可以使用如下子查询:
select * from customers where customer_id in (select distinct customer_id from orders);
这个子查询先从orders表中获取所有下过订单的customer_id,然后外层查询从customers表中查询这些customer_id对应的客户信息。
2.4.2 多行子查询
语法格式:
select * from table1 where id in (select id from table2 where...);
多行子查询与单行子查询类似,不过它返回的是多个值,使用in关键字来匹配这些值。例如:
select * from products where product_id in (select product_id from order_items where quantity > 10);
这个查询会返回在order_items表中被订购数量大于10的所有产品信息。
子查询可以多次嵌套,以实现更复杂的查询逻辑。例如:
select *
from customers
where customer_id in (
select customer_id
from orders
where order_date > '2023-01-01' and customer_id in (
select customer_id
from customers
where region = 'asia'
)
);
这个嵌套子查询首先筛选出亚洲地区的客户customer_id,然后在这些客户中筛选出在2023年1月1日之后下过订单的客户customer_id,最后查询出这些客户的详细信息。
2.5 合并查询
合并查询用于将两个或多个查询的结果合并到一个结果集中,分为去重合并和不去重合并。
2.5.1 显示去重
语法格式:
select * from table1 union select * from table2;
union关键字会将两个查询结果合并,并去除重复的行。
2.5.2 不显示去重
语法格式:
select * from table1 union all select * from table2;
union all关键字会将两个查询结果直接合并,保留所有的行,包括重复的行。
2.6 一条sql语句的执行顺序
了解一条sql语句的执行顺序对于编写高效准确的查询非常重要。sql语句的执行顺序如下:
from:指定需要查询的表。join on:取笛卡尔积并根据连接条件进行连接。where:使用限制条件过滤数据。group by:对数据进行分组查询。having:对分组后的结果进行过滤。select:筛选需要显示的列。distinct:对结果进行去重(如果有该关键字)。order by:对结果进行排序。limit:限制返回的行数。
总结
到此这篇关于sql中的分组查询与联合查询举例详解的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关sql分组查询与联合查询内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!




发表评论