线程是并发编程的基础概念之一。在现代应用程序中,我们通常需要执行多个任务并行处理,以提高性能。c# 提供了多种并发编程工具,如thread、task、异步编程和parallel等。
thread 类
thread 类是最基本的线程实现方法。使用thread类,我们可以创建并管理独立的线程来执行任务。
基本使用thread
创建一个新的实例对象,将一个方法直接给thread类,并使用实例对象启动线程运行。
static void test() {
console.writeline("test事件开始执行");
thread.sleep(1000);
console.writeline("test事件睡眠之后打印数据");
console.writeline("test事件id: " + thread.currentthread.managedthreadid);
}
static void main(string[] args)
{
#region //主线程id
console.writeline("主线程id: " + thread.currentthread.managedthreadid);
#endregion
#region //传递一个方法给线程,执行方法
thread t = new thread(test);
t.start();
#endregion
}线程数据传输
传递单个参数
thread 提供了一个 start(object parameter) 方法,可以在启动线程时传递一个参数。
static int downlod(object obj) {
string str = obj as string;
console.writeline(str);
}
static void main(string[] args)
{
thread t1 = new thread(downlod);
//这里传递的参数是字符串
t1.start("数据传递方法执行 ,数据传递方法id: "+thread.currentthread.managedthreadid);
}这种方式适用于需要传递单个参数的情况。
使用类的实例方法传递多个参数
先new一个类的实例,给实例字段赋值,调用类的实例,通过实例调用方法,构造函数接收参数,然后在线程中调用该实例的方法。
static void main(string[] args)
{
// 使用 downloadtool 实例化并传递数据
downloadtool downloadtool = new downloadtool("www.baidu.com", "这是下载链接哦");
thread thread = new thread(downloadtool.download);
thread.start();
}
public class downloadtool
{
private string url;
private string message;
public downloadtool(string url, string message)
{
this.url = url;
this.message = message;
}
public void download()
{
console.writeline("下载链接: " + url);
console.writeline("提示信息: " + message);
console.writeline("download 线程 id: " + thread.currentthread.managedthreadid);
}
}
当 thread 线程启动时,它会执行 downloadtool.download() 方法,输出传递的数据。
线程优先级
在 c# 中,可以使用 thread.priority 属性来设置线程的优先级。线程优先级决定了操作系统在多线程环境中调度线程的顺序,但并不保证高优先级的线程总是比低优先级的线程更早或更频繁地执行。
线程优先级级别
c# 提供了五个线程优先级级别,定义在 threadpriority 枚举中:
- lowest:最低优先级。操作系统尽可能少地调度这个优先级的线程。
- belownormal:低于正常的优先级。优先级比 normal 低,但高于 lowest。
- normal:默认优先级,大多数线程默认的优先级。适用于一般用途。
- abovenormal:高于正常的优先级。操作系统更倾向于调度这个优先级的线程。
- highest:最高优先级。操作系统尽可能多地调度这个优先级的线程。
internal class program
{
static void a()
{
int i = 0;
while (true)
{
i++;
console.writeline($"a 输出第{i}");
thread.sleep(1000);
}
}
static void b()
{
int i = 0;
while (true)
{
i++;
console.writeline($"b 输出第{i}");
thread.sleep(1000);
}
}
static void main(string[] args)
{
//在c#中,线程的优先级可以通过thread.priority属性来设置和获取。
// lowest: 线程的优先级是最低的。在系统中存在其他活动线程时,此优先级的线程很少得到执行。
//belownormal: 线程的优先级低于正常线程。
//normal: 线程的优先级是普通的,这是线程的默认优先级。
//abovenormal: 线程的优先级高于正常线程。
//highest: 线程的优先级是最高的。此优先级的线程会尽量优先于其他所有优先级的线程执行。
thread a = new thread(a);
thread b = new thread(b);
a.priority = threadpriority.highest;
a.start();
b.priority = threadpriority.lowest;
b.start();
console.writeline("按任意键停止线程...");
console.readkey();
a.join();
b.join();
console.writeline("线程已停止");
}
}a被设置为最高优先级threadpriority.highest。b被设置为最低优先级threadpriority.lowest。
注意事项
- 优先级不是绝对控制:操作系统可能会忽略优先级设置,特别是在资源有限的系统中。高优先级线程不一定会一直执行,也不能阻止低优先级线程的执行。
- 使用优先级的适用场景:设置线程优先级可能适用于实时系统(例如,某些任务需要优先处理)。但是,大多数应用程序通常可以使用默认的
normal优先级。 - 避免使用过多的高优先级线程:如果所有线程都被设置为
highest,系统的整体性能可能会下降,甚至导致线程争用 cpu 资源的情况。 - cpu 密集型任务:在 cpu 密集型任务中,优先级可能会对性能产生较大影响,因为优先级高的线程可能会占用更多的 cpu 时间。
线程优先级的最佳实践
- 默认使用
normal优先级,除非有特殊原因。 - 避免滥用
highest优先级,因为它会对系统资源产生影响。 - 在 i/o 密集型的线程中,优先级通常不会有显著差异,因为这些线程在等待 i/o 操作完成时,cpu 会调度其他线程。
通过合理设置线程优先级,可以帮助操作系统更好地调度线程,以满足应用程序的需求。 但通常在 .net 应用程序中,多数情况下使用默认的 normal 优先级就足够了。
线程池
线程池 (threadpool) 是一种高效的管理和调度线程的方式。线程池自动管理线程的创建、重用和销毁,从而减少了手动创建和管理线程的开销。
为什么使用线程池
- 性能更高:线程池会重用现有的线程,减少了创建和销毁线程的开销。
- 自动管理:线程池会根据系统负载动态调整线程数量。
- 避免线程资源不足:线程池限制了同时运行的线程数,避免了线程过多导致的资源耗尽问题。
基本使用 threadpool.queueuserworkitem 方法将任务排入线程池队列。
using system;
using system.threading;
class program
{
static void main(string[] args)
{
// 将任务排入线程池
threadpool.queueuserworkitem(dowork, "任务 1");
threadpool.queueuserworkitem(dowork, "任务 2");
console.writeline("主线程完成");
thread.sleep(3000); // 等待线程池中的任务完成
}
static void dowork(object state)
{
string taskname = (string)state;
console.writeline($"{taskname} 开始执行 - 线程id: {thread.currentthread.managedthreadid}");
thread.sleep(1000); // 模拟耗时操作
console.writeline($"{taskname} 执行完成 - 线程id: {thread.currentthread.managedthreadid}");
}
}运行结果queueuserworkitem自动分配线程来执行任务。

queueuserworkitem 方法将任务排入线程池。它接收一个委托(即方法)和一个可选的状态对象(传递给方法的数据)。
dowork 方法接受一个参数 state,这是从 queueuserworkitem 传递的。
thread.sleep(3000) 确保主线程不会立即退出,使得线程池中的任务有机会完成。
使用带返回值的线程池任务
c# 中的 threadpool 通常不直接支持返回值。如果需要获得任务结果,可以使用 task,因为 task 本质上也是线程池的一部分。task 更适合于带返回值的异步操作。这里使用 task.run 来代替 threadpool:
static void main(string[] args)
{
//使用tesk多线程
int a= task.run(() =>
{
int a = dowload();
return a;
}).result;
task<int> task = task<int>.run(()=>{
int a = dowload();
return a;
});
//初始化一个cancellationtokensource实例
cancellationtokensource source = new cancellationtokensource();
//task.start();
task.wait(1000);
source.cancel();
int result = task.result;
console.writeline(result);
console.writeline($"tesk返回值{a}");
}
static int dowload() {
int a = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
a= a + i + 1;
}
int? id= task.currentid;
console.writeline("current thread id: " + id);
return a;
}线程池的限制
- 任务运行时间过长:线程池中的线程本质上是共享资源,如果某个任务运行时间太长,将会占用线程池中的线程,导致其他任务无法及时执行。
- 不适合实时系统:线程池中的任务调度是由系统管理的,无法保证精确的实时性。
- 有限的线程数量:在高并发场景中,如果线程池中的线程全部被占用,新的任务将会等待,直到有线程可用。
线程池总结
线程池是一种高效的并发处理方式,适合于大多数轻量级的后台任务。在现代 c# 编程中,建议使用 task 和 async/await 进行异步操作,因为它们能简化代码,并且使用底层的线程池来管理线程。如果需要精确控制线程的执行,通常建议使用手动管理的 thread 等。
线程锁
使用多线程,在多线程编程中,如果多个线程同时访问和修改共享资源(如全局变量、文件、数据库等),可能会导致数据不一致或竞争条件。为了避免这种情况,多线程锁通过控制对共享资源的访问来保证线程安全性。
资源冲突示例:
static void main(string[] args)
{
//调用方法循环创建新的线程来执行方法
stateobject state = new stateobject();
for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++)
{
thread thread = new thread(state.changstate);
thread.start();
}
console.readkey();
}
//一个stateobject类
public class stateobject
{
private int state = 5;
//里面有个状态改变方法,当状态等于5的时候进入到方法中,然后state+1 打印的应该是6 和线程id
public void changstate()
{
if (state == 5)
{
state++;
console.writeline($"state:{state} 线程id:" + thread.currentthread.managedthreadid);
}
state = 5;
}
}运行结果:
因为资源冲突的原因,有一些线程执行的时候,可能另外一个线程没有执行完,另外一个线程就已经进入到方法里面了。因为有修改的操作导致state状态混乱,资源冲突。这时候我们就需要一个东西来维护,让线程执行指定方法时一个一个的执行,不会冲突。
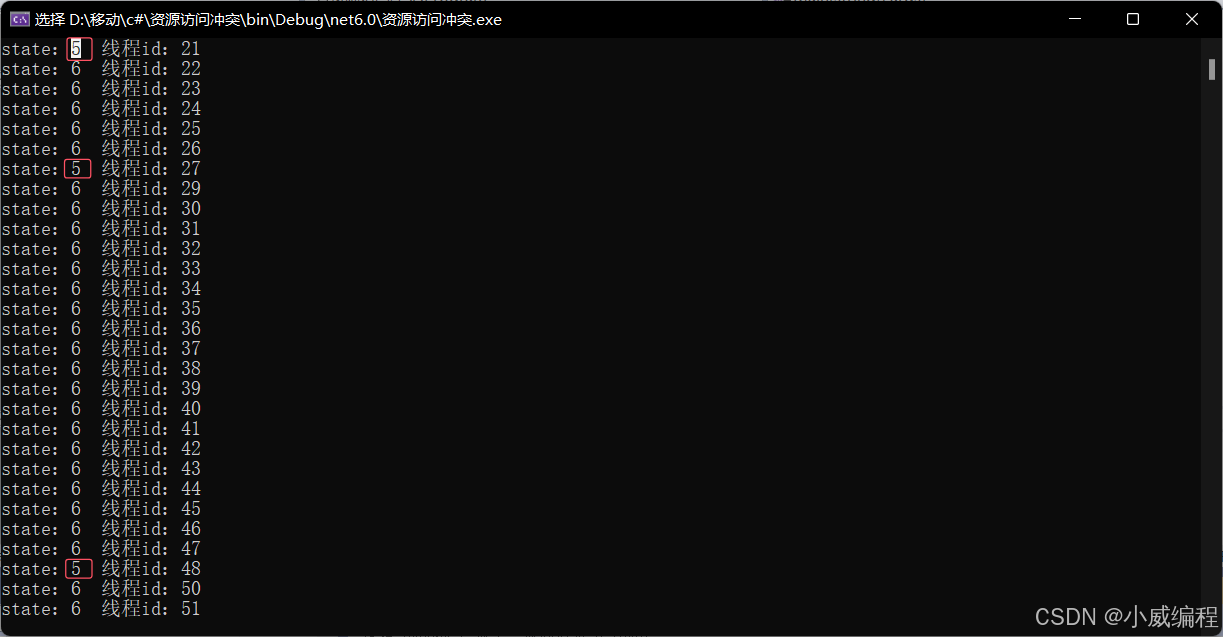
简单使用lock锁
1.创建一个private readonly object lockobject = new object(); // 锁对象
2.使用lock (lockobject){
//业务代码,执行到有修改的操作的代码
} // 使用锁对象来确保线程安全
static void main(string[] args)
{
stateobject state = new stateobject();
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++)
{
thread thread = new thread(state.changstate);
thread.start();
}
console.readkey();
}
public class stateobject
{
private object _lock = new object();
private int state = 5;
public void changstate()
{
//使用锁保证每次执行方法的都是一个线程,防止资源冲突
lock (_lock)
{
if (state == 5)
{
state++;
console.writeline($"state:{state} 线程id:" + thread.currentthread.managedthreadid);
}
state = 5;
}
}
}这样运行起来就能把每个线程操作隔离开,保证state的状态不会冲突。
为什么要创建一个 object 对象作为锁?
- 专用性:创建一个专用的锁对象(如
private readonly object lockobject = new object();),可以确保锁定的是特定的同步逻辑,而不是其他对象。这有助于避免意外的锁冲突或死锁。 - 避免使用其他共享对象:虽然可以使用任意的引用类型对象作为锁对象(包括
this或type对象),但这可能会带来不必要的风险,尤其是在public方法或对象中,这样可能会导致意外的锁定冲突。
常见问题死锁:
锁并不是万能,也不是有锁就是最好,要看情况使用,锁也会产生问题,常见的问题就是死锁等问题。
演示死锁:
thread1方法1 的锁里面嵌套锁住了thread2的锁,thread2方法2的锁里面嵌套锁住了thread1的锁,这种锁与锁嵌套使用,就是容易出问题。导致线程锁死程序无法动弹。
static void main(string[] args)
{
deadlockexample deadlockexample = new deadlockexample();
thread t1 = new thread(deadlockexample.thread1);
thread t2 = new thread(deadlockexample.thread2);
t1.start();
t2.start();
t1.join();
t2.join();
console.readkey();
}
}
public class deadlockexample
{
private static object lock1 = new object();
private static object lock2 = new object();
public void thread1()
{
lock (lock1)
{
console.writeline("线程1:已获取锁1,正在等待锁2。。。");
thread.sleep(100); // 模拟某些工作
lock (lock2)
{
console.writeline("线程1:获得锁2");
}
}
}
public void thread2()
{
lock (lock2)
{
console.writeline("线程2:已获取锁2,正在等待锁1。。。");
thread.sleep(100); // 模拟某些工作
lock (lock1)
{
console.writeline("线程2:获得锁1");
}
}
}
}运行结果:
死锁发生在两个或多个线程相互等待对方持有的资源,导致所有线程都无法继续执行。
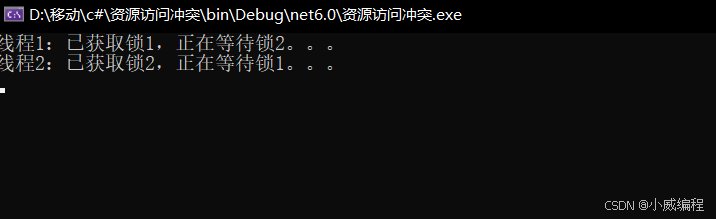
总结:
多线程锁在 c# 中主要用于解决以下问题:
- 竞态条件:通过锁机制防止多个线程同时访问和修改共享资源,确保数据一致性。
- 死锁:防止多个线程相互等待资源,通过锁的顺序或者避免嵌套锁来解决。
- 资源饥饿:确保每个线程都能获取资源,使用
monitor.tryenter等机制防止无限等待。 - 读写锁:允许多个线程并发读取资源,但写入时互斥,适合读多写少的场景。
c# 提供了多种锁机制,开发者可以根据应用场景选择合适的锁类型。
如果不想使用 lock 关键字,c# 还提供了其他锁机制,比如 mutex、semaphore、monitor 等
到此这篇关于c#多线程基本使用和探讨的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关c#多线程使用内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!



发表评论