wandb指南(视频教程 - 入门必看):https://docs.wandb.ai/guides
wandb教程(示例代码):w&b tutorials
wandb教程(示例代码 - jupyter):intro_to_weights_&_biases.ipynb
一、wandb简介
wandb(weights&biases, w&b):用于跟踪、可视化和协作机器学习实验的工具,支持在线和离线。它提供了一个简单的 python api,可以轻松地将实验数据发送到云端,并通过 web 应用程序进行访问和可视化。
备注:若登陆(在线版本),则在个人主页的profile - projects中保存实验记录,且每运行一次都将新增一条可视化数据,而不是只保留最近一次的运行结果。
备注:若不登陆(离线版本);
备注:无论是否登录,都将在当前路径下自动新建一个wandb文件夹,且每运行一次都将新增一个保存实验记录的文件夹。
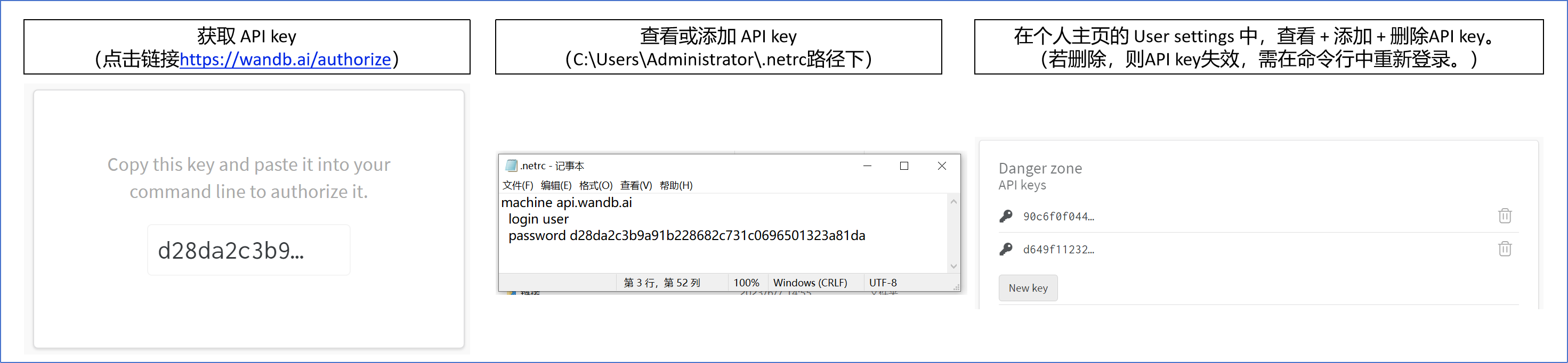
二、wandb注册与登陆(网页) —— 若登录,则支持在线功能
三、wandb安装与登陆(命令行) —— 若不登录,则只保留离线功能
(1)若显示如下,则输入命令行:wandb login --relogin。用于更换账号
"""
wandb: currently logged in as: anony-moose-837920374001732497. use `wandb login --relogin` to force relogin
"""
(2)若显示如下,则点击第二个链接获取api key(在个人主页的user settings中也可以获取),复制后并在命令行中粘贴(此时命令行没有显示),无需理会直接回车。
"""
wandb: logging into wandb.ai. (learn how to deploy a w&b server locally: https://wandb.me/wandb-server)
wandb: you can find your api key in your browser here: https://wandb.ai/authorize
wandb: paste an api key from your profile and hit enter, or press ctrl+c to quit:
"""
(3)若显示如下,登录成功(在c:\users\administrator\.netrc路径下可以查看或添加api key)。
"""
wandb: appending key for api.wandb.ai to your netrc file: c:\users\administrator\.netrc
"""
(4)若显示如下,是由于api key失效或丢失,需重新登录。
"""
wandb: w&b api key is configured. use `wandb login --relogin` to force relogin
wandb: error error while calling w&b api: user is not logged in (<response [401]>)
wandb: error the api key you provided is either invalid or missing. if the `wandb_api_key` environment variable is set, make sure it is correct. otherwise, to resolve this issue, you may try running the 'wandb login --relogin' command. if you are using a local server, make sure that you're using the correct hostname. if you're not sure, you can try logging in again using the 'wandb login --relogin --host [hostname]' command.(error 401: unauthorized)
"""
四、函数详解
wandb.init() :初始化一个新的 wandb 实验,并开始记录实验的信息和结果。
wandb.config.update() :更新实验的配置参数。
wandb.log() :记录实验指标和日志信息。
wandb.finish() :结束实验记录。
wandb.save() :保存实验结果和模型文件。
wandb.restore :从 wandb 云存储中恢复实验记录的模型参数或文件。
wandb.watch() :监视模型的梯度和参数。
wandb.api() :访问 wandb 云服务的 api。
wandb.table() :创建一个表格对象,用于显示数据。
wandb.plot() :创建并显示图表。
wandb.image() :创建并显示图像。
wandb.video() :创建并显示视频。
wandb.audio() :创建并播放音频。
4.1、wandb.init() —— 初始化一个新的 wandb 实验,并开始记录实验的信息和结果。
"""#########################################################################
函数功能:用于初始化一个新的 wandb 实验,并开始记录实验的信息和结果。
函数说明:wandb.init(project=none, entity=none, group=none, job_type=none, config=none,
tags=none, resume=false, dir=none, name=none, notes=none, id=none,
magic=none, anonymous=none, allow_val_change=false, reinit=false, settings=none,)
参数说明:
project:实验所属的项目名称。
entity:实验所属的实体(例如,团队或用户)。
group:实验的分组名称。
job_type:实验的类型(例如,训练、评估等)。
config:实验的配置参数,可以是一个字典或 namespace 对象。
tags:实验的标签,可以是一个字符串列表。
resume:如果为 true,则尝试恢复先前的实验。默认为 false。
dir:存储实验数据和日志的目录路径。
name:实验的名称。
notes:实验的说明或注释。
id:实验的唯一标识符。
magic:用于指定特殊功能的魔法命令。
anonymous:如果为 true,则匿名上传实验结果。默认为 false。
allow_val_change:如果为 true,则允许修改已存在的配置参数。默认为 false。
reinit:如果为 true,则重新初始化实验,忽略先前的配置。默认为 false。
settings:一个字典,用于设置实验的其他参数。
返回参数:
一个 wandb.run 对象,代表当前的实验运行。
#########################################################################"""
4.2、wandb.config.update() —— 更新实验的配置参数
"""#########################################################################
函数功能:用于更新当前实验的配置参数。 ———— 配置参数是在 wandb.init() 函数中指定的,并且可以在实验的整个运行过程中进行更新。
函数说明:wandb.config.update(new_config=none, allow_val_change=none, **kwargs)
参数说明:
new_config:一个字典或 namespace 对象,包含要更新的配置参数。
allow_val_change:如果为 true,则允许修改已存在的配置参数。默认为 false。
**kwargs:关键字参数,用于更新配置参数。
#########################################################################"""
4.3、wandb.log() —— 记录实验指标和日志信息。
"""#########################################################################
函数功能:用于记录实验中的指标、损失、评估结果、日志信息等,并将它们保存到 weights & biases(wandb)平台上,以便后续分析和可视化。
函数说明:wandb.log(data, step=none, commit=true, sync=true)
参数说明:
data:要记录的数据,可以是一个字典、列表、数字、字符串等。通常用于记录指标、损失等信息。
step:可选参数,表示记录的步骤或轮数。如果不提供,则默认为当前步骤或轮数。
commit:可选参数,表示是否立即提交记录。默认为 true,表示立即提交。
sync:可选参数,表示是否同步记录到云端。默认为 true,表示同步记录。
#########################################################################"""
4.4、wandb.finish() —— 结束实验记录。
"""#########################################################################
函数功能:用于结束当前的实验记录,并将记录的数据保存到 wandb平台上。
函数说明:wandb.finish(exit_code: optional[int] = none, quiet: optional[bool] = none)
参数说明:
exit_code 设置为 0 以外的值将运行标记为失败
quiet 设置为 true 以最小化日志输出
#########################################################################"""
五、项目实战
wandb教程(示例代码):w&b tutorials
wandb教程(示例代码 - jupyter):intro_to_weights_&_biases.ipynb
5.1、入门教程
5.1.1、在pycharm中可视化结果
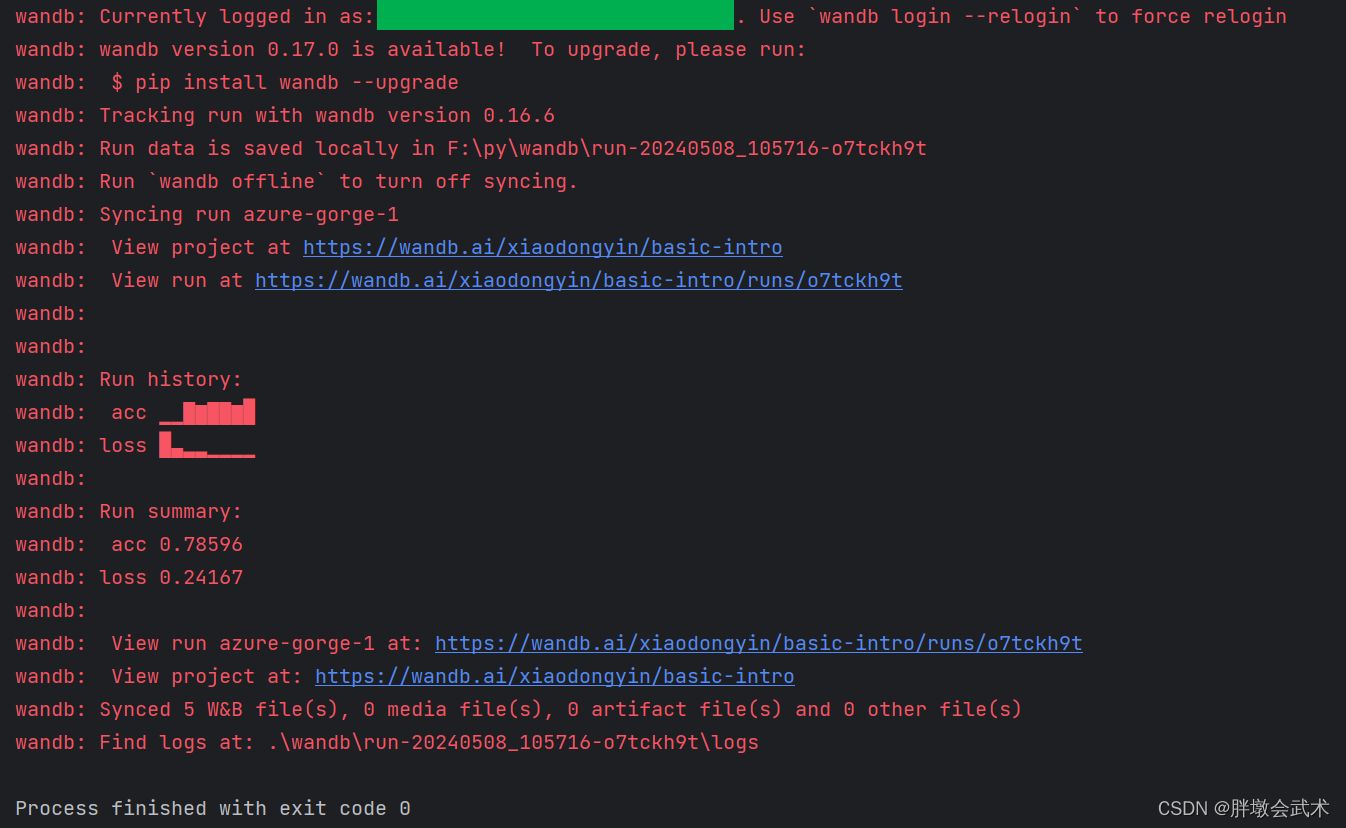
import wandb
import random
# 🐝 1️⃣ start a new run to track this script
wandb.init(
# set the project where this run will be logged
project="basic-intro",
# we pass a run name (otherwise it’ll be randomly assigned, like sunshine-lollypop-10)
name=f"experiment",
# track hyperparameters and run metadata
config={
"learning_rate": 0.02,
"architecture": "cnn",
"dataset": "cifar-100",
"epochs": 10,
})
# this simple block simulates a training loop logging metrics
epochs = 10
offset = random.random() / 5
for epoch in range(2, epochs):
acc = 1 - 2 ** -epoch - random.random() / epoch - offset
loss = 2 ** -epoch + random.random() / epoch + offset
# 🐝 2️⃣ log metrics from your script to w&b
wandb.log({"acc": acc, "loss": loss})
# mark the run as finished
wandb.finish()
5.1.2、在仪表盘中可视化结果(网页)
仪表盘(dashboard):是 wandb 提供的一个可视化界面,用户可以在网页浏览器中访问,并通过它查看、分析和管理实验结果。在仪表盘上,用户可以看到实验的指标、损失曲线、模型参数、日志信息等,并可以进行比较、筛选、筛选和导出等操作。
5.2、简单的 pytorch 神经网络
wandb教程(示例代码):w&b tutorials
wandb教程(示例代码 - jupyter):intro_to_weights_&_biases.ipynb
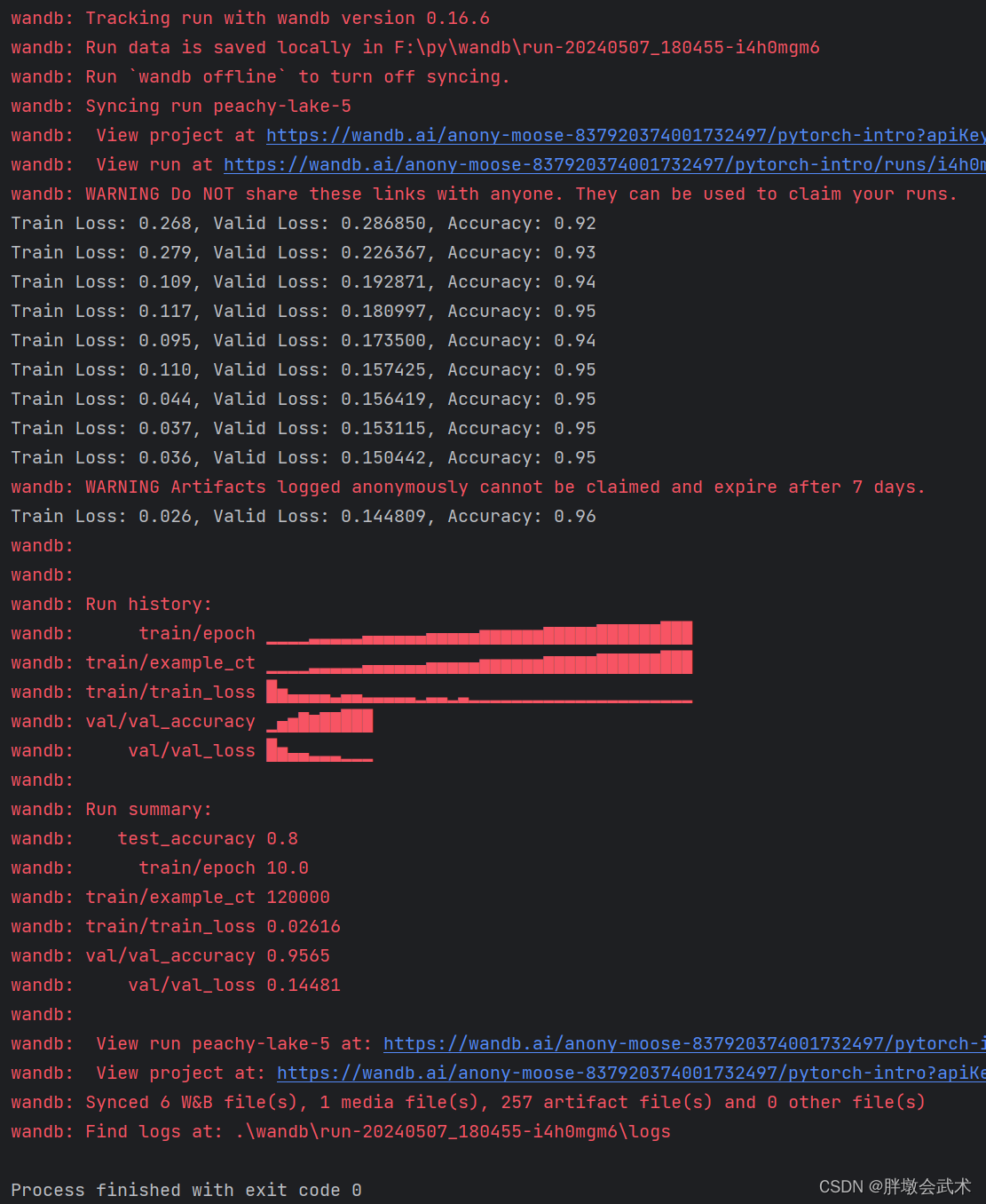
import wandb
import math
import random
import torch, torchvision
import torch.nn as nn
import torchvision.transforms as t
device = "cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
def get_dataloader(is_train, batch_size, slice=5):
"get a training dataloader"
full_dataset = torchvision.datasets.mnist(root=".", train=is_train, transform=t.totensor(), download=true)
sub_dataset = torch.utils.data.subset(full_dataset, indices=range(0, len(full_dataset), slice))
loader = torch.utils.data.dataloader(dataset=sub_dataset,
batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=true if is_train else false,
pin_memory=true, num_workers=2)
return loader
def get_model(dropout):
"a simple model"
model = nn.sequential(nn.flatten(),
nn.linear(28*28, 256),
nn.batchnorm1d(256),
nn.relu(),
nn.dropout(dropout),
nn.linear(256,10)).to(device)
return model
def validate_model(model, valid_dl, loss_func, log_images=false, batch_idx=0):
"compute performance of the model on the validation dataset and log a wandb.table"
model.eval()
val_loss = 0.
with torch.inference_mode():
correct = 0
for i, (images, labels) in enumerate(valid_dl):
images, labels = images.to(device), labels.to(device)
# forward pass ➡
outputs = model(images)
val_loss += loss_func(outputs, labels)*labels.size(0)
# compute accuracy and accumulate
_, predicted = torch.max(outputs.data, 1)
correct += (predicted == labels).sum().item()
# log one batch of images to the dashboard, always same batch_idx.
if i==batch_idx and log_images:
log_image_table(images, predicted, labels, outputs.softmax(dim=1))
return val_loss / len(valid_dl.dataset), correct / len(valid_dl.dataset)
def log_image_table(images, predicted, labels, probs):
"log a wandb.table with (img, pred, target, scores)"
# 🐝 create a wandb table to log images, labels and predictions to
table = wandb.table(columns=["image", "pred", "target"]+[f"score_{i}" for i in range(10)])
for img, pred, targ, prob in zip(images.to("cpu"), predicted.to("cpu"), labels.to("cpu"), probs.to("cpu")):
table.add_data(wandb.image(img[0].numpy()*255), pred, targ, *prob.numpy())
wandb.log({"predictions_table":table}, commit=false)
if __name__ == "__main__":
# launch 5 experiments, trying different dropout rates
for _ in range(5):
# 🐝 initialise a wandb run
wandb.init(
project="pytorch-intro",
config={
"epochs": 10,
"batch_size": 128,
"lr": 1e-3,
"dropout": random.uniform(0.01, 0.80),
})
# copy your config
config = wandb.config
# get the data
train_dl = get_dataloader(is_train=true, batch_size=config.batch_size)
valid_dl = get_dataloader(is_train=false, batch_size=2 * config.batch_size)
n_steps_per_epoch = math.ceil(len(train_dl.dataset) / config.batch_size)
# a simple mlp model
model = get_model(config.dropout)
# make the loss and optimizer
loss_func = nn.crossentropyloss()
optimizer = torch.optim.adam(model.parameters(), lr=config.lr)
# training
example_ct = 0
step_ct = 0
for epoch in range(config.epochs):
model.train()
for step, (images, labels) in enumerate(train_dl):
images, labels = images.to(device), labels.to(device)
outputs = model(images)
train_loss = loss_func(outputs, labels)
optimizer.zero_grad()
train_loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
example_ct += len(images)
metrics = {"train/train_loss": train_loss,
"train/epoch": (step + 1 + (n_steps_per_epoch * epoch)) / n_steps_per_epoch,
"train/example_ct": example_ct}
if step + 1 < n_steps_per_epoch:
# 🐝 log train metrics to wandb
wandb.log(metrics)
step_ct += 1
val_loss, accuracy = validate_model(model, valid_dl, loss_func, log_images=(epoch == (config.epochs - 1)))
# 🐝 log train and validation metrics to wandb
val_metrics = {"val/val_loss": val_loss,
"val/val_accuracy": accuracy}
wandb.log({**metrics, **val_metrics})
print(f"train loss: {train_loss:.3f}, valid loss: {val_loss:3f}, accuracy: {accuracy:.2f}")
# if you had a test set, this is how you could log it as a summary metric
wandb.summary['test_accuracy'] = 0.8
# 🐝 close your wandb run
wandb.finish()

发表评论