文章地址:
yolov5算法实现(一):算法框架概述
yolov5算法实现(二):模型搭建
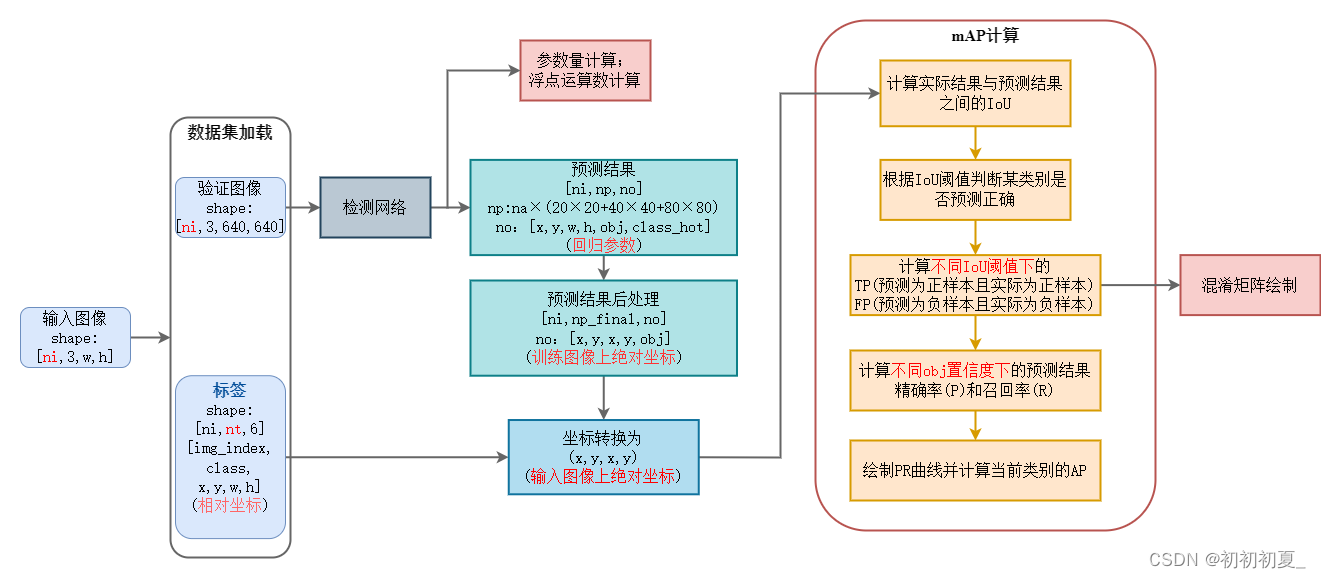
yolov5算法实现(三):数据集加载
yolov5算法实现(四):正样本匹配与损失计算
yolov5算法实现(五):预测结果后处理
yolov5算法实现(六):评价指标及实现
yolov5算法实现(七):模型训练
yolov5算法实现(八):模型验证
yolov5算法实现(九):模型预测
0 引言
本篇文章实现目标检测评价指标的实现,主要包含以下几个指标:
空间复杂度:参数量( parameters )
时间复杂度:浮点运算数( flops )
精度:精确率( p )、召回率( r )、混淆矩阵; 均值平均精度( map )
p
=
t
p
t
p
+
f
p
p = {{tp} \over {tp + fp}}
p=tp+fptp
r
=
t
p
t
p
+
f
n
r = {{tp} \over {tp + fn}}
r=tp+fntp
m
a
p
=
∑
a
p
n
{\rm{m}}ap = {{\sum {ap} } \over n}
map=n∑ap
t
p
tp
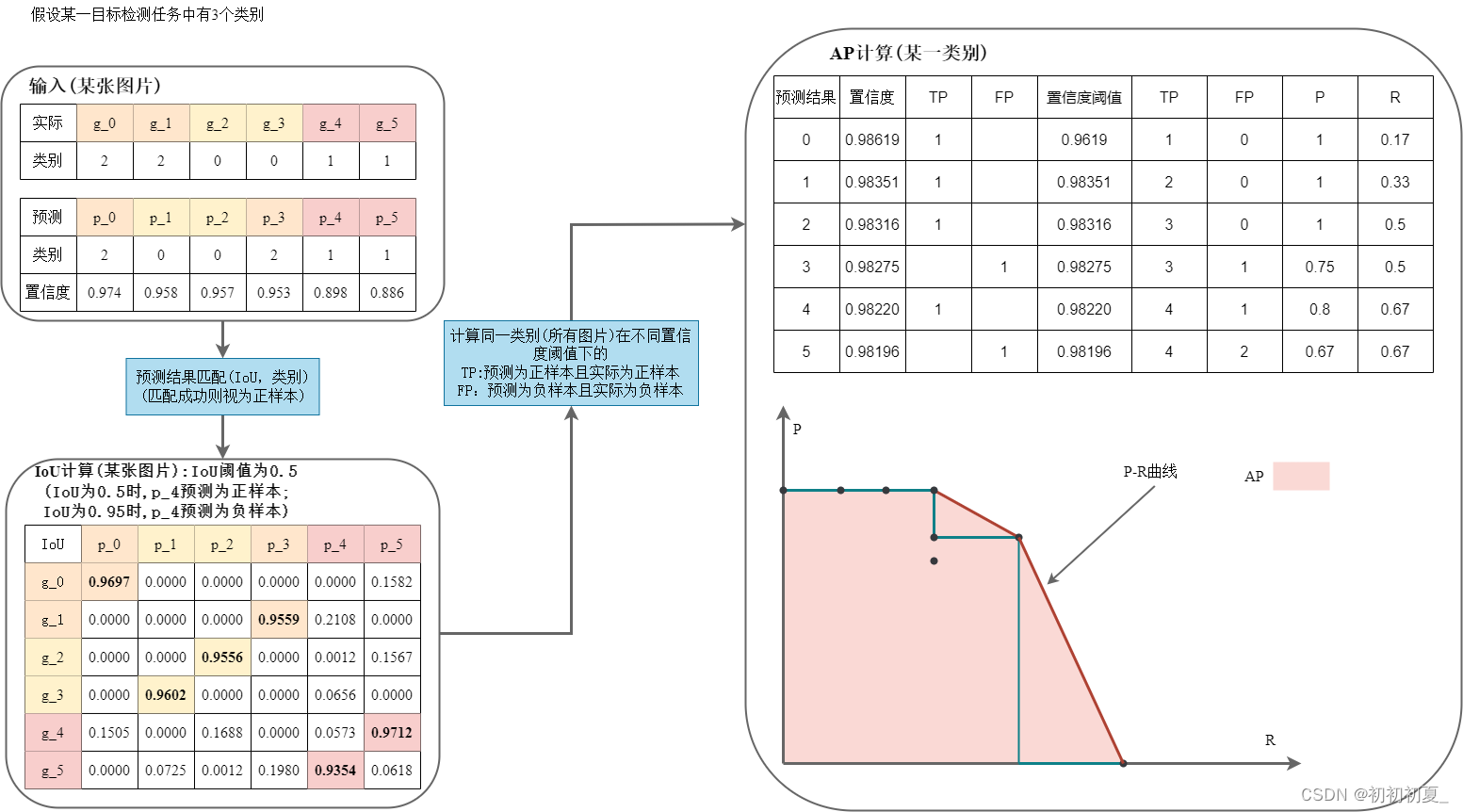
tp表示预测为正样本且实际为正样本数量,
f
p
fp
fp表示预测为正样本但实际为负样本数量。在目标检测中,根据iou阈值和类别对预测结果进行和实际标签的匹配,若匹配成功则该检测结果视为
t
p
tp
tp,反之则视为
f
p
fp
fp。
a
p
ap
ap为在不同的类别置信度下,类别
p
−
r
p-r
p−r值围成的曲线面积,
m
a
p
map
map为所有类别的
a
p
ap
ap值的平均值。
假设某目标检测任务中类别数为3,具体的
m
a
p
map
map计算过程如图2所示。
1 参数量和浮点运算数计算
def param_flops_cal(model, verbose=false, imgsz=640):
'''
打印模型信息
:param model: 模型
:param imgsz:
'''
n_p = sum(x.numel() for x in model.parameters()) # 参数量
n_g = sum(x.numel() for x in model.parameters() if x.requires_grad) # 更新参数量
print(
f"{'layer':>5} {'name':>40} {'gradient':>9} {'parameters':>12} {'shape':>20} {'mu':>10} {'sigma':>10}")
for i, (name, p) in enumerate(model.named_parameters()):
name = name.replace('module_list.', '')
print('%5g %40s %9s %12g %20s %10.3g %10.3g' %
(i, name, p.requires_grad, p.numel(), list(p.shape), p.mean(), p.std()))
try: # flops
p = next(model.parameters())
stride = max(int(model.stride.max()), 32) if hasattr(model, 'stride') else 32 # max stride
im = torch.empty((1, p.shape[1], stride, stride), device=p.device) # input image in bchw format
flops = thop.profile(deepcopy(model), inputs=(im,), verbose=false)[0] / 1e9 * 2 # stride gflops
imgsz = imgsz if isinstance(imgsz, list) else [imgsz, imgsz] # expand if int/float
fs = f', {flops * imgsz[0] / stride * imgsz[1] / stride:.1f} gflops' # 640x640 gflops
except exception:
fs = ''
name = path(model.yaml_file).stem.replace('yolov5', 'yolov5') if hasattr(model, 'yaml_file') else 'model'
printf(f"{name} summary: {len(list(model.modules()))} layers, {n_p}({n_p / 1e6:.2f}m) parameters, {n_g} gradients{fs}")
2 map计算
def ap_per_class(tp, conf, pred_cls, target_cls, plot=false, save_dir='.', names=(), eps=1e-16, prefix=''):
""" compute the average precision, given the recall and precision curves.
source: https://github.com/rafaelpadilla/object-detection-metrics.
# arguments
tp: 所有预测结果在不同iou下的预测结果 [n, 10]
conf: 所有预测结果的置信度
pred_cls: 所有预测结果得到的类别
target_cls: 所有图片上的实际类别
plot: plot precision-recall curve at map@0.5
save_dir: plot save directory
# returns
the average precision as computed in py-faster-rcnn.
"""
# sort by objectness
i = np.argsort(-conf) # 根据置信度从大到小排序
tp, conf, pred_cls = tp[i], conf[i], pred_cls[i]
# 得到所有类别及其对应数量
unique_classes, nt = np.unique(target_cls, return_counts=true)
nc = unique_classes.shape[0] # number of classes
# create precision-recall curve and compute ap for each class (针对每一个类别计算p,r曲线)
px, py = np.linspace(0, 1, 1000), [] # for plotting
ap, p, r = np.zeros((nc, tp.shape[1])), np.zeros((nc, 1000)), np.zeros((nc, 1000))
for ci, c in enumerate(unique_classes): # 对每一个类别进行p,r计算
i = pred_cls == c
n_l = nt[ci] # number of labels 该类别的实际数量(正样本数量)
n_p = i.sum() # number of predictions 预测结果数量
if n_p == 0 or n_l == 0:
continue
# accumulate fps and tps, cumsum 轴向的累加和
fpc = (1 - tp[i]).cumsum(0) # fp累加和(预测为负样本且实际为负样本)
tpc = tp[i].cumsum(0) # tp累加和(预测为正样本且实际为正样本)
# recall
recall = tpc / (n_l + eps) # recall curve
r[ci] = np.interp(-px, -conf[i], recall[:, 0], left=0) # 在不同置信度下的召回率
# precision
precision = tpc / (tpc + fpc) # precision curve
p[ci] = np.interp(-px, -conf[i], precision[:, 0], left=1) # 在不同置信度下的精确率
# ap from recall-precision curve(在不同的iou下的pr曲线)
for j in range(tp.shape[1]):
ap[ci, j], mpre, mrec = compute_ap(recall[:, j], precision[:, j])
if plot and j == 0:
py.append(np.interp(px, mrec, mpre)) # precision at map@0.5
# compute f1 (harmonic mean of precision and recall)
f1 = 2 * p * r / (p + r + eps)
# names = [v for k, v in names.items() if k in unique_classes] # list: only classes that have data
# names = dict(enumerate(names)) # to dict
if plot:
plot_pr_curve(px, py, ap, path(save_dir) / f'{prefix}pr_curve.png', names)
plot_mc_curve(px, f1, path(save_dir) / f'{prefix}f1_curve.png', names, ylabel='f1')
plot_mc_curve(px, p, path(save_dir) / f'{prefix}p_curve.png', names, ylabel='precision')
plot_mc_curve(px, r, path(save_dir) / f'{prefix}r_curve.png', names, ylabel='recall')
i = smooth(f1.mean(0), 0.1).argmax() # max f1 index
p, r, f1 = p[:, i], r[:, i], f1[:, i]
tp = (r * nt).round() # true positives
fp = (tp / (p + eps) - tp).round() # false positives
return tp, fp, p, r, f1, ap, unique_classes.astype(int)
def compute_ap(recall, precision):
""" compute the average precision, given the recall and precision curves
# arguments
recall: the recall curve (list)
precision: the precision curve (list)
# returns
average precision, precision curve, recall curve
"""
# 增加初始值(p=1.0 r=0.0) 和 末尾值(p=0.0, r=1.0)
mrec = np.concatenate(([0.0], recall, [1.0]))
mpre = np.concatenate(([1.0], precision, [0.0]))
# compute the precision envelope np.maximun.accumulate
# (返回一个数组,该数组中每个元素都是该位置及之前的元素的最大值)
mpre = np.flip(np.maximum.accumulate(np.flip(mpre)))
# integrate area under curve
method = 'interp' # methods: 'continuous', 'interp'
if method == 'interp': # np.interp(新的横坐标,原始数据横坐标,原始数据纵坐标) 线性插点
x = np.linspace(0, 1, 101) # 101-point interp (coco))
# 积分(求曲线面积)
ap = np.trapz(np.interp(x, mrec, mpre), x) # integrate
else: # 'continuous'
i = np.where(mrec[1:] != mrec[:-1])[0] # points where x axis (recall) changes
ap = np.sum((mrec[i + 1] - mrec[i]) * mpre[i + 1]) # area under curve
return ap, mpre, mrec


发表评论