sql,group by分组后分别计算组内不同值的数量
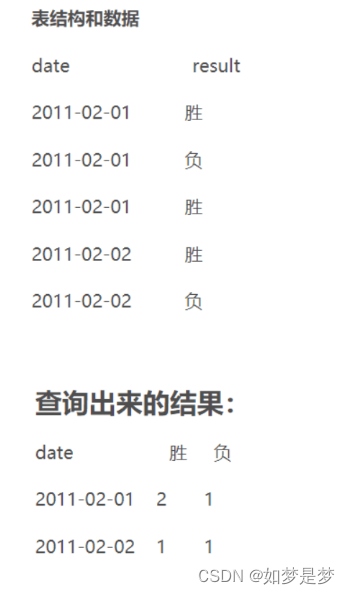
如现有一张购物表shopping
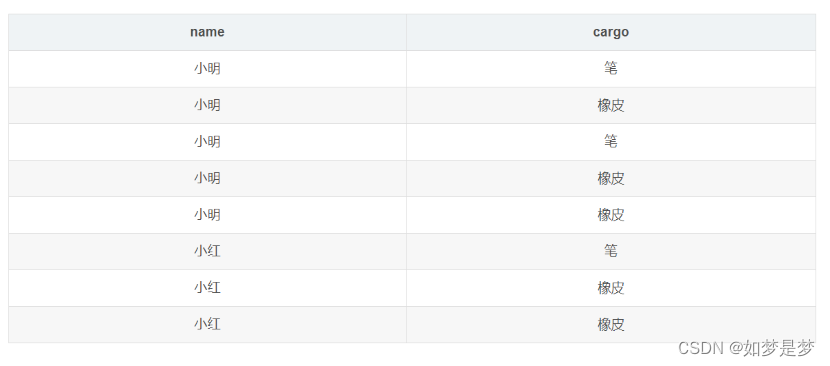
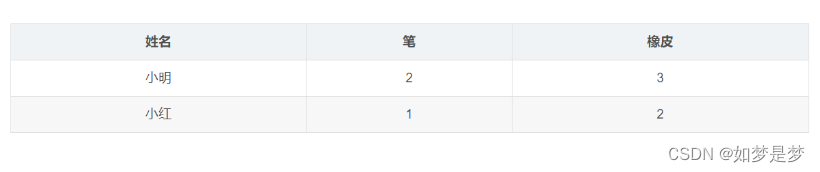
先要求小明和小红分别买了多少笔和多少橡皮,形成以下格式
select 'name',count(*)
from 'shopping'
group by 'name';
select name as 姓名,sum( case when cargo = '笔' then 1 else 0 end) as 笔, sum(case when cargo = '橡皮' then 1 else 0 end) as 橡皮 from shopping group by name;注:这里不能用count计算行数,count只是分组后每组有行的数目
mysql中case when then else end 的用法
语法:
case
when condition1 then result1
when condition2 then result2
when conditionn then resultn
end;
select
case ----------------------------如果
when sex = '1' then '男' ----------------------------sex=‘1’,则返回值‘男’
when sex = '2' then '女' ----------------------------sex=‘2’,则返回值‘女’
else 0 ----------------------------其他的返回‘其他’
nd ----------------------------结束
from user ----------------------------整体理解:在user表中如果 sex=‘1’,则返回值‘男’;如果
sex=‘2’,则返回值‘女
----用法一:
select
case
when state = '1' then '成功'
when state = '2' then '失败'
else '其他'
end
from table
---用法二:
select state
case
when '1' then '成功'
when '2' then '失败'
else '其他'
end
from table
案例:有员工表empinfo employee(员工)
create table 'empinfo' (
'id' int(11) not null auto_increment,
'name' varchar(10) not null,
'age' int(11) not null,
'salary' int(11) not null,
primary key('id')
)假如数据量很大约1000万条;写一个你认为最高效的sql,用一个sql计算以下四种人:
salary>9999 and age>35
salary>9999 and age<35
salary<9999 and age>35
salary<9999 and age<35
每种员工的数量;
select
sum(case when salary>9999 and age>35 then 1 else 0 end) as 'salary>9999 age>35',
sum(case when salary>9999 and age<35 then 1 else 0 end) as 'salary>9999 age<35',
sum(case when salary<9999 and age>35 then 1 else 0 end) as 'salary<9999 age>35',
sum(case when salary<9999 and age<35 then 1 else 0 end) as 'salary<9999 age<35'
from empinfo; 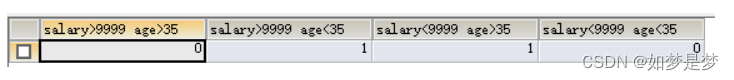
练习:用一个sql语句完成下面不同条件的分组
有如下数据:

按照国家和性别进行分组,得出如下结果:
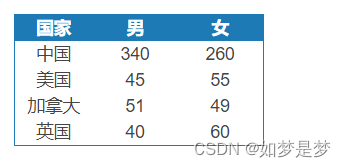
select country,
sum ( case when sex = '1' then
population else 0 end),
sum ( case when sex = '2' then
popution else 0 end)
from table_a
group by country;
根据条件有选择的update。
例,有如下更新条件
工资5000以上的员工,工资减少10%
工资在2000到4600之间的员工,工资增加15%
很容易考虑的是选择执行两次update语句,如下所示
----条件一:
update personnel
set salary = salary * 0.9
where salary >= 5000;
----条件二:
update personnel
set salary = salary*1.15
where salary >= 2000 and salary < 4600;
但是事情没有想象的那么简单,假设有个人工资5000块。首先,按照条件1,工资减少10%,变成工资4500.接下来运行第二个sql的时候,因为这个人的工资是4500在2000到4600的范围之内,需要增加15%,最后这个人的工资结果是5175,不但没有减少,反而还增加了。如果反过来执行,那么工资4600的人相反会变成减少工资。暂且不管这个规章是多么荒诞,如果想要一个sql语句实现这个功能的话,我们需要用到case函数。代码如下:
update personnel
set salary = case when salary >= 5000 then salary * 0.9
when salary >= 2000 and salary < 4600 then salary * 1.15
else salary end;这里要注意一点,最后一行的else salary 是必须的,要是没有这行,不符合这两个条件的人的工资将会被写成null,那可就大事不妙了。在case函数中else部分的默认值是null,这点是需要注意的地方。

update t
set a = case
when a > 100 then a = a-100
when a < 100 then a = a+100
else a end;
select courseid, coursename,score,(case when score < 60 then 'fail' else 'pass' end) as mark from course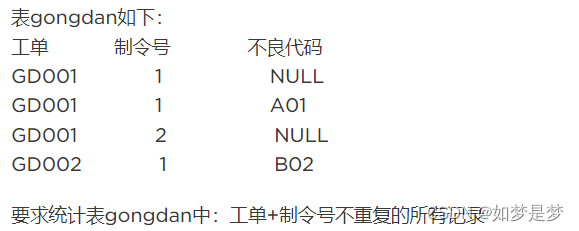
select distinct 工单,制令号 from gomgdan
要求统计表gongdan中:工单·+制令号不重复的所有记录的数量
把中间查询到的结果当成一张表使用
select count(*) from (select distinct 工单,制令号 from gongdan) as b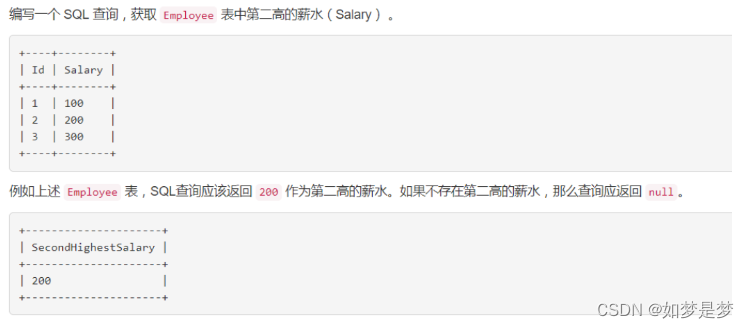
select salary from employee group by salary desc limit 1, 1;
select ifnull
((select salary from employee group by salary desc limit 1,1),null)
as secondhighestsalary;ifnull(expr1,expr2)
如果expr1不是null,ifnull()返回expr1,否则它返回expr2
拷贝表(拷贝数据,源表名:a 目标表名:b)
sql:insert into b(a,b,c) select d, e, f from a;
insert into b(a,b,c) select a,b,c from b;





发表评论