
✨ 人生到处知何似,应似飞鸿踏雪泥 🌏
📃个人主页:
🔥个人专栏:c++学习
🚀 欢迎关注:👍点赞 👂🏽留言 😍收藏 💞 💞 💞

🚀前言:
【c++深度学习】二叉搜索树的全面解析与高效实现-csdn博客
通过之前对二叉搜索树的学习,我相信大家对set和map也应该有所了解,set就类似于二叉搜索树的k模型,而map就类似于二叉搜索树的kv模型,下面就让我们进入对其的了解吧,踏上这神秘的学习之旅
1. 关联式容器
📒在初阶阶段,我们已经接触过stl中的部分容器,比如:vector、list、deque、
forward_list(c++11)等,这些容器统称为序列式容器,因为其底层为线性序列的数据结构,里面存储的是元素本身
📙关联式容器(associative containers) 是c++标准模板库(stl)中的一类重要容器,主要用于存储和快速检索键值对(key-value pairs)形式的数据。这类容器与序列式容器(如vector、deque、list)的主要区别在于,关联式容器中的元素是按照特定的排序准则(通常是键的大小)进行排序的,从而允许通过键来快速查找、插入和删除元素。
2. 键值对

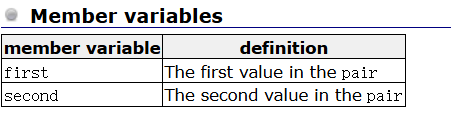
sgi-stl中关于键值对的定义:(示例)
template <class t1, class t2>
struct pair
{
typedef t1 first_type;
typedef t2 second_type;
t1 first;
t2 second;
pair(): first(t1()), second(t2())
{}
pair(const t1& a, const t2& b)
: first(a)
, second(b)
{}
};
3. 树形结构的关联式容器
📕根据应用场景的不桶,stl总共实现了两种不同结构的管理式容器:树型结构与哈希结构
📕关联式容器是c++ stl中一类重要的容器,它们通过键值对的形式存储数据,并支持快速的查找、插入和删除操作。常见的关联式容器包括set、multiset、map和multimap等,它们在不同的应用场景下提供了高效的解决方案
4. set && multiset
📜set的概念
概念: set 是 c++ 标准模板库 (stl) 中的一个关联式容器,它包含的元素是唯一的,且默认情况下元素会按照升序排序。set 的内部实现通常使用红黑树来保持其有序性和唯一性
📙set特征:
🎈multiset的概念
概念:multiset 是 c++ 标准库 中的一个容器,它允许存储重复的元素。与 set 不同,set 中的元素是唯一的,而 multiset 中的元素可以重复
简单演示一下差别:
void test3()
{
multiset<int> s;
s.insert(5); s.insert(5);
s.insert(2); s.insert(2); s.insert(2);
s.insert(1);
s.insert(9);
s.insert(7);
//set<int>::iterator it = s.begin();
auto it = s.begin();
while (it != s.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
int x;
cin >> x;
auto pos = s.find(x); //查找x时,返回中序第一个
while (pos != s.end() && *pos == x)
{
cout << *pos << " ";
++pos;
}
cout << endl;
}📒set使用
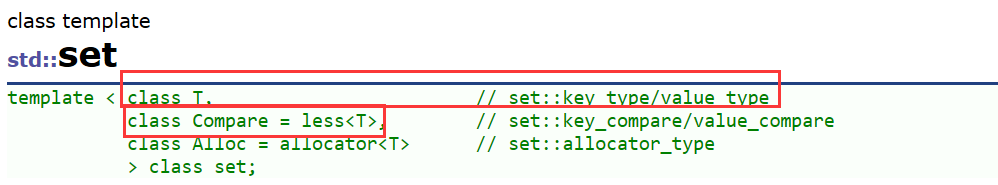
🌈set的模板参数列表
void test1()
{
set<int> s;
s.insert(5); s.insert(5);
s.insert(2); s.insert(2);
s.insert(1);
s.insert(9);
s.insert(7);
//set<int>::iterator it = s.begin();
auto it = s.begin();
while (it != s.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
for (auto e : s)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
auto rit = s.rbegin();
while (rit != s.rend())
{
cout << *rit << " ";
++rit;
}
cout << endl;
int x;
cin >> x;
if (s.find(x) != s.end()) cout << "存在" << endl;
else cout << "不存在" << endl;
auto pos1 = find(s.begin(), s.end(), x); //o(n)
auto pos2 = s.find(x); // o(log(n))
if (s.count(x)) //o(log(n))
cout << "存在" << endl;
else cout << "不存在" << endl;
s.insert(x);
cout << "插入:";
for (auto e : s)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
cout << "删除:";
s.erase(s.begin(),s.end());
for (auto e : s)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test2()
{
std::set<int> myset;
std::set<int>::iterator itlow, itup;
for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++) myset.insert(i * 10); // 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90
// [30, 60]
// >= 30
itlow = myset.lower_bound(24); //
// > 60
itup = myset.upper_bound(34);
cout << *itlow << " " << *itup << endl;
myset.erase(itlow, itup); // 10 20 70 80 90
std::cout << "myset contains:";
for (std::set<int>::iterator it = myset.begin(); it != myset.end(); ++it)
std::cout << ' ' << *it;
std::cout << '\n';
}
在上面中:
在set的这些函数中,用的最多的就是insert,find,erase
🌈insert
🌈find

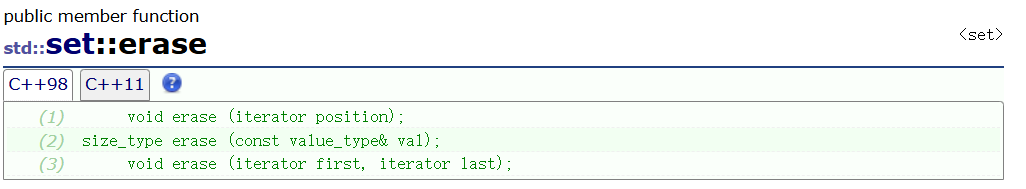
🌈erase
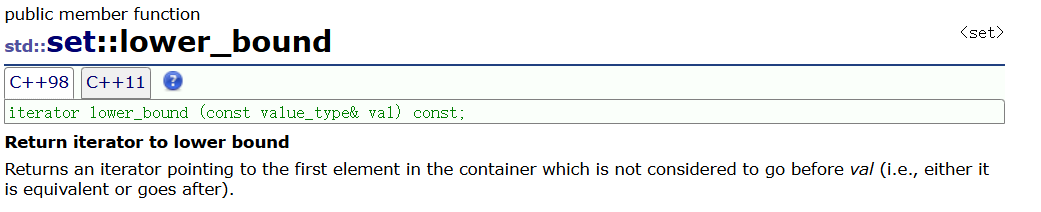
🌈lower_bound 和 upper_bound
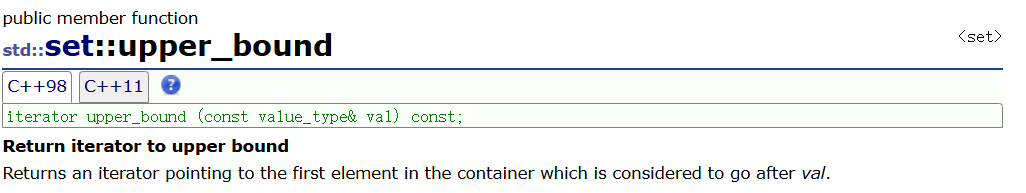
这两个函数通常可以和erase结合使用删除一段迭代器区间
5. map 与 multimap
🎩map的概念
📚概念: map 是 c++ 标准库中的一个关联容器,它存储的元素都是键值对(key-value pairs),并且键(key)是唯一的。在map中,键值key通常用于排序和惟一地标识元素,而值value中存储与此键值key关联的内容。键值key和值value的类型可能不同,并且在map的内部,key与value通过成员类型value_type绑定在一起,为其取别名称为pair:
typedef pair<const key, t> value_type;
🎩特点:
🎈multimap的概念
概念: multimap 是 c++ 标准库 中的一个关联容器,它允许存储具有相同键的多个值。与 map 不同,map 中的键是唯一的,而 multimap 中的键可以重复
multimap中的接口可以参考map,功能都是类似的。
🧩map的使用
void test1() //遍历
{
/*map<string, string> dict;
pair<string, string> kv1("left", "左边");*/
map的多种初始化方式
//dict.insert(kv1);
//dict.insert(pair<string, string>("right", "右边"));
//dict.insert(make_pair("insert", "插入"));
pair<string, string> kv2 = {"string","字符串" };
//dict.insert({ "string", "字符串" });
map<string, string> dict = { {"left", "左边"}, {"right", "右边"},{"insert", "插入"},{ "string", "字符串" } };
map<string, string>::iterator it = dict.begin();
while (it != dict.end())
{
//cout << (*it).first <<":"<<(*it).second << endl;
//cout << (*it).first << ":" << (*it).second << endl;
cout << it->first << ":" << it->second << endl;
++it;
}
cout << endl;
for (const auto& e : dict)
{
cout << e.first << ":" << e.second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
for (auto& [x, y] : dict) //c++17支持
{
cout << x << ":" << y << endl;
}
cout << endl;
string str;
while (cin >> str)
{
auto ret = dict.find(str);
if (ret != dict.end())
{
cout << "->" << ret->second << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "无此单词,请重新输入" << endl;
}
}
}
void test3() //插入
{
map<string, string> dict;
dict.insert(make_pair("sort", "排序"));
//插入 + 修改
dict["left"] = "左边";
//修改
dict["left"] = "左边 + 修改";
//key不存在->插入<"insert", "">
dict["insert"];
//存在->查找
cout << dict["left"] << endl;
}
🌈map的模板参数说明
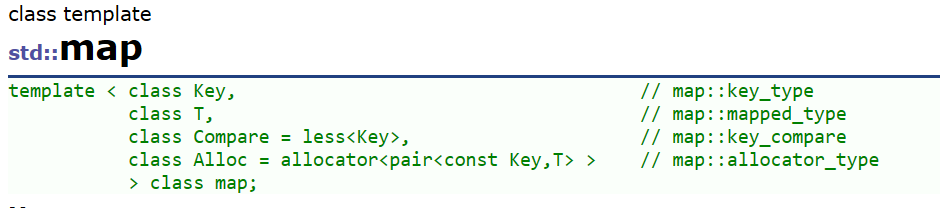
🌈insert

在insert插入中,所需要的元素类型是value_type - > pair
insert:插入成功 pair<新插入key所在节点的iterator, true>插入失败 pair<已经存在的key所在节点的iterator,false>
🌈map的成员类型

🌈pair

pair可以支持带参构造,无参构造和拷贝构造
map插入代码演示:
int main()
{
map<string,string> d;
d.insert(pair<string, string>("insert", "插入"));
d.insert(pair<const char*, const char*>("find", "查找"));
return 0;
}
🌈make_pair
而一般我们并不会这没写,因为有make_pair的存在,我们往往使用make_pair

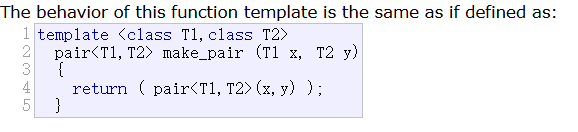
make_pair是一个函数模板,他可以自己推演类型
int main()
{
map<string,string> d;
d.insert(make_pair("erase", "删除"));
return 0;
}
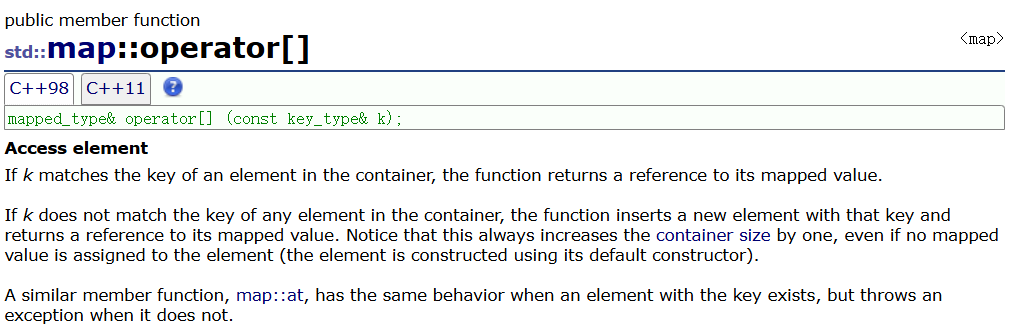
🌈operator[ ]
map中重载了[]运算符,因为其需要通过key获取value,set没有
在使用operator[ ]时,它会自动插入一个元素,在插入成功时,返回该位置的second(默认为0),在插入失败时,它就会返回已有位置的second。
💧map实际应用
✨计数
void test2() //映射计数
{
string arr[] = { "苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "香蕉", "苹果", "香蕉" };
int i = int(); //匿名构造, 为0
int j = int(10);
map<string, int> counttree; //故其second的值最初为0
for (const auto& str : arr)
{
// 先查找水果在不在搜索树中
// 1、不在,说明水果第一次出现,则插入<水果, 1>
// 2、在,则查找到的节点中水果对应的次数++
//bstreenode<string, int>* ret = counttree.find(str);
auto ret = counttree.find(str);
if (ret == counttree.end()) //没有找到
{
counttree.insert({ str, 1 });
}
else
{
ret->second++;
}
}
for (const auto& e : counttree)
{
cout << e.first << ":" << e.second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
map<string, int> counttree1; //第二种统计方法
for (const auto& str : arr)
{
counttree1[str]++;
}
for (const auto& e : counttree1)
{
cout << e.first << ":" << e.second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
📖6. 总结拓展
💧在实际中的练习与运用
这里推荐两个题目让大家练习一下,方便巩固set与map
前k个高频单词
两个数组的交集






发表评论