目录
1.jdk中类似lrucahe的数据结构linkedhashmap
一、什么是lru cache?
lru cache(least recently used的缩写,即最近最少使用,它是一种cache的替换算法。看cache替换算法这篇文章)是一种常见的缓存淘汰算法。用于在有限的缓存空间中管理数据对象。lru cache 的核心思想是基于时间局部性原理,即最近被访问的数据在未来可能会被再次访问。
注意:lru cache 应该更准确地归类为一种缓存淘汰算法,而非传统意义上的数据结构。尽管 lru cache 在实现时通常会利用数据结构(如双向链表和哈希表),但它本身更像是一种策略,用于管理缓存中的数据对象。
二、lru cache的实现
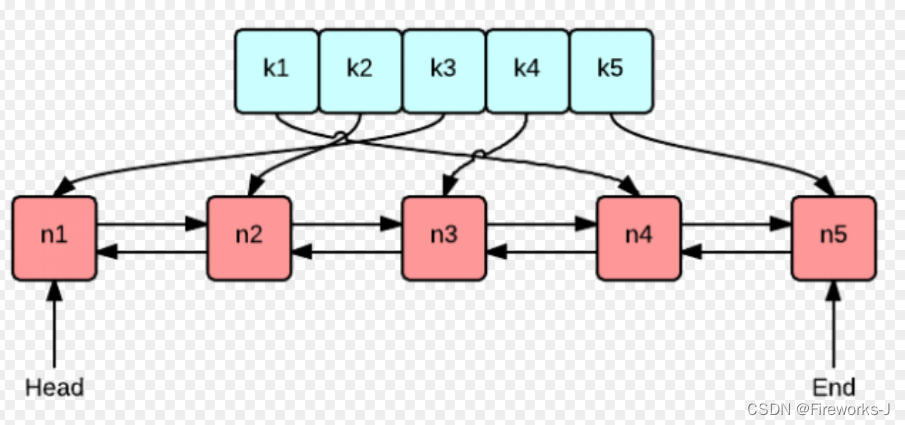
实现lru cache的方法和思路很多,但是要保持高效实现o(1)的put和get,那么使用双向链表和哈希表的搭配是最高效和经典的。
使用双向链表是因为双向链表可以实现任意位置o(1)的插入和删除,双向链表用于记录数据对象的访问顺序,每当一个数据对象被访问时,就将其移动到链表的头部。这样,链表头部的数据对象就是最近被访问的数据,而链表尾部的数据对象则是最久未被访问的数据。同时,使用哈希表能够以 o(1) 的时间复杂度进行数据对象的查找。
当缓存空间达到上限时,需要淘汰最久未被访问的数据对象。这时只需从链表尾部删除相应的数据对象,并在哈希表中删除对应的索引即可。
1.jdk中类似lrucahe的数据结构linkedhashmap
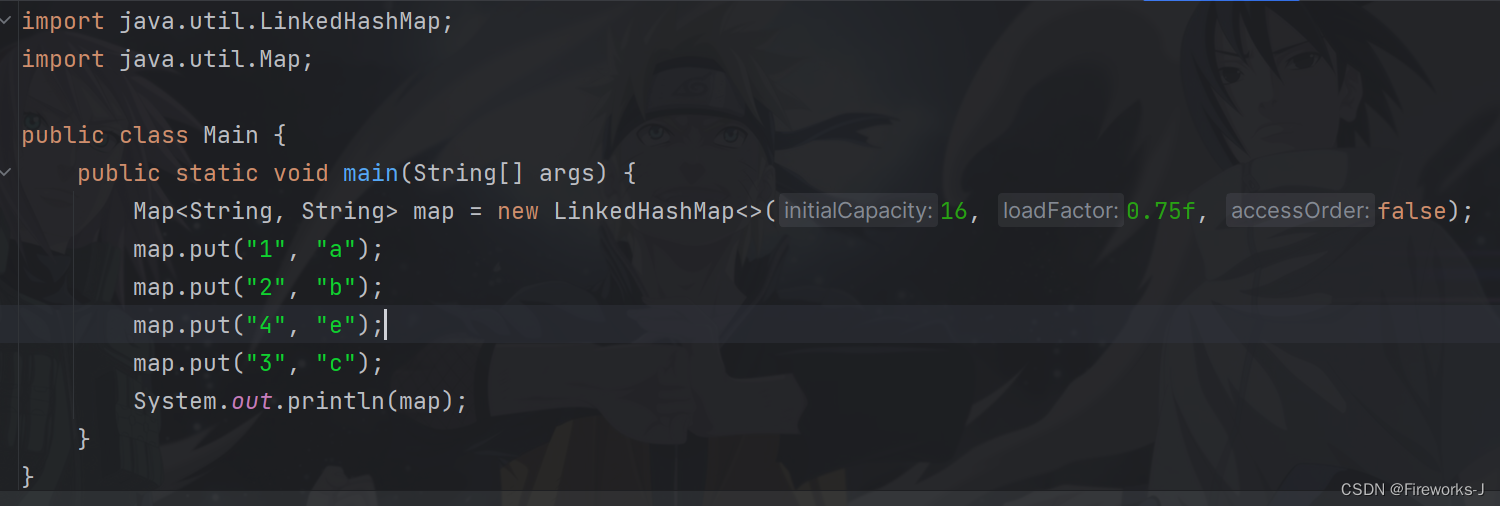
linkedhashmap中有一个这样的构造方法:

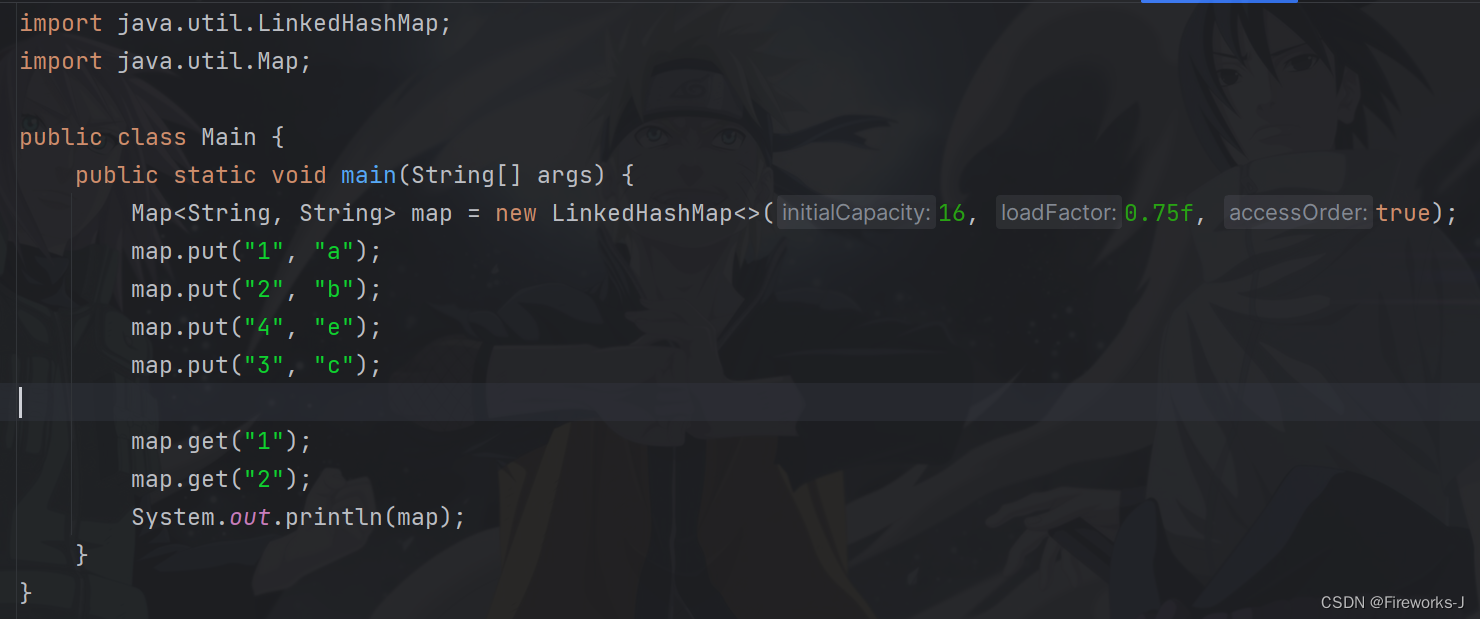
重点的accessorder:
accessorder 是一个 boolean 类型的参数,用于指定是否按照访问顺序来排序条目。当accessorder 被设置为 true 时,表示按照访问顺序排序条目;当 accessorder 被设置为 false 或未指定时(默认情况下),则按照插入顺序排序条目。
示例1:当accessorder的值为false的时候
输出结果:
import java.util.linkedhashmap;
import java.util.map;
public class lrucache extends linkedhashmap<integer, integer> {
private final int capacity;
public lrucache(int capacity) {
//accessorder设置为false时,会按照插入顺序进行排序,当accessorder为true时,会按照访问顺序
super(capacity, 0.75f, true);
this.capacity = capacity;
}
@override
public integer get(object key) {
//如果get不到,返回默认值-1
return super.getordefault(key, -1);
}
@override
public integer put(integer key, integer value) {
return super.put(key, value);
}
@override
protected boolean removeeldestentry(map.entry<integer, integer> eldest) {
//如果集合内元素个数超过capacity,会将最不常用的元素出队,并将新元素插在尾部
return size() > capacity;
}
}
测试:
当然在面试时这个做法肯定不会符合面试官的要求,更好的做法是自己实现一个双向链表。
2.自己实现双向链表
前面说到:
- 双向链表用于记录数据对象的访问顺序,每当一个数据对象被访问时,就将其移动到链表的头部。这样,链表头部的数据对象就是最近被访问的数据,而链表尾部的数据对象则是最久未被访问的数据。同时,使用哈希表能够以 o(1) 的时间复杂度进行数据对象的查找。
- 当缓存空间达到上限时,需要淘汰最久未被访问的数据对象。这时只需从链表尾部删除相应的数据对象,并在哈希表中删除对应的索引即可。
为方便测试,我重写了tostring方法,测试代码也包含在里面,根据需求删除即可。
import java.util.hashmap;
import java.util.map;
//双向链表 + 哈希表
public class mylrucache {
//双向链表的节点类
static class dlinkednode {
//键值对
int key;
int val;
dlinkednode next;
dlinkednode prev;
public dlinkednode() {
}
public dlinkednode(int key, int val) {
this.key = key;
this.val = val;
}
}
private map<integer, dlinkednode> cache; //缓存
private final int capacity;
private int size;
//虚拟的头尾节点(哨兵)
private dlinkednode head;
private dlinkednode tail;
public mylrucache(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
this.cache = new hashmap<>();
//连接虚拟头尾节点
this.head = new dlinkednode();
this.tail = new dlinkednode();
head.next = tail;
tail.prev = head;
}
//插入数据
public void put(int key, int value) {
//两种情况:元素是否存在
if (!cache.containskey(key)) {
//1.元素不存在
//1.1 新元素加到cache集合中
dlinkednode newnode = new dlinkednode(key, value);
cache.put(key, newnode);
//1.2 插到尾部
addlast(newnode);
size++;
//1.3 判断当前的元素个数是否超过容量
if (size > capacity) {
//1.4 删除第一个节点,即最近最久未使用
dlinkednode del = removefirst();
//同时需要把该元素从cache中删除
cache.remove(del.key);
size--;
}
} else {
//2.元素存在,修改链表的顺序,将该节点放到尾部(最近一次使用的)
dlinkednode node = cache.get(key);
//2.1 以新的值将该节点移动到尾部
node.val = value;
movelast(node);
}
}
//将节点移动到尾部
private void movelast(dlinkednode node) {
//1.删除当前节点
removenode(node);
//2.尾插到链表
addlast(node);
}
//删除节点
private void removenode(dlinkednode node) {
node.prev.next = node.next;
node.next.prev = node.prev;
}
//删除第一个节点
private dlinkednode removefirst() {
dlinkednode del = head.next;
head.next = del.next;
head.next.prev = head;
return del;
}
//尾插到链表
private void addlast(dlinkednode node) {
//连接最后一个节点和新的尾节点
tail.prev.next = node;
node.prev = tail.prev;
//连接新尾节点和傀儡尾节点
tail.prev = node;
node.next = tail;
}
//获取数据
public int get(int key) {
//1.cache集合中拿到这个节点
dlinkednode node = cache.get(key);
//2.判断是否有这个节点
if (node != null) {
//2.1 有该节点 将该节点移动到尾部(最近一次使用的)
movelast(node);
return node.val;
}
//2.2 没有该节点,返回-1
return -1;
}
//删除数据
public boolean remove(int key) {
//1.看缓存中存不存在
dlinkednode node = cache.get(key);
//2.不存在,直接返回
if (node == null) {
return false;
}
//3.存在
//3.1 删除链表的节点
removenode(node);
//3.2 删除cache集合的数据
cache.remove(key);
size--;
return true;
}
@override
public string tostring() {
stringbuilder sbu = new stringbuilder();
dlinkednode cur = head.next;
sbu.append("{");
while (cur != tail) {
if (cur.next != tail) {
sbu.append(cur.key).append("=").append(cur.val).append(", ");
} else {
sbu.append(cur.key).append("=").append(cur.val);
}
cur = cur.next;
}
sbu.append("}");
return sbu.tostring();
}
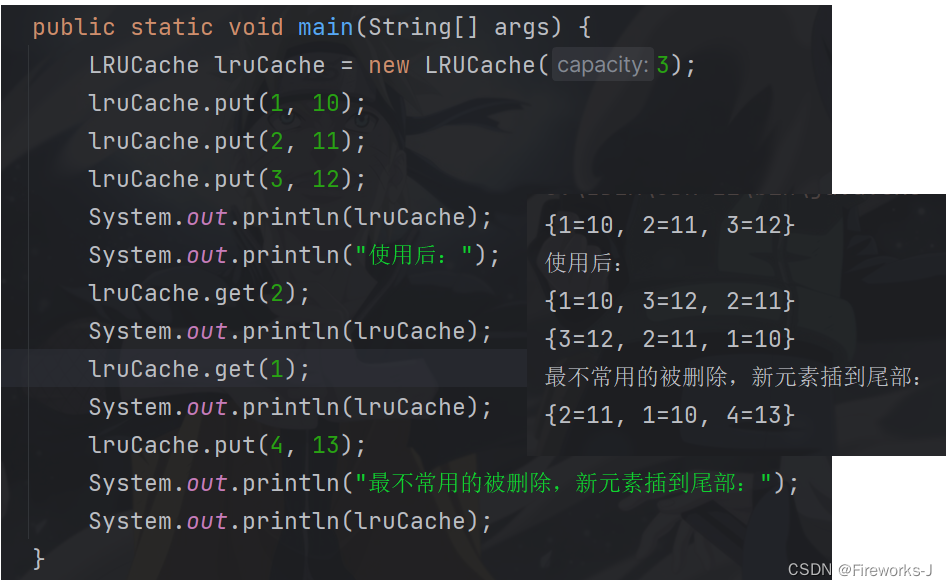
public static void main(string[] args) {
mylrucache lrucache = new mylrucache(3);
lrucache.put(1, 10);
lrucache.put(2, 11);
lrucache.put(3, 12);
system.out.println(lrucache);
system.out.println("使用后:");
lrucache.get(2);
system.out.println(lrucache);
lrucache.get(1);
system.out.println(lrucache);
lrucache.put(4, 13);
system.out.println("最不常用的被删除,新元素插到尾部:");
system.out.println(lrucache);
}
}
三、lru cache的oj
leetcode 热题100 链表专题的最后一题
146. lru 缓存 - 力扣(leetcode) https://leetcode.cn/problems/lru-cache/solutions/259678/lruhuan-cun-ji-zhi-by-leetcode-solution/?envtype=study-plan-v2&envid=top-100-liked前面两种实现中,mylrucache的get方法在获取不到数据时返回的是-1的原因就是根据这道题的要求做的,并且多写了一个remove方法。提交时将类名和构造方法改成原题默认的lrucache,且不要main方法即可。
https://leetcode.cn/problems/lru-cache/solutions/259678/lruhuan-cun-ji-zhi-by-leetcode-solution/?envtype=study-plan-v2&envid=top-100-liked前面两种实现中,mylrucache的get方法在获取不到数据时返回的是-1的原因就是根据这道题的要求做的,并且多写了一个remove方法。提交时将类名和构造方法改成原题默认的lrucache,且不要main方法即可。




发表评论