一、链表的回文结构

思路:
快慢指针找到链表的中间节点
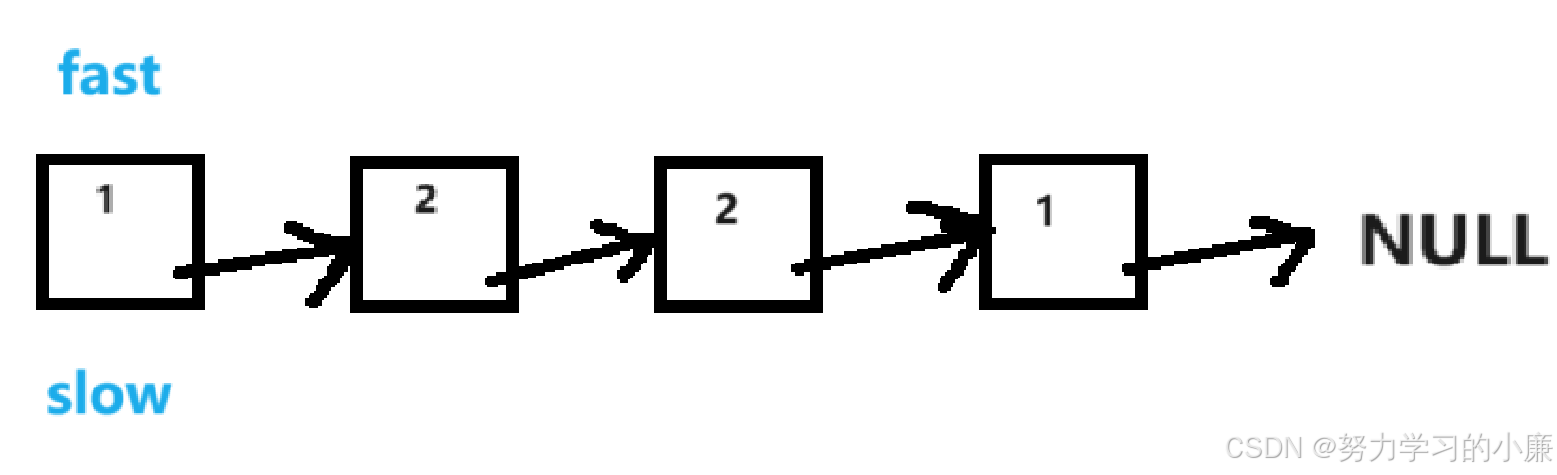
slow指针指向的就是中间节点

逆置链表后半部分

逆置链表后半部分

遍历链表前半部分和后半部分

如果left和right指向的数据不相等,就跳出循环,返回false;如果遍历到left或者right为null,数据都相等,那么链表具有回文结构,返回true。

这里如果是奇数个节点:
遍历结束后:
class palindromelist {
public:
//找链表中间节点
listnode* listmid(listnode* phead)
{
listnode* fast, *slow;
fast=slow=phead;
while(fast && fast->next)
{
slow=slow->next;
fast=fast->next;
}
return slow;
}
//逆置
listnode* reverse(listnode* phead)
{
listnode* l1,*l2,*l3;
l1=null;
l2=phead;
while(l2)
{
l3=l2->next;
l2->next=l1;
l1=l2;
l2=l3;
}
return l1;
}
bool chkpalindrome(listnode* a) {
// write code here
//找到链表中间节点
listnode* mid=listmid(a);
//逆置后半部分
listnode* phead = reverse(mid);
//比较
listnode* left, *right;
left=a;
right=phead;
while(right && left)
{
if(right->val!=left->val)
{
return false;
}
left=left->next;
right=right->next;
}
return true;
}
};二、相交链表

判断两个链表是否相交,如果相交就返回相交节点,如果链表不相交,那就返回null;
思路:
typedef struct listnode listnode;
struct listnode* getintersectionnode(struct listnode* heada,
struct listnode* headb) {
if (heada == null) {
return null;
}
if (headb == null) {
return null;
}
int sizea = 0, sizeb = 0;
listnode *l1, *l2;
l1 = heada;
l2 = headb;
while (l1) {
sizea++;
l1 = l1->next;
}
while (l2) {
sizeb++;
l2 = l2->next;
}
listnode* shortlist = heada;
listnode* longlist = headb;
int s = abs(sizea - sizeb);
if (sizea > sizeb) {
shortlist = headb;
longlist = heada;
}
while (s) {
s--;
longlist = longlist->next;
}
while (longlist && shortlist) {
if (longlist == shortlist) {
return longlist;
}
longlist = longlist->next;
shortlist = shortlist->next;
}
return null;
}三、环形链表1

判断 链表中是否存在环,如果存在就返回true,如果不存在就返回false;
思路:快慢指针
根据题目所给示例来分析一下:
首先定义两个指针 fast slow

fast向前走两步,slow向前走一步
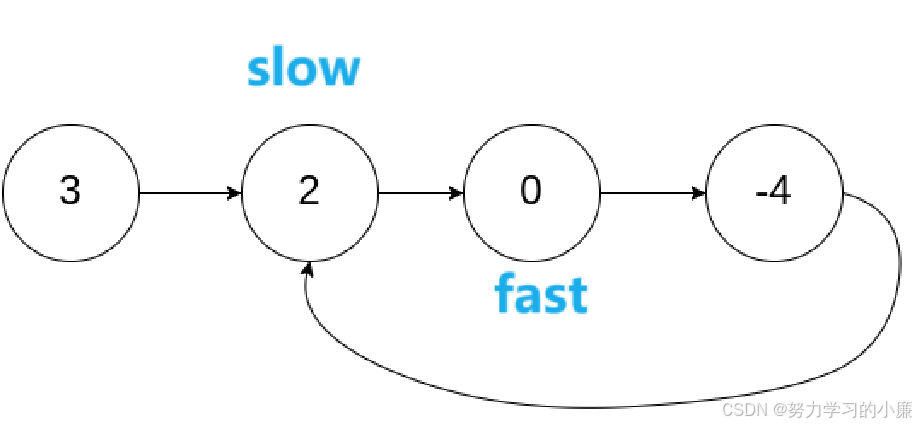
fast向前走两步,slow向前走一步

fast向前走两步,slow向前走一步

此时,fast和slow相遇,证明链表中存在环,返回true。
如果链表不存在环结构,遍历过程中fast或者fast->next指针会等于null,将这个作为结束条件即可。
typedef struct listnode listnode;
bool hascycle(struct listnode *head) {
listnode* fast, *slow;
fast=slow=head;
while(fast && fast->next)
{
fast=fast->next->next;
slow=slow->next;
if(slow == fast)
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}四、环形链表2

上面只是让我们判断链表是否带环,这道题让我们返回链表环的起始节点,如果不存在环就返回null。
思路:
根据题目的示例来分析:
先找到链表快慢指针的相遇节点:

定义两个指针从链表头部和相遇节点开始遍历链表

遍历链表直到两个指针相遇
两个指针相遇,此时指针指向的节点就是链表环的起始节点。
typedef struct listnode listnode;
listnode* hascycle(struct listnode *head) {
listnode* fast, *slow;
fast=slow=head;
while(fast && fast->next)
{
fast=fast->next->next;
slow=slow->next;
if(slow == fast)
{
return slow;
}
}
return null;
}
struct listnode *detectcycle(struct listnode *head) {
//找到快慢指针相遇节点
listnode* pos=hascycle(head);
if(pos==null)
{
return null;
}
//从头结点和相遇节点开始遍历
listnode* ptail=head;
while(1)
{
if(pos==ptail)
{
return pos;
}
pos=pos->next;
ptail=ptail->next;
}
}五、随机链表的复制

这里题目上提到了一个深拷贝
 思路:
思路:
深拷贝原链表

拷贝过后
给random指针赋值

断开新链表和原链表之前的连接

这样就深拷贝了原链表,返回新链表的头节点即可。
typedef struct node node;
// 创建节点
node* buynode(int x) {
node* newnode = (node*)malloc(sizeof(node));
newnode->next = newnode->random = null;
newnode->val = x;
return newnode;
}
// 深拷贝
void copylist(node** head) {
node* ptail = *head;
node* next = null;
while (ptail) {
next = ptail->next;
node* newnode = buynode(ptail->val);
newnode->next = next;
ptail->next = newnode;
ptail = next;
}
}
void connect(node** head) {
node* ptail = *head;
node* copy = (*head)->next;
while (ptail) {
copy = ptail->next;
if (ptail->random)
copy->random = ptail->random->next;
ptail = copy->next;
}
}
struct node* copyrandomlist(struct node* head) {
if (head == null)
{
return null;
}
// 深拷贝原链表
copylist(&head);
// 连接random指针
connect(&head);
// 断开链表
node* ptail = head;
node* newhead = head->next;
node* copy = head->next;
while (ptail->next->next) {
ptail=copy->next;
copy->next = copy->next->next;
copy = copy->next;
}
return newhead;
}



发表评论