文章目录
1.图的基本概念
-
图的定义
-
有向图
-
无向图
-
简单图、多重图
-
顶点的度、入度、出度
-
顶点-顶点的关系描述
-
连通图、强连通图
-
子图、生成子图
-
连通分量
-
强连通分量
-
生成树
-
生成森林
-
边的权、带权图
-
特殊形态的图
-
重点小结
2.图的存储
2.1 邻接矩阵
-
不带权值的邻接矩阵法
-
求度
-
存储带权图的邻接矩阵法
-
邻接矩阵法的性能分析
-
邻接矩阵的性质
2.2 邻接表
-
定义——顺序+链式存储
-
性能分析
-
注:邻接矩阵表示法是唯一的,但图的邻接表表示法不唯一(∵孩子的链接顺序不唯一)
-
邻接表和邻接矩阵的对比
2.3 十字链表
-
只存储有向图
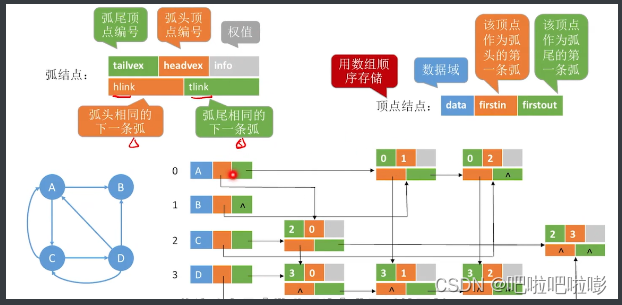
-
空间复杂度: o ( ∣ v ∣ + ∣ e ∣ ) o(|v|+|e|) o(∣v∣+∣e∣)
-
如何找到指定顶点的所有出边?——顺着绿色路线
如何找到指定顶点的所有入边?——顺着橙色路线
-
好处:
解决了邻接矩阵空间复杂度太高的问题,也解决邻接表找入边不方便必须遍历的问题。
2.4 邻接多重表
-
只存储无向图
可方便删除结点和边
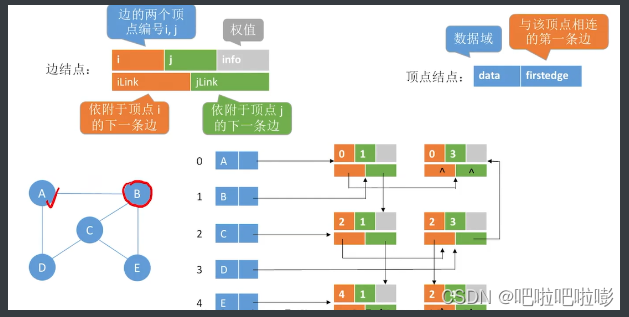
-
空间复杂度: o ( ∣ v ∣ + ∣ e ∣ ) o(|v|+|e|) o(∣v∣+∣e∣)
-
好处:
解决了邻接矩阵空间复杂度太高的问题,也解决邻接表删除边和结点不方便的问题。
2.5 四种存储方式的对比
| 邻接矩阵 | 邻接表 | 十字链表 | 邻接多重表 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 空间复杂度 | $o( | v | ^2)$ | 无向图$o( |
| 适用于 | 稠密图 | 稀疏图 | 只存有向图 | 只存无向图 |
| 表示方法 | 唯一 | 不唯一 | 不唯一 | 不唯一 |
| 计算度/出度/入度 | 必须遍历对应行或列 | 计算有向图的度和入度不方便,其余方便。 | ||
| 找相邻的边 | 必须遍历对应行和列 | 找有向图入边不方便,其余方便 | 很方便 | 很方便 |
| 删除边和顶点 | 删除边很方便,删除顶点需要大量移动数据 | 都不方便 | 很方便 | 很方便 |
3.图的基本操作
3.1 基本操作
| 函数名 | 函数作用 | 邻接矩阵 | 邻接表 |
|---|---|---|---|
adjacent(g,x,y) | 判断图g是否存在边<x,y>或(x,y) |
o
(
1
)
o(1)
o(1) 很方便,只需判断g[x][y]是否为0。 | o ( 1 ) o(1) o(1)~ o ( v ) o(v) o(v) 要遍历所有边。 |
neighbors(g,x) | 列出图g中与结点x相邻的边 | $o( | v |
insertvertex(g,x) | 在图g中插入顶点x | o ( 1 ) o(1) o(1) 在矩阵末尾插入信息 | o ( 1 ) o(1) o(1) 在表末尾插入信息 |
deletevertex(g,x) | 从图g中删除顶点x | $o( | v |
addedge(g,x,y) | 若无向边(x,y)或有向边<x,y>不存在,则向图g中添加该边 | o ( 1 ) o(1) o(1) 直接在矩阵中写1 | o ( 1 ) o(1) o(1) 用头插法把新边的信息插入到链表中 |
removeedge(g,x,y) | 若(x,y)或<x,y>存在,则删除该边 | o ( 1 ) o(1) o(1) 直接在矩阵中写0 | o ( 1 ) o(1) o(1)~$o( |
firstneighbor(g,x) | 求图g中顶点x的第一个邻接点。有则返回顶点号,无则返回-1。 | o ( 1 ) o(1) o(1)~$o( | v |
nextneighbor(g,x,y) | 假设图g中顶点y是顶点x的一个邻接点,返回除y之外顶点x的下一个邻接点顶点号,如果没有则返回-1 | o ( 1 ) o(1) o(1)~$o( | v |
get_edge_value(g,x,y) | 获取权值 | o ( 1 ) o(1) o(1) | o ( 1 ) o(1) o(1)~$o( |
set_edge_value(g,x,y) | 设置权值 | o ( 1 ) o(1) o(1) | o ( 1 ) o(1) o(1)~$o( |
3.2 邻接表代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define maxvertexnum 100 // 最大顶点数定义为100
#define inf 9999 // 代表无穷大的定义为9999
// 边结点的定义
typedef struct arcnode {
int adjvex; // 边指向哪个结点
int weight; // 边权值
struct arcnode *next; // 指向下一条弧的指针
} arcnode;
// 顶点结点的定义
typedef struct vnode {
int data; // 顶点信息
arcnode *first; // 第一条边
} vnode, adjlist[maxvertexnum]; // 邻接表的定义
// 图的定义
typedef struct {
adjlist vertices; // 顶点数组
int vexnum, arcnum; // 顶点数和边数
} algraph;
// 初始化邻接表图
void initalgraph(algraph *g, int vexnum, int arcnum) {
g->vexnum = vexnum; // 初始化顶点数
g->arcnum = arcnum; // 初始化边数
for (int i = 0; i < vexnum; i++) { // 遍历顶点数组
g->vertices[i].data = i; // 顶点信息为i
g->vertices[i].first = null; // 第一条边为空
}
}
// 添加有向图的边
void addedgedirectedalgraph(algraph *g, int v1, int v2, int weight) {
arcnode *arcnode = (arcnode *)malloc(sizeof(arcnode)); // 分配边结点内存
arcnode->adjvex = v2; // 边指向v2
arcnode->weight = weight; // 边权值为weight
arcnode->next = g->vertices[v1].first; // 将边插入到顶点v1的边链表中
g->vertices[v1].first = arcnode;
}
// 添加无向图的边
void addedgeundirectedalgraph(algraph *g, int v1, int v2, int weight) {
// 添加v1到v2的边
arcnode *arcnode1 = (arcnode *)malloc(sizeof(arcnode)); // 分配边结点内存
arcnode1->adjvex = v2; // 边指向v2
arcnode1->weight = weight; // 边权值为weight
arcnode1->next = g->vertices[v1].first; // 将边插入到顶点v1的边链表中
g->vertices[v1].first = arcnode1;
// 添加v2到v1的边
arcnode *arcnode2 = (arcnode *)malloc(sizeof(arcnode)); // 分配边结点内存
arcnode2->adjvex = v1; // 边指向v1
arcnode2->weight = weight; // 边权值为weight
arcnode2->next = g->vertices[v2].first; // 将边插入到顶点v2的边链表中
g->vertices[v2].first = arcnode2;
}
// 打印邻接表图
void printalgraph(algraph g) {
for (int i = 0; i < g.vexnum; i++) { // 遍历顶点数组
printf("%d -> ", g.vertices[i].data); // 打印顶点信息
arcnode *p = g.vertices[i].first; // 获取顶点i的第一条边
while (p != null) { // 遍历顶点i的边链表
printf("(%d, %d) ", p->adjvex, p->weight); // 打印边的信息
p = p->next; // 指向下一条边
}
printf("\n");
}
}
// 判断两个顶点之间是否有边相连
int adjacent(algraph g, int x, int y) {
arcnode *p = g.vertices[x].first; // 获取顶点x的第一条边
while (p != null) { // 遍历顶点x的边链表
if (p->adjvex == y) // 如果边的另一端是y
return 1; // 返回1,表示存在边<x, y>
p = p->next; // 指向下一条边
}
return 0; // 遍历完所有边仍未找到,返回0,表示不存在边<x, y>
}
// 打印顶点x的邻居顶点
void neighbors(algraph g, int x) {
arcnode *p = g.vertices[x].first; // 获取顶点x的第一条边
printf("neighbors of vertex %d: ", x); // 打印提示信息
while (p != null) { // 遍历顶点x的边链表
printf("%d ", p->adjvex); // 打印邻居顶点
p = p->next; // 指向下一条边
}
printf("\n");
}
// 插入顶点
void insertvertex(algraph *g, int x) {
g->vertices[g->vexnum].data = x; // 在最后一个位置插入顶点x的信息
g->vertices[g->vexnum].first = null; // 边链表为空
g->vexnum++; // 顶点数加一
}
// 删除顶点
void deletevertex(algraph *g, int x) {
for (int i = 0; i < g->vexnum; i++) { // 遍历顶点数组
arcnode *p = g->vertices[i].first; // 获取顶点i的第一条边
arcnode *pre = null; // 初始化前一个边结点为null
while (p != null) { // 遍历顶点i的边链表
if (p->adjvex == x) { // 如果边的另一端是x
if (pre == null) // 如果是第一条边
g->vertices[i].first = p->next; // 将顶点i的第一条边指向下一条边
else
pre->next = p->next; // 将前一条边的next指针指向下一条边
free(p); // 释放删除的边结点的内存
break; // 结束循环
}
pre = p; // 更新前一个边结点
p = p->next; // 指向下一条边
}
}
// 删除顶点x
for (int i = x; i < g->vexnum - 1; i++) // 从顶点x开始,将后面的顶点信息依次往前移动
g->vertices[i] = g->vertices[i + 1]; // 将后一个顶点信息覆盖前一个顶点信息
g->vexnum--; // 顶点数减一
}
// 添加边
void addedge(algraph *g, int x, int y, int weight) {
if (!adjacent(*g, x, y)) { // 如果两个顶点之间不存在边相连
addedgeundirectedalgraph(g, x, y, weight); // 添加边<x, y>
}
}
// 删除边
void removeedge(algraph *g, int x, int y) {
if (adjacent(*g, x, y)) { // 如果两个顶点之间存在边相连
arcnode *p = g->vertices[x].first; // 获取顶点x的第一条边
arcnode *pre = null; // 初始化前一个边结点为null
while (p != null) { // 遍历顶点x的边链表
if (p->adjvex == y) { // 如果边的另一端是y
if (pre == null) // 如果是第一条边
g->vertices[x].first = p->next; // 将顶点x的第一条边指向下一条边
else
pre->next = p->next; // 将前一条边的next指针指向下一条边
free(p); // 释放删除的边结点的内存
break; // 结束循环
}
pre = p; // 更新前一个边结点
p = p->next; // 指向下一条边
}
// 如果是无向图,还需要删除另一个方向的边
if (g->vertices[y].first != null) { // 如果顶点y有边相连
p = g->vertices[y].first; // 获取顶点y的第一条边
pre = null; // 初始化前一个边结点为null
while (p != null) { // 遍历顶点y的边链表
if (p->adjvex == x) { // 如果边的另一端是x
if (pre == null) // 如果是第一条边
g->vertices[y].first = p->next; // 将顶点y的第一条边指向下一条边
else
pre->next = p->next; // 将前一条边的next指针指向下一条边
free(p); // 释放删除的边结点的内存
break; // 结束循环
}
pre = p; // 更新前一个边结点
p = p->next; // 指向下一条边
}
}
}
}
// 获取顶点x的第一个邻居顶点
int firstneighbor(algraph g, int x) {
if (g.vertices[x].first != null) // 如果顶点x有边相连
return g.vertices[x].first->adjvex; // 返回第一个邻居顶点的信息
else
return -1; // 否则返回-1,表示没有邻居顶点
}
// 获取顶点x的邻居顶点y的下一个邻居顶点
int nextneighbor(algraph g, int x, int y) {
arcnode *p = g.vertices[x].first; // 获取顶点x的第一条边
while (p != null && p->adjvex != y) // 遍历顶点x的边链表,直到找到邻居顶点y
p = p->next; // 指向下一条边
if (p != null && p->next != null) // 如果邻居顶点y后面还有邻居顶点
return p->next->adjvex; // 返回邻居顶点y的下一个邻居顶点的信息
else
return -1; // 否则返回-1,表示没有下一个邻居顶点
}
// 获取边<x, y>的权值
int get_edge_value(algraph g, int x, int y) {
arcnode *p = g.vertices[x].first; // 获取顶点x的第一条边
while (p != null) { // 遍历顶点x的边链表
if (p->adjvex == y) // 如果边的另一端是y
return p->weight; // 返回边的权值
p = p->next; // 指向下一条边
}
return inf; // 遍历完所有边仍未找到,返回无穷大,表示不存在边<x, y>
}
// 设置边<x, y>的权值为v
void set_edge_value(algraph *g, int x, int y, int v) {
arcnode *p = g->vertices[x].first; // 获取顶点x的第一条边
while (p != null) { // 遍历顶点x的边链表
if (p->adjvex == y) { // 如果边的另一端是y
p->weight = v; // 设置边的权值为v
break; // 结束循环
}
p = p->next; // 指向下一条边
}
}
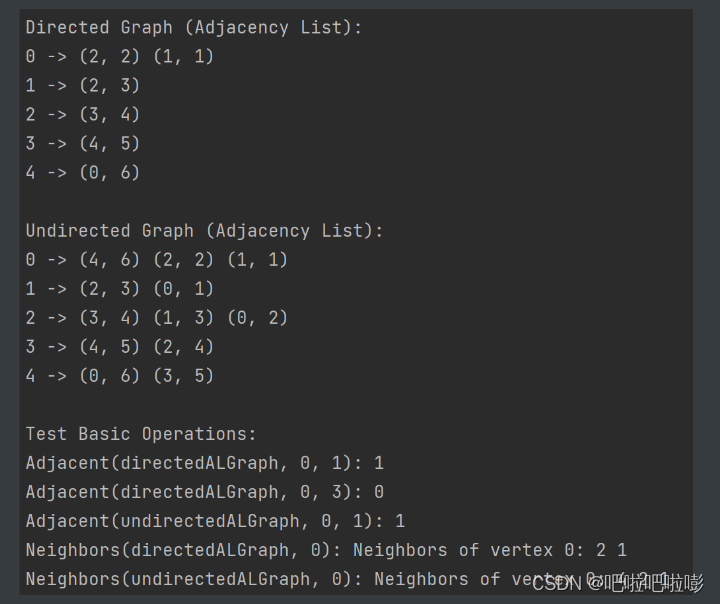
int main() {
// 创建有向图的邻接表表示
algraph directedalgraph; // 定义有向图
initalgraph(&directedalgraph, 5, 6); // 初始化有向图
addedgedirectedalgraph(&directedalgraph, 0, 1, 1); // 添加边
addedgedirectedalgraph(&directedalgraph, 0, 2, 2); // 添加边
addedgedirectedalgraph(&directedalgraph, 1, 2, 3); // 添加边
addedgedirectedalgraph(&directedalgraph, 2, 3, 4); // 添加边
addedgedirectedalgraph(&directedalgraph, 3, 4, 5); // 添加边
addedgedirectedalgraph(&directedalgraph, 4, 0, 6); // 添加边
// 创建无向图的邻接表表示
algraph undirectedalgraph; // 定义无向图
initalgraph(&undirectedalgraph, 5, 6); // 初始化无向图
addedgeundirectedalgraph(&undirectedalgraph, 0, 1, 1); // 添加边
addedgeundirectedalgraph(&undirectedalgraph, 0, 2, 2); // 添加边
addedgeundirectedalgraph(&undirectedalgraph, 1, 2, 3); // 添加边
addedgeundirectedalgraph(&undirectedalgraph, 2, 3, 4); // 添加边
addedgeundirectedalgraph(&undirectedalgraph, 3, 4, 5); // 添加边
addedgeundirectedalgraph(&undirectedalgraph, 4, 0, 6); // 添加边
printf("\ndirected graph (adjacency list):\n");
printalgraph(directedalgraph); // 打印有向图的邻接表表示
printf("\nundirected graph (adjacency list):\n");
printalgraph(undirectedalgraph); // 打印无向图的邻接表表示
// 测试基本操作
printf("\ntest basic operations:\n");
printf("adjacent(directedalgraph, 0, 1): %d\n", adjacent(directedalgraph, 0, 1)); // 测试两个顶点之间是否有边相连
printf("adjacent(directedalgraph, 0, 3): %d\n", adjacent(directedalgraph, 0, 3)); // 测试两个顶点之间是否有边相连
printf("adjacent(undirectedalgraph, 0, 1): %d\n", adjacent(undirectedalgraph, 0, 1)); // 测试两个顶点之间是否有边相连
printf("neighbors(directedalgraph, 0): ");
neighbors(directedalgraph, 0); // 打印顶点0的邻居顶点
printf("neighbors(undirectedalgraph, 0): ");
neighbors(undirectedalgraph, 0); // 打印顶点0的邻居顶点
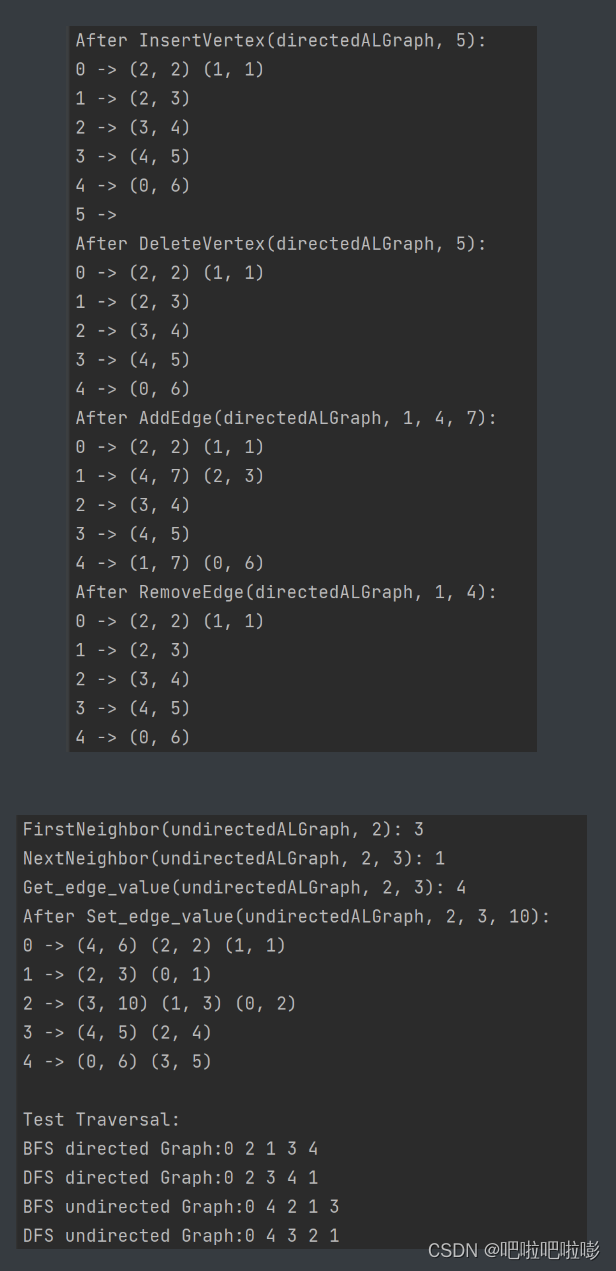
insertvertex(&directedalgraph, 5); // 插入顶点5
printf("after insertvertex(directedalgraph, 5):\n");
printalgraph(directedalgraph); // 打印有向图的邻接表表示
deletevertex(&directedalgraph, 5); // 删除顶点5
printf("after deletevertex(directedalgraph, 5):\n");
printalgraph(directedalgraph); // 打印有向图的邻接表表示
addedge(&directedalgraph, 1, 4, 7); // 添加边
printf("after addedge(directedalgraph, 1, 4, 7):\n");
printalgraph(directedalgraph); // 打印有向图的邻接表表示
removeedge(&directedalgraph, 1, 4); // 删除边
printf("after removeedge(directedalgraph, 1, 4):\n");
printalgraph(directedalgraph); // 打印有向图的邻接表表示
printf("firstneighbor(undirectedalgraph, 2): %d\n", firstneighbor(undirectedalgraph, 2)); // 获取顶点2的第一个邻居顶点
printf("nextneighbor(undirectedalgraph, 2, 3): %d\n", nextneighbor(undirectedalgraph, 2, 3)); // 获取顶点2的邻居顶点3的下一个邻居顶点
printf("get_edge_value(undirectedalgraph, 2, 3): %d\n", get_edge_value(undirectedalgraph, 2, 3)); // 获取边
set_edge_value(&undirectedalgraph, 2, 3, 10);
printf("after set_edge_value(undirectedalgraph, 2, 3, 10):\n");
printalgraph(undirectedalgraph);
return 0;
}
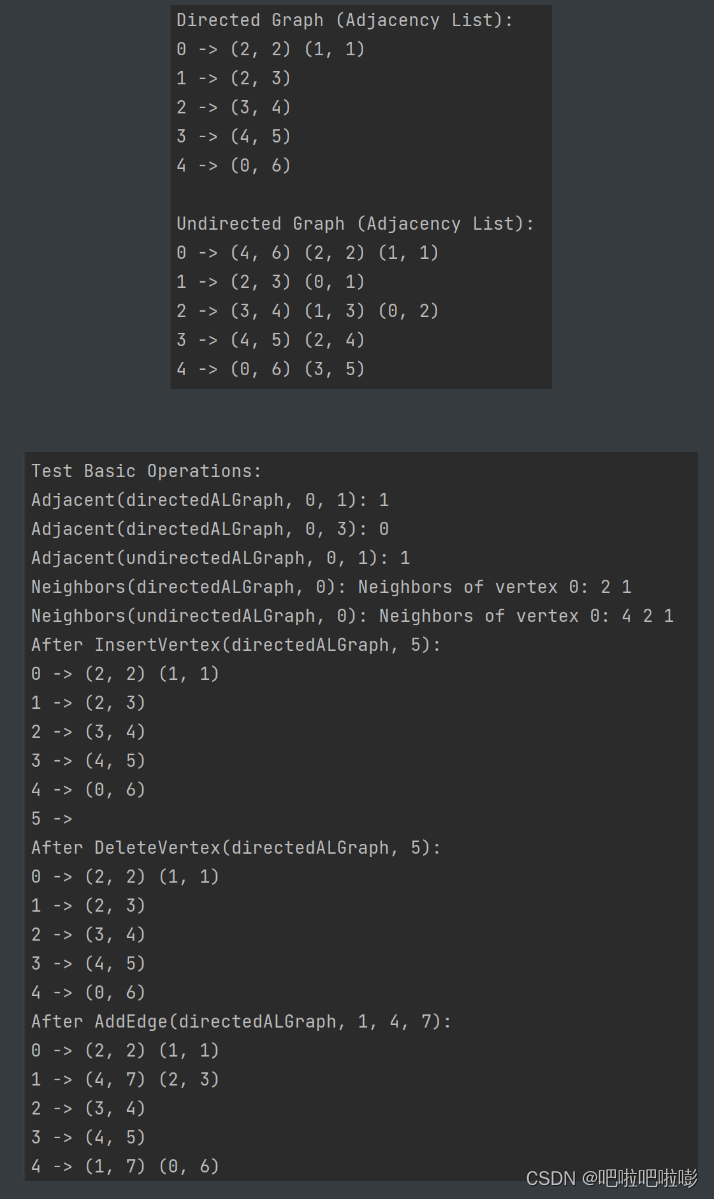

3.3 邻接矩阵代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define maxvertexnum 100
#define infinity 9999 // 代表无穷大
// 邻接矩阵存储有向图和无向图
typedef struct {
char vex[maxvertexnum]; // 顶点表
int edge[maxvertexnum][maxvertexnum]; // 邻接矩阵,边表
int vexnum, arcnum; // 图当前顶点数/弧数
int weight[maxvertexnum][maxvertexnum]; // 权值
} mgraph;
// 初始化邻接矩阵图
void initmgraph(mgraph *g, int vexnum, int arcnum) {
g->vexnum = vexnum;
g->arcnum = arcnum;
for (int i = 0; i < vexnum; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < vexnum; j++) {
g->edge[i][j] = 0; // 初始化边为0,表示无连接
g->weight[i][j] = infinity; // 初始化权值为无穷大
}
}
}
// 添加有向图邻接矩阵的边
void addedgedirectedmgraph(mgraph *g, int v1, int v2, int weight) {
g->edge[v1][v2] = 1; // 有连接的边置为1
g->weight[v1][v2] = weight; // 设置权值
}
// 添加无向图邻接矩阵的边
void addedgeundirectedmgraph(mgraph *g, int v1, int v2, int weight) {
g->edge[v1][v2] = 1; // 有连接的边置为1
g->edge[v2][v1] = 1; // 对称位置也置为1
g->weight[v1][v2] = weight; // 设置权值
g->weight[v2][v1] = weight; // 对称位置设置权值
}
// 打印邻接矩阵图
void printmgraph(mgraph g) {
for (int i = 0; i < g.vexnum; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < g.vexnum; j++) {
printf("%d ", g.edge[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
}
// 判断图g是否存在边<x, y>或(x, y),并返回权值
int adjacent(mgraph g, int x, int y) {
if (g.edge[x][y] == 1 || g.edge[y][x] == 1) {
return g.weight[x][y]; // 返回边的权值
} else {
return infinity; // 不存在边<x, y>或(x, y),返回无穷大
}
}
// 列出图g中与结点x邻接的边
void neighbors(mgraph g, int x) {
printf("neighbors of vertex %d: ", x);
for (int i = 0; i < g.vexnum; i++) {
if (g.edge[x][i] == 1) {
printf("%d ", i);
}
}
printf("\n");
}
// 在图g中插入顶点x
void insertvertex(mgraph *g, int x) {
if (g->vexnum < maxvertexnum) {
g->vex[g->vexnum] = x;
g->vexnum++;
} else {
printf("exceeding maximum vertex number!\n");
}
}
// 从图g中删除顶点x
void deletevertex(mgraph *g, int x) {
if (x >= g->vexnum) {
printf("vertex does not exist!\n");
return;
}
// 删除顶点x的边
for (int i = 0; i < g->vexnum; i++) {
g->edge[i][x] = 0;
g->edge[x][i] = 0;
g->weight[i][x] = infinity; // 删除边同时将权值设置为无穷大
g->weight[x][i] = infinity;
}
// 移动顶点表,覆盖被删除的顶点
for (int i = x; i < g->vexnum - 1; i++) {
g->vex[i] = g->vex[i + 1];
}
g->vexnum--;
}
// 若无向边(x, y)或有向边<x, y>不存在,则向图g中添加该边
void addedge(mgraph *g, int x, int y, int weight) {
if (g->edge[x][y] == 0) {
g->edge[x][y] = 1;
g->edge[y][x] = 1; // 对于无向图,要同时设置对称位置
g->weight[x][y] = weight;
g->weight[y][x] = weight; // 对称位置设置权值
}
}
// 若无向边(x, y)或有向边<x, y>存在,则从图g中删除该边
void removeedge(mgraph *g, int x, int y) {
if (g->edge[x][y] == 1) {
g->edge[x][y] = 0;
g->edge[y][x] = 0; // 对于无向图,要同时设置对称位置
g->weight[x][y] = infinity;
g->weight[y][x] = infinity; // 对称位置设置权值为无穷大
}
}
// 求图g中顶点x的第一个邻接点,若有则返回顶点号,若x没有邻接点或图中不存在x,则返回-1
int firstneighbor(mgraph g, int x) {
for (int i = 0; i < g.vexnum; i++) {
if (g.edge[x][i] == 1) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
// 返回除y之外顶点x的下一个邻接点的顶点号,若y是x的最后一个邻接点,则返回-1
int nextneighbor(mgraph g, int x, int y) {
for (int i = y + 1; i < g.vexnum; i++) {
if (g.edge[x][i] == 1) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
// 获取图g中边(x, y)或<x, y>对应的权值
int get_edge_value(mgraph g, int x, int y) {
return g.weight[x][y];
}
// 设置图g中边(x, y)或<x, y>对应的权值为v
void set_edge_value(mgraph *g, int x, int y, int v) {
g->weight[x][y] = v;
g->weight[y][x] = v; // 对称位置设置权值
}
int main() {
// 创建有向图的邻接矩阵表示
mgraph directedmgraph;
initmgraph(&directedmgraph, 5, 6);
addedgedirectedmgraph(&directedmgraph, 0, 1, 2);
addedgedirectedmgraph(&directedmgraph, 0, 2, 3);
addedgedirectedmgraph(&directedmgraph, 1, 2, 4);
addedgedirectedmgraph(&directedmgraph, 2, 3, 5);
addedgedirectedmgraph(&directedmgraph, 3, 4, 6);
addedgedirectedmgraph(&directedmgraph, 4, 0, 7);
// 创建无向图的邻接矩阵表示
mgraph undirectedmgraph;
initmgraph(&undirectedmgraph, 5, 6);
addedgeundirectedmgraph(&undirectedmgraph, 0, 1, 2);
addedgeundirectedmgraph(&undirectedmgraph, 0, 2, 3);
addedgeundirectedmgraph(&undirectedmgraph, 1, 2, 4);
addedgeundirectedmgraph(&undirectedmgraph, 2, 3, 5);
addedgeundirectedmgraph(&undirectedmgraph, 3, 4, 6);
addedgeundirectedmgraph(&undirectedmgraph, 4, 0, 7);
// 打印结果
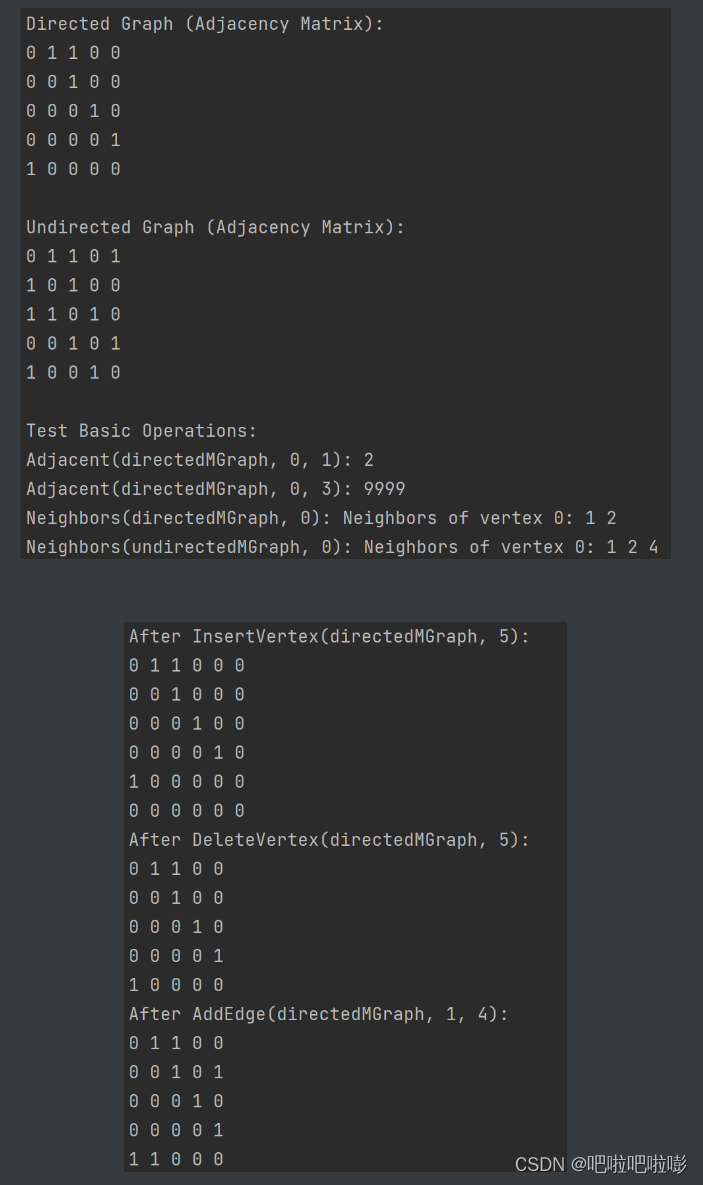
printf("directed graph (adjacency matrix):\n");
printmgraph(directedmgraph);
printf("\nundirected graph (adjacency matrix):\n");
printmgraph(undirectedmgraph);
// 测试基本操作
printf("\ntest basic operations:\n");
printf("adjacent(directedmgraph, 0, 1): %d\n", adjacent(directedmgraph, 0, 1));
printf("adjacent(directedmgraph, 0, 3): %d\n", adjacent(directedmgraph, 0, 3));
printf("neighbors(directedmgraph, 0): ");
neighbors(directedmgraph, 0);
printf("neighbors(undirectedmgraph, 0): ");
neighbors(undirectedmgraph, 0);
insertvertex(&directedmgraph, 5);
printf("after insertvertex(directedmgraph, 5):\n");
printmgraph(directedmgraph);
deletevertex(&directedmgraph, 5);
printf("after deletevertex(directedmgraph, 5):\n");
printmgraph(directedmgraph);
addedge(&directedmgraph, 1, 4, 8);
printf("after addedge(directedmgraph, 1, 4):\n");
printmgraph(directedmgraph);
removeedge(&directedmgraph, 1, 4);
printf("after removeedge(directedmgraph, 1, 4):\n");
printmgraph(directedmgraph);
printf("firstneighbor(undirectedmgraph, 2): %d\n", firstneighbor(undirectedmgraph, 2));
printf("nextneighbor(undirectedmgraph, 2, 3): %d\n", nextneighbor(undirectedmgraph, 2, 3));
printf("get_edge_value(undirectedmgraph, 2, 3): %d\n", get_edge_value(undirectedmgraph, 2, 3));
set_edge_value(&undirectedmgraph, 2, 3, 10);
printf("after set_edge_value(undirectedmgraph, 2, 3, 10):\n");
printmgraph(undirectedmgraph);
return 0;
}
4.图的遍历
4.1 广度优先遍历
-
树的广度优先遍历==层序遍历
-
图的广度优先遍历(bfs)
bool visited[max_vertex_num];//访问标记数组
//对图g进行广度优先遍历
void bfstraverse(graph g){
int i;
for(i=0;i<g.vexnum;++i)
visited[i]=false; //访问标记数组初始化
initqueue(q); //初始化辅助队列
//从0号结点开始遍历
for(i=0;i<g.vexnum;++i){
if(!visited[i]) //对每个连通分量调用一次bfs
bfs(g,i); //vi未被访问,则从vi开始bfs
}
}
//广度优先遍历
void bfs(graph g,int v){ //从顶点v出发,广度优先遍历图g
visit(v); //访问初始顶点v
visited[v]=true; //对v做已访问标记
enqueue(q,v); //顶点v入队列q
while(!isempty(q)){
dequeue(q,v); //顶点v出队列
for(w=firstneighbor(g,v);w>=0;w=nextneighbor(g,v,w)){
//检测v所有邻接点
if(!visited[w]){ //w为v的尚未访问的邻接顶点
visited(w); //访问w
visited[w]=true; //标记w已被访问
enqueue(q,w); //顶点w入队
}
}
}
}
-
复杂度分析
-
广度优先生成树/森林
4.2 深度优先遍历
-
树的深度优先遍历 相当于树的先根遍历
-
图的深度优先遍历
bool visited[max_vertex_num]; //访问标记数组
void dfstraverse(graph g){
for(v=0;v<g.vexnum;++v){
visited[v]=false;
}
for(v=0;v<g.vexnum;++v){ //从第0个结点开始遍历
if(!visited[v])
dfs(g,v);
}
}
void dfs(graph g,int v){
visit(v); //访问顶点v
visited[v]=true; //设已访问标记
for(w=firstneighbor(g,v);w>=0;w=nextneighbor(g,v,w)){
if(!visited[w]){
dfs(g,w);
}
}
}
-
空间复杂度:
-
时间复杂度=访问各结点所需时间+探索各条边所需的时间
-
深度优先生成树/森林
4.3 图的遍历与图的连通性
-
对无向图进行bfs/dfs遍历
-
对有向图进行bfs/dfs遍历
*完整代码 邻接矩阵
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define maxvertexnum 100
#define infinity 9999 // 代表无穷大
// 邻接矩阵存储有向图和无向图
typedef struct {
char vex[maxvertexnum]; // 顶点表
int edge[maxvertexnum][maxvertexnum]; // 邻接矩阵,边表
int vexnum, arcnum; // 图当前顶点数/弧数
int weight[maxvertexnum][maxvertexnum]; // 权值
} mgraph;
// 初始化邻接矩阵图
void initmgraph(mgraph *g, int vexnum, int arcnum) {
g->vexnum = vexnum;
g->arcnum = arcnum;
for (int i = 0; i < vexnum; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < vexnum; j++) {
g->edge[i][j] = 0; // 初始化边为0,表示无连接
g->weight[i][j] = infinity; // 初始化权值为无穷大
}
}
}
// 添加有向图邻接矩阵的边
void addedgedirectedmgraph(mgraph *g, int v1, int v2, int weight) {
g->edge[v1][v2] = 1; // 有连接的边置为1
g->weight[v1][v2] = weight; // 设置权值
}
// 添加无向图邻接矩阵的边
void addedgeundirectedmgraph(mgraph *g, int v1, int v2, int weight) {
g->edge[v1][v2] = 1; // 有连接的边置为1
g->edge[v2][v1] = 1; // 对称位置也置为1
g->weight[v1][v2] = weight; // 设置权值
g->weight[v2][v1] = weight; // 对称位置设置权值
}
// 打印邻接矩阵图
void printmgraph(mgraph g) {
for (int i = 0; i < g.vexnum; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < g.vexnum; j++) {
printf("%d ", g.edge[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
}
// 判断图g是否存在边<x, y>或(x, y),并返回权值
int adjacent(mgraph g, int x, int y) {
if (g.edge[x][y] == 1 || g.edge[y][x] == 1) {
return g.weight[x][y]; // 返回边的权值
} else {
return infinity; // 不存在边<x, y>或(x, y),返回无穷大
}
}
// 列出图g中与结点x邻接的边
void neighbors(mgraph g, int x) {
printf("neighbors of vertex %d: ", x);
for (int i = 0; i < g.vexnum; i++) {
if (g.edge[x][i] == 1) {
printf("%d ", i);
}
}
printf("\n");
}
// 在图g中插入顶点x
void insertvertex(mgraph *g, int x) {
if (g->vexnum < maxvertexnum) {
g->vex[g->vexnum] = x;
g->vexnum++;
} else {
printf("exceeding maximum vertex number!\n");
}
}
// 从图g中删除顶点x
void deletevertex(mgraph *g, int x) {
if (x >= g->vexnum) {
printf("vertex does not exist!\n");
return;
}
// 删除顶点x的边
for (int i = 0; i < g->vexnum; i++) {
g->edge[i][x] = 0;
g->edge[x][i] = 0;
g->weight[i][x] = infinity; // 删除边同时将权值设置为无穷大
g->weight[x][i] = infinity;
}
// 移动顶点表,覆盖被删除的顶点
for (int i = x; i < g->vexnum - 1; i++) {
g->vex[i] = g->vex[i + 1];
}
g->vexnum--;
}
// 若无向边(x, y)或有向边<x, y>不存在,则向图g中添加该边
void addedge(mgraph *g, int x, int y, int weight) {
if (g->edge[x][y] == 0) {
g->edge[x][y] = 1;
g->edge[y][x] = 1; // 对于无向图,要同时设置对称位置
g->weight[x][y] = weight;
g->weight[y][x] = weight; // 对称位置设置权值
}
}
// 若无向边(x, y)或有向边<x, y>存在,则从图g中删除该边
void removeedge(mgraph *g, int x, int y) {
if (g->edge[x][y] == 1) {
g->edge[x][y] = 0;
g->edge[y][x] = 0; // 对于无向图,要同时设置对称位置
g->weight[x][y] = infinity;
g->weight[y][x] = infinity; // 对称位置设置权值为无穷大
}
}
// 求图g中顶点x的第一个邻接点,若有则返回顶点号,若x没有邻接点或图中不存在x,则返回-1
int firstneighbor(mgraph g, int x) {
for (int i = 0; i < g.vexnum; i++) {
if (g.edge[x][i] == 1) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
// 返回除y之外顶点x的下一个邻接点的顶点号,若y是x的最后一个邻接点,则返回-1
int nextneighbor(mgraph g, int x, int y) {
for (int i = y + 1; i < g.vexnum; i++) {
if (g.edge[x][i] == 1) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
// 获取图g中边(x, y)或<x, y>对应的权值
int get_edge_value(mgraph g, int x, int y) {
return g.weight[x][y];
}
// 设置图g中边(x, y)或<x, y>对应的权值为v
void set_edge_value(mgraph *g, int x, int y, int v) {
g->weight[x][y] = v;
g->weight[y][x] = v; // 对称位置设置权值
}
void visit(int v){
printf("%d ",v);
}
// 定义队列结点
typedef struct queuenode {
int data;
struct queuenode* next;
} queuenode;
// 定义队列
typedef struct {
queuenode *front;
queuenode *rear;
} queue;
// 初始化队列
void initqueue(queue *q) {
q->front = q->rear = null;
}
// 入队操作
void enqueue(queue *q, int data) {
queuenode *newnode = (queuenode *)malloc(sizeof(queuenode));
newnode->data = data;
newnode->next = null;
if (q->rear == null) {
q->front = q->rear = newnode;
} else {
q->rear->next = newnode;
q->rear = newnode;
}
}
// 出队操作
int dequeue(queue *q) {
if (q->front == null)
return -1; // 队列为空
queuenode *temp = q->front;
int data = temp->data;
q->front = q->front->next;
if (q->front == null)
q->rear = null;
free(temp);
return data;
}
// 判断队列是否为空
int isqueueempty(queue q) {
return q.front == null;
}
// 广度优先遍历
void bfs(mgraph g, int v, bool visited[], queue *q) { // 从顶点v出发,广度优先遍历图g
visit(v); // 访问初始顶点v
visited[v] = true; // 对v做已访问标记
enqueue(q, v); // 顶点v入队列q
while (!isqueueempty(*q)) {
int w;
w=dequeue(q); // 顶点v出队列
for (w = firstneighbor(g, v); w >= 0; w = nextneighbor(g, v, w)) {
// 检测v所有邻接点
if (!visited[w]) { // w为v的尚未访问的邻接顶点
visit(w); // 访问w
visited[w] = true; // 标记w已被访问
enqueue(q, w); // 顶点w入队
}
}
}
}
// 广度优先遍历
// 对图g进行广度优先遍历
void bfstraverse(mgraph g) {
bool visited[maxvertexnum] = {false};
queue q;
initqueue(&q); // 初始化辅助队列
// 从0号结点开始遍历
for (int i = 0; i < g.vexnum; ++i) {
if (!visited[i]) // 对每个连通分量调用一次bfs
bfs(g, i, visited, &q); // vi未被访问,则从vi开始bfs
}
}
// 深度优先遍历
void dfs(mgraph g, int v, bool visited[]) {
visit(v); // 访问顶点v
visited[v] = true; // 设已访问标记
for (int w = firstneighbor(g, v); w >= 0; w = nextneighbor(g, v, w)) {
if (!visited[w]) {
dfs(g, w, visited);
}
}
}
void dfstraverse(mgraph g) {
bool visited[maxvertexnum] = {false};
for (int i = 0; i < g.vexnum; ++i) {
if (!visited[i]) {
dfs(g, i, visited);
}
}
}
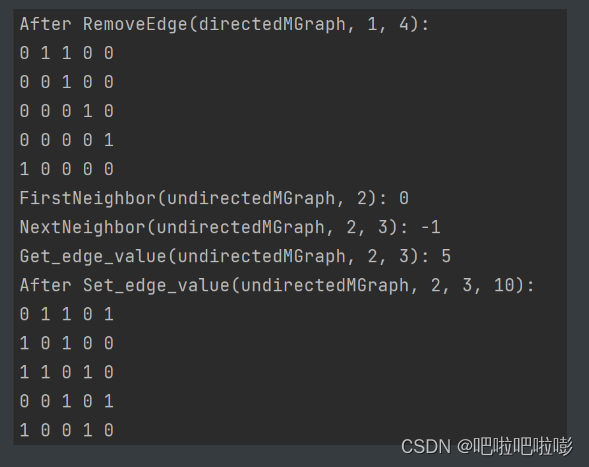
int main() {
// 创建有向图的邻接矩阵表示
mgraph directedmgraph;
initmgraph(&directedmgraph, 5, 6);
addedgedirectedmgraph(&directedmgraph, 0, 1, 2);
addedgedirectedmgraph(&directedmgraph, 0, 2, 3);
addedgedirectedmgraph(&directedmgraph, 1, 2, 4);
addedgedirectedmgraph(&directedmgraph, 2, 3, 5);
addedgedirectedmgraph(&directedmgraph, 3, 4, 6);
addedgedirectedmgraph(&directedmgraph, 4, 0, 7);
// 创建无向图的邻接矩阵表示
mgraph undirectedmgraph;
initmgraph(&undirectedmgraph, 5, 6);
addedgeundirectedmgraph(&undirectedmgraph, 0, 1, 2);
addedgeundirectedmgraph(&undirectedmgraph, 0, 2, 3);
addedgeundirectedmgraph(&undirectedmgraph, 1, 2, 4);
addedgeundirectedmgraph(&undirectedmgraph, 2, 3, 5);
addedgeundirectedmgraph(&undirectedmgraph, 3, 4, 6);
addedgeundirectedmgraph(&undirectedmgraph, 4, 0, 7);
// 打印结果
printf("directed graph (adjacency matrix):\n");
printmgraph(directedmgraph);
printf("\nundirected graph (adjacency matrix):\n");
printmgraph(undirectedmgraph);
// 测试基本操作
printf("\ntest basic operations:\n");
printf("adjacent(directedmgraph, 0, 1): %d\n", adjacent(directedmgraph, 0, 1));
printf("adjacent(directedmgraph, 0, 3): %d\n", adjacent(directedmgraph, 0, 3));
printf("neighbors(directedmgraph, 0): ");
neighbors(directedmgraph, 0);
printf("neighbors(undirectedmgraph, 0): ");
neighbors(undirectedmgraph, 0);
insertvertex(&directedmgraph, 5);
printf("after insertvertex(directedmgraph, 5):\n");
printmgraph(directedmgraph);
deletevertex(&directedmgraph, 5);
printf("after deletevertex(directedmgraph, 5):\n");
printmgraph(directedmgraph);
addedge(&directedmgraph, 1, 4, 8);
printf("after addedge(directedmgraph, 1, 4):\n");
printmgraph(directedmgraph);
removeedge(&directedmgraph, 1, 4);
printf("after removeedge(directedmgraph, 1, 4):\n");
printmgraph(directedmgraph);
printf("firstneighbor(undirectedmgraph, 2): %d\n", firstneighbor(undirectedmgraph, 2));
printf("nextneighbor(undirectedmgraph, 2, 3): %d\n", nextneighbor(undirectedmgraph, 2, 3));
printf("get_edge_value(undirectedmgraph, 2, 3): %d\n", get_edge_value(undirectedmgraph, 2, 3));
set_edge_value(&undirectedmgraph, 2, 3, 10);
printf("after set_edge_value(undirectedmgraph, 2, 3, 10):\n");
printmgraph(undirectedmgraph);
// 测试广度优先遍历和深度优先遍历
printf("\ntest traversal:\n");
printf("bfs directed graph:");
bfstraverse(directedmgraph); // 广度优先遍历有向图,起始节点为0
printf("\ndfs directed graph:");
dfstraverse(directedmgraph); // 深度优先遍历有向图,起始节点为0
printf("\nbfs undirected graph:");
bfstraverse(undirectedmgraph); // 广度优先遍历无向图,起始节点为0
printf("\ndfs undirected graph:");
dfstraverse(undirectedmgraph); // 深度优先遍历无向图,起始节点为0
return 0;
}

*完整代码 邻接表
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define maxvertexnum 100 // 最大顶点数定义为100
#define inf 9999 // 代表无穷大的定义为9999
// 边结点的定义
typedef struct arcnode {
int adjvex; // 边指向哪个结点
int weight; // 边权值
struct arcnode *next; // 指向下一条弧的指针
} arcnode;
// 顶点结点的定义
typedef struct vnode {
int data; // 顶点信息
arcnode *first; // 第一条边
} vnode, adjlist[maxvertexnum]; // 邻接表的定义
// 图的定义
typedef struct {
adjlist vertices; // 顶点数组
int vexnum, arcnum; // 顶点数和边数
} algraph;
// 初始化邻接表图
void initalgraph(algraph *g, int vexnum, int arcnum) {
g->vexnum = vexnum; // 初始化顶点数
g->arcnum = arcnum; // 初始化边数
for (int i = 0; i < vexnum; i++) { // 遍历顶点数组
g->vertices[i].data = i; // 顶点信息为i
g->vertices[i].first = null; // 第一条边为空
}
}
// 添加有向图的边
void addedgedirectedalgraph(algraph *g, int v1, int v2, int weight) {
arcnode *arcnode = (arcnode *)malloc(sizeof(arcnode)); // 分配边结点内存
arcnode->adjvex = v2; // 边指向v2
arcnode->weight = weight; // 边权值为weight
arcnode->next = g->vertices[v1].first; // 将边插入到顶点v1的边链表中
g->vertices[v1].first = arcnode;
}
// 添加无向图的边
void addedgeundirectedalgraph(algraph *g, int v1, int v2, int weight) {
// 添加v1到v2的边
arcnode *arcnode1 = (arcnode *)malloc(sizeof(arcnode)); // 分配边结点内存
arcnode1->adjvex = v2; // 边指向v2
arcnode1->weight = weight; // 边权值为weight
arcnode1->next = g->vertices[v1].first; // 将边插入到顶点v1的边链表中
g->vertices[v1].first = arcnode1;
// 添加v2到v1的边
arcnode *arcnode2 = (arcnode *)malloc(sizeof(arcnode)); // 分配边结点内存
arcnode2->adjvex = v1; // 边指向v1
arcnode2->weight = weight; // 边权值为weight
arcnode2->next = g->vertices[v2].first; // 将边插入到顶点v2的边链表中
g->vertices[v2].first = arcnode2;
}
// 打印邻接表图
void printalgraph(algraph g) {
for (int i = 0; i < g.vexnum; i++) { // 遍历顶点数组
printf("%d -> ", g.vertices[i].data); // 打印顶点信息
arcnode *p = g.vertices[i].first; // 获取顶点i的第一条边
while (p != null) { // 遍历顶点i的边链表
printf("(%d, %d) ", p->adjvex, p->weight); // 打印边的信息
p = p->next; // 指向下一条边
}
printf("\n");
}
}
// 判断两个顶点之间是否有边相连
int adjacent(algraph g, int x, int y) {
arcnode *p = g.vertices[x].first; // 获取顶点x的第一条边
while (p != null) { // 遍历顶点x的边链表
if (p->adjvex == y) // 如果边的另一端是y
return 1; // 返回1,表示存在边<x, y>
p = p->next; // 指向下一条边
}
return 0; // 遍历完所有边仍未找到,返回0,表示不存在边<x, y>
}
// 打印顶点x的邻居顶点
void neighbors(algraph g, int x) {
arcnode *p = g.vertices[x].first; // 获取顶点x的第一条边
printf("neighbors of vertex %d: ", x); // 打印提示信息
while (p != null) { // 遍历顶点x的边链表
printf("%d ", p->adjvex); // 打印邻居顶点
p = p->next; // 指向下一条边
}
printf("\n");
}
// 插入顶点
void insertvertex(algraph *g, int x) {
g->vertices[g->vexnum].data = x; // 在最后一个位置插入顶点x的信息
g->vertices[g->vexnum].first = null; // 边链表为空
g->vexnum++; // 顶点数加一
}
// 删除顶点
void deletevertex(algraph *g, int x) {
for (int i = 0; i < g->vexnum; i++) { // 遍历顶点数组
arcnode *p = g->vertices[i].first; // 获取顶点i的第一条边
arcnode *pre = null; // 初始化前一个边结点为null
while (p != null) { // 遍历顶点i的边链表
if (p->adjvex == x) { // 如果边的另一端是x
if (pre == null) // 如果是第一条边
g->vertices[i].first = p->next; // 将顶点i的第一条边指向下一条边
else
pre->next = p->next; // 将前一条边的next指针指向下一条边
free(p); // 释放删除的边结点的内存
break; // 结束循环
}
pre = p; // 更新前一个边结点
p = p->next; // 指向下一条边
}
}
// 删除顶点x
for (int i = x; i < g->vexnum - 1; i++) // 从顶点x开始,将后面的顶点信息依次往前移动
g->vertices[i] = g->vertices[i + 1]; // 将后一个顶点信息覆盖前一个顶点信息
g->vexnum--; // 顶点数减一
}
// 添加边
void addedge(algraph *g, int x, int y, int weight) {
if (!adjacent(*g, x, y)) { // 如果两个顶点之间不存在边相连
addedgeundirectedalgraph(g, x, y, weight); // 添加边<x, y>
}
}
// 删除边
void removeedge(algraph *g, int x, int y) {
if (adjacent(*g, x, y)) { // 如果两个顶点之间存在边相连
arcnode *p = g->vertices[x].first; // 获取顶点x的第一条边
arcnode *pre = null; // 初始化前一个边结点为null
while (p != null) { // 遍历顶点x的边链表
if (p->adjvex == y) { // 如果边的另一端是y
if (pre == null) // 如果是第一条边
g->vertices[x].first = p->next; // 将顶点x的第一条边指向下一条边
else
pre->next = p->next; // 将前一条边的next指针指向下一条边
free(p); // 释放删除的边结点的内存
break; // 结束循环
}
pre = p; // 更新前一个边结点
p = p->next; // 指向下一条边
}
// 如果是无向图,还需要删除另一个方向的边
if (g->vertices[y].first != null) { // 如果顶点y有边相连
p = g->vertices[y].first; // 获取顶点y的第一条边
pre = null; // 初始化前一个边结点为null
while (p != null) { // 遍历顶点y的边链表
if (p->adjvex == x) { // 如果边的另一端是x
if (pre == null) // 如果是第一条边
g->vertices[y].first = p->next; // 将顶点y的第一条边指向下一条边
else
pre->next = p->next; // 将前一条边的next指针指向下一条边
free(p); // 释放删除的边结点的内存
break; // 结束循环
}
pre = p; // 更新前一个边结点
p = p->next; // 指向下一条边
}
}
}
}
// 获取顶点x的第一个邻居顶点
int firstneighbor(algraph g, int x) {
if (g.vertices[x].first != null) // 如果顶点x有边相连
return g.vertices[x].first->adjvex; // 返回第一个邻居顶点的信息
else
return -1; // 否则返回-1,表示没有邻居顶点
}
// 获取顶点x的邻居顶点y的下一个邻居顶点
int nextneighbor(algraph g, int x, int y) {
arcnode *p = g.vertices[x].first; // 获取顶点x的第一条边
while (p != null && p->adjvex != y) // 遍历顶点x的边链表,直到找到邻居顶点y
p = p->next; // 指向下一条边
if (p != null && p->next != null) // 如果邻居顶点y后面还有邻居顶点
return p->next->adjvex; // 返回邻居顶点y的下一个邻居顶点的信息
else
return -1; // 否则返回-1,表示没有下一个邻居顶点
}
// 获取边<x, y>的权值
int get_edge_value(algraph g, int x, int y) {
arcnode *p = g.vertices[x].first; // 获取顶点x的第一条边
while (p != null) { // 遍历顶点x的边链表
if (p->adjvex == y) // 如果边的另一端是y
return p->weight; // 返回边的权值
p = p->next; // 指向下一条边
}
return inf; // 遍历完所有边仍未找到,返回无穷大,表示不存在边<x, y>
}
// 设置边<x, y>的权值为v
void set_edge_value(algraph *g, int x, int y, int v) {
arcnode *p = g->vertices[x].first; // 获取顶点x的第一条边
while (p != null) { // 遍历顶点x的边链表
if (p->adjvex == y) { // 如果边的另一端是y
p->weight = v; // 设置边的权值为v
break; // 结束循环
}
p = p->next; // 指向下一条边
}
}
void visit(int v){
printf("%d ",v);
}
// 定义队列结点
typedef struct queuenode {
int data;
struct queuenode* next;
} queuenode;
// 定义队列
typedef struct {
queuenode *front;
queuenode *rear;
} queue;
// 初始化队列
void initqueue(queue *q) {
q->front = q->rear = null;
}
// 入队操作
void enqueue(queue *q, int data) {
queuenode *newnode = (queuenode *)malloc(sizeof(queuenode));
newnode->data = data;
newnode->next = null;
if (q->rear == null) {
q->front = q->rear = newnode;
} else {
q->rear->next = newnode;
q->rear = newnode;
}
}
// 出队操作
int dequeue(queue *q) {
if (q->front == null)
return -1; // 队列为空
queuenode *temp = q->front;
int data = temp->data;
q->front = q->front->next;
if (q->front == null)
q->rear = null;
free(temp);
return data;
}
// 判断队列是否为空
int isqueueempty(queue q) {
return q.front == null;
}
// 广度优先遍历
void bfs(algraph g, int v, bool visited[], queue *q) { // 从顶点v出发,广度优先遍历图g
visit(v); // 访问初始顶点v
visited[v] = true; // 对v做已访问标记
enqueue(q, v); // 顶点v入队列q
while (!isqueueempty(*q)) {
int w;
w=dequeue(q); // 顶点v出队列
for (w = firstneighbor(g, v); w >= 0; w = nextneighbor(g, v, w)) {
// 检测v所有邻接点
if (!visited[w]) { // w为v的尚未访问的邻接顶点
visit(w); // 访问w
visited[w] = true; // 标记w已被访问
enqueue(q, w); // 顶点w入队
}
}
}
}
// 广度优先遍历
// 对图g进行广度优先遍历
void bfstraverse(algraph g) {
bool visited[maxvertexnum] = {false};
queue q;
initqueue(&q); // 初始化辅助队列
// 从0号结点开始遍历
for (int i = 0; i < g.vexnum; ++i) {
if (!visited[i]) // 对每个连通分量调用一次bfs
bfs(g, i, visited, &q); // vi未被访问,则从vi开始bfs
}
}
// 深度优先遍历
void dfs(algraph g, int v, bool visited[]) {
visit(v); // 访问顶点v
visited[v] = true; // 设已访问标记
for (int w = firstneighbor(g, v); w >= 0; w = nextneighbor(g, v, w)) {
if (!visited[w]) {
dfs(g, w, visited);
}
}
}
void dfstraverse(algraph g) {
bool visited[maxvertexnum] = {false};
for (int i = 0; i < g.vexnum; ++i) {
if (!visited[i]) {
dfs(g, i, visited);
}
}
}
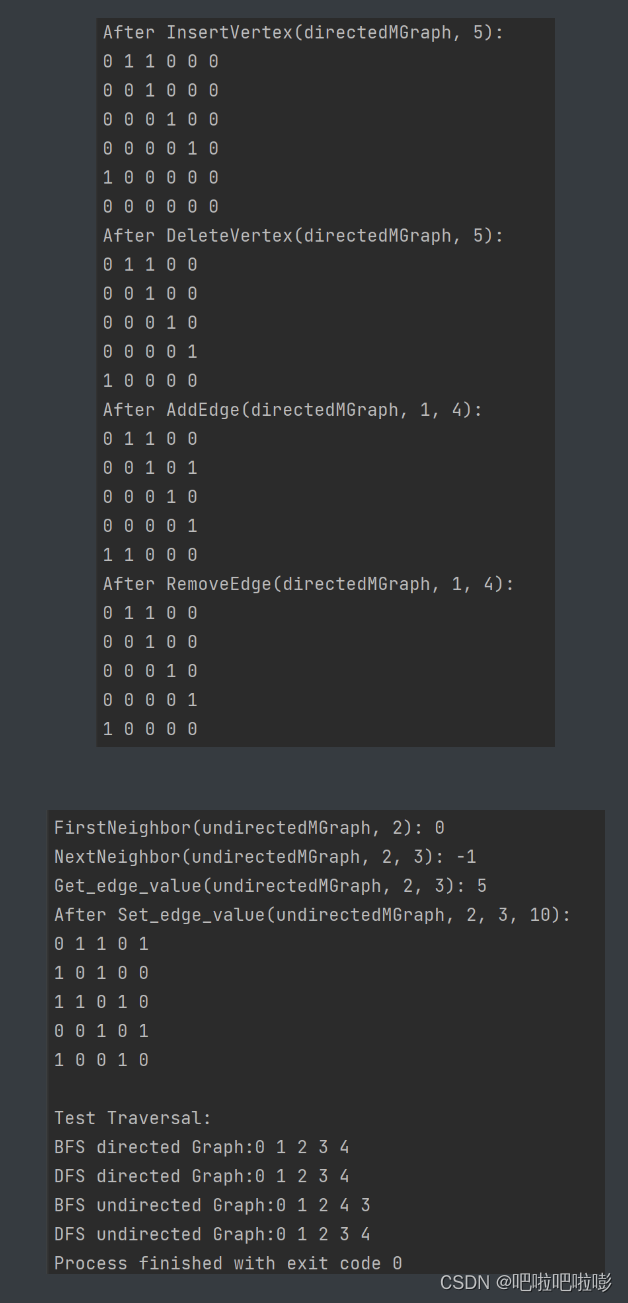
int main() {
// 创建有向图的邻接表表示
algraph directedalgraph; // 定义有向图
initalgraph(&directedalgraph, 5, 6); // 初始化有向图
addedgedirectedalgraph(&directedalgraph, 0, 1, 1); // 添加边
addedgedirectedalgraph(&directedalgraph, 0, 2, 2); // 添加边
addedgedirectedalgraph(&directedalgraph, 1, 2, 3); // 添加边
addedgedirectedalgraph(&directedalgraph, 2, 3, 4); // 添加边
addedgedirectedalgraph(&directedalgraph, 3, 4, 5); // 添加边
addedgedirectedalgraph(&directedalgraph, 4, 0, 6); // 添加边
// 创建无向图的邻接表表示
algraph undirectedalgraph; // 定义无向图
initalgraph(&undirectedalgraph, 5, 6); // 初始化无向图
addedgeundirectedalgraph(&undirectedalgraph, 0, 1, 1); // 添加边
addedgeundirectedalgraph(&undirectedalgraph, 0, 2, 2); // 添加边
addedgeundirectedalgraph(&undirectedalgraph, 1, 2, 3); // 添加边
addedgeundirectedalgraph(&undirectedalgraph, 2, 3, 4); // 添加边
addedgeundirectedalgraph(&undirectedalgraph, 3, 4, 5); // 添加边
addedgeundirectedalgraph(&undirectedalgraph, 4, 0, 6); // 添加边
printf("\ndirected graph (adjacency list):\n");
printalgraph(directedalgraph); // 打印有向图的邻接表表示
printf("\nundirected graph (adjacency list):\n");
printalgraph(undirectedalgraph); // 打印无向图的邻接表表示
// 测试基本操作
printf("\ntest basic operations:\n");
printf("adjacent(directedalgraph, 0, 1): %d\n", adjacent(directedalgraph, 0, 1)); // 测试两个顶点之间是否有边相连
printf("adjacent(directedalgraph, 0, 3): %d\n", adjacent(directedalgraph, 0, 3)); // 测试两个顶点之间是否有边相连
printf("adjacent(undirectedalgraph, 0, 1): %d\n", adjacent(undirectedalgraph, 0, 1)); // 测试两个顶点之间是否有边相连
printf("neighbors(directedalgraph, 0): ");
neighbors(directedalgraph, 0); // 打印顶点0的邻居顶点
printf("neighbors(undirectedalgraph, 0): ");
neighbors(undirectedalgraph, 0); // 打印顶点0的邻居顶点
insertvertex(&directedalgraph, 5); // 插入顶点5
printf("after insertvertex(directedalgraph, 5):\n");
printalgraph(directedalgraph); // 打印有向图的邻接表表示
deletevertex(&directedalgraph, 5); // 删除顶点5
printf("after deletevertex(directedalgraph, 5):\n");
printalgraph(directedalgraph); // 打印有向图的邻接表表示
addedge(&directedalgraph, 1, 4, 7); // 添加边
printf("after addedge(directedalgraph, 1, 4, 7):\n");
printalgraph(directedalgraph); // 打印有向图的邻接表表示
removeedge(&directedalgraph, 1, 4); // 删除边
printf("after removeedge(directedalgraph, 1, 4):\n");
printalgraph(directedalgraph); // 打印有向图的邻接表表示
printf("firstneighbor(undirectedalgraph, 2): %d\n", firstneighbor(undirectedalgraph, 2)); // 获取顶点2的第一个邻居顶点
printf("nextneighbor(undirectedalgraph, 2, 3): %d\n", nextneighbor(undirectedalgraph, 2, 3)); // 获取顶点2的邻居顶点3的下一个邻居顶点
printf("get_edge_value(undirectedalgraph, 2, 3): %d\n", get_edge_value(undirectedalgraph, 2, 3)); // 获取边
set_edge_value(&undirectedalgraph, 2, 3, 10);
printf("after set_edge_value(undirectedalgraph, 2, 3, 10):\n");
printalgraph(undirectedalgraph);
// 测试广度优先遍历和深度优先遍历
printf("\ntest traversal:\n");
printf("bfs directed graph:");
bfstraverse(directedalgraph); // 广度优先遍历有向图,起始节点为0
printf("\ndfs directed graph:");
dfstraverse(directedalgraph); // 深度优先遍历有向图,起始节点为0
printf("\nbfs undirected graph:");
bfstraverse(undirectedalgraph); // 广度优先遍历无向图,起始节点为0
printf("\ndfs undirected graph:");
dfstraverse(undirectedalgraph); // 深度优先遍历无向图,起始节点为0
return 0;
}



发表评论