开发板:esp32-s3-devkitc-1(esp32-s3-wroom-1-n16r8模块)
开发软件:vs code(espressif idf插件) + anaconda3 + pycharm
开发框架:esp-idf (版本v5.0.4)
训练框架:tensorflow 2.1.0
部署框架:esp-dl
💡💡💡💡: 在stm32上跑神经网络做手势识别 🚀
📍说明:
- 不同手势姿态之间需要具有明显的不同,在使用过程中,手势姿态需要做到位;(可能数据集不足)
- 影响体表温度的因素比较多,由于影响因素的变化,存在部分位置接近环境温度情况,所以即使加入了数据标准化,依然存在推理不准问题;(可能数据集不足)
- 在使用测试中,某个动作出现判断出错,可以将该动作添加到数据集中,在上一次权重文件基础上再训练,修修补补;
- 距离传感器较远,细节难以捕捉,不同手势差异较小,已经无法通过增加数据集来提高预测正确率;
- 该数据集动作主要在中心位置,所以使用过程中动作保持在中心;
- 本示例通过分类任务实现手势识别,如果出现新的手势类别,预测结果就很迷,采用rnn、lstm等的方式,使用效果应该会较好。
一、开发环境搭建与新建工程模板
1.1、开发环境搭建与卸载
考虑 esp-dl 库所支持的版本为 esp-idf v5.0,所以这里安装的不是最新版本。
在安装 vs code插件 (espressif idf) 后,可以选择两种安装方式:
这里采用离线安装+手动配置(vs code下完成程序编辑和编译操作) 💡。
① esp-idf 开发环境搭建:
- 下载esp-idf离线版本:esp-idf windows installer download 🚀
- 离线安装
esp-idf,安装完成后,安装路径下有三个重要的目录;- frameworks/esp-idf-v5.0.4:内含示例代码和组件源代码等;
- tools:编译器等程序;
- python_env/idf5.0_py3.11_env:python虚拟运行环境,内含python.exe、pip.exe以及依赖的库等。
- 打开
vs code,安装插件espressif idf; - vs code 手动配置;
a) 打开vscode左侧的插件管理页 => 找到espressif idf => 点击该插件旁边的小齿轮 => 扩展设置,就能看到 esp-idf 的配置属性;
b) 将路径信息添加到这些变量中:custom extra paths、custom extra vars、esp idf path win、esp idf path win、git path、python bin path、tools path win;(参考:esp32 开发环境:windows10 + esp-idf v4.4 + vscode + 插件 espressif idf 搭建踩坑 🚀) - 重启一下vs code。
② 打开一个example进行测试:
- 按住
ctrl+shift+p打开命令行,这里输入esp-idf show,点击esp-idf: show eaxmples projects,点击需要使用的 esp-idf 路径; - 左边栏中选择 hello word 工程,点击
create project using example hello_world。
- 选择这个项目的保存路径,任意路径均可;
- 烧录过程配置;
- 点击编译,成功后就可以进行烧录了。
③ 卸载esp-idf: 控制面板 => 卸载程序 => esp-idf tools offline 5.0.4 右键卸载。(vs code 下的配置直接重置就好)
1.2、新建工程目录
- 打开
vs code,此时界面可能是很干净,没有打开项目;这里需要随便打开一个目录(不然第二步操作完发现没响应); - 按住
ctrl+shift+p打开命令行,输入esp-idf: create project from extension template,点击;然后就按照提示操作就可以了; - 选择项目保存目录;
- 这里选择
template-app,接着就弹出了一个新的vs code界面,关掉前一个vs code界面; - 这时候指定目录下就有一个生成的文件夹,修改文件夹名称,方便以后管理(该操作不影响编译);
- 打开该目录根目录下的
cmakelists.txt,将project(template-app)修改为project(xxx),这样之后生成的可执行文件的名称就是xxx.bin,而不是template-app.bin。点击一下编译查看是否有问题。
1.3、自定义组件
到这一步就可以开发了,为了项目条理更加清晰,还需要引入【自定义组件】。
- 打开
esp-idf 5.0 cmd终端,切换到待创建的目录,输入idf.py -c components create-component led;(当然可以手动创建目录和文件)
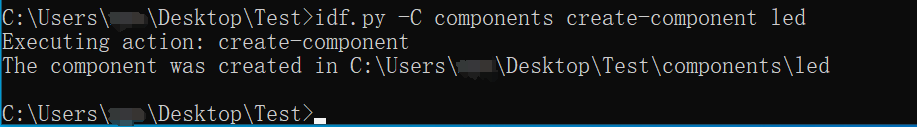
生成后项目目录树如下:
---test
|---.devcontainer
|---.vscode
|---build
|---cmakelists.txt
|---sdkconfig
|---components
|---led
|---include
|---led.h
|---cmakelists.txt
|---led.c
|---key
|---include
|---key.h
|---cmakelists.txt
|---key.c
|---main
|---cmakelists.txt
|---main.c
-
将组件中的头文件添加到main.c中,这样就可以进行编译了。
-
如果led组件需要key组件的函数,则:
- led.h 中加入
#include "key.h" - 方式一:led 组件中的 cmakelists.txt 中加入头文件路径:
include_dirs "include" "../key/include"(注意这里可是没指定链接路径,但还是能找到) - 方式二:led 组件中的 cmakelists.txt 中加入依赖组件:
requires driver key(这里led依赖两个组件:driver和key)
- led.h 中加入
-
在 idf 5.0 的版本之后,driver 组件不作为公共依赖项,所以使用的时候,必须在 cmakelists.txt 中声明依赖 driver 组件后才能使用:
idf_component_register(srcs "led.c"
include_dirs "include"
requires driver)
参考:
[1]: esp-idf编程指南 🚀
[2]: esp—idf开发(1)创建模板工程 🚀
[3]: esp32学习笔记(21)——构建自己的工程和组件库 🚀
[4]: esp32 esp-idf自定义组件 🚀
[5]: esp32开发 cmakelists包含同级目录.h文件,error: gpiox.h: no such file or directory 🚀
二、驱动移植与应用开发
管脚布局:
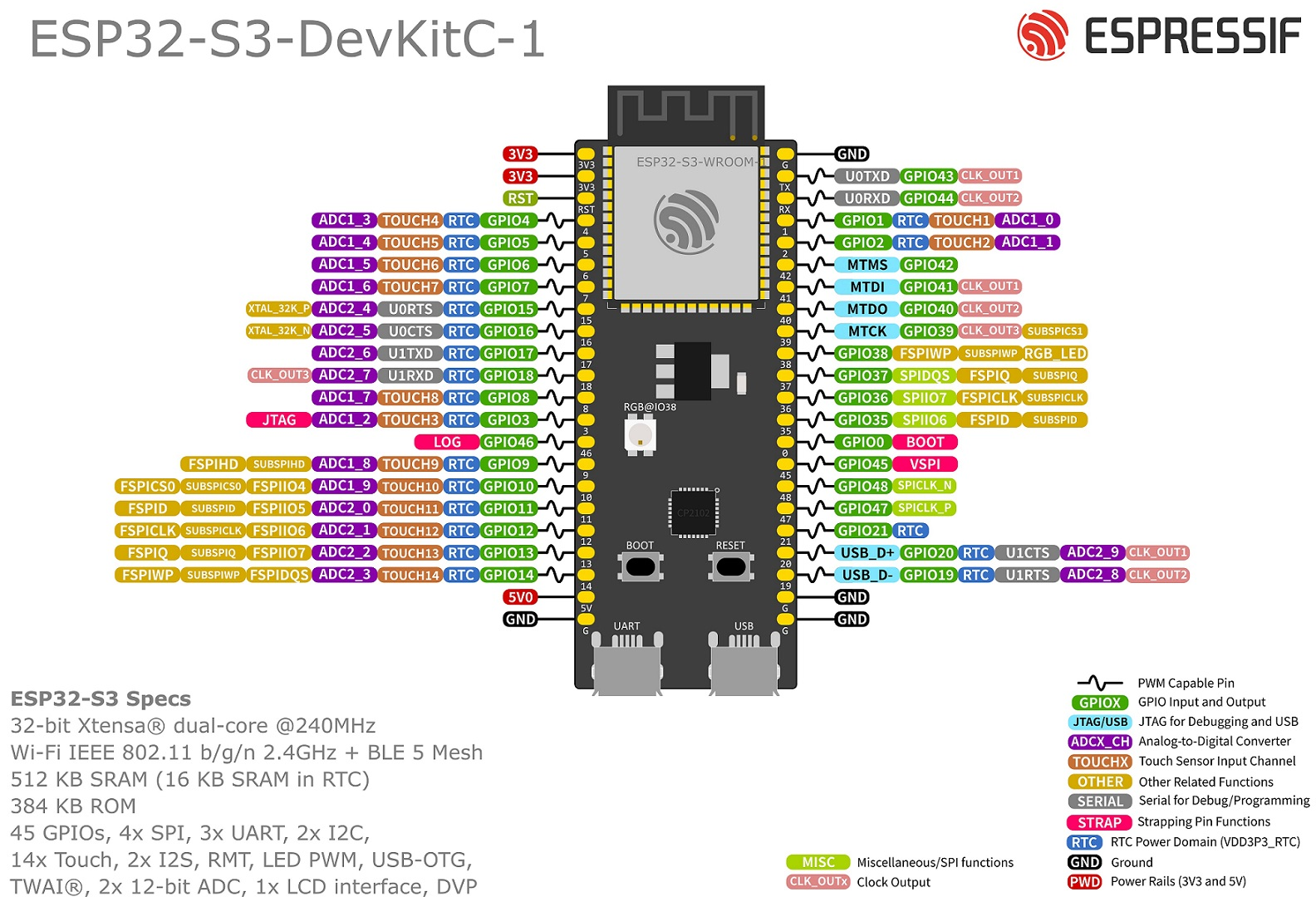
i2c0引脚资源使用情况: 支持任意 gpio 管脚
------------------------------------
| amg8833 | esp32 |
------------------------------------
| vin | 3.3v |
| gnd | gnd |
| scl | gpio2 |
| sda | gpio1 |
| int | / |
| ad0 | gnd |
------------------------------------
spi3引脚资源使用情况: 支持任意 gpio 管脚
------------------------------------
| lcd screen | esp32 |
------------------------------------
| gnd | gnd |
| vcc | vcc(3.3v) |
| scl | gpio5(sclk) |
| sda | gpio6(mosi) |
| res | gpio7 |
| dc | gpio15 |
| cs | gpio16 |
| blk | gpio17 |
------------------------------------
2.1、i2c驱动移植与amg8833应用开发
esp32-s3 有2个 i2c 控制器,每个控制器都可以设置为主机或从机,本次示例中作为主机使用。
- 当 8x8 中某个测点出现超过极限值就会触发int引脚电平变化,esp32 通过 int 引脚触发外部中断;esp32 通过读取寄存器的值就可以确定哪个矩阵测点触发电平变化。
- amg8833 scl最大支持
400khz。 ad0(ad_select)为 i2c设备地址选择脚。拉低,设备地址为110 1000,即0x68。拉高,设备地址为110 1001,即0x69。- eps32-s3 的 i2c 引脚原则上可选择任意引脚,在 i2c 初始化的时候指定即可,并将引脚设置为
enable gpio pull-up resistor。
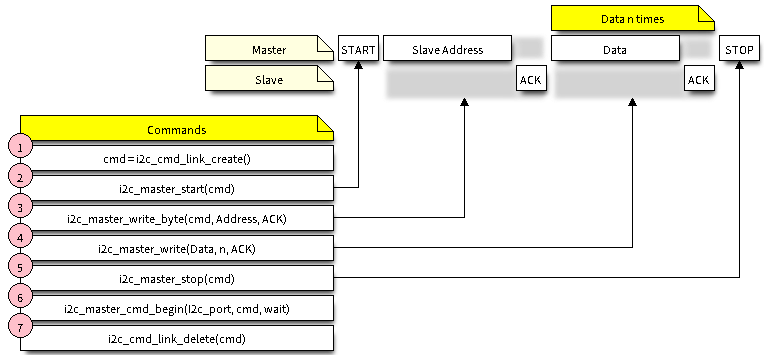
主机写入数据:
- 使用
i2c_cmd_link_create()创建一个命令链接。然后,将一系列待发送给从机的数据填充命令链接:
a. 启动位 -i2c_master_start()
b. 从机地址 -i2c_master_write_byte()。提供单字节地址作为调用此函数的实参。
c. 数据 - 一个或多个字节的数据作为i2c_master_write()的实参。 - 通过调用
i2c_master_cmd_begin()来触发 i2c 控制器执行命令链接。一旦开始执行,就不能再修改命令链接。(一般报错出现在该语句) - 命令发送后,通过调用
i2c_cmd_link_delete()释放命令链接使用的资源。
主机读取数据的步骤基本相似。
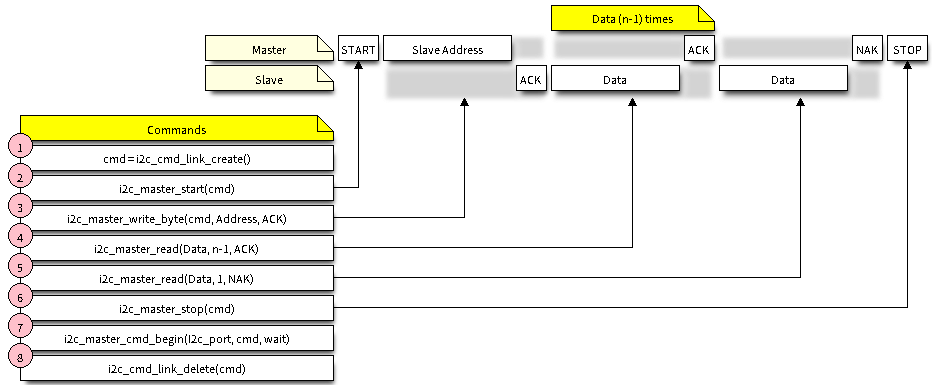
esp-idf 对这两个过程进行了封装:
- 主机读取数据:
i2c_master_write_read_device() - 主机写入数据:
i2c_master_write_to_device()
基本过程同上面一致,本示例依据这两个函数源代码,进行简单修改。
amg8833 需要进行初始化寄存器:正常读取前需要进行初始化操作。
- power control寄存器:设置amg8833的工作模式;
- reset寄存器:进行软复位;
- frame rate寄存器:设定帧率;
- interrupt control寄存器:配置中断功能;
amg8833 temperature寄存器:红外点阵测量的温度值。
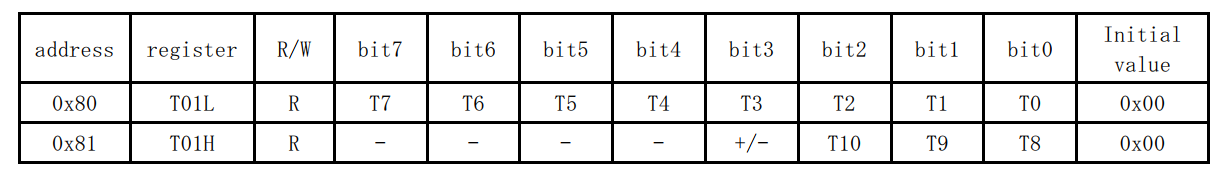
两个寄存器的数据组合起来获得一个测点的温度值。有12位数据,最高位为符号位,0为正,1为负。最小变化单位为0.25℃。
在读取64个像素点温度值时候,i2c只需要指定第一个寄存器地址以及读取的字节数量,amg8833自动发送后面地址的数据。
/* arduino框架下测试代码, 用于对比在esp-idf框架下驱动与应用是否正常
* 这里在测试代码的基础上增加/修改了两条语句:
* => wire.setpins(1,2); // 设置新的i2c引脚
* => status = amg.begin(0x68, &wire); //amg8833初始化, 0x68为amg8833设备地址
*/
#include <wire.h>
#include <adafruit_amg88xx.h>
adafruit_amg88xx amg;
float pixels[amg88xx_pixel_array_size];
void setup() {
serial.begin(9600);
serial.println(f("amg88xx pixels"));
bool status;
wire.setpins(1,2); //new sda scl pins
// default settings
status = amg.begin(0x68, &wire);
if (!status) {
serial.println("could not find a valid amg88xx sensor, check wiring!");
while (1);
}
serial.println("-- pixels test --");
serial.println();
delay(100); // let sensor boot up
}
void loop() {
//read all the pixels
amg.readpixels(pixels);
serial.print("[");
for(int i=1; i<=amg88xx_pixel_array_size; i++){
serial.print(pixels[i-1]);
serial.print(", ");
if( i%8 == 0 ) serial.println();
}
serial.println("]");
serial.println();
//delay a second
delay(1000);
}
参考:
[1]: esp_idf—i2c 驱动程序 🚀
[2]: esp32 之 esp-idf 教学(六)——硬件i2c总线外设(i²c) 🚀
[3]: amg8833的使用与stm32驱动代码 🚀
[4]: esp32 i2c自定义引脚 🚀
[5]: esp32-s3入门arduino开发(一)–arduino环境搭建 🚀
2.2、spi驱动移植与lcd应用开发
esp32-s3-devkitc-1 开发板采用 esp32-s3-wroom-1/1u 或 esp32-s3-wroom-2/2u 模组,而这些模组采用 esp32-s3芯片。
esp32-s3 芯片集成了四个 spi 控制器:
- spi0
- spi1
- 通用 spi2,即gp-spi2
- 通用 spi3,即gp-spi3
spi0 和 spi1 控制器主要供内部使用以访问外部 flash 及 psram,如上图所示。这里采用 spi3 作为 lcd 通信控制器。
spi有多种模式:为兼容lcd通信规范,这里采用普通 spi 模式。
- 普通 spi 模式
- 双线输出模式
- 双线输出模式
- 四线输出模式
- 四线 i/o 模式
- 八线输出模式
- opi 模式
lcd驱动和应用编写:
- spi初始化:引脚指定、频率、最大传输数据大小、是否开启dma等,主要配置
spi_bus_config_t和spi_device_interface_config_t结构体;通过spi_bus_initialize和spi_bus_add_device函数完成配置;
- 普通gpio初始化:dc、rst、bck引脚不在spi协议所规定的引脚,所以需要单独进行初始化;
- 编写命令/数据spi发送函数;
- 编写lcd初始化;
- 编写矩形绘制和图片显示函数,验证程序工作正常。
参考:
[1]: esp32-idf开发笔记 | 03 - 使用spi外设驱动st7789 spilcd 🚀
[2]: 【esp32-idf】 02-4 外设-spi 🚀
[3]: esp-idf 编程指南:spi 主机驱动程序 🚀
2.3、绘制温度云图
camcolors全局变量数组,里面保存颜色数据(rgb565),共有256种颜色,0索引保存为蓝色,255索引保存为红色。
最大温度记作:
t
m
a
x
t_{max}
tmax;最小温度记作:
t
m
i
n
t_{min}
tmin;当前温度记作:
t
c
u
r
t_{cur}
tcur。
最小索引值记作:
i
d
x
idx
idx。
建立温度和颜色的映射关系:
t m a x − t m i n 255 − 0 = t c u r − t m i n x − 0 \frac{t_{max}-t_{min}}{255-0}=\dfrac{t_{cur}-t_{min}}{x-0} 255−0tmax−tmin=x−0tcur−tmin
转换为:
x = 255 ∗ t c u r − t m i n t m a x − t m i n x=255*\dfrac{t_{cur}-t_{min}}{t_{max}-t_{min}} x=255∗tmax−tmintcur−tmin
arduino 框架官方提供了映射函数——map函数,主题思想一致的,细节上有些差异,具体表示如下:
x = 255 ∗ ( t c u r − t m i n ) + ( t m a x − t m i n ) / 2 t m a x − t m i n + i d x = 255 ∗ t c u r − t m i n t m a x − t m i n + 0.5 + i d x x=\dfrac{255*{(t_{cur}-t_{min})}+(t_{max}-t_{min})/2}{t_{max}-t_{min}}+idx=255*\dfrac{t_{cur}-t_{min}}{t_{max}-t_{min}}+0.5+idx x=tmax−tmin255∗(tcur−tmin)+(tmax−tmin)/2+idx=255∗tmax−tmintcur−tmin+0.5+idx
浮点型赋值给整型,小数部分舍去,这里加上0.5,实现四舍五入。
2.4、启用psram(可选)
- 点击齿轮

- 输入 ram查找一下两项,勾选
support for external, spi-connected ram以及模式选择octal mode psram。
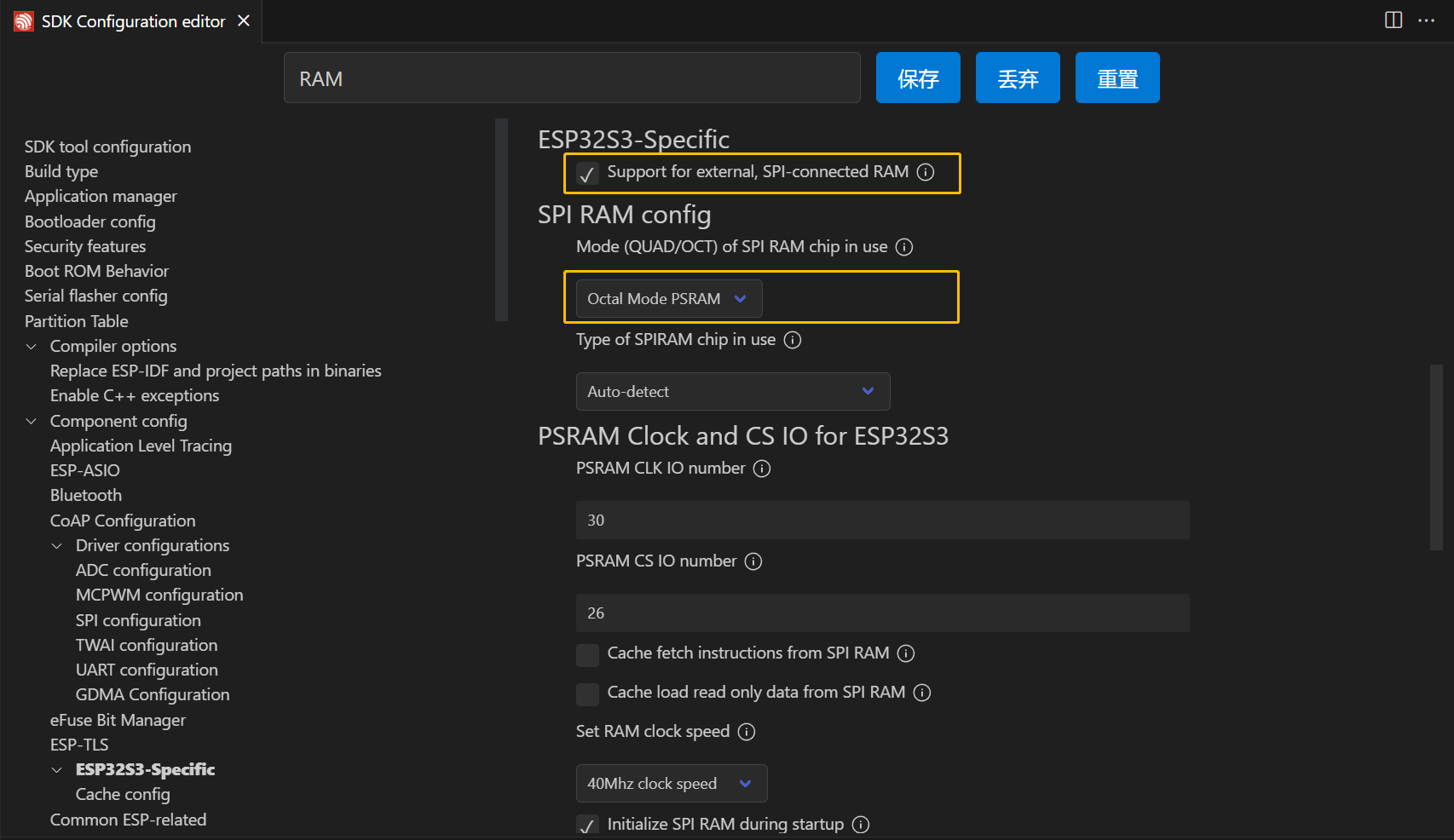
- 选择
make ram alloctable using heap_caps_malloc(...,malloc_cap_spiram),也可以选择make ram allocatable using malloc() as well,之所以选择前者是从存储器的使用上考虑:若从片上 sram 分配空间,则使用malloc函数,若从片外 psram 上分配空间,则使用heap_caps_malloc函数。
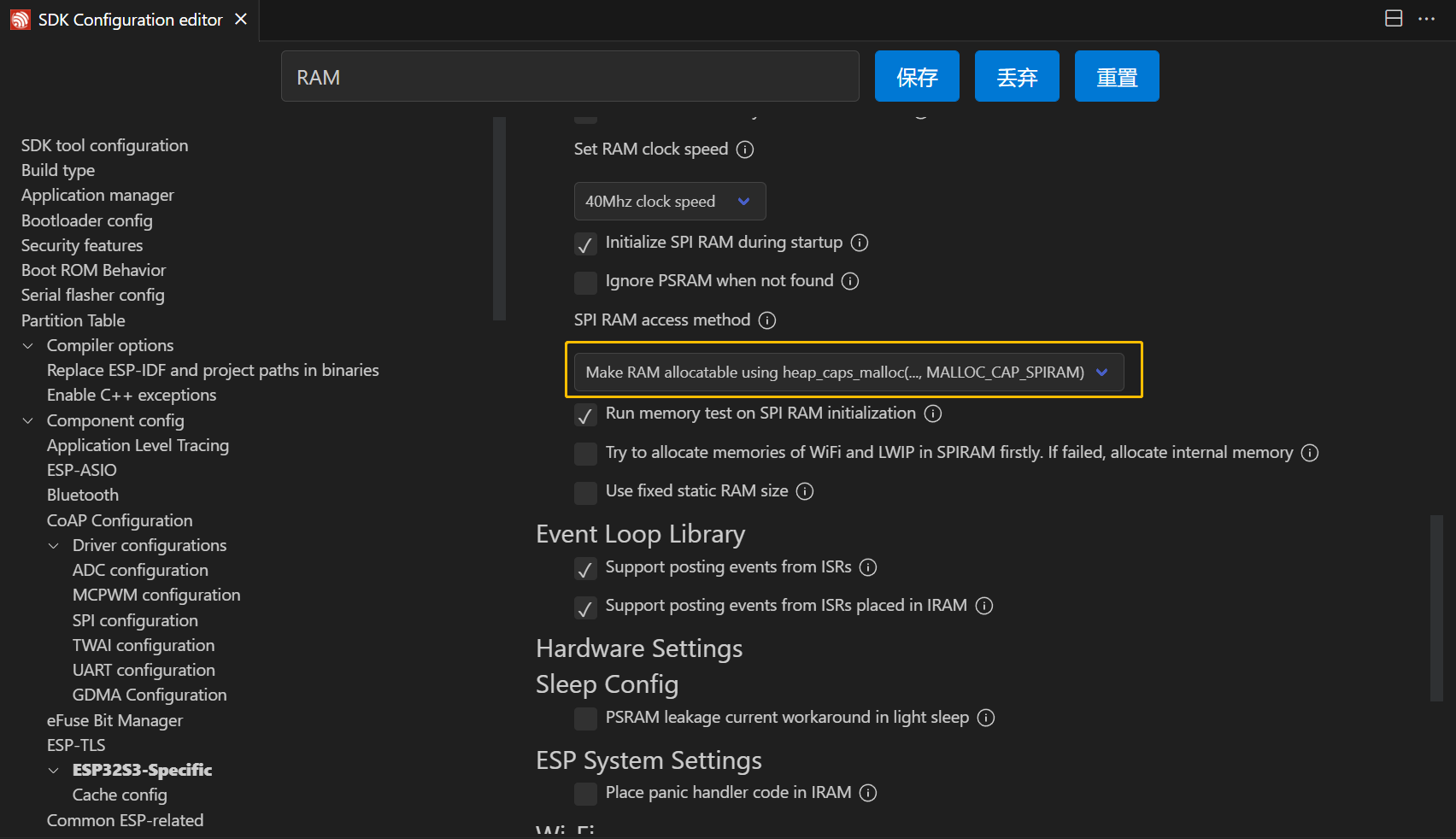
- 其它参数可使用默认。
- 保存,然后编译。
2.5、画面动静和距离检测
这里画面动静判断采用帧间差分法,以目标温度较小值为分界点,区分背景和目标,将两帧温度矩阵(24x24)的对应点进行相减,并取其绝对值,若大于阈值(目标和背景采用不同阈值)则计数值加1,当计数值大于某个值(距离不同,检测到目标的大小也不同,这个值是实时调整)后,则认为画面中存在运动目标。
在实现过程中,由于对比两帧数据,所以需要保存前一帧温度矩阵数据,一帧数据大小为24x24x4(float) = 2.25kb,这里采用 异步内存拷贝(asynchronous memory copy),其核心技术在于dma,通过给dma发送命令,实现内存拷贝,此时不需要cpu参与,当传输完成后通过回调函数发送信号通知被阻塞的任务。
异步内存拷贝:
/*-------------------> 安装 <-------------------*/
config = async_memcpy_default_config();
config.backlog = 16; // update the maximum data stream supported by underlying dma engine
async_memcpy_t mem_driver = null;
esp_error_check(esp_async_memcpy_install(&config, &mem_driver)); // install driver with default dma engine
semaphorehandle_t my_semphr = xsemaphorecreatebinary(); // create a semaphore used to report the completion of async memcpy
/*--------------> 发送内存拷贝请求 <--------------*/
esp_error_check(esp_async_memcpy(mem_driver, out_img_buf_pre, out_img_buf, copy_len, my_async_memcpy_cb, &myflags));
/*-----------> 拷贝完成后调用回调函数 <-----------*/
// callback function, running in isr context
static bool my_async_memcpy_cb(async_memcpy_t mcp_hdl, async_memcpy_event_t *event, void *cb_args)
{
/*可自定义标志*/
basetype_t high_task_wakeup = pdfalse;
xsemaphoregivefromisr(my_semphr, &high_task_wakeup); // high_task_wakeup set to pdtrue if some high priority task unblocked
return high_task_wakeup == pdtrue;
}
/*-----------> 阻塞等待内存拷贝完成 <-----------*/
xsemaphoretake(my_semphr, portmax_delay); // wait until the buffer copy is done
画面动静判断逻辑:
//获取第一帧24x24温度矩阵
readpixels{}
//保存第一帧数据
mem2mem{
1.发送内存拷贝请求
2.sigflag = 1
}
while(1){
readpixels{} //获取24x24温度矩阵
motion_detection{
if(sigflag == 1){
1.阻塞等待内存拷贝完成
2.sigflag == 0
}
/*画面动静判断*/
if(运动){
mem2mem{} // 如果运动, 保存当前帧数据
}
else{ // 静止, 不保存数据
}
}
}
- 获取第一帧24x24温度矩阵;
- 保存第一帧数据;
- 获取第二帧24x24温度矩阵;
- 因为是第一帧,所以等待第一帧保存完成;
- 判断是否运动,若为运动,保存当前帧(第二帧),下一次和第二帧做比较,若为静止,不用保存,下一次和第一帧做比较;
- 开始第二次循环,获取第三帧24x24温度矩阵;
- 是否之前有保存操作,没有就不用阻塞等待,有就阻塞等待;
- 判断是否运动,继续循环往复。
参考:
[1]: 运动目标检测——帧间差分法(temporal difference)简介 🚀
[2]: 🚀
[3]: the async memcpy api 🚀
目标距离检测实现原理:靠近传感器温度高,远离传感器温度低。
这种方式存在一个问题:如果目标远离检测范围那么温度也会下降,进入检测范围那么温度也会上升,更复杂是前后左右平移+上下平移的复合动作,这里暂时不考虑,只考虑上下平移。🔍
2.6、图像放大之双三次插值法:权重计算 | 插值计算 | 程序设计
对于低分辨图像在高分辨率的设备上显示,如果不做任何处理,那么实际显示区域会很小,为了扩大显示区域,就需要对低分辨率的图像进行数值图像放大处理,就是将低分辨率的图像变成高分辨率的图像,多出来的像素怎么获得?—— 插值算法。
虽然变成了高分辨率图像,但是这是由低分辨率的数据生成的,所以不会很高清。
常见的插值算法:自适应和非自适应。
非自适应算法:最近邻,双线性,双三次,样条等。双三次插值效果较好,但是时间开销比较大。
基本步骤:
- 计算权重
- 计算放大图像后的像素值
1、权重计算
原图片:8x8
放大后的图片:16x16
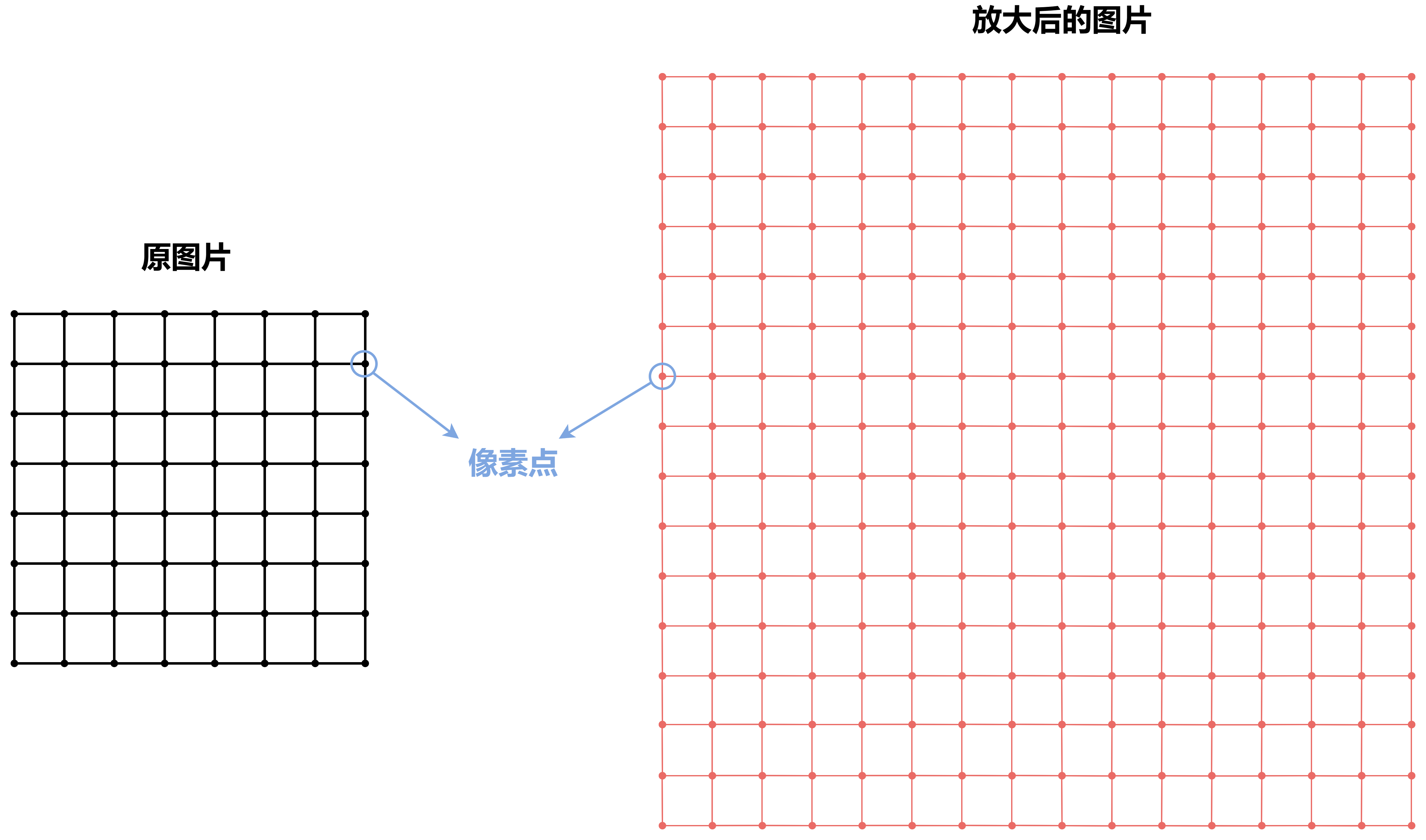
将【放大后的图片】缩小到【原图片】的大小,如下图所示:
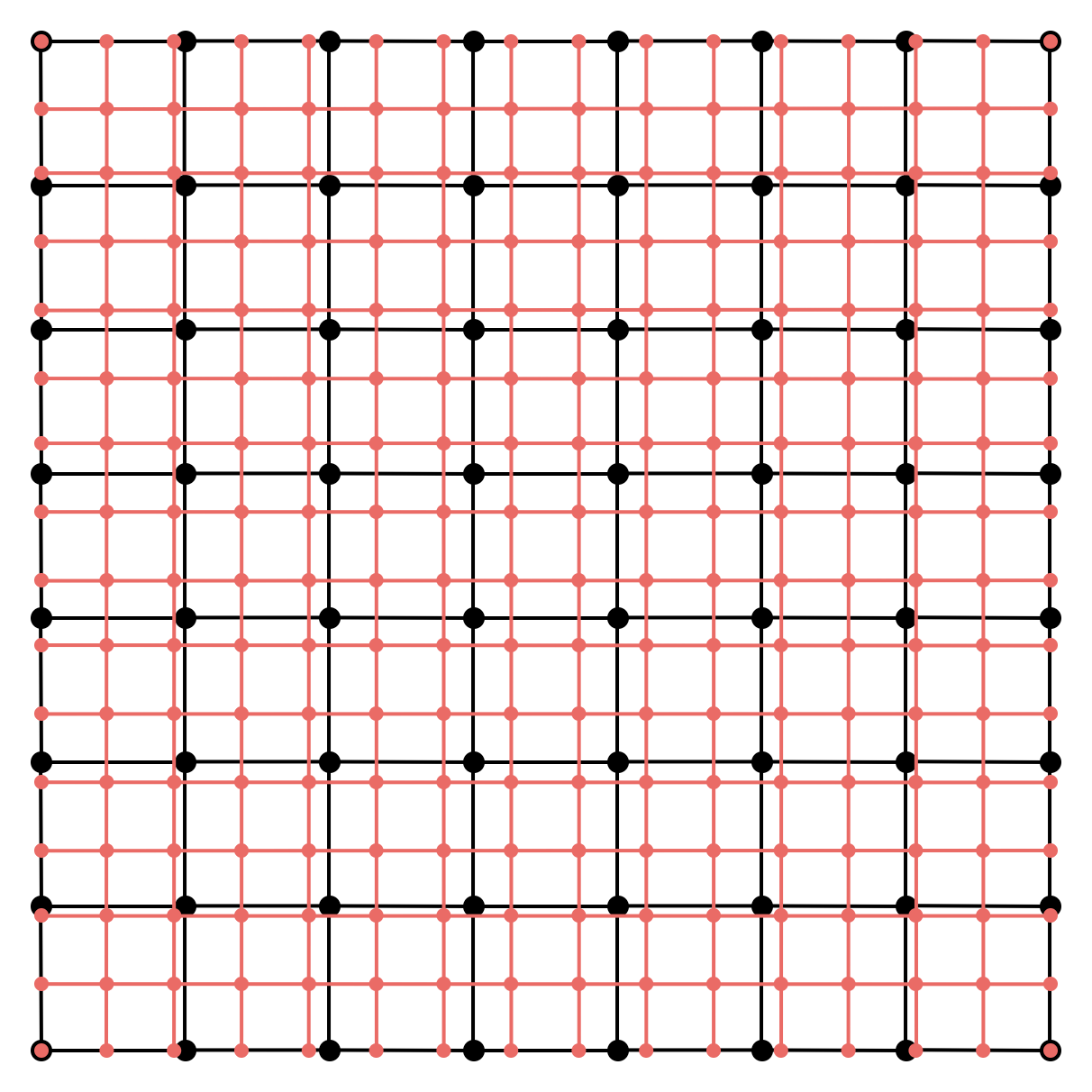
缩小后,每个像素(共16x16个)都需要计算权值。当计算某个像素权值时,取该像素上下左右邻近的四个点,在这四个点为基础,向外再扩充一圈,总共取16个点,如下图所示:
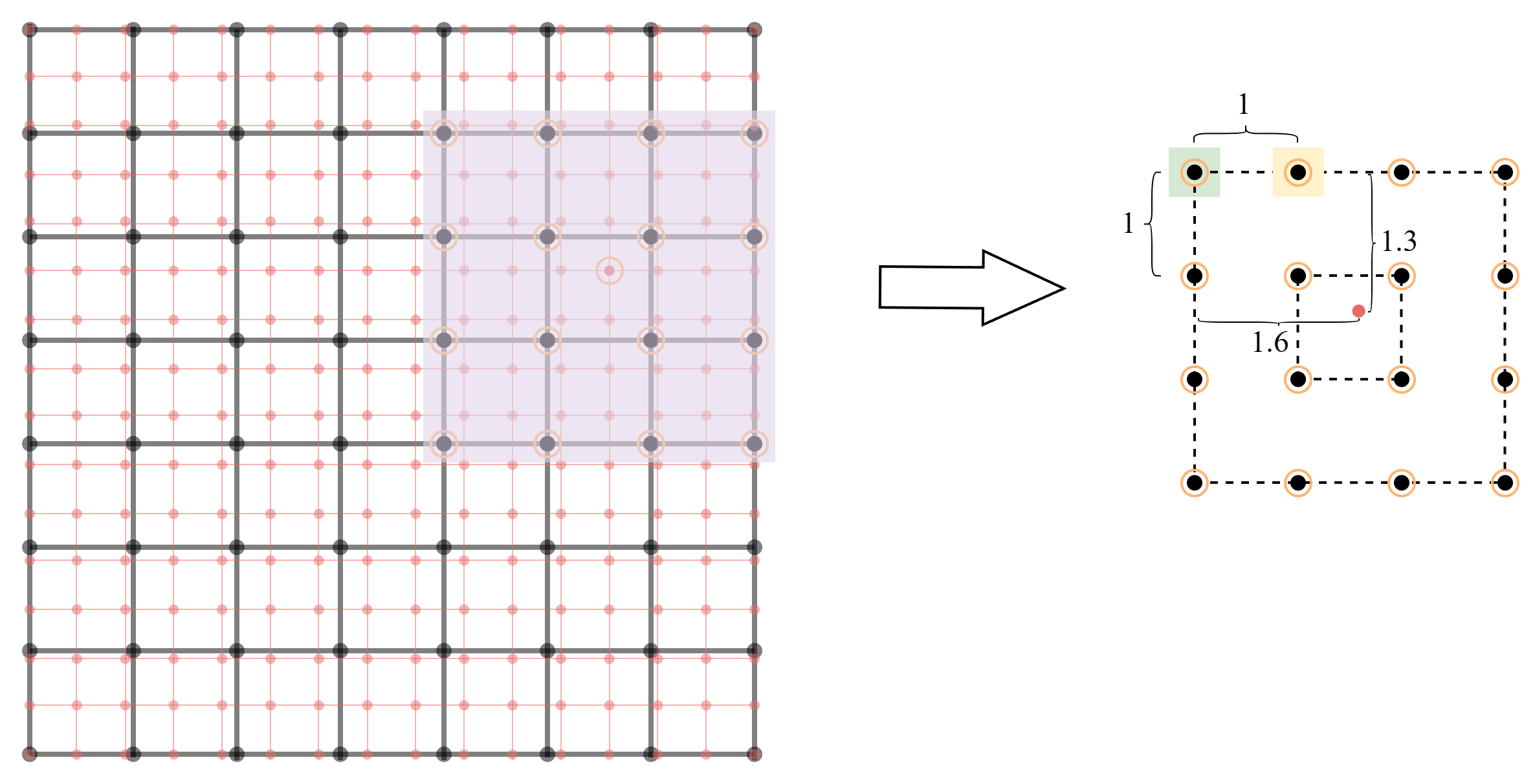
将上面的距离数据代入权重计算公式:
w ( x ) = { ( a + 2 ) ∣ x ∣ 3 − ( a + 3 ) ∣ x ∣ 2 + 1 f o r ∣ x ∣ ≤ 1 a ∣ x ∣ 3 − 5 a ∣ x ∣ 2 + 8 a ∣ x ∣ − 4 a f o r 1 ≤ ∣ x ∣ ≤ 2 0 o t h e r s w(x)= \begin{cases} (a+2)|x|^3-(a+3)|x|^2+1 \,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,for\,\,\, |x|≤1\\ a|x|^3-5a|x|^2+8a|x|-4a \,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\, for \,\,\, 1≤|x| ≤2\\ 0 \,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,others \end{cases} w(x)=⎩ ⎨ ⎧(a+2)∣x∣3−(a+3)∣x∣2+1for∣x∣≤1a∣x∣3−5a∣x∣2+8a∣x∣−4afor1≤∣x∣≤20others
式中, x x x 为目标像素点距离邻近像素点的距离; a a a 一般取 − 0.5 -0.5 −0.5。
对于【米黄色】的点,x轴方向距离为0.6,y轴方向距离为1.3。
-
x轴方向:
w ( x ) = ( a + 2 ) ∣ x ∣ 3 − ( a + 3 ) ∣ x ∣ 2 + 1 = ( − 0.5 + 2 ) ∗ ∣ 0.6 ∣ 3 − ( − 0.5 + 3 ) ∗ ∣ 0.6 ∣ 2 + 1 = 0.424 \begin{aligned} w(x) &= (a+2)|x|^3-(a+3)|x|^2+1 \\ &= (-0.5+2)*|0.6|^3-(-0.5+3)*|0.6|^2+1\\ &= 0.424 \end{aligned} w(x)=(a+2)∣x∣3−(a+3)∣x∣2+1=(−0.5+2)∗∣0.6∣3−(−0.5+3)∗∣0.6∣2+1=0.424 -
y轴方向:
w ( y ) = a ∣ x ∣ 3 − 5 a ∣ x ∣ 2 + 8 a ∣ x ∣ − 4 a = ( − 0.5 ) ∗ ∣ 1.3 ∣ 3 − 5 ∗ ( − 0.5 ) ∗ ∣ 1.3 ∣ 2 + 8 ∗ ( − 0.5 ) ∗ ∣ 1.3 ∣ − 4 ∗ ( − 0.5 ) = − 0.0735 \begin{aligned} w(y) &= a|x|^3-5a|x|^2+8a|x|-4a \\ &= (-0.5)*|1.3|^3-5*(-0.5)*|1.3|^2+8*(-0.5)*|1.3|-4*(-0.5)\\ &= -0.0735 \end{aligned} w(y)=a∣x∣3−5a∣x∣2+8a∣x∣−4a=(−0.5)∗∣1.3∣3−5∗(−0.5)∗∣1.3∣2+8∗(−0.5)∗∣1.3∣−4∗(−0.5)=−0.0735
对于【浅绿色】的点,x轴方向距离为1.6,y轴方向距离为1.3。
-
x轴方向:
w ( x ) = a ∣ x ∣ 3 − 5 a ∣ x ∣ 2 + 8 a ∣ x ∣ − 4 a = ( − 0.5 ) ∗ ∣ 1.6 ∣ 3 − 5 ∗ ( − 0.5 ) ∗ ∣ 1.6 ∣ 2 + 8 ∗ ( − 0.5 ) ∗ ∣ 1.6 ∣ − 4 ∗ ( − 0.5 ) = − 0.048 \begin{aligned} w(x) &= a|x|^3-5a|x|^2+8a|x|-4a \\ &= (-0.5)*|1.6|^3-5*(-0.5)*|1.6|^2+8*(-0.5)*|1.6|-4*(-0.5)\\ &= -0.048 \end{aligned} w(x)=a∣x∣3−5a∣x∣2+8a∣x∣−4a=(−0.5)∗∣1.6∣3−5∗(−0.5)∗∣1.6∣2+8∗(−0.5)∗∣1.6∣−4∗(−0.5)=−0.048 -
y轴方向:
w ( y ) = a ∣ x ∣ 3 − 5 a ∣ x ∣ 2 + 8 a ∣ x ∣ − 4 a = ( − 0.5 ) ∗ ∣ 1.3 ∣ 3 − 5 ∗ ( − 0.5 ) ∗ ∣ 1.3 ∣ 2 + 8 ∗ ( − 0.5 ) ∗ ∣ 1.3 ∣ − 4 ∗ ( − 0.5 ) = − 0.0735 \begin{aligned} w(y) &= a|x|^3-5a|x|^2+8a|x|-4a \\ &= (-0.5)*|1.3|^3-5*(-0.5)*|1.3|^2+8*(-0.5)*|1.3|-4*(-0.5)\\ &= -0.0735 \end{aligned} w(y)=a∣x∣3−5a∣x∣2+8a∣x∣−4a=(−0.5)∗∣1.3∣3−5∗(−0.5)∗∣1.3∣2+8∗(−0.5)∗∣1.3∣−4∗(−0.5)=−0.0735
每个插值的像素都是由16个原图中像素加权计算所得,每一行x轴方向权重相同,每一列y轴方向权重相同,所以一个插值的像素需要进行8次权重计算。
2、插值计算
计算红点位置的像素值,取4x4区域中的16个点。

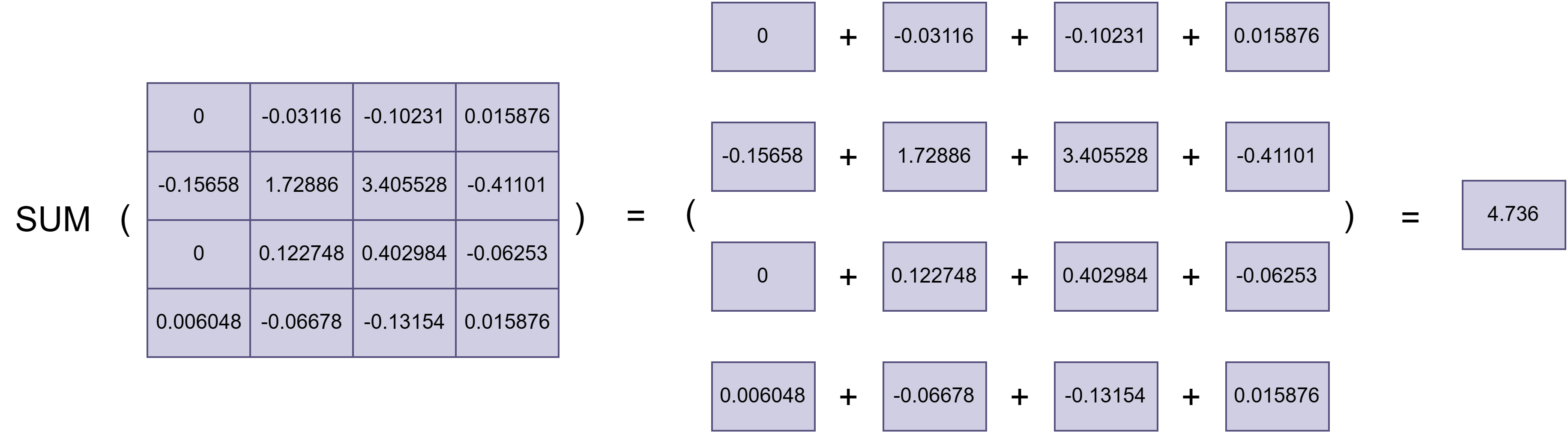
然后计算原图像素和权重的hadamard积:
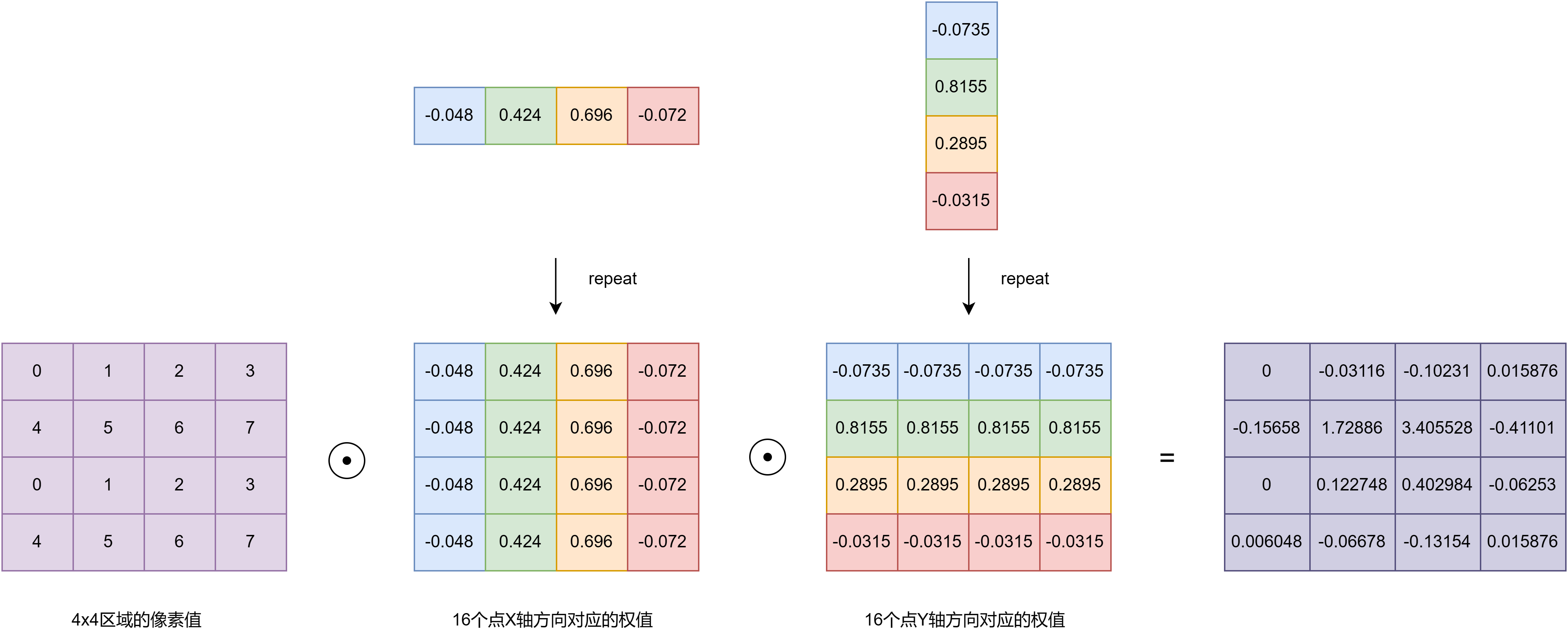
最后,将矩阵中所有元素相加得到了插值的像素值。
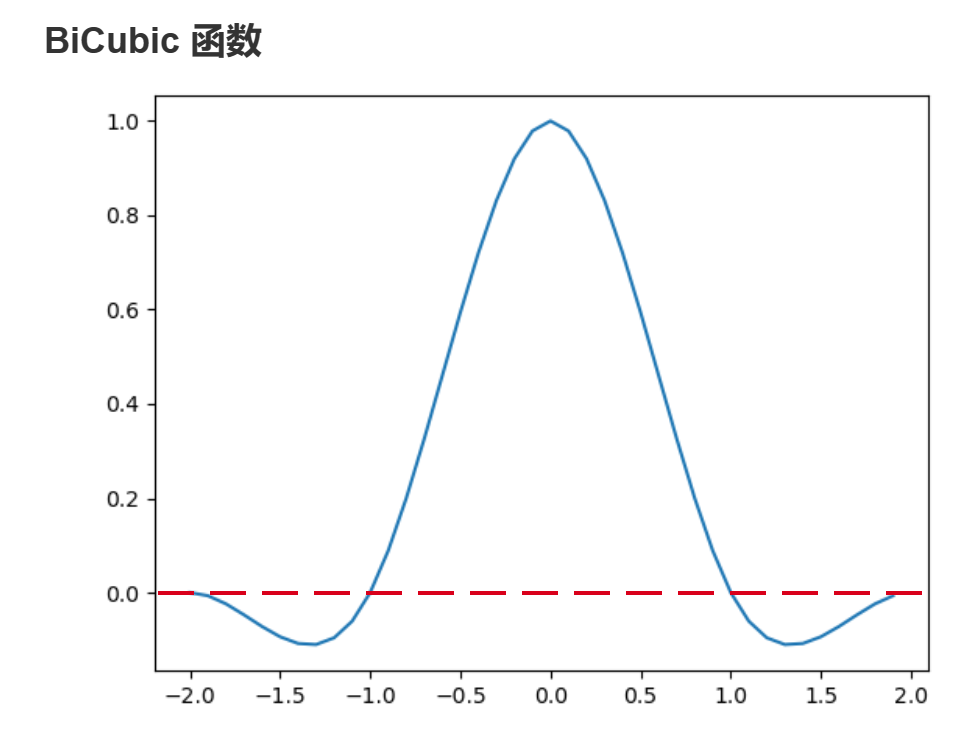
由上图可知:
- 当距离为0的时候, w = 1 w=1 w=1
- 当距离为-1或1的时候, w = 0 w=0 w=0
- 当距离为-2或2的时候, w = 0 w=0 w=0
所以当【放大后的图片】像素点与【原图片】像素点重合的时候,距离绝对值取值可能为0、1和2,那么最后插值计算的结果就是重合原图片像素点。
参考:
[1]: 用于数字成像的双三次插值技术 🚀
[2]: 插值算法 | 双三次插值算法 🚀(视频中a = -0.75)
3、程序设计
按照上述基本原理进行程序实现,具体函数在 gesture_display.cpp 文件中,其中有两个主要接口:
interpolate_image函数:实现8x8温度值放大成24x24温度值;temp_cloud_map_display函数:将温度值通过云图方式在lcd上显示;
+----------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| +-------------------------------+|
| ==> getw_x() ==> weight_xy_adjust2d() ==> | matrix_hadamard_pruduct() ||
| ==> getw_y() ==> weight_xy_adjust2d() ==> | img_matrix_hadamard_pruduct() ||
| ==> img8x8_pad_to_img12x12() ===========> | matrix_elem_sum() ||
| +-------------------------------+|
|----------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| ************************* interpolate_image() ************************* |
+----------------------------------------------------------------------------+
参考:
[1]: 图像的放大:双三次插值算法(c++实现) 🚀
四、数据集获取
上位机程序(pc):get_data/get_data.py
下位机程序(esp32):get_data/esp_dl_for_bixin

使用逻辑:
- lcd显示采集温度云图,若符合要求,按下键盘
任意键+回车; - 按下后,通过串口发送给esp32,esp32收到命令后,申请互斥锁,阻塞温度采集和插补计算,绘制当前温度云图,确认温度云图是否符合预期;
- 上位机输入标签或者放弃该数据,若输入数字标签(
0-背景,1-放大,2-捏住,3-减小),则将命令发送给esp32,等待esp32将点阵数据发送;若放弃,输入数字4,则将命令发送给esp32,重新进行温度采样; - pc设备在收到串口数据后,复原图像,然后根据标签将数据和图片保存到对应目录下,文件名自动加1;(若上位机程序中途退出,下次运行时候,需要将当前的文件数量覆盖num1/num2/num3/num3变量)
- 然后重新开始第一步。
五、cnn模型训练
5.1、环境配置:anconda3 | tf2.1.0 | pycharm
python:3.7(anaconda3)
开发框架:tensorflow 2.1.0
ide:pycharm
① python安装:
anaconda:python编译器和python包管理工具合在一起的一个软件。
安装配置教程: 🚀
# 虚拟环境常用命令
conda info -e # 查看已经创建的所有虚拟环境
conda create -n xxx python=3.7 # 创建一个python3.7 名为xxx的虚拟环境
conda activate xxx # 切换/激活到xx虚拟环境
② tensorflow安装:
// gpu 版本
pip install --upgrade tensorflow-gpu==2.0.0 -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
// cpu 版本
pip install --upgrade tensorflow-cpu==2.1.0 -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
检测是否安装成功:切换到虚拟环境——>输入python ——> 载入tensorflow (import tensorflow as tf) ——> 查看版本号(print(tf.__version__))
③ pycharm安装:
可以直接从 pycharm 官网下载,但是可能由于 anaconda 版本比较老,添加 python 解释器比较麻烦,所以这里采用这位博主提供的版本,具体软件安装、解释器添加教程可 🚀。
5.2、生成数据集 | 预处理
由第四章中所构建的数据集,*.txt 文件中保存的数据为温度值,数据的排布格式如上所示,将*.txt文件中的数据变成数据集需要考虑以下事情:
- 【生成数据集】保存的数据按照分类分别保存在不同的目录下,所以需要统计数据集目录下所有的数据,将数据打乱,按照60%训练-20%测试-20%验证的比例划分。
- 【预处理】
*.txt文件中的数据类型为字符串,而训练时候所需要的数据为 float。
5.2.1、生成数据集:统计数据集 | 数据集随机化 | 数据集划分
- 创建数字编码表,即手势行为与数字的对应关系,
background=0,increase=1,pinch=2,reduce=3; - 遍历文件夹下的所有文件,以列表的方式保存所有文件的路径;
- 通过 random.shuffle 打乱顺序;
- 读取列表每个元素值然后拆解,由于原先存放的顺序以类别分别存放在对应的目录下,所以从拆解的结果可以知道该数据对应的标签,将【数据路径(*.txt)】和【标签】保存到 csv 文件中;
- 从 csv 文件中读出数据,按【数据路径】和【标签】分别保存到两个变量中,返回;
- 按照比例,以切片的方式,得到训练集、测试集、验证集,注意这里的数据还只是数据的路径,后面输入到神经网络需要将数据提取处出来,这部分工作交给预处理来完成。
目录结构:
---xxx
|---dataset
|---background
|---1.jpg
|---1.txt
|---...
|---increase
|---1.jpg
|---1.txt
|---...
|---pinch
|---1.jpg
|---1.txt
|---...
|---reduce
|---1.jpg
|---1.txt
|---...
|---tmp_data.csv
|---geture_train.py
代码如下:
# 作用:将文件统计存入csv文件,然后读出csv文件内容
# root:数据集根目录
# filename:csv文件名
# name2label:类别名编码表
def load_csv(root, filename, name2label):
if not os.path.exists(os.path.join(root, filename)):
tmp_data = []
for name in name2label.keys():
# 'dataset\\increase\\1.txt
tmp_data += glob.glob(os.path.join(root, name, '*.txt'))
# 200, 'dataset\increase\\1.txt'...
print(len(tmp_data), tmp_data)
random.shuffle(tmp_data)
with open(os.path.join(root, filename), mode='w', newline='') as f:
writer = csv.writer(f)
for img in tmp_data: # 'dataset\\increase\\1.txt'
name = img.split(os.sep)[-2]
label = name2label[name]
# 'dataset\\increase\\1.png', 1
writer.writerow([img, label])
print('written into csv file:', filename)
# read from csv file
tmp_data, labels = [], []
with open(os.path.join(root, filename)) as f:
reader = csv.reader(f)
for row in reader:
# 'dataset\\increase\\1.txt', 1
tmp, label = row
label = int(label)
tmp_data.append(tmp)
labels.append(label)
assert len(tmp_data) == len(labels)
return tmp_data, labels
# root:数据集根目录
def load_gesture(root, mode='train'):
# 创建数字编码表
name2label = {} # "sq...":0
for name in sorted(os.listdir(os.path.join(root))):
if not os.path.isdir(os.path.join(root, name)):
continue
# 给每个类别编码一个数字
# 如: name2label['increase'] = 1
name2label[name] = len(name2label.keys())
print(name2label)
# 读取label信息
# [file1,file2,], [3,1]
images, labels = load_csv(root, 'tmp_data.csv', name2label)
if mode == 'train': # 60%
images = images[:int(0.6 * len(images))]
labels = labels[:int(0.6 * len(labels))]
elif mode == 'val': # 20% = 60%->80%
images = images[int(0.6 * len(images)):int(0.8 * len(images))]
labels = labels[int(0.6 * len(labels)):int(0.8 * len(labels))]
else: # 20% = 80%->100%
images = images[int(0.8 * len(images)):]
labels = labels[int(0.8 * len(labels)):]
return images, labels, name2label
5.2.2、预处理:string类型转换为float | 数据标准化 | one-hot encoding
预处理工作通过map的方式实现,将每个路径的 txt 加载进来替换掉,变成 txt 本身的内容,即 x x x 由原先路径,变成 [24, 24] 温度矩阵数据, y y y 为标签数据。
- 读取
*.txt中的数据,该数据为一个字符串; - 删除字符串中的
空格和\r\n字符,然后以这些字符,分割字符串,产生 576 个字符串,以列表的方式保存; - 将 576 个字符串转换为 float 类型,此时列表为 576 个 float 类型元素,shape为 [576];
- 将 [576] shape 转换为 [24, 24] shape,并进行扩展维度,将 [24, 24] shape 转变为 [24, 24, 1];
- 采用
最大最小标准化(min-max normalization): x ′ = x − m i n ( x ) m a x ( x ) − m i n ( x ) x^{'}=\dfrac{x-min(x)}{max(x)-min(x)} x′=max(x)−min(x)x−min(x) (对 x x x 数据进行标准化处理); - 将 label 数据(
y
y
y)转换为 tensor 类型,并进行
one-hot encoding处理(共 4 种类型,数字0,编码后变成 [1,0,0,0]); - 导出 x x x 和 y y y 两种 tensor 数据。
代码如下:
def preprocess(x, y): # 这个顺序和from_tensor_slices中的 x,y 对应
# 读入txt数据
data = tf.io.read_file(x)
# 分割每行数据
data = tf.strings.split(data) # "22.11 22.11 ...\r\n22.11 22.11...\r\n" => ["22.11" "22.11" ...]
data = tf.strings.to_number(data) # ["22.11" "22.11" ...] (string) => [22.11 22.11 ...] (float32)
data = tf.reshape(data, [24, 24]) # shape [576] => shape [24, 24]
data = tf.expand_dims(data, axis=2) # shape [24, 24] => shape [24, 24, 1]
# data数据归一化
max_data = tf.reduce_max(data) # 标量
min_data = tf.reduce_min(data) # 标量
data = (data - min_data)/(max_data-min_data) # broadcat 张量维度扩张
y = tf.convert_to_tensor(y)
y = tf.one_hot(y, depth=4) # one-hot encoding
return data, y
5.3、构建训练模型
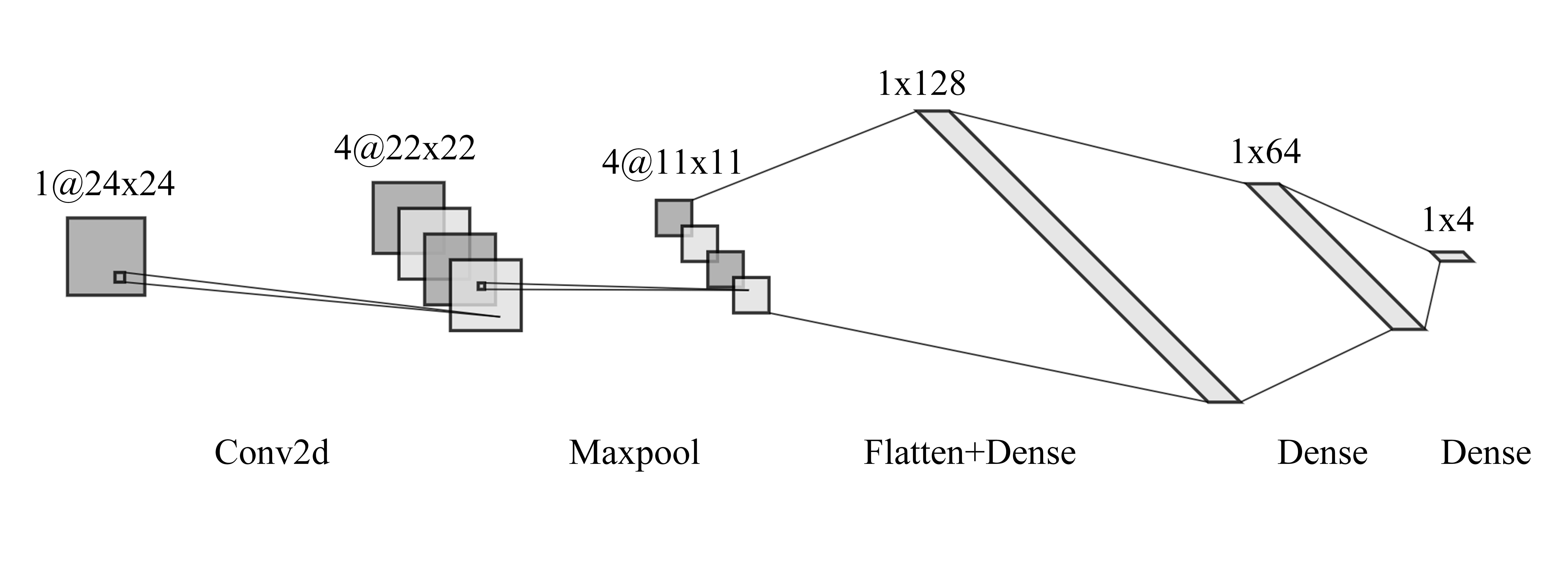
conv_layers = [
# kernel_size:3x3, 卷积核个数:4
layers.conv2d(4, input_shape=(24, 24, 1), kernel_size=[3, 3], padding="valid", activation=tf.nn.relu), # [b, 24, 24, 1] => [b, 22, 22, 4]
layers.maxpool2d(pool_size=[2, 2], strides=2, padding='valid'), # [b, 22, 22, 4] => [b, 11, 11, 4]
layers.flatten(), # [b, 11, 11, 4] => [b, 484]
layers.dense(128, activation=tf.nn.relu), # [b, 484] => [b, 128]
layers.dense(64, activation=tf.nn.relu), # [b, 128] => [b, 64]
layers.dense(4, activation=tf.nn.softmax), # [b, 64] => [b, 4]
]
def main():
print(tf.__version__)
train_images, train_labels, train_table = load_gesture('.\\dataset', 'train')
val_images, val_labels, val_table = load_gesture('.\\dataset', 'val')
train_db = tf.data.dataset.from_tensor_slices((train_images, train_labels))
train_db = train_db.map(preprocess).batch(300)
val_db = tf.data.dataset.from_tensor_slices((val_images, val_labels))
val_db = val_db.map(preprocess).batch(300)
# [b, 24, 24, 1] => [b, 4]
network = sequential(conv_layers)
# network.build(input_shape=[none, 24, 24, 1])
network.compile(optimizer=optimizers.adam(lr=1e-4), # adam优化器配置
loss=tf.losses.categoricalcrossentropy(from_logits=false), # 损失函数: 交叉熵
metrics=['accuracy']) # 准确率计算
# 打印网络信息
network.summary()
# 模型训练和验证
network.fit(train_db, epochs=200, validation_data=val_db, validation_freq=1)
构建模型的时候,输入张量设置方式有多种,上面的是直接在模型conv_layers 中添加,或者可以使用model.build(input_shape=[none, 24, 24, 1]),这两种方式存在一定的差异,至少在onnx模型转换的时候,第二种方式会报错:‘sequential’ object has no attribute ‘output_names’;并且二者的ckpt权值文件也是不通用的,提示:shapes (128,) and (64,) are incompatible。
5.4、训练结果保存和准确率
在构建模型的基础上,添加权值保存语句:
checkpoint_path = "gesture_train-{epoch:02d}.ckpt" # ckpt保存文件名, 占位符将会被epoch值和传入on_epoch_end的logs所填入
cp_callback = tf.keras.callbacks.modelcheckpoint(filepath=checkpoint_path, # 保存文件名
save_best_only=true, # 当设置为true时,将只保存在验证集上性能最好的模型
save_weights_only=true, # 若设置为true,则只保存模型权重,否则将保存整个模型(包括模型结构,配置信息等)
verbose=1, # 为1表示输出epoch模型保存信息,默认为0表示不输出该信息
save_freq='epoch' # checkpoint之间的间隔的epoch数
)
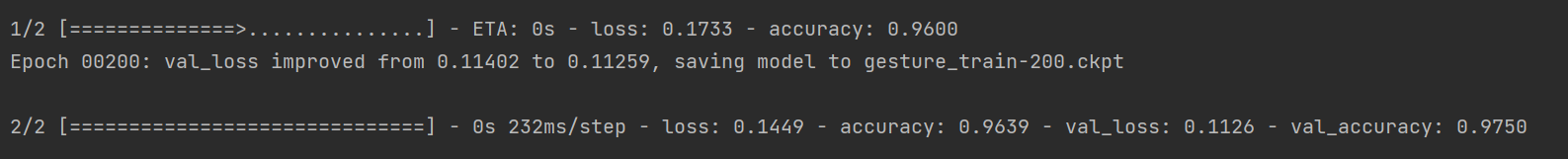
network.fit(train_db, epochs=200, validation_data=val_db, validation_freq=1, callbacks=[cp_callback])
训练结果准确率: 有部分数据集在采集过程中,距离传感器较远,相关特征不能很好的采集,所以验证集中若包含该数据,那么准确率不是很高,差不多在80%。若验证集中不包含该部分数据,准确率能到100%。
参考:
[1]: tensorflow 2.1 完成权重或模型的保存和加载 🚀
[2]: modelcheckpoint详解 🚀
5.5、onnx模型转换和校准集导出
【onnx模型】和【校准集】用于模型量化,校准集可以是训练集或验证集的子集,这里取训练集和验证集的集合作为校准集。
① onnx模型转换:
这一步开始参考 esp-dl 示例程序中的代码,下载:https://github.com/espressif/esp-dl 🚀(解压后目录名称为 esp-dl-master);
参考esp-dl-master\tools\quantization_tool\examples\tensorflow_to_onnx 提供的代码,做简单的修改,应用于本模型。
其余不用修改,注释掉main(),添加下列代码:
if __name__ == '__main__':
# main()
model = sequential(conv_layers)
model.load_weights('gesture_train-06.ckpt')
model.summary()
# export model to onnx format
spec = (tf.tensorspec((none, 24, 24, 1), tf.float32, name="input"),) # 函数签名
output_path = "gesture.onnx"
model_proto, _ = tf2onnx.convert.from_keras(model, input_signature=spec, opset=13, output_path=output_path)
# checker.check_graph(model_proto.graph)
- –opset 11:onnx是一个不断发展的标准,它将添加更多的新操作并增强现有的操作,因此不同的opset版本将包含不同的操作,它们可能会有些不同 。这里参考示例程序,选择
opset 13。
② 校准集导出: 训练集 + 验证集
- .pkl数据文件 :python中,pickle模块将任意一个python对象转换成一系统字节。
import pickle
# obj: 序列化对象
# file: 保存到的待写入的文件对象
# protocol: 序列化模式,默认是0(最原始的人类可读版本)
pickle.dump(obj, file, protocol=none, *, fix_imports=true, buffer_callback=none)
pickle.load() # 反序列化
查看 esp-dl 示例中的 pickle 文件(esp-dl-master\tools\quantization_tool\examples\mnist_test_data.pickle),本数据集参考该方式转换;
f = open('mnist_test_data.pickle', 'rb') # 打开pickle文件
info = pickle.load(f)
print('type', type(info), len(info))
print(info[0])
print(info[1])
f.close() # 关闭pickle文件
示例中的 pickle 文件的保存类型为list,info[0] 为图像数据,info[1] 为label数据。
导出 pickle 文件:
# loc_train_db: 用于训练的数据集
# loc_val_db: 用于验证的数据集
def pkl_dataset_create(loc_train_db, loc_val_db):
global pkl_train_savepath, pkl_cal_savepath
loc_train_sample = [[], []]
loc_val_sample = [[], []]
for step, (x, y) in enumerate(loc_train_db):
if step == 0:
loc_train_sample[0] = x
loc_train_sample[1] = y
else:
loc_train_sample[0] = tf.concat([loc_train_sample[0], x], axis=0) # shape [300,24,24,1] + shape [300,24,24,1] => shape [600, 24, 24, 1]
loc_train_sample[1] = tf.concat([loc_train_sample[1], y], axis=0) # shape [300,4] + shape [300, 4] => shape [600, 4]
for step, (x, y) in enumerate(loc_val_db):
if step == 0:
loc_val_sample[0] = x
loc_val_sample[1] = y
else:
loc_val_sample[0] = tf.concat([loc_val_sample[0], x], axis=0)
loc_val_sample[1] = tf.concat([loc_val_sample[1], y], axis=0)
print('train:', 'x-', loc_train_sample[0].shape, 'y-', loc_train_sample[1].shape)
print('val:', 'x-', loc_val_sample[0].shape, 'y-', loc_val_sample[1].shape)
loc_train_sample[0] = tf.concat([loc_train_sample[0], loc_val_sample[0]], axis=0)
loc_train_sample[1] = tf.concat([loc_train_sample[1], loc_val_sample[1]], axis=0)
print('train:', 'x-', loc_train_sample[0].shape, 'y-', loc_train_sample[1].shape)
pkl_train_db = [loc_train_sample[0].numpy(), loc_train_sample[1].numpy()]
with open(pkl_train_savepath, 'wb') as f:
pickle.dump(pkl_train_db, f, -1)
print('pkl save done!')
函数参数传递进来后,进入取训练集的数据循环,若训练集总数为720,验证集总数为80,则:
- 第一次循环后,loc_train_sample[0] 的 shape 为 [300, 24, 24, 1],loc_train_sample[1] 的 shape 为 [300, 4];(300是因为训练的时候batchsize取300)
- 第二次循环后,loc_train_sample[0] 的 shape 为 [300, 24, 24, 1],loc_train_sample[1] 的 shape 为 [300, 4],和上一次循环结果进行合并;
- 第三次循环后,loc_train_sample[0] 的 shape 为[120, 24, 24, 1],loc_train_sample[1] 的 shape 为[120, 4],和上一次循环结果进行合并;
上述数据的类型为 tensor,存储为pickle后,在后续量化中出现:‘your cpu supports instructions that this tensorflow binary was not compiled to use: avx2’(主机为amd处理器)。因此这里使用loc_val_sample[0].numpy()语句,将tensor类型转换为numpy类型。
参考:
[1]: 手写图像数据集mnist下载,处理为numpy格式后存为.pkl格式 🚀
[2]: python中 pickle 模块的 dump() 和 load() 方法详解 🚀
[3]: pickle — python object serialization 🚀
六、模型量化与部署
6.1、模型量化
顺利到这一步,已经有如下文件:gesture_train.pickle 和 gesture.onnx。
参考 tools/quantization_tool/examples/example.py,示例目录如下,
---quantization_tool
|---examples
|---example.py
|---optimizer.py
|---windows
|---calibrator.pyd
|---calibrator_acc.pyd
|---evaluator.pyd
复制上述文件,创建如下目录,
---quantization
|---examples
|---quantization.py(原example.py)
|---gesture_train.pickle
|---gesture.onnx
|---optimizer.py
|---windows
|---calibrator.pyd
|---calibrator_acc.pyd
|---evaluator.pyd
① 进入虚拟环境
conda activate mt_for_esp
其中,mt_for_esp是<虚拟环境名称>。
② 安装 python 依赖包
pip install numba==0.53.1
pip install --upgrade onnx==1.9.0 # 环境中若已安装可以直接更新
pip install onnxruntime==1.7.0
pip install onnxoptimizer==0.2.6
③ esp-dl组件下载:https://github.com/espressif/esp-dl 🚀
④ 进行修改quantization.py
1.修改pickle和onnx文件名;
2.删除test_images = test_images / 255.0, 数据集已经完成标准化;
3.calib_dataset = test_images[0:5000:50] => calib_dataset = test_images[0:1040:10];
4.batch_size = 10;
5.test_labels外层增加np.argmax, 原版本label没有one-hot, 这里 pickle 文件中label完成one-hot;
⑤ 输入 python quantization.py,输出如下文件和信息
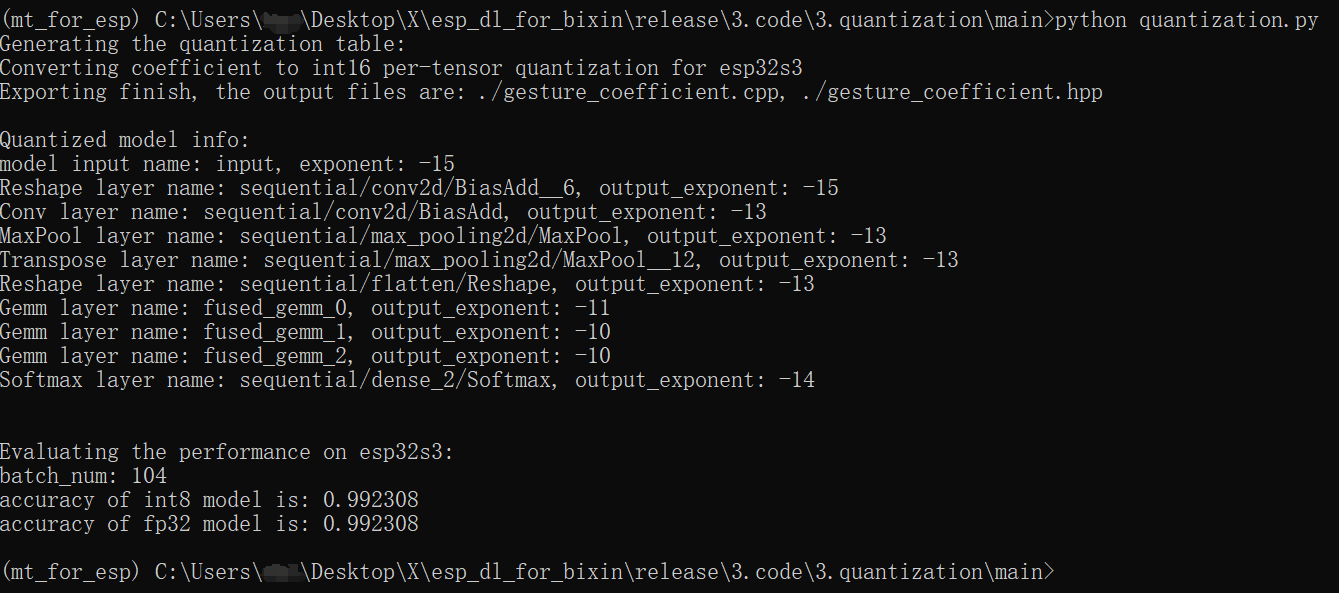
- gesture_cal.pickle
- gesture_coefficient.cpp
- gesture_coefficient.hpp
- gesture_optimized.onnx
参考:手动部署模型 🚀
6.2、esp-dl组件添加
- esp-dl组件下载:https://github.com/espressif/esp-dl 🚀(解压后目录名称为
esp-dl-master); - 创建组件,这里叫做
esp-dl; - 将
esp-dl-master/include目录下的文件复制到esp-dl组件中的include目录下;(有些文件不是很必要可以根据需求调整) - 将
esp-dl-master/lib/esp32s3目录下的libdl.a复制到esp-dl组件根目录下,组件结构如下;
---esp-dl
|---include
|---detect
|---image
|---layer
|---math
|---nn
|---tool
|---tvm
|---typedef
|---dl_define.hpp
|---cmakelists.txt
|---libdl.a
- 修改
esp-dl组件下的cmakelists.txt,如下
idf_component_register(srcs
include_dirs "include" "include/detect" "include/image" "include/layer" "include/math" "include/nn" "include/tool" "include/tvm" "include/typedef")
target_link_libraries(${component_lib} interface "${cmake_current_list_dir}/libdl.a")
- (可选)到上面这一步就可以了,这里通过官方示例提供的 mnist 测试添加
esp-dl组件是否编译正常,(example:esp-dl-master/tutorial/quantization_tool_example); - (可选)创建
model组件,文件结构如下:
---|---esp-dl
|---model
|---include
|---mnist_coefficient.hpp
|---mnist_model.hpp
|---mnist_coefficient.cpp
|---cmakelists.txt
- (可选)
model组件下的cmakelists.txt如下,该组件依赖于 esp-dl 组件,所以需要添加requires esp-dl,
idf_component_register(srcs "mnist_coefficient"
include_dirs "include"
requires esp-dl)
- (可选)
main.app文件替换一下,替换前注意备份老版本,直接编译即可。(若运行的时候发现推理时间官方示例不同,可考虑将sdkconfig配置的同官方一致)
参考:使用 esp-idf 生成第三方的 .a 静态库并使用的流程 🚀
6.3、esp 数据标准化(网络输入)
数据集为关于温度的矩阵(24x24),在训练的时候有一个预处理的过程,其中包含归一化,对于网络而言,输入是归一化后的结果,所以推理的时候,输入网络中的数据也应该是归一化后的数据。
// 寻找最大值和最小值
template<typename t>
void max_min(t *ptr, uint16_t count, t *max, t *min)
{
*max = ptr[0];
*min = ptr[0];
for(int i=1; i<count; i++){
if(*max < ptr[i]){
*max = ptr[i];
}
if(*min > ptr[i]){
*min = ptr[i];
}
}
}
__attribute__((aligned(16))) float example_element[576];
__attribute__((aligned(16))) float tmp[576];
int main(void){
float max, min;
max_min(example_element, &max, &min);
for(int i = 0; i<576; i++){
// normalization
tmp[i] = (example_element[i]-min)/(max-min);
}
}
6.4、构建模型与优化
创建 model 组件,将 gesture_coefficient.cpp 和 gesture_coefficient.hpp 加入到该组件中,目录如下,
---model
|---include
|---gesture_coefficient.hpp
|---gesture_model.hpp
|---cmakelists.txt
|---gesture_coefficient.cpp
cmakelists.txt 内容如下,
idf_component_register(srcs "gesture_coefficient.cpp"
include_dirs "include"
requires esp-dl)
在 gesture_model.hpp 中完成模型构建,主要步骤如下,
- 模型类派生一个新类,由于量化时配置的为
int16量化,故模型以及之后的层均继承<int16_t>类型; - 将层声明为成员变量;
- 用构造函数初始化层;
- 实现
void build(tensor<input_t> &input); - 实现
void call(tensor<input_t> &input);
按照量化工具优化后的网络模型,构建网络模型如下:
reshape<int16_t> l1; // shape(24,24,1) => shape(24,24,1)
conv2d<int16_t> l2; // shape(24,24,1) => shape(22,22,4)
maxpool2d<int16_t> l3; // shape(22,22,4) => shape(11,11,4)
transpose<int16_t> l4; // shape(11,11,4) => shape(11,11,4)
reshape<int16_t> l5; // shape(11,11,4) => shape(1,484)
fullyconnected<int16_t, int16_t> l6; // shape(1,484) => shape(128)
fullyconnected<int16_t, int16_t> l7; // shape(128) => shape(64)
fullyconnected<int16_t, int16_t> l8; // shape(64) => shape(4)
reshape<int16_t> l9; // shape(4) => shape(1,1,4)
softmax<int16_t> l10; // shape(1,1,4) => shape(1,1,4)
优化:删除不必要的层
- l 1 l1 l1层在刚开始设置数据集的时候可以指定,所以这一层可以删除;
- l 4 l4 l4层之后的 l 5 l5 l5层直接打平,可以选择直接从 l 3 l3 l3到 l 5 l5 l5,所以删除 l 4 l4 l4;
优化后的模型如下:
conv2d<int16_t> l1; // shape(24,24,1) => shape(22,22,4)
maxpool2d<int16_t> l2; // shape(22,22,4) => shape(11,11,4)
reshape<int16_t> l3; // shape(11,11,4) => shape(1,484)
fullyconnected<int16_t, int16_t> l4; // shape(1,484) => shape(128)
fullyconnected<int16_t, int16_t> l5; // shape(128) => shape(64)
fullyconnected<int16_t, int16_t> l6; // shape(64) => shape(4)
reshape<int16_t> l7; // shape(4) => shape(1,1,4)
softmax<int16_t> l8; // shape(1,1,4) => shape(1,1,4)
6.5、esp硬件加速:修改sdkconfig配置
esp32-s3的存储器如下:
-
内部存储器
- 片内rom(384kb):存放系统底层软件的rom代码,如一级引导程序。
- 片内sram(512kb):用于保存data段、bss段、堆栈等,以及部分text段(iram_attr修饰的函数)和icache、dcache。
- rtc 快速存储器(8kb)
- rtc 慢速存储器(8kb)
- 片内psram(8mb)
-
外部存储器
- 片外flash(16mb):用于保存二级引导程序(bootloader)和应用启动程序,加之链接脚本设置data/bss/(部分)text的地址空间为iram,所以在执行主函数之前需要完成data/(部分)text搬运。
主要加速点:
-
提高dcache大小和访问速率:cpu通过spi得到flash上的代码和数据的速度不及来自cache(片内sram),根据cpu从flash取数据的原理,如果cache足够大,那么地址命中率提高,有效减少片外flash访问。
-
提高spi通讯速率:如果将spi通讯速率提升,也能提高flash访问速度。
-
提高cpu主频:若cpu的主频足够快,理论上计算速度也足够快。(该网络主要性能瓶颈在存储器读写,所以160mhz提高到240mhz提升不明显)
sdkconfig主要配置如下:【idf.py menuconfig】
-
修改cpu主频,160mhz => 240mhz
- component config —> esp system settings —> cpu frequency (160 mhz) —> (x) 240 mhz
-
修改片外flash
- spi 模式,qio:spiserial flasher config —> flash spi mode (dio) —> (x) qio;
- spi 速度,80mhz:spiserial flasher config —> flash spi speed (80 mhz) ;
- flash 大小,4mb:spiserial flasher config —> flash size (2mb) —> (x) 4mb;
-
修改片内psram
- spi 模式为8线(octal mode):component config —> esp psram —> support for external, spi-connected ram —> spi ram config —> mode (quad/oct) of spi ram chip in use (quad mode psram) —> (x) octal mode psram
- spi 频率为80mhz:component config —> esp psram —> support for external, spi-connected ram —> spi ram config —> set ram clock speed (40mhz clock speed) —> (x) 80mhz
-
修改data cache
- 设置 data cache size为64kb:component config —> esp system settings —> cache config —> data cache size (32kb) —> (x) 64kb
- 设置 data cache line size为64b:component config —> esp system settings —> cache config —> data cache line size (32 bytes) —> (x) 64 bytes
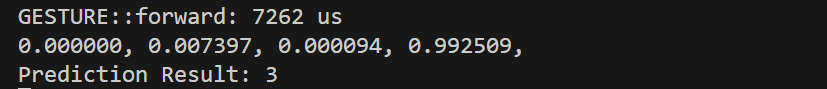
【无softmax层】推理耗时:7020us

【有softmax层】推理耗时:7262us
参考:
[1]: esp32/esp32-s2 cpu加速建议 🚀
[2]: esp32 cpu时钟设置 240mhz 🚀
[3]: 【esp32-idf】03-1 系统-内存管理 🚀
[4]: esp32 程序的内存模型 🚀
七、应用逻辑设计
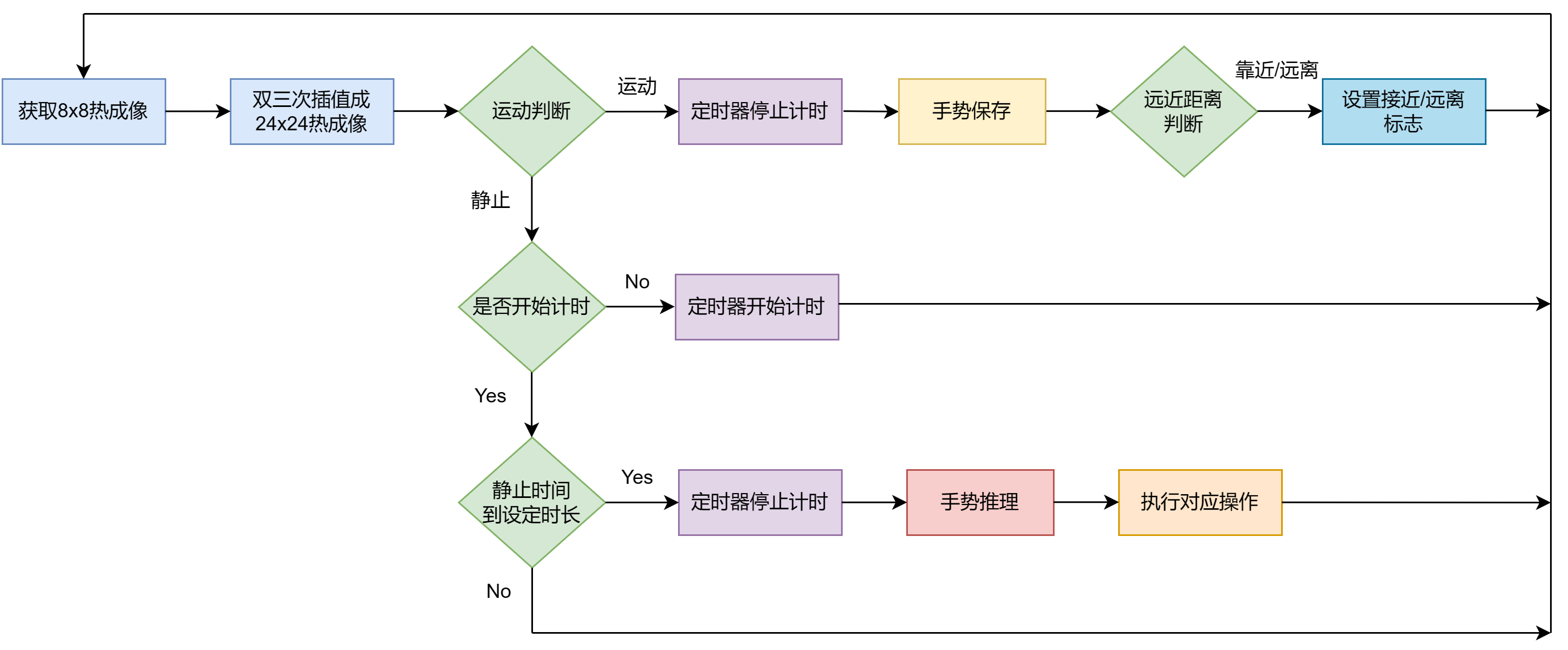
7.1、获取静止状态手势 | 定时器引入
① 获取静止状态手势程序逻辑:
② 定时器引入
对于esp32-s3部署平台,该模型推理过程约7ms,这对于实际应用过程中,能保持较好的实时性,然而,由于该模型未采用rnn/lstm等时序处理模型,所以只能针对某一个动作进行推理。试想一下,当手指由交叉状变成捏住状态,在这个改变过程中的某一个状态,可能被采集被推理为增大,但是实际应该是减小。基于此,通过引入定时器,当某个动作保持一定时间后,才对这个动作进行推理。
esp_timer 内部使用 52 位硬件定时器,对于 esp32-s3 使用的是 systimer。其 api 集支持单次定时器和周期定时器、微秒级的时间分辨率。
定时器回调可通过以下两种方式调度:
esp_timer_task:定时器回调函数是从高优先级的esp_timer任务中调度的,如果有优先级高于esp_timer的其他任务正在运行,则回调调度将延迟,直至esp_timer能够运行。esp_timer_isr:定时器回调由定时器中断处理程序直接调度。对旨在降低延迟的简单回调,建议使用此途径。
定时器可以以单次模式和周期模式启动。
- 单次模式:定时器计时结束,调用回调函数,随后停止;
- 周期模式:定时器计时结束,调用回调函数,随后重新开始,周而复始。
这里采用单次模式+esp_timer_task配置,api接口如下:
esp_timer_create:创建定时器;esp_timer_delete:删除定时器;esp_timer_start_once:启动单次模式定时器;esp_timer_stop:停止定时器,下一次启动使用esp_timer_start_once;esp_timer_get_time:获取从boot开始时间,单位为微秒。
多任务中存在对临界资源的访问,这里通过【互斥锁】加以保护。
测试代码:
#include "esp_timer.h"
esp_timer_handle_t oneshot_timer;
volatile char stillness_time_flag = 0; // 临界资源
semaphorehandle_t xsemaphore = null;
static const char* tag = "example";
static void oneshot_timer_callback(void* arg)
{
xsemaphoretake(xsemaphore, portmax_delay);
stillness_time_flag = 1;
xsemaphoregive(xsemaphore);
}
const esp_timer_create_args_t oneshot_timer_args = {
.callback = &oneshot_timer_callback,
/* argument specified here will be passed to timer callback function */
.arg = null,
.name = "one-shot"};
extern "c" void app_main(void)
{
esp_error_check(esp_timer_create(&oneshot_timer_args, &oneshot_timer)); //定时器
xsemaphore = xsemaphorecreatemutex(); //创建互斥量
assert(xsemaphore != null);
esp_logi(tag, "time since boot: %lld us", esp_timer_get_time());
esp_timer_stop(oneshot_timer);
usleep(2000000); 休眠2s
esp_timer_start_once(oneshot_timer, 200000);
esp_logi(tag, "time since boot: %lld us", esp_timer_get_time());
}
参考:
[1]: 高分辨率定时器(esp 定时器) 🚀
[2]: esp_timer_example_main.c 🚀
7.2、交互方式选择:交互方式1
到这一步,通过上述动作设定,只需要最后静止的动作是训练的那些动作,就能完成捏住/增加/减小/松开的操作。
- 捏住状态: 选中操作对象;
- 捏住+上移:向右移动,选择操作对象;
- 捏住+下移:向左移动,选择操作对象;
- 交叉状态:操作对象增加;
- 松开状态:操作对象减小;
- 背景状态:取消对象选中。
7.3、交互方式选择:交互方式2
- 捏住=>交叉:操作对象增加;【判断逻辑同交互方式1】
- 交叉=>捏住:操作对象减小;
- 捏住=>松开:操作对象取消选择;【只需要判断最后一个动作即可】
- 松开=>捏住:选中操作对象;
- 捏住+上移:向右移动,选择操作对象;【判断逻辑同交互方式1】
- 捏住+下移:向左移动,选择操作对象。【判断逻辑同交互方式1】
对于交互方式2,在运动过程中,边采集数据边推理,一些动作未加入训练集中训练,所以存在推理错误的情况,然而该组动作最后的操作结果依据这些操作序列得出,就可能导致判断出错。所所所所所以,上面的逻辑是理想的推理!
交互方式切换使用条件编译的方式进行选择:gesture_display.h文件下
#define interactive_methods 1 // 1表示交互方式1, 2表示交互方式2
八、others
8.1、跑一下示例程序(mnist)
- 下载 esp-dl,可以使用以下命令,当然也可以直接在 github 🚀网页中下载;
git clone https://github.com/espressif/esp-dl.git
- 打开终端
esp-idf 5.0 cmd,进入tutorial/convert_tool_example文件夹:
c: # windows下切换到c盘
dir # 查看当前路径下的文件列表
cd ~/esp-dl/tutorial/convert_tool_example # 切换路径
- 使用以下命令设置目标芯片:(当前芯片为 esp32s3)
idf.py set-target esp32s3
-
将psram模式设置为
octal mode psram:终端输入idf.py menuconfig => component config => esp psram => spi ram config => moda (quad/oct) of spi ram chip in use (quad mode psram) => octal mode psram -
烧录固件,打印结果
idf.py flash monitor
参考:获取 esp-dl 并运行示例 🚀
8.2、数据集补充程序
对于分类任务,或多或少有些类别没有被添加到数据集,且当前网络无法做到正确推理,所以在前面的基础上写了个数据集补充程序。
程序分为:pc端上位机(python)和 esp32端下位机(c/c++)
程序操作步骤:
- 运行上位机程序,马上重启esp32;
- esp32采集手势数据(只要一直在运动就不停止数据采集,当停止采集后,就开始推理,并将推理结果发送到上位机);
- 上位机中输入label(0-背景/1-增加/2-捏住/3-减小)或者放弃(4-不添加该数据);
- 下位机收到数字后,若为标签数值,则将手势数据上传,若为放弃,则丢弃数据;
- 然后,开始新一轮的循环。



发表评论