应用程序的生命周期
在wpf中,应用程序会经历简单的生命周期。本质上,visual studio为application类使用的模型与用于窗口的模型相同。起点是xaml模板,默认情况下该模板命名为app.xaml:
创建application对象
<application x:class="wpfapp3.app"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:wpfapp3"
startupuri="mainwindow.xaml">
<application.resources>
</application.resources>
</application>startupuri属性来确定主窗口的xaml文档。因此不需要代码显式地实例化窗口,xaml解析器自动完成这项工作。自动生成的部分在项目中是不可见的,看起来如下:
using system;
using system.windows;
public partial class app:application
{
[stathread()]
public static void main()
{
wpfapp3.app app = new wpfapp3.app();
app.initializecomponent();
app.run();
}
public void initializecomponent()
{
this.startupuri = new uri("window1.xaml", system.urikind.relative);
}
}应用程序的关闭方式
通常,只要有窗口未关闭,application类就保持应用程序处于有效状态。
可通过appliaction.shutdownmode属性修改关闭模式,枚举值:
- onlastwindowclose:默认行为,只少有一个窗口存在,应用程序就保持运行状态。
- onmainwindowclose:传统方式,只要主窗口还处于打开状态,应用程序就保持运行状态。
- onexplictitshutdown:除非调用application.shutdown()方法,否则应用程序不会结束。
app.xaml文件中添加shutdownmode=“onmainwindowclose”
<application x:class="wpfapp3.app"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:wpfapp3"
startupuri="mainwindow.xaml"
shutdownmode="onmainwindowclose">
<application.resources>
</application.resources>
</application>应用程序事件
app.xaml.cs文件里可添加代码来处理应用程序事件。
应用程序事件:
- startup:该事件在调用application.run()方法之后,并且在主窗口显示之前。
- exit:该事件在应用程序关闭时,并在run()方法即将返回之前发生。
- sessionending:该事件在window对话结束时发生。
- activated:当激活应用程序中的窗口是发生该事件。
- deactivated:当取消激活用用程序中的窗口时发生该事件。
- dispatcherunhandledexception:在应用程序中的任何位置,只要发送未处理的异常,就会发生该事件。
- 处理事件两种方法:
- 关联事件处理程序;
重写相应的受保护方法。
关联事件处理程序,如xmal中添加事件处理dispatcherunhandledexception=“application_dispatcherunhandledexception”
app.xaml
<application x:class="wpfapp3.app"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:wpfapp3"
startupuri="mainwindow.xaml"
dispatcherunhandledexception="application_dispatcherunhandledexception">
<application.resources>
</application.resources>
</application>app.xaml.cs:
private void application_dispatcherunhandledexception(object sender, system.windows.threading.dispatcherunhandledexceptioneventargs e)
{
}
代码重写事件方法窗口事件:
using system.configuration;
using system.data;
using system.windows;
namespace wpfapp3
{
/// <summary>
/// interaction logic for app.xaml
/// </summary>
public partial class app : application
{
private bool unsavedate = false;
public bool unsavedate
{
get { return unsavedate; }
set { unsavedate = value; }
}
protected override void onstartup(startupeventargs e)
{
base.onstartup(e);
unsavedate = true;
}
protected override void onsessionending(sessionendingcanceleventargs e)
{
base.onsessionending(e);
if (unsavedate)
{
e.cancel = true;
messagebox.show("测试:"+e.reasonsessionending.tostring());
}
}
}
}application类的任务
显示初始界面
wpf应用程序的运行速度快,但并不能在瞬间启动。第一次启动应用程序时,会有一些延迟,因为公共语言运行时(common language runtime,clr)首先需要初始化.net环境,然后启动应用程序。通常这一延时时间很短。但如果具有更耗时的初始化步骤,可使用wpf提供的简单初始界面特性,添加加初始界面的方法:
- 为项目添加图像文件(.bmp,.png,.jpg文件)。
- 在solution explorer中选择图像文件。
- 将build action修改为splashscreen。
下次运行应用程序时,图像会立即在屏幕中央显示出来。当添加初始界面时,wpf编译器为自动生成的app.cs文件添加与下面类似的代码:
splashscreen splashscreen = new splashscreen("splashscreenimage.png");
splashscreen.show(true);
myapplication.app app = new myapplication.app();
app.initializecomponent();
app.run();
处理命令行参数
为处理命令行参数,需要响应application.startup事件。命令行参数是通过startupeventargs.args属性作为字符串数组提供的。
例如,假定希望加载文档,文档名作为命令行参数传递。通过代码实例化主窗口。
public partial class app : application
{
private static void app_startup(object sender, startupeventargs e)
{
fileviewer win = new fileviewer();
if (e.args.length > 0)
{
string file = e.args[0];
if (system.io.file.exists(file))
{
win.loadfile(file);
}
else
{
}
}
}
}访问当前application对象
通过静态的application.current属性,可在应用程序的任何位置获取当前应用程序的实例,从而在窗口之间进行基本交互,任何窗口都可以访问当前application对象,并通过application对象获取主窗口的引用:
window main = application.current.mainwindow;
messagebox.show("the main window is " + main.title);如果希望访问在自定义窗口类中添加的任意方法、属性或事件,需要将窗口对象转装换为正确类型。
mainwindow main = (mainwindow)application.current.mainwindow; main.dosomething();
在窗口中还可以检查application.windows集合的内容:
foreach( window window in application.current.windows)
{
messagebox.show(window.title + " is open.");
}在窗口之间进行交互
应用程序类还可以很好地达到另一个目的:保存重要窗口的引用,使一个窗口可访问另一个窗口。
窗口分为模态和非模态:
- 模态窗口:模态窗口会中断应用程序流,直到窗口关闭为止。
- 非模态窗口:非模态窗口则不中断应用程序流。
示例,每个文档窗口由名为document的类实例表示:
public partial class app : application
{
private list<document> documents = new list<document>();
public list<document> documents
{
get {return documents};
set {documents = value;}
}
}
下面是响应按钮点击事件的处理程序:
private void cmdcreate_click(object sender, routeeventargs e)
{
document doc = new document();
doc.owner = this;
doc.show();
((app)application.current).documents.add(doc);
}
程序集资源
wpf应用程序中的程序集资源与其他.net应用程序中的程序集资源在本质上是相同的。基本概念是为项目添加文件,从二visual studio可将其嵌入到编译过的应用程序的exe或dll文件中。
添加资源
通过向项目添加文件,并在properties窗口中将其build action属性设置为resource来添加资源。
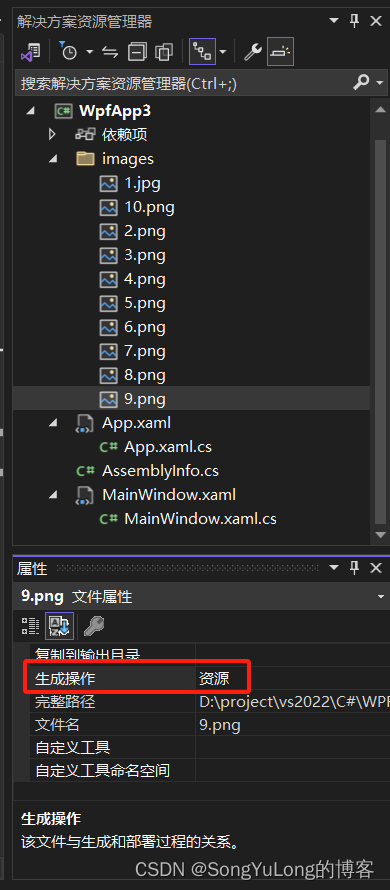
为成功地使用程序集资源,未必注意一下两点:
- 不能将build action属性错误地设置为embedded resource。
- 不要在project properties窗口中使用resource选项卡。
检索资源
可以采用多种方法来使用资源。
低级方法是检索封装数据的streamresourceinfo对象,然后决定如何使用该对象。
streamresourceinfo sri = application.getresourcestream(new uri(“images/winter.jpg”, urikind.relative));
xmal:
<\image source=“images/1.jpg”></image>
使用bitmapimage对象,该对象使用uri确定希望显示的图像位置。
绝对路径:
img.source = new bitmapimage(new uri((@“d:\img\jpgs\2.jpg”));
相对路径:
img.source = new bitmapimage(new uri(“images/6.jpg”, urikind.relative));
pack uri
wpf使用pack uri语法寻址编译个的资源。使用相对uri来引用资源
内容文件
当嵌入式文件作为资源时,会将文件放到编译过的程序集中,并且可以确保文件总是可用的。
如下情况不适合使用这种方法:
- 希望改变资源文件,有不想重新编译应用程序;
- 资源文件非常大;
- 资源文件是可选的,并且可以不随程序集一起部署;
- 资源是声音文件(wpf声音类不支持程序集资源);
wpf为程序集添加了assemblyassociatedcontentfile特性,声明每个内容文件的存在。
为项目添加音频文件:
在solution explorer中选择该文件,并在properties中将build action属性改为content。
<\mediaelement name=“sound” source=“sounds/1.wav” loadebehavior=“manual”></mediaelement>
到此这篇关于c# wpf编程之application类的使用详解的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关c# application类内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!



发表评论