1. 引言
浏览器中如何创建文件夹、写入文件呢?
答曰:可以借助jszip这个库来实现在浏览器内存中创建文件与文件夹,最后只需下载这个.zip文件,就是最终得结果
类似的使用场景如下:
- 在线下载很多图片,希望这些图片能分类保存到各个文件夹并最终下载成一个zip文件
- 在线下载很多文档,希望这些文档能分类保存到各个文件夹并最终下载成一个zip文件
本质上都是希望浏览器能创建文件夹和创建文件,最终保存成一个文件来提供下载
jszip的github站点:stuk/jszip: create, read and edit .zip files with javascript (github.com)
一个可用的中文站点:jszip参考手册 (asprain.cn)
下面主要记录一下基础使用,详细的api请参考上述文档
2. 使用
2.1 安装
使用npm:
npm install jszip
使用在线cdn:
<script src="https://cdn.bootcdn.net/ajax/libs/jszip/3.10.1/jszip.js"></script>
为了可以代码可以快速复现,笔者这里使用cdn的方式引入
2.2 创建zip实例
一个jszip实例是读写.zip文件的基础
const zip = new jszip();
2.3 读取zip文件
读取官方的示例文件text.zip
const zip = new jszip();
fetch("https://stuk.github.io/jszip/test/ref/text.zip") // 1) fetch the url
.then(function (response) { // 2) filter on 200 ok
if (response.status === 200 || response.status === 0) {
return promise.resolve(response.blob());
} else {
return promise.reject(new error(response.statustext));
}
})
.then(data => zip.loadasync(data)) // 3) 加载数据
.then(function (zip) {
zip.foreach(function (relativepath, file) { // 4) 遍历压缩包内的文件
console.log(`path: ${relativepath}, file: ${file.name}`)
// 输出:path: hello.txt, file: hello.txt
});
})因为hello.txt是个文本文件,可以直接使用string的方式读取内部的数据
const zip = new jszip();
fetch("https://stuk.github.io/jszip/test/ref/text.zip") // 1) fetch the url
.then(function (response) { // 2) filter on 200 ok
if (response.status === 200 || response.status === 0) {
return promise.resolve(response.blob());
} else {
return promise.reject(new error(response.statustext));
}
})
.then(data => zip.loadasync(data)) // 3) chain with the zip promise
.then(function (zip) {
return zip.file("hello.txt").async("string"); // 4) 读取hello.txt文件
})
.then(function success(text) {
console.log(text); // 输出:hello world
}, function error(e) {
console.error(e);
});2.4 创建zip文件
写入文件与数据
zip.file("file.txt", "content");
new promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve(zip.file("file.txt").async("string"))
}).then(data => {
console.log(data); // 输出:content
})写入指定文件夹下的指定文件
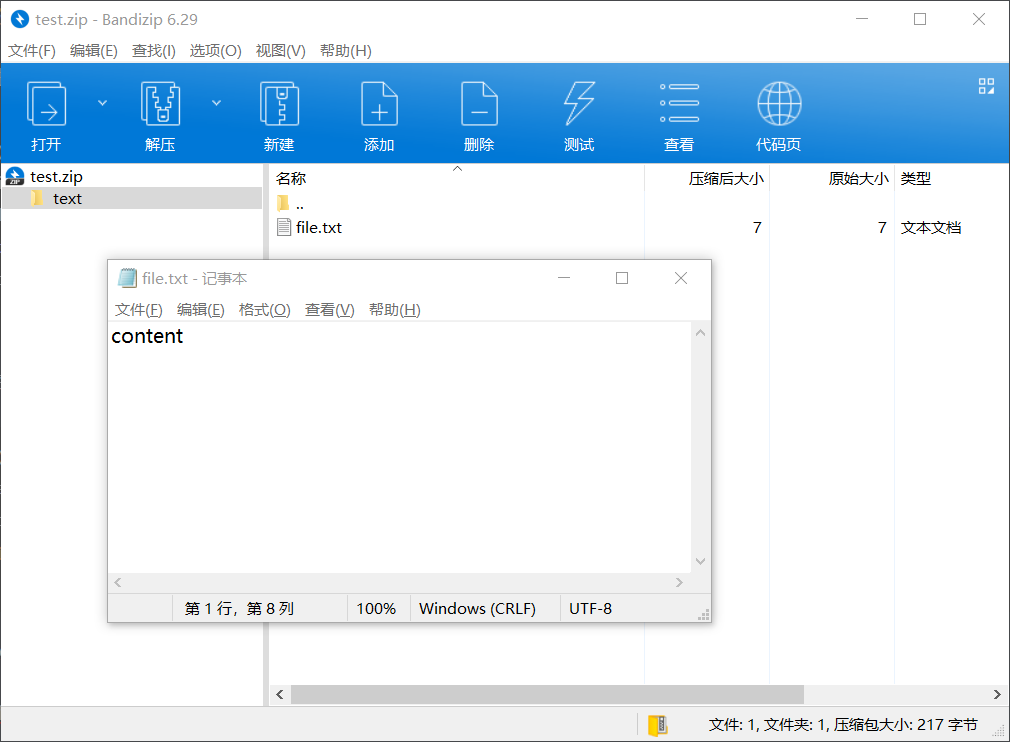
zip.file("text/file.txt", "content");
zip.foreach(function (relativepath, file) {
console.log(`path: ${relativepath}, file: ${file.name}`)
// 输出:path: text/file.txt, file: text/file.txt
});最后的目录结构可以参考下图
2.5 下载zip文件
这里将上面的file.txt下载为zip,使用a链接的方式
zip.generateasync({ type: "blob" }).then(function (content) {
document.body.appendchild(document.createelement("a"));
document.queryselector("a").href = url.createobjecturl(content);
document.queryselector("a").download = "test.zip";
document.queryselector("a").click();
});
完整的代码如下:
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>document</title>
<script src="https://cdn.bootcdn.net/ajax/libs/jszip/3.10.1/jszip.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<script>
const zip = new jszip();
// fetch("https://stuk.github.io/jszip/test/ref/text.zip") // 1) fetch the url
// .then(function (response) { // 2) filter on 200 ok
// if (response.status === 200 || response.status === 0) {
// return promise.resolve(response.blob());
// } else {
// return promise.reject(new error(response.statustext));
// }
// })
// .then(data => zip.loadasync(data)) // 3) chain with the zip promise
// .then(function (zip) {
// return zip.file("hello.txt").async("string"); // 4) chain with the text content
// })
// .then(function success(text) {
// console.log(text);
// }, function error(e) {
// console.error(e);
// });
zip.file("text/file.txt", "content");
zip.foreach(function (relativepath, file) {
console.log(`path: ${relativepath}, file: ${file.name}`)
});
zip.generateasync({ type: "blob" }).then(function (content) {
document.body.appendchild(document.createelement("a"));
document.queryselector("a").href = url.createobjecturl(content);
document.queryselector("a").download = "test.zip";
document.queryselector("a").click();
});
</script>
</body>
</html>到此这篇关于详解如何使用jszip实现在浏览器中操作文件与文件夹的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关jszip操作文件与文件夹内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!







发表评论