应用场景
不同的接口服务器处理不同的应用,我们会在实际应用中将a服务器的数据提交给b服务器进行数据接收并处理业务。
比如我们想要处理一个office文件,由用户上传到a服务器,上传成功后,由b服务器负责进行数据处理和下载工作,这时我们就需要 post a服务器的文件数据到b服务器进行处理。
实现原理
将用户上传的数据或a服务器已存在的数据,通过form-data的形式post到b服务器,b服务由指定ashx文件进行数据接收,并转由指定的业务逻辑程序进行处理。如下图:
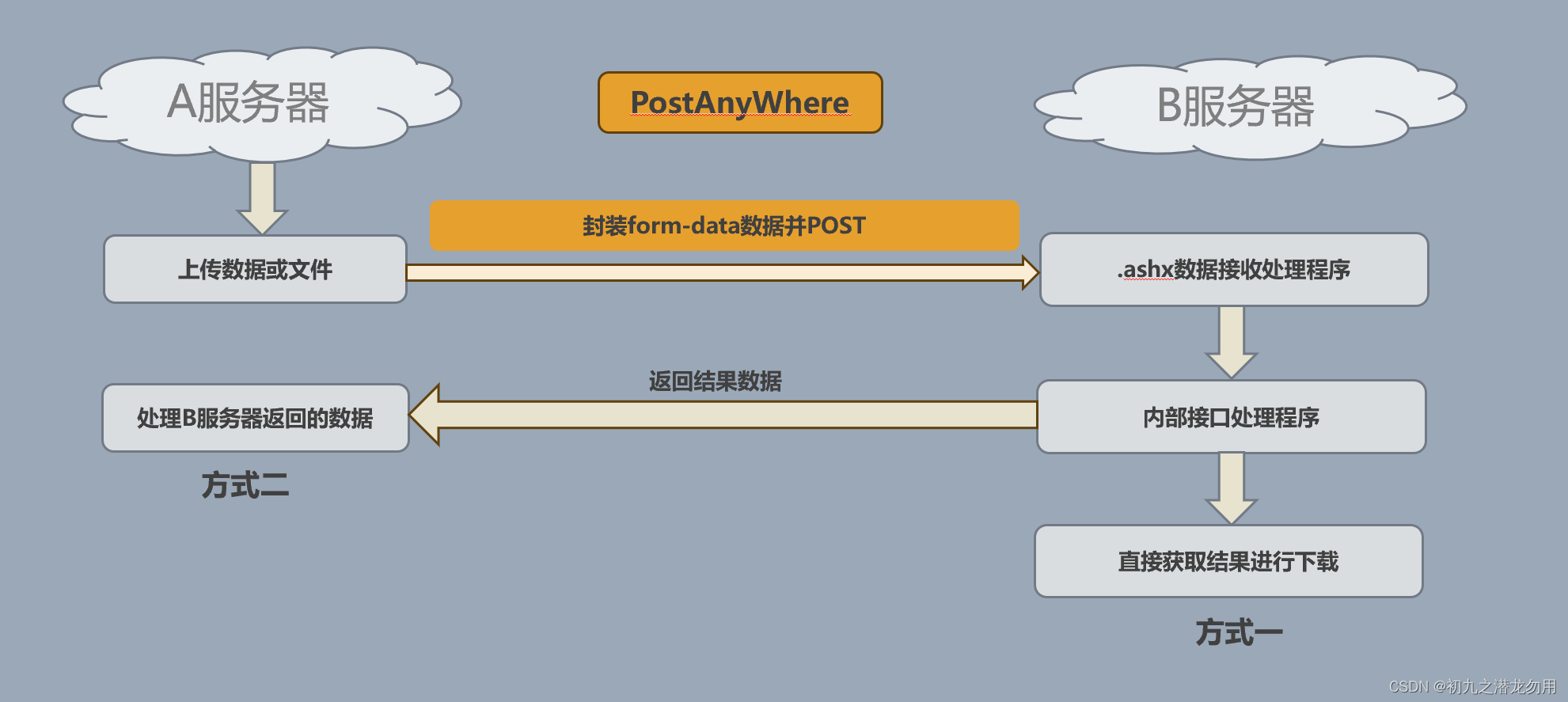
实现代码
postanywhere类
创建一个 postanywhere 类,
该类具有如下属性:
(1)public string posturl 要提交的服务器url
(2)public list<postfileitem> postdata 要准备的数据(postfileitem类可包括数据和文件类型)
该类包含的关键方法如下:
(1)public void addtext(string key, string value)
该方法将指定的字典数据加入到postdata中
(2)public void addfile(string name, string srcfilename, string desname, string contenttype = "text/plain")
该方法将指定的文件添加到postdata中,其中 srcfilename 表示要添加的文件名,desname表示接收数据生成的文件名
(3)public string send()
该方法将开始post传送数据
代码如下:
public class postanywhere
{
public string posturl { get; set; }
public list<postfileitem> postdata { get; set; }
public postanywhere()
{
this.postdata = new list<postfileitem>();
}
public void addtext(string key, string value)
{
this.postdata.add(new postfileitem { name = key, value = value });
}
public void addfile(string name, string srcfilename, string desname,string at, string contenttype = "text/plain")
{
string[] srcname = path.getfilename(srcfilename).split('.');
string exname = "";
if (srcname.length > 1)
{
exname = "."+srcname[srcname.length-1];
}
this.posturl = "https://www.xxx.com/test.ashx?guid=" + desname;
readyfile(name, getbinarydata(srcfilename), exname,contenttype);
}
void readyfile(string name, byte[] filebytes, string fileexname = "", string contenttype = "text/plain")
{
this.postdata.add(new postfileitem
{
type = postfileitemtype.file,
name = name,
filebytes = filebytes,
filename = fileexname,
contenttype = contenttype
});
}
public string send()
{
var boundary = "----------------------------" + datetime.now.ticks.tostring("x");
var request = (httpwebrequest)webrequest.create(this.posturl);
request.contenttype = "multipart/form-data; boundary=" + boundary;
request.method = "post";
request.keepalive = true;
stream memstream = new system.io.memorystream();
var boundarybytes = system.text.encoding.ascii.getbytes("\r\n--" + boundary + "\r\n");
var endboundarybytes = system.text.encoding.ascii.getbytes("\r\n--" + boundary + "--");
var formdatatemplate = "\r\n--" + boundary + "\r\ncontent-disposition: form-data; name=\"{0}\";\r\n\r\n{1}";
var formfields = this.postdata.where(m => m.type == postfileitemtype.text).tolist();
foreach (var d in formfields)
{
var textbytes = system.text.encoding.utf8.getbytes(string.format(formdatatemplate, d.name, d.value));
memstream.write(textbytes, 0, textbytes.length);
}
const string headertemplate = "content-disposition: form-data; name=\"{0}\"; filename=\"{1}\"\r\ncontent-type: {2}\r\n\r\n";
var files = this.postdata.where(m => m.type == postfileitemtype.file).tolist();
foreach (var fe in files)
{
memstream.write(boundarybytes, 0, boundarybytes.length);
var header = string.format(headertemplate, fe.name, fe.filename ?? "system.byte[]", fe.contenttype ?? "text/plain");
var headerbytes = system.text.encoding.utf8.getbytes(header);
memstream.write(headerbytes, 0, headerbytes.length);
memstream.write(fe.filebytes, 0, fe.filebytes.length);
}
memstream.write(endboundarybytes, 0, endboundarybytes.length);
request.contentlength = memstream.length;
httpwebresponse response;
try
{
using (var requeststream = request.getrequeststream())
{
memstream.position = 0;
var tempbuffer = new byte[memstream.length];
memstream.read(tempbuffer, 0, tempbuffer.length);
memstream.close();
requeststream.write(tempbuffer, 0, tempbuffer.length);
}
response = (httpwebresponse)request.getresponse();
}
catch (webexception webexception)
{
response = (httpwebresponse)webexception.response;
}
if (response == null)
{
throw new exception("httpwebresponse is null");
}
var responsestream = response.getresponsestream();
if (responsestream == null)
{
throw new exception("responsestream is null");
}
using (var streamreader = new streamreader(responsestream))
{
return streamreader.readtoend();
}
}
}
public class postfileitem
{
public postfileitem()
{
this.type = postfileitemtype.text;
}
public postfileitemtype type { get; set; }
public string value { get; set; }
public byte[] filebytes { get; set; }
public string name { get; set; }
public string filename { get; set; }
public string contenttype { get; set; }
}
public enum postfileitemtype
{
text = 0,
file = 1
}
public byte[] getbinarydata(string filename)
{
if(!file.exists(filename))
{
return null;
}
try
{
filestream fs = new filestream(filename, filemode.open, fileaccess.read);
byte[] imagedata = new byte[fs.length];
fs.read( imagedata, 0,convert.toint32(fs.length));
fs.close();
return imagedata;
}
catch(exception)
{
return null;
}
finally
{
}
} ashx文件部署
在b服务器上部署ashx文件接收数据,ashx程序即,一般处理程序(httphandler),一个httphandler接受并处理一个http请求,需要实现ihttphandler接口,这个接口有一个isreusable成员,一个待实现的方法processrequest(httpcontextctx) 。.ashx程序适合产生供浏览器处理的、不需要回发处理的数据格式。
示例代码如下:
<%@ webhandler language="c#" class="handler" %>
using system;
using system.web;
using system.io;
public class handler : ihttphandler {
public void processrequest (httpcontext context) {
if (context.request.files.count > 0)
{
string strpath = system.web.httpcontext.current.server.mappath("~/app_data/test/");
string strname = context.request.files[0].filename;
string ext=path.getextension(strname);
string filename =httpcontext.current.request.querystring["guid"].tostring()+path.getfilenamewithoutextension(strname);
if(ext!=""){
filename = filename + ext;
}
context.request.files[0].saveas(system.io.path.combine(strpath, filename));
}
}
public bool isreusable {
get {
return false;
}
}
}小结
ashx处理接收的数据后,后续还需要配合实际的接口功能继续处理应用。另外,对于ashx页面,实际的应用则需要使用安全访问控制,只有正常登录或提供合法访问令牌的用户才可以进行访问。
到此这篇关于c#实现post数据或文件到指定的服务器进行接收的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关c# post数据或文件到指定服务器内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!






发表评论