在现代企业级应用中,异步处理任务是提升系统性能和响应速度的关键手段之一。
spring 框架通过 @async 注解为我们提供了简洁易用的异步任务支持,但在真实的业务场景中,我们往往需要更灵活、更安全的线程池配置,以确保系统能高效、稳定地运行。
一、为什么要自定义线程池?
虽然 spring 默认提供了一个简单的异步执行器(simpleasynctaskexecutor),但它的设计比较基础,并不适合生产环境。
在企业级项目中,我们通常会遇到以下问题:
- ✅ 任务执行时间较长:需要限制线程池大小,防止线程爆炸占用过多资源;
- ✅ 拒绝策略控制:当线程池满载时,如何优雅地处理新任务;
- ✅ 可观测性:通过自定义线程名称前缀,更方便定位性能瓶颈和异常。
因此,自定义线程池可以让我们:
- 更好地控制线程数量;
- 灵活管理任务队列;
- 提升调试和监控的可维护性。
二、配置线程池
(threadpoolconfig.java)
要实现统一线程池管理,我们可以让配置类实现 asyncconfigurer 接口,并重写其 getasyncexecutor() 方法,在其中返回自定义的 threadpooltaskexecutor。
代码示例
package com.example.demo.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.configuration;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.asyncconfigurer;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.enableasync;
import org.springframework.scheduling.concurrent.threadpooltaskexecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.executor;
@configuration
@enableasync
public class threadpoolconfig implements asyncconfigurer {
/**
* 创建一个全局统一的线程池
*/
@override
public executor getasyncexecutor() {
return taskexecutor(); // 指定全局默认线程池
}
@bean
public threadpooltaskexecutor taskexecutor() {
threadpooltaskexecutor executor = new threadpooltaskexecutor();
executor.setcorepoolsize(5); // 核心线程数
executor.setmaxpoolsize(10); // 最大线程数
executor.setqueuecapacity(25); // 队列容量
executor.setthreadnameprefix("asyncexecutor-"); // 线程名前缀
executor.initialize();
return executor;
}
}
三、创建异步任务服务
(asyncservice.java)
package com.example.demo.service;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.async;
import org.springframework.stereotype.service;
@service
public class asyncservice {
@async
public void executeasynctask() {
try {
system.out.println(thread.currentthread().getname() + " - task start");
thread.sleep(2000);
system.out.println(thread.currentthread().getname() + " - task end");
} catch (interruptedexception e) {
e.printstacktrace();
}
}
}
四、创建控制器触发异步任务
(asynccontroller.java)
package com.example.demo.controller;
import com.example.demo.service.asyncservice;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.getmapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.restcontroller;
@restcontroller
public class asynccontroller {
@autowired
private asyncservice asyncservice;
@getmapping("/start-task")
public string startasynctask() {
asyncservice.executeasynctask();
return "task started!";
}
}
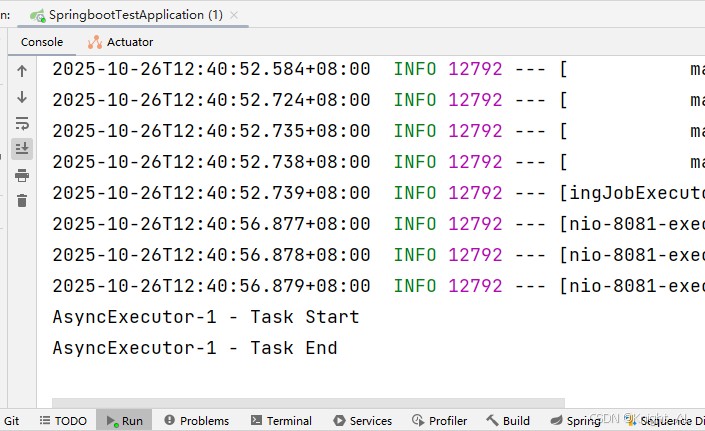
五、运行效果
访问 http://localhost:8080/start-task,你会看到控制台输出:
六、为什么企业项目推荐使用 implements asyncconfigurer
1、两种写法的核心差别
| 写法 | 线程池绑定方式 | 谁决定用哪个线程池 |
|---|---|---|
| 实现 asyncconfigurer | 全局绑定(统一入口) | spring 框架自动选择 |
| 不实现 asyncconfigurer | 局部绑定(按名称匹配) | 每个开发者自己写 @async("xxx") |
2、问题出在哪?
小项目(单人开发)
如果是 demo 或简单服务,一个线程池、几行代码就够了:
@async("taskexecutor")
没问题。
但在多人协作的大型项目里,这样写就容易出大问题👇
场景一:每个模块各自定义线程池
| 模块 | 开发者 | bean 名称 |
|---|---|---|
| 用户模块 | 小李 | @bean("userexecutor") |
| 聊天模块 | 小王 | @bean("chatexecutor") |
| 消息模块 | 小陈 | @bean("taskexecutor") |
大家都在写:
@async("taskexecutor")
如果有人打错名字,或者模块没被 spring 扫描到,就会直接报错:
no qualifying bean of type 'executor' available: expected single matching bean but found 3
结果:应用无法启动,异步任务执行失败。
场景二:维护成本爆炸
假设项目有 30 多个异步任务。
某天运维说:“把线程池从 10 改到 30。”
- ❌ 没有 asyncconfigurer:得挨个模块修改 bean 配置;
- ✅ 有了 asyncconfigurer:只改一个配置类,全项目自动生效。
场景三:多个线程池协同使用
| 线程池 | 用途 |
|---|---|
| chatexecutor | 主业务线程池 |
| wsexecutor | websocket 推送 |
| slowtaskexecutor | 定时任务或慢操作 |
如果没人统一管理,可能会:
- 有人忘记写 @async("xxx");
- spring 退回默认线程池(simpleasynctaskexecutor);
- 结果性能崩溃,线程乱飞。
3、asyncconfigurer的企业级优势
| 优点 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 全局统一入口 | 所有 @async 方法默认使用统一线程池(getasyncexecutor() 返回的那个)。 |
| 集中维护 | 修改线程数、拒绝策略等配置只需改一处。 |
| 兼容多线程池 | 可定义主线程池 + 业务专用池。 |
| 避免命名冲突 | 无需担心 bean 名称重复或漏写。 |
| 增强代码规范 | 新人接手项目时能一眼看懂异步执行机制。 |
4、形象类比
🚫 不实现 asyncconfigurer:
像每个开发者自己带锅做饭,火候、油量、味道都不同。容易糊锅。✅ 实现 asyncconfigurer:
像公司统一配“中央厨房”,所有菜统一标准、火候可控、安全可追踪。
5、完整示例
@configuration
@enableasync
public class threadpoolconfig implements asyncconfigurer {
@override
public executor getasyncexecutor() {
return mallchatexecutor();
}
@bean("chatexecutor")
public threadpooltaskexecutor mallchatexecutor() {
threadpooltaskexecutor executor = new threadpooltaskexecutor();
executor.setcorepoolsize(10);
executor.setmaxpoolsize(30);
executor.setqueuecapacity(100);
executor.setthreadnameprefix("mallchat-");
executor.initialize();
return executor;
}
@bean("wsexecutor")
public threadpooltaskexecutor wsexecutor() {
threadpooltaskexecutor executor = new threadpooltaskexecutor();
executor.setcorepoolsize(5);
executor.setmaxpoolsize(10);
executor.setqueuecapacity(50);
executor.setthreadnameprefix("websocket-");
executor.initialize();
return executor;
}
}
@service
public class chatservice {
@async // 默认使用 chatexecutor
public void sendmessage() {}
@async("wsexecutor") // 指定 websocket 专用线程池
public void pushtoclient() {}
}
到此这篇关于spring使用 asyncconfigurer 自定义线程池实现高效异步任务管理的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关spring asyncconfigurer 自定义线程池内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!






发表评论