一、注解校验概述
1.1 为什么需要注解校验?
在实际开发中,我们经常需要对输入数据进行校验:
// 传统方式:代码冗长、难以维护
public void createuser(string username, string email, integer age) {
if (username == null || username.length() < 3 || username.length() > 20) {
throw new illegalargumentexception("用户名长度必须在3-20之间");
}
if (email == null || !email.matches("^[a-za-z0-9+_.-]+@(.+)$")) {
throw new illegalargumentexception("邮箱格式不正确");
}
if (age == null || age < 18 || age > 120) {
throw new illegalargumentexception("年龄必须在18-120之间");
}
//...
}
// ✅ 注解校验:简洁、声明式、可复用
public void createuser(@valid userdto userdto) {
//...
}注解校验的优势:
- ✅ 声明式:通过注解声明校验规则,代码更简洁
- ✅ 可复用:校验逻辑可以复用,避免重复代码
- ✅ 易维护:校验规则集中管理,易于维护
- ✅ 标准化:遵循jsr-303/jsr-380标准
- ✅ 国际化:支持国际化错误消息
1.2 常用校验注解

jakarta bean validation提供的注解:
| 注解 | 说明 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
| @notnull | 值不能为null | @notnull string name |
| @notempty | 集合、字符串、数组不能为空 | @notempty list<string> items |
| @notblank | 字符串不能为空白(去除首尾空格后长度>0) | @notblank string content |
| @size(min, max) | 大小必须在指定范围内 | @size(min=3, max=20) string name |
| @min(value) | 数值必须大于等于指定值 | @min(18) integer age |
| @max(value) | 数值必须小于等于指定值 | @max(120) integer age |
| 必须是有效的邮箱格式 | @email string email | |
| @pattern(regexp) | 必须匹配指定的正则表达式 | @pattern(regexp="^1[3-9]\\d{9}$") string phone |
| @past | 日期必须是过去的时间 | @past date birthdate |
| @future | 日期必须是未来的时间 | @future date appointmentdate |
| @asserttrue | 布尔值必须是true | @asserttrue boolean agreed |
| @negative | 数值必须是负数 | @negative integer balance |
| @positive | 数值必须是正数 | @positive integer amount |
二、@valid vs @validated
2.1 核心区别
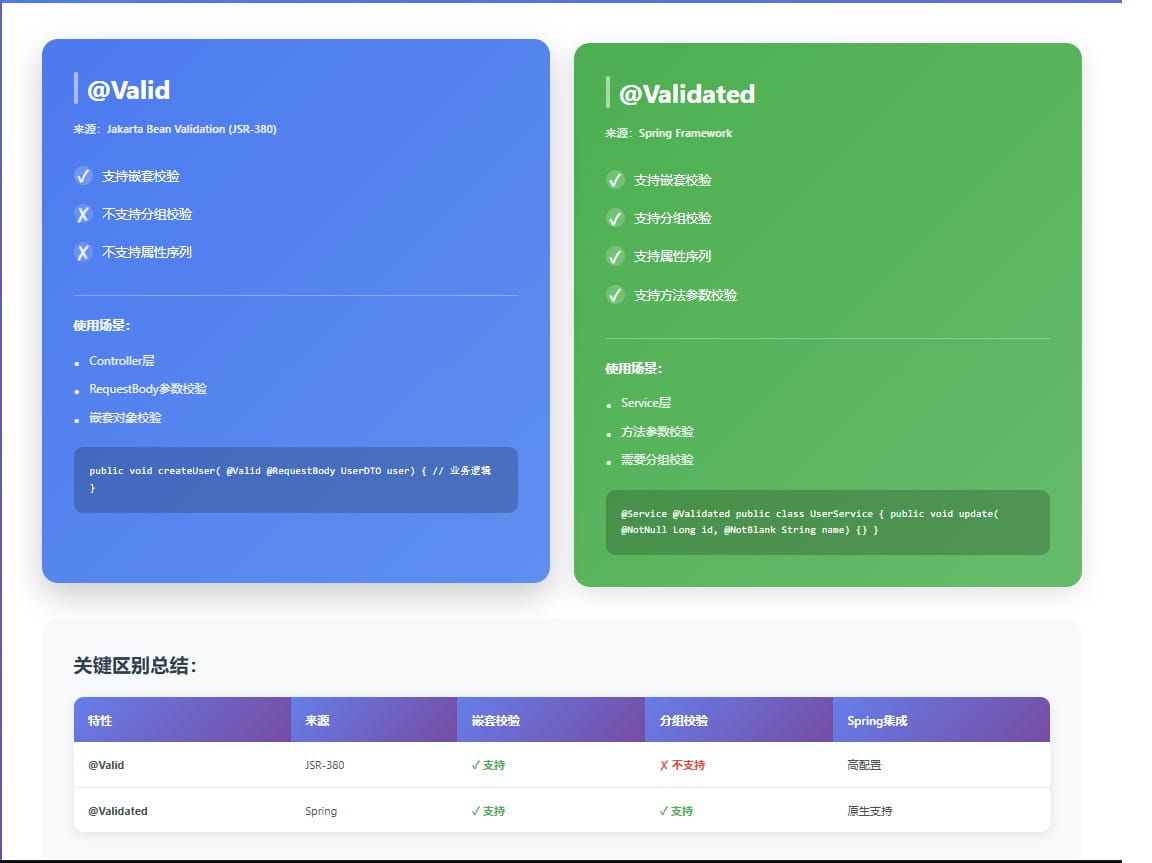
这两个注解虽然功能相似,但有关键区别:
| 特性 | @valid | @validated |
|---|---|---|
| 来源 | jakarta bean validation (jsr-380) | spring framework |
| 位置 | 方法、字段、构造器参数 | 方法、类型、参数 |
| 嵌套校验 | ✅ 支持 | ✅ 支持 |
| 分组校验 | ❌ 不支持 | ✅ 支持 |
| 校验组序列 | ❌ 不支持 | ✅ 支持 |
| spring集成 | 需要配置 | 原生支持 |
2.2 @valid的使用
基本用法:
@data
public class userdto {
@notnull(message = "用户id不能为空")
private long id;
@notblank(message = "用户名不能为空")
@size(min = 3, max = 20, message = "用户名长度必须在3-20之间")
private string username;
@email(message = "邮箱格式不正确")
@notblank(message = "邮箱不能为空")
private string email;
@min(value = 18, message = "年龄必须大于等于18岁")
@max(value = 120, message = "年龄必须小于等于120岁")
private integer age;
}在controller中使用:
@restcontroller
@requestmapping("/api/users")
public class usercontroller {
// 使用@valid触发校验
@postmapping
public responseentity<string> createuser(@valid @requestbody userdto userdto) {
// 如果校验失败,会自动抛出methodargumentnotvalidexception
return responseentity.ok("用户创建成功");
}
}嵌套校验:
@data
public class orderdto {
@notnull(message = "订单id不能为空")
private long orderid;
@valid // 关键:必须使用@valid才能触发嵌套对象的校验
@notnull(message = "用户信息不能为空")
private userdto user;
@valid
@notempty(message = "订单项不能为空")
private list<orderitemdto> items;
}
@data
public class orderitemdto {
@notnull(message = "商品id不能为空")
private long productid;
@min(value = 1, message = "数量必须大于0")
private integer quantity;
}2.3 @validated的使用
基本用法:
@service
@validated // 类级别添加@validated,启用方法参数校验
public class userservice {
// 简单参数校验
public void updateuser(
@notnull(message = "用户id不能为空") long id,
@notblank(message = "用户名不能为空") string username) {
// 业务逻辑...
}
// 对象校验
public void createuser(@valid userdto userdto) {
// 业务逻辑...
}
}分组校验(@validated独有):
public interface creategroup {}
public interface updategroup {}
@data
public class userdto {
@null(groups = creategroup.class, message = "创建时id必须为空")
@notnull(groups = updategroup.class, message = "更新时id不能为空")
private long id;
@notblank(groups = {creategroup.class, updategroup.class})
private string username;
}
@restcontroller
@requestmapping("/api/users")
public class usercontroller {
@postmapping
public responseentity<string> create(
@validated(creategroup.class) @requestbody userdto userdto) {
return responseentity.ok("创建成功");
}
@putmapping
public responseentity<string> update(
@validated(updategroup.class) @requestbody userdto userdto) {
return responseentity.ok("更新成功");
}
}2.4 选择建议
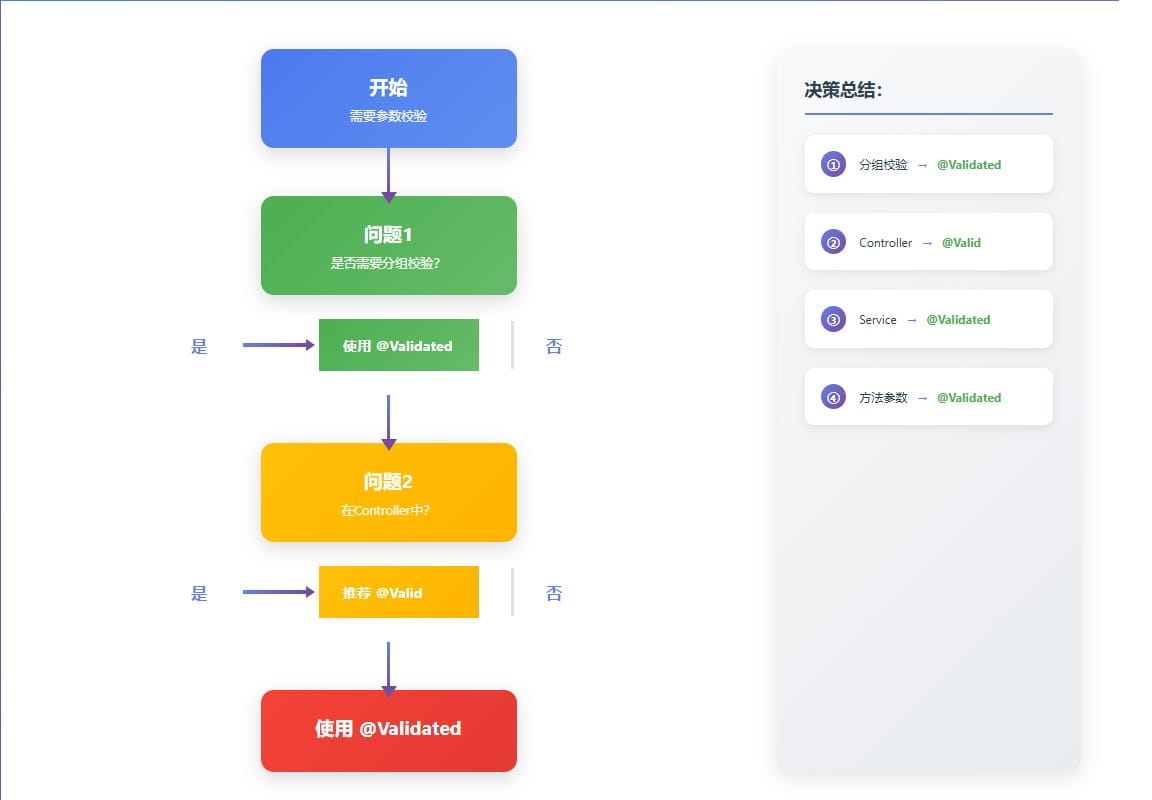
选择决策树:
是否需要分组校验?
├─ 是 → 使用 @validated
└─ 否 → 是否在controller中?
├─ 是 → 两者都可以,推荐 @valid
└─ 否 → 使用 @validated最佳实践:
- controller层:使用
@valid(简洁、够用) - service层:使用
@validated(支持方法参数校验) - 需要分组:必须使用
@validated - 嵌套对象:在嵌套对象字段上添加
@valid
三、校验组(validation groups)
3.1 为什么需要校验组?
不同场景下,同一对象的校验规则可能不同:
// 场景1:新增用户 // - id为空(由数据库生成) // - username必填 // - password必填 // 场景2:更新用户 // - id必填(根据id更新) // - username可选 // - password可选(不修改则不传)
3.2 定义校验组
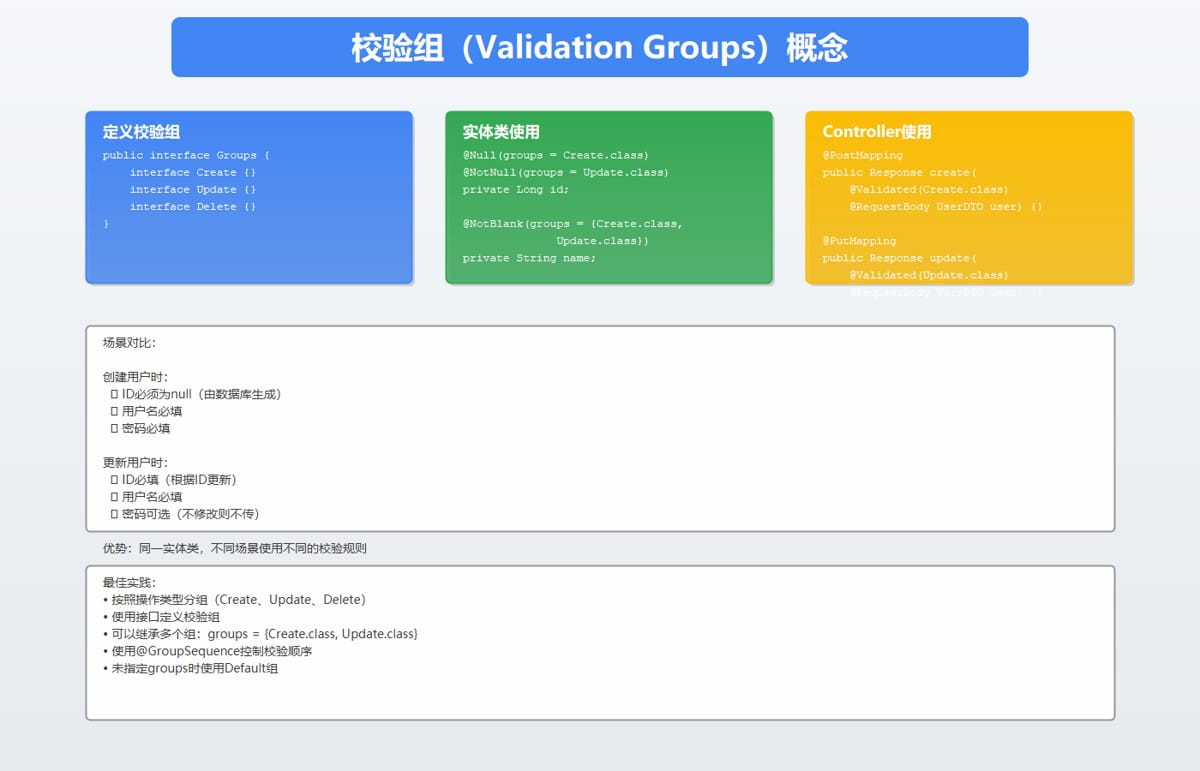
/**
* 校验组定义
*/
public interface validationgroups {
// 新增操作
interface create {}
// 更新操作
interface update {}
// 删除操作
interface delete {}
// 默认组(不指定group时使用)
interface default {}
}3.3 在实体类中使用分组
@data
public class userdto {
// 创建时id必须为空,更新时id不能为空
@null(groups = validationgroups.create.class,
message = "创建用户时id必须为空")
@notnull(groups = {validationgroups.update.class,
validationgroups.delete.class},
message = "更新/删除用户时id不能为空")
private long id;
@notblank(groups = {validationgroups.create.class,
validationgroups.update.class},
message = "用户名不能为空")
@size(min = 3, max = 20,
groups = {validationgroups.create.class,
validationgroups.update.class},
message = "用户名长度必须在3-20之间")
private string username;
@email(groups = validationgroups.create.class,
message = "邮箱格式不正确")
@notblank(groups = validationgroups.create.class,
message = "邮箱不能为空")
private string email;
// 创建时密码必填,更新时可选
@notblank(groups = validationgroups.create.class,
message = "密码不能为空")
@size(min = 6, max = 20,
groups = validationgroups.create.class,
message = "密码长度必须在6-20之间")
private string password;
@notnull(groups = validationgroups.create.class,
message = "年龄不能为空")
@min(value = 18, groups = validationgroups.create.class,
message = "年龄必须大于等于18岁")
private integer age;
}3.4 使用校验组
@restcontroller
@requestmapping("/api/users")
public class usercontroller {
@postmapping
public responseentity<?> create(
@validated(validationgroups.create.class)
@requestbody userdto userdto) {
// 只校验create组中定义的规则
return responseentity.ok("创建成功");
}
@putmapping("/{id}")
public responseentity<?> update(
@pathvariable long id,
@validated(validationgroups.update.class)
@requestbody userdto userdto) {
// 只校验update组中定义的规则
return responseentity.ok("更新成功");
}
@deletemapping("/{id}")
public responseentity<?> delete(
@pathvariable long id,
@validated(validationgroups.delete.class)
@requestbody userdto userdto) {
// 只校验delete组中定义的规则
return responseentity.ok("删除成功");
}
}3.5 组序列(group sequence)
控制校验组的执行顺序,默认按照定义的顺序依次校验:
@groupsequence({creategroup.class, updategroup.class, default.class})
public interface orderedgroup {
}
@restcontroller
public class usercontroller {
@postmapping
public responseentity<?> create(
@validated(orderedgroup.class)
@requestbody userdto userdto) {
return responseentity.ok("创建成功");
}
}注意:一旦某个组校验失败,后续组不会再执行。
四、自定义校验注解
4.1 自定义注解的应用场景
当内置注解无法满足需求时,可以创建自定义校验注解:
- 手机号校验:
@phonenumber - 身份证号校验:
@idcard - 枚举值校验:
@enumvalue - 字段互斥:
@fieldmatch - 密码强度:
@strongpassword

4.2 实现手机号校验注解
第一步:定义注解
@target({elementtype.field, elementtype.parameter})
@retention(retentionpolicy.runtime)
@constraint(validatedby = phonenumbervalidator.class)
@documented
public @interface phonenumber {
// 必须的三个属性
string message() default "手机号格式不正确";
class<?>[] groups() default {};
class<? extends payload>[] payload() default {};
// 自定义属性:是否支持国际化号码
boolean international() default false;
// 自定义属性:支持的国家代码
string[] countrycodes() default {"+86"};
}第二步:实现校验器
public class phonenumbervalidator
implements constraintvalidator<phonenumber, string> {
private boolean international;
private string[] countrycodes;
// 中国大陆手机号正则
private static final string china_phone_pattern =
"^1[3-9]\\d{9}$";
@override
public void initialize(phonenumber constraintannotation) {
this.international = constraintannotation.international();
this.countrycodes = constraintannotation.countrycodes();
}
@override
public boolean isvalid(string value,
constraintvalidatorcontext context) {
// null值由@notnull处理
if (value == null) {
return true;
}
// 国际号码校验
if (international) {
return validateinternational(value);
}
// 中国手机号校验
return value.matches(china_phone_pattern);
}
private boolean validateinternational(string phone) {
// 简单的国际号码校验逻辑
for (string code : countrycodes) {
if (phone.startswith(code)) {
string number = phone.substring(code.length());
return number.matches("^\\d{6,15}$");
}
}
return false;
}
}第三步:使用注解
@data
public class userdto {
@phonenumber(message = "手机号格式不正确")
private string mobile;
@phonenumber(international = true,
countrycodes = {"+86", "+1", "+44"},
message = "国际手机号格式不正确")
private string internationalphone;
}4.3 实现密码强度校验
注解定义:
@target({elementtype.field, elementtype.parameter})
@retention(retentionpolicy.runtime)
@constraint(validatedby = strongpasswordvalidator.class)
@documented
public @interface strongpassword {
string message() default "密码强度不足";
class<?>[] groups() default {};
class<? extends payload>[] payload() default {};
// 最小长度
int minlength() default 8;
// 是否需要大写字母
boolean requireuppercase() default true;
// 是否需要小写字母
boolean requirelowercase() default true;
// 是否需要数字
boolean requiredigit() default true;
// 是否需要特殊字符
boolean requirespecialchar() default true;
}校验器实现:
public class strongpasswordvalidator
implements constraintvalidator<strongpassword, string> {
private int minlength;
private boolean requireuppercase;
private boolean requirelowercase;
private boolean requiredigit;
private boolean requirespecialchar;
private static final pattern uppercase_pattern =
pattern.compile("[a-z]");
private static final pattern lowercase_pattern =
pattern.compile("[a-z]");
private static final pattern digit_pattern =
pattern.compile("\\d");
private static final pattern special_char_pattern =
pattern.compile("[!@#$%^&*()_+\\-=\\[\\]{};':\"\\\\|,.<>\\/?]");
@override
public void initialize(strongpassword constraintannotation) {
this.minlength = constraintannotation.minlength();
this.requireuppercase = constraintannotation.requireuppercase();
this.requirelowercase = constraintannotation.requirelowercase();
this.requiredigit = constraintannotation.requiredigit();
this.requirespecialchar = constraintannotation.requirespecialchar();
}
@override
public boolean isvalid(string password,
constraintvalidatorcontext context) {
if (password == null) {
return true;
}
if (password.length() < minlength) {
return false;
}
if (requireuppercase && !uppercase_pattern.matcher(password).find()) {
return false;
}
if (requirelowercase && !lowercase_pattern.matcher(password).find()) {
return false;
}
if (requiredigit && !digit_pattern.matcher(password).find()) {
return false;
}
if (requirespecialchar && !special_char_pattern.matcher(password).find()) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
}4.4 跨字段校验
实现"密码"和"确认密码"必须一致的校验:
注解定义:
@target({elementtype.type})
@retention(retentionpolicy.runtime)
@constraint(validatedby = fieldmatchvalidator.class)
@documented
public @interface fieldmatch {
string message() default "字段值不匹配";
class<?>[] groups() default {};
class<? extends payload>[] payload() default {};
// 第一个字段名
string first();
// 第二个字段名
string second();
}校验器实现:
public class fieldmatchvalidator
implements constraintvalidator<fieldmatch, object> {
private string firstfieldname;
private string secondfieldname;
@override
public void initialize(fieldmatch constraintannotation) {
this.firstfieldname = constraintannotation.first();
this.secondfieldname = constraintannotation.second();
}
@override
public boolean isvalid(object value,
constraintvalidatorcontext context) {
if (value == null) {
return true;
}
try {
field firstfield = value.getclass().getdeclaredfield(firstfieldname);
firstfield.setaccessible(true);
object firstvalue = firstfield.get(value);
field secondfield = value.getclass().getdeclaredfield(secondfieldname);
secondfield.setaccessible(true);
object secondvalue = secondfield.get(value);
return objects.equals(firstvalue, secondvalue);
} catch (exception e) {
return false;
}
}
}使用示例:
@data
@fieldmatch(first = "password", second = "confirmpassword",
message = "两次输入的密码不一致")
public class registerrequest {
private string username;
private string password;
private string confirmpassword;
}
五、生产环境实战
5.1 统一异常处理
在生产环境中,需要统一处理校验异常:
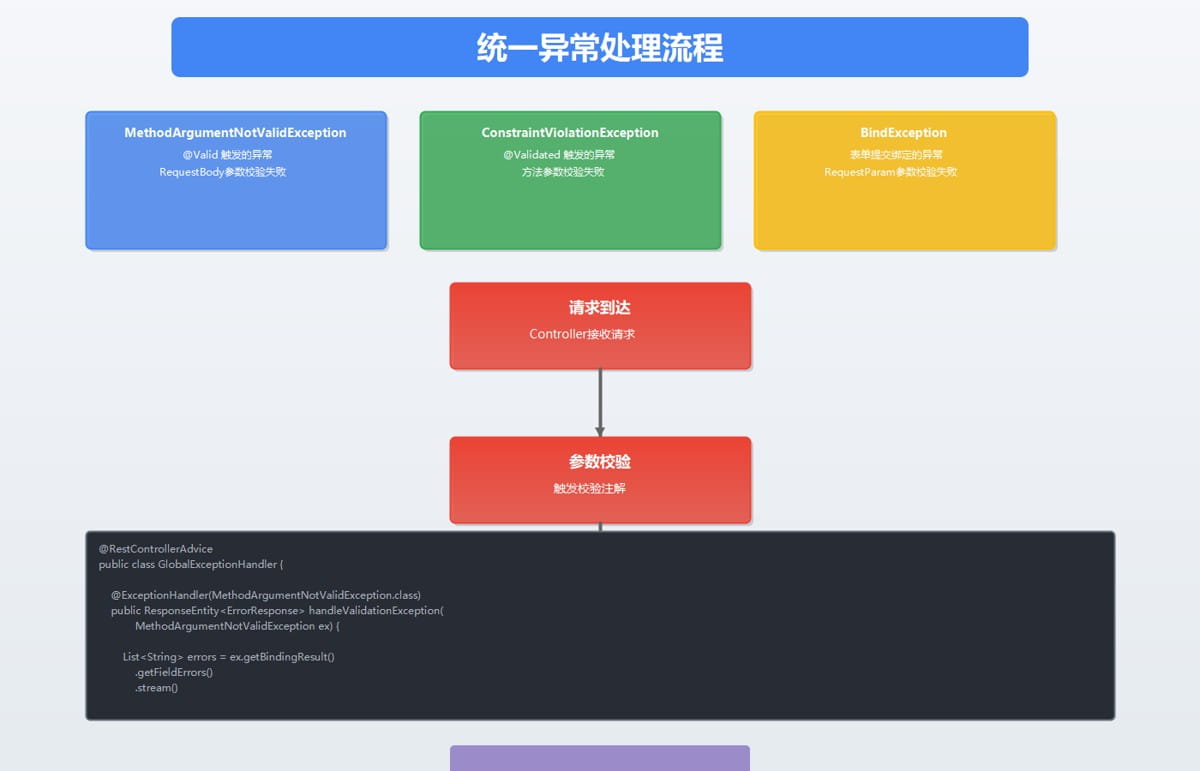
@restcontrolleradvice
public class globalexceptionhandler {
/**
* 处理 @valid 触发的校验异常
*/
@exceptionhandler(methodargumentnotvalidexception.class)
public responseentity<errorresponse> handlevalidationexception(
methodargumentnotvalidexception ex) {
list<string> errors = ex.getbindingresult()
.getfielderrors()
.stream()
.map(error -> error.getfield() + ": " + error.getdefaultmessage())
.collect(collectors.tolist());
errorresponse response = errorresponse.builder()
.code(400)
.message("参数校验失败")
.errors(errors)
.timestamp(localdatetime.now())
.build();
return responseentity.badrequest().body(response);
}
/**
* 处理 @validated 触发的校验异常
*/
@exceptionhandler(constraintviolationexception.class)
public responseentity<errorresponse> handleconstraintviolation(
constraintviolationexception ex) {
list<string> errors = ex.getconstraintviolations()
.stream()
.map(violation -> violation.getpropertypath() + ": " + violation.getmessage())
.collect(collectors.tolist());
errorresponse response = errorresponse.builder()
.code(400)
.message("参数校验失败")
.errors(errors)
.timestamp(localdatetime.now())
.build();
return responseentity.badrequest().body(response);
}
/**
* 处理请求参数绑定异常
*/
@exceptionhandler(bindexception.class)
public responseentity<errorresponse> handlebindexception(bindexception ex) {
list<string> errors = ex.getbindingresult()
.getfielderrors()
.stream()
.map(error -> error.getfield() + ": " + error.getdefaultmessage())
.collect(collectors.tolist());
errorresponse response = errorresponse.builder()
.code(400)
.message("参数绑定失败")
.errors(errors)
.timestamp(localdatetime.now())
.build();
return responseentity.badrequest().body(response);
}
}
@data
@builder
class errorresponse {
private integer code;
private string message;
private list<string> errors;
private localdatetime timestamp;
}5.2 快速失败机制
默认情况下,bean validation会校验所有约束并返回所有错误。如果需要在第一个错误时就停止:
@configuration
public class validationconfig {
@bean
public validator validator() {
validatorfactory factory = validation.bydefaultprovider()
.configure()
.failfast(true) // 启用快速失败
.buildvalidatorfactory();
return factory.getvalidator();
}
@bean
public methodvalidationpostprocessor methodvalidationpostprocessor() {
methodvalidationpostprocessor processor = new methodvalidationpostprocessor();
processor.setvalidator(validator());
return processor;
}
}5.4 手动触发校验
在service层手动触发校验:
@service
@requiredargsconstructor
public class userservice {
private final validator validator;
public void createuser(userdto userdto) {
// 手动校验
set<constraintviolation<userdto>> violations =
validator.validate(userdto, default.class);
if (!violations.isempty()) {
throw new constraintviolationexception(violations);
}
// 业务逻辑...
}
}六、最佳实践
6.1 设计原则

- 单一职责:每个注解只负责一个校验规则
- 组合使用:多个简单注解组合成复杂规则
- 错误消息清晰:提供具体、可操作的错误提示
- 分组管理:使用校验组区分不同场景
- 自定义注解:复杂业务逻辑创建自定义注解
6.2 性能优化
- 避免过度校验:只校验必要的数据
- 校验顺序:将简单的校验放在前面
- 缓存validator:validator实例可以复用
- 异步校验:对于复杂校验,考虑异步处理
七、总结
本文系统地介绍了java注解校验的核心概念和实践:
- @valid vs @validated:理解两者的区别和适用场景
- 校验组:使用分组管理不同场景的校验规则
- 自定义注解:创建符合业务需求的校验注解
- 生产实践:异常处理、国际化、性能优化
到此这篇关于java注解校验实战指南的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关java注解校验内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!





发表评论