spring boot与mybatis的配置
一、简介
spring boot是一个用于创建独立的、基于spring的生产级应用程序的框架,它简化了spring应用的初始搭建以及开发过程。mybatis是一款优秀的持久层框架,它支持定制化sql、存储过程以及高级映射。将spring boot和mybatis结合使用,可以高效地开发数据驱动的应用程序。
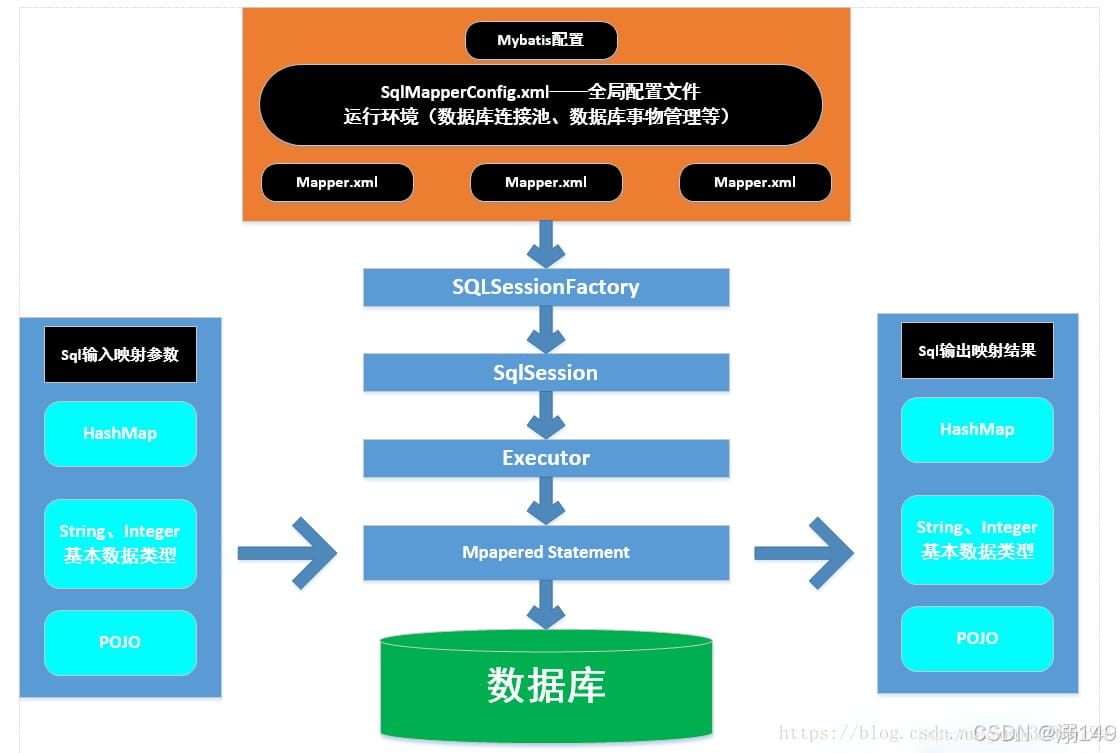
二、环境准备
(一)创建spring boot项目
- 可以使用spring initializr(https://start.spring.io/)来创建一个基础的spring boot项目。
- 在创建项目时,选择合适的项目元数据,如项目的group和artifact等信息。
- 可以选择添加一些常用的依赖,如web依赖(如果项目需要提供web服务)等。不过,对于mybatis的集成,初始创建时不需要专门添加mybatis相关依赖,我们后续手动添加。
- 下载生成的项目压缩包并解压到本地开发环境。
(二)添加mybatis依赖
在项目的pom.xml(如果是maven项目)中添加mybatis和相关数据库驱动的依赖。
对于mybatis本身:
org.mybatis.spring.boot
mybatis - spring - boot - starter
2.2.2如果使用mysql数据库,添加mysql驱动依赖:
mysql
mysql - connector - java
8.0.26三、数据库配置
(一)配置数据源
在spring boot的配置文件(application.properties或者application.yml)中配置数据源相关信息。
如果使用application.properties:
spring.datasource.url = jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb?usessl = false&servertimezone = utc spring.datasource.username = root spring.datasource.password = your_password spring.datasource.driver - class - name = com.mysql.cj.jdbc.driver
如果使用application.yml:
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb?usessl = false&servertimezone = utc
username: root
password: your_password
driver - class - name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.driver四、mybatis配置
(一)实体类创建
根据数据库表结构创建对应的实体类。例如,如果有一个名为“user”的表,结构如下:
create table user (
id int primary key auto_increment,
username varchar(50),
password varchar(50)
);对应的java实体类为:
public class user {
private integer id;
private string username;
private string password;
// 生成getter和setter方法
public integer getid() {
return id;
}
public void setid(integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public string getusername() {
return username;
}
public void setusername(string username) {
this.username = username;
}
public string getpassword() {
return password;
}
public void setpassword(string password) {
this.password = password;
}
}(二)mapper接口创建
创建mapper接口来定义与数据库交互的方法。
例如,创建一个usermapper接口:
@mapper
public interface usermapper {
user selectuserbyid(integer id);
int insertuser(user user);
int updateuser(user user);
int deleteuserbyid(integer id);
}这里的@mapper注解(如果使用注解方式)用于将该接口标记为mybatis的mapper接口,这样spring boot就能够识别并自动创建该接口的代理实现。
(三)mapper xml文件创建(如果使用xml方式)
如果不使用注解方式编写sql语句,而是使用xml文件,则需要创建mapper xml文件。
在resources/mapper目录下创建usermapper.xml(假设项目采用的是maven的标准目录结构)。
内容如下:
select * from user where id = #{id}
insert into user (username, password) values (#{username}, #{password})
update user set username = #{username}, password = #{password} where id = #{id}
delete from user where id = #{id}这里的namespace属性的值要与对应的mapper接口的全限定名相同。
(四)配置mybatis扫描路径
如果使用xml方式的mapper文件,需要在spring boot配置文件中配置mybatis的mapper扫描路径。
在application.properties中:
mybatis.mapper - locations = classpath:mapper/*.xml
在application.yml中:
mybatis: mapper - locations: classpath:mapper/*.xml
五、使用mybatis进行数据操作
(一)在service层调用mapper方法
创建一个userservice类来调用usermapper中的方法。
例如:
@service
public class userservice {
@autowired
private usermapper usermapper;
public user getuserbyid(integer id) {
return usermapper.selectuserbyid(id);
}
public int adduser(user user) {
return usermapper.insertuser(user);
}
public int updateuserinfo(user user) {
return usermapper.updateuser(user);
}
public int deleteuser(int id) {
return usermapper.deleteuserbyid(id);
}
}这里通过@autowired注解注入usermapper实例,然后就可以在service方法中调用mapper中的数据操作方法。
(二)在controller层调用service方法(如果是web应用)
创建一个usercontroller类(假设是一个web应用,需要提供restful接口等)。
@restcontroller
public class usercontroller {
@autowired
private userservice userservice;
@getmapping("/user/{id}")
public user getuserbyid(@pathvariable("id") integer id) {
return userservice.getuserbyid(id);
}
@postmapping("/user")
public int adduser(@requestbody user user) {
return userservice.adduser(user);
}
@putmapping("/user")
public int updateuser(@requestbody user user) {
return userservice.updateuserinfo(user);
}
@deletemapping("/user/{id}")
public int deleteuser(@pathvariable("id") integer id) {
return userservice.deleteuser(id);
}
}这里同样通过@autowired注解注入userservice实例,然后在controller的各个方法中调用service方法,实现了从web请求到数据操作的完整流程。
六、事务管理
在spring boot中管理mybatis的事务非常方便。
如果要在某个service方法上添加事务管理,可以使用@transactional注解。例如:
@service
public class userservice {
@autowired
private usermapper usermapper;
@transactional
public int adduser(user user) {
// 一些业务逻辑判断等操作
int result = usermapper.insertuser(user);
// 如果插入成功后还有其他操作,如更新相关联的数据等
return result;
}
}这样,如果在adduser方法中的任何一个数据库操作出现异常,整个事务都会回滚,保证数据的一致性。
七、高级配置
(一)配置mybatis的缓存
- mybatis提供了一级缓存和二级缓存。
- 一级缓存是基于sqlsession的,默认是开启的。
- 二级缓存可以通过在mapper接口或者mapper xml文件中配置开启。
- 在mapper xml文件中配置二级缓存:
- 这里的标签用于配置二级缓存的相关属性,如缓存的清除策略(eviction)、刷新间隔(flushinterval)、缓存大小(size)和是否只读(readonly)等。
(二)配置mybatis的插件
mybatis允许使用插件来扩展其功能。例如,可以使用pagehelper插件来实现分页功能。
首先添加pagehelper的依赖:
com.github.pagehelper
pagehelper - spring - boot - starter
1.3.0然后在配置文件中进行简单配置(以application.yml为例):
pagehelper: helper - dialect: mysql reasonable: true support - methods - arguments: true
在使用分页查询时,在mapper接口方法调用之前使用pagehelper.startpage方法即可。例如:
public class userservice {
@autowired
private usermapper usermapper;
public list getusersbypage(int pagenum, int pagesize) {
pagehelper.startpage(pagenum, pagesize);
return usermapper.selectallusers();
}
}通过以上的配置和操作步骤,就可以在spring boot项目中成功地集成和使用mybatis进行高效的数据持久化操作,无论是简单的crud操作还是涉及到高级功能如事务管理、缓存和插件的使用等。
到此这篇关于spring boot与mybatis配置与操作实战指南的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关spring boot与mybatis配置内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!







发表评论