前言
jdk 1.8 引入的 stream api 是 java 函数式编程的核心特性之一,它提供了一种高效、声明式的方式来处理集合数据(如 list、set 等),支持链式操作、并行处理和惰性求值。
什么是 stream?
- stream 不是数据结构,不存储元素,而是对数据源(如集合、数组)进行计算的一系列操作(操作数据的管道)。
- 不可变:不会修改原始数据源。
- 惰性求值(lazy evaluation):中间操作(如 filter、map)不会立即执行,只有遇到终端操作(如 collect、foreach)才会触发整个流水线。
- 可并行处理(parallelstream):提高大数据处理效率
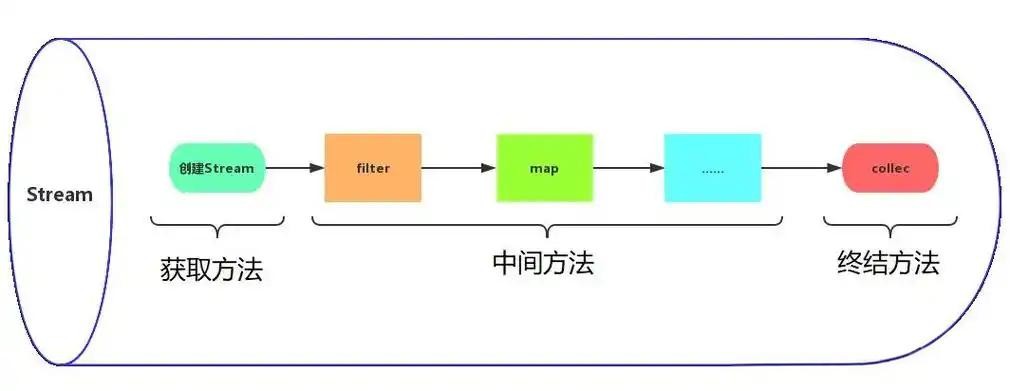
stream api 的基本概念
数据源:可以是任何实现了 collection 接口的数据结构,或者是数组、迭代器等。
中间操作:一系列按需惰性处理数据的管道操作,如过滤、映射、排序等。
终止操作:执行计算并返回结果的操作,如收集、聚合等。一旦执行了终止操作,流就会被消费掉,不能再被重复使用。
中间操作
中间操作可以链接起来形成流水线,常见的中间操作有:
filter(predicate):过滤元素
map(function):映射转换
flatmap(function):扁平化映射(将流中的每个元素转为流,再合并)
distinct():去重
sorted() / sorted(comparator):排序
peek(consumer):调试用,对每个元素执行操作但不改变流
limit(long):截取前 n 个
skip(long):跳过前 n 个
public static void main(string[] args) {
list<string> list = arrays.aslist("apple", "banana", "orange", "avocado","apple");
// 过滤
list<string> list1 = list.stream()
.filter(s -> s.startswith("a"))
.filter(s -> s.length() > 5).collect(collectors.tolist());
system.out.println(list1);//[avocado]
// 映射
// 将字符串映射为对应的长度
list<integer> list2 = list.stream().map(string::length).collect(collectors.tolist());
system.out.println(list2);//[5, 6, 6, 7, 5]
// 将字符串映射为大写
list<string> list3 = list.stream().map(string::touppercase).collect(collectors.tolist());
system.out.println(list3);//[apple, banana, orange, avocado, apple]
// 映射为指定字符串
list<string> list4 = list.stream().map(item->item+"z").collect(collectors.tolist());
system.out.println(list4);//[applez, bananaz, orangez, avocadoz, applez]
// 去重
list<string> list5 = list.stream().distinct().collect(collectors.tolist());
system.out.println(list5);//[apple, banana, orange, avocado]
// 排序
list<string> list6 = list.stream().sorted().collect(collectors.tolist());
system.out.println(list6);//[apple, apple, avocado, banana, orange]
list<string> list7 = list.stream()
.sorted((s1, s2) -> s2.compareto(s1)).collect(collectors.tolist());
system.out.println(list7);//[orange, banana, avocado, apple, apple]
// 限制和跳过
// 取前3个
list<string> list8 = list.stream()
.limit(3).collect(collectors.tolist());
system.out.println(list8);//[apple, banana, orange]
// 跳过第1个
list<string> list9 = list.stream()
.skip(1).collect(collectors.tolist());
system.out.println(list9);//[banana, orange, avocado, apple]
}终止操作
终止操作会触发流的执行,并且返回结果。常见的终止操作包括:
foreach(consumer):遍历
collect(collector):聚合成集合、字符串等(最常用)
reduce(binaryoperator):归约(如求和、拼接)
count():元素个数
min() / max(comparator):最值
anymatch(predicate) / allmatch / nonematch:匹配检查
findfirst() / findany():查找元素(optional)
public static void main(string[] args) {
list<string> list = arrays.aslist("a", "b", "c", "a");
// 遍历
list.stream().foreach(system.out::println);
// 转换为数组
string[] array = list.stream().toarray(string[]::new);
system.out.println(array);//["a", "b", "c", "a"]
// 聚合操作
optional<string> first = list.stream().findfirst();
system.out.println(first.get());//a
// 检查列表中是否存在以字母"a"开头的字符串
boolean anymatch = list.stream().anymatch(s -> s.startswith("a"));
system.out.println(anymatch);//true
// 检查列表中所有字符串的长度是否都等于1
boolean allmatch = list.stream().allmatch(s -> s.length() == 1);
system.out.println(allmatch);//true
// 检查列表中是否没有任何空字符串
boolean nonematch = list.stream().nonematch(s -> s.isempty());
system.out.println(nonematch);//true
// 计数
long count = list.stream().count();
system.out.println(count);//4
list<integer> list2 = arrays.aslist(4,5,6,7);
// 最值
// 获取最大值
integer max = list2.stream().max(integer::compareto).orelse(0);
system.out.println("最大值: " + max);//最大值: 7
int max2 = list2.stream().maptoint(integer::intvalue).max().orelse(0);
system.out.println("最大值: " + max2);//最大值: 7
// 获取最小值
integer min = list2.stream().min(integer::compareto).orelse(0);
system.out.println("最小值: " + min);//最小值: 4
int min2 = list2.stream().maptoint(integer::intvalue).min().orelse(0);
system.out.println("最小值: " + min2);//最小值: 4
// 平均值
double avg = list2.stream().maptoint(integer::intvalue).average().orelse(0.0);
system.out.println("平均数: " + avg);//平均数: 5.5
//求和
int sum = list2.stream().maptoint(integer::intvalue).sum();
system.out.println("累计总和: " + sum);//累计总和: 22
// 或者使用reduce方法计算总和
integer sum2 = list2.stream().reduce(integer::sum).orelse(0);
system.out.println("使用reduce计算总和: " + sum2);//使用reduce计算总和: 22
//orelse()方法,主要作用是提供默认值。
list<integer> list3 = new arraylist<>();
integer max3 = list3.stream().max(integer::compareto).orelse(999);
system.out.println("最大值: " + max3);//最大值: 999
intsummarystatistics stats = list2.stream()
.collect(collectors.summarizingint(integer::intvalue));
system.out.println("计数: " + stats.getcount()); // 计数: 4
system.out.println("总和: " + stats.getsum()); // 总和: 22
system.out.println("平均值: " + stats.getaverage()); // 平均值: 5.5
system.out.println("最大值: " + stats.getmax()); // 最大值: 7
system.out.println("最小值: " + stats.getmin()); // 最小值: 4
}集合元素为类的处理
public static void main(string[] args) {
list<person> person = arrays.aslist(
new person("john", 25, "北京"),
new person("jane", 30, "深圳"),
new person("bob", 30, "上海"),
new person("mike", 20, "深圳"),
new person("lucy", 20, "深圳")
);
//tomap
map<string, person> personmap = person.stream().collect(collectors.tomap(person::getname, item -> item));
system.out.println(json.tojsonstring(personmap));//{"mike":{"age":20,"city":"深圳","name":"mike"},"bob":{"age":30,"city":"上海","name":"bob"},"john":{"age":25,"city":"北京","name":"john"},"lucy":{"age":20,"city":"深圳","name":"lucy"},"jane":{"age":30,"city":"深圳","name":"jane"}}
//处理key值冲突,当有冲突时保留上一个
map<integer, person> personmap2 = person.stream().collect(collectors.tomap(person::getage, item -> item, (k1, k2) -> k1));
system.out.println(json.tojsonstring(personmap2));//{20:{"age":20,"city":"深圳","name":"mike"},25:{"age":25,"city":"北京","name":"john"},30:{"age":30,"city":"深圳","name":"jane"}}
//分组
map<string, list<person>> groupingmap = person.stream()
.collect(collectors.groupingby(person::getcity));
system.out.println(json.tojsonstring(groupingmap));//{"上海":[{"age":30,"city":"上海","name":"bob"}],"深圳":[{"age":30,"city":"深圳","name":"jane"},{"age":20,"city":"深圳","name":"mike"},{"age":20,"city":"深圳","name":"lucy"}],"北京":[{"age":25,"city":"北京","name":"john"}]}
// 多级分组
map<string, map<integer, list<person>>> multigroupingmap = person.stream()
.collect(collectors.groupingby(
person::getcity,
collectors.groupingby(person::getage)
));
system.out.println(json.tojsonstring(multigroupingmap));//{"上海":{30:[{"age":30,"city":"上海","name":"bob"}]},"深圳":{20:[{"age":20,"city":"深圳","name":"mike"},{"age":20,"city":"深圳","name":"lucy"}],30:[{"age":30,"city":"深圳","name":"jane"}]},"北京":{25:[{"age":25,"city":"北京","name":"john"}]}}
// 分区(分成true/false两组)
map<boolean, list<person>> partition = person.stream()
.collect(collectors.partitioningby(p -> p.getage() > 25));
system.out.println(json.tojsonstring(partition));//{false:[{"age":25,"city":"北京","name":"john"},{"age":20,"city":"深圳","name":"mike"},{"age":20,"city":"深圳","name":"lucy"}],true:[{"age":30,"city":"深圳","name":"jane"},{"age":30,"city":"上海","name":"bob"}]}
}
// 静态内部类
static class person {
private string name;
private integer age;
private string city;
public person(string name, integer age, string city) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.city = city;
}
public string getname() { return name; }
public integer getage() { return age; }
public string getcity() { return city; }
@override
public string tostring() {
return "person{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", city='" + city + '\'' +
'}';
}
}并行流
public static void main(string[] args) {
list<person> list = new arraylist<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 50000; i++) {
int j = i % 30;
person person = new person("用户"+i, j, "test"+i);
list.add(person);
}
long starttime = system.currenttimemillis();
list<person> test1 = list.stream().filter(item -> item.getage() > 20).map(item -> {
item.setage(item.getage() * 2);
return item;
}).collect(collectors.tolist());
long endtime = system.currenttimemillis();
system.out.println("执行时间: " + (endtime - starttime) + " 毫秒");//执行时间: 63 毫秒
long starttime2 = system.currenttimemillis();
list<person> test2 = list.parallelstream().filter(item -> item.getage() > 20).map(item -> {
item.setage(item.getage() * 2);
return item;
}).collect(collectors.tolist());
long endtime2 = system.currenttimemillis();
system.out.println("执行时间: " + (endtime2 - starttime2) + " 毫秒");//执行时间: 19 毫秒
}
// 静态内部类
static class person {
private string name;
private integer age;
private string city;
public person(string name, integer age, string city) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.city = city;
}
public string getname() { return name; }
public integer getage() { return age; }
public string getcity() { return city; }
public void setname(string name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setage(integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public void setcity(string city) {
this.city = city;
}
@override
public string tostring() {
return "person{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", city='" + city + '\'' +
'}';
}
}到此这篇关于jdk8中stream中常用方法的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关jdk8 stream方法内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!







发表评论