一、mybatis简介与crud基础
mybatis是一款优秀的持久层框架,它支持自定义sql、存储过程以及高级映射。mybatis避免了几乎所有的jdbc代码和手动设置参数以及获取结果集的工作。
1.1 传统jdbc的问题
在传统jdbc编程中,我们经常遇到以下问题:
// jdbc中繁琐的结果集处理
while(rs.next()) {
user user = new user();
user.setid(rs.getstring("id"));
user.setidcard(rs.getstring("idcard"));
user.setusername(rs.getstring("username"));
// ... 需要为每个属性手动赋值
userlist.add(user);
}这种方式存在以下缺点:
- 代码冗余,每个字段都需要手动映射
- 容易出错,字段名写错会导致运行时错误
- 维护困难,表结构变化时需要修改大量代码

二、mybatis中使用map实现crud
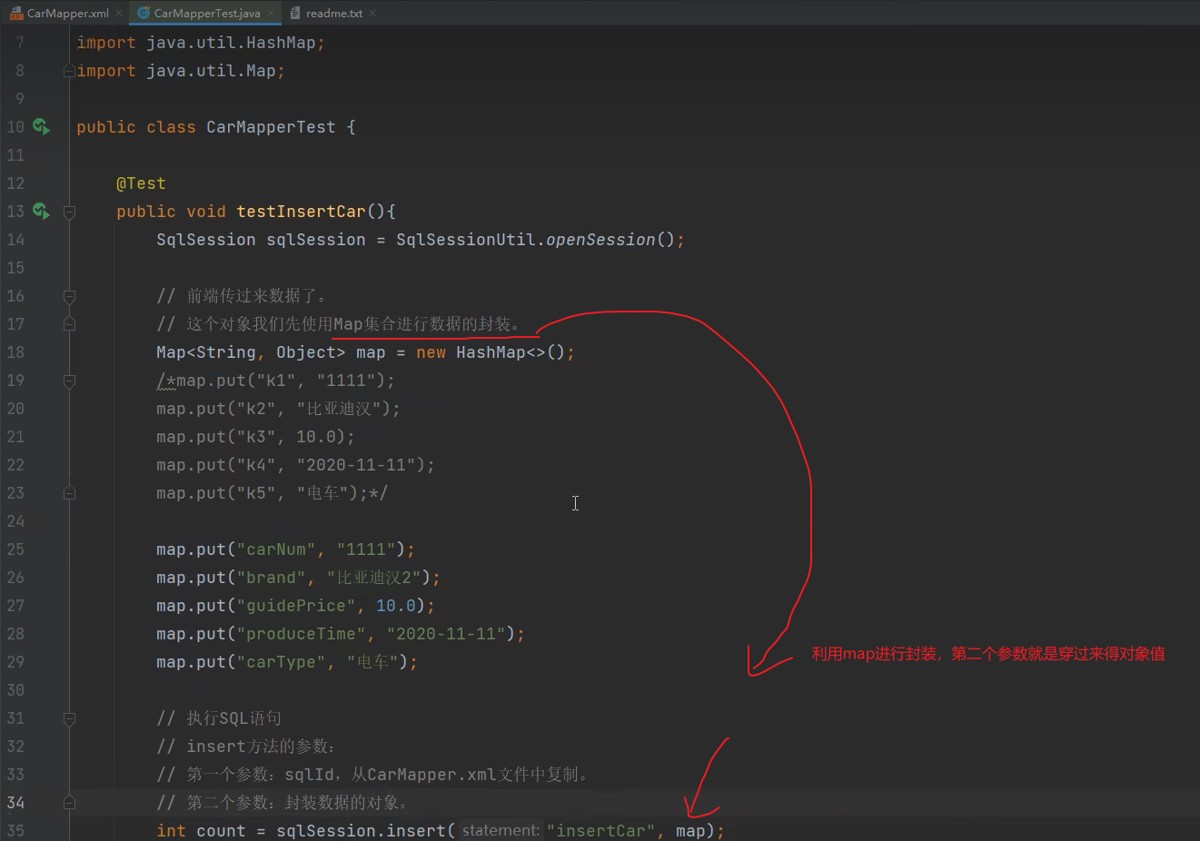
2.1 使用map进行数据插入
map集合提供了灵活的键值对存储方式,适合不确定参数数量或临时性的数据操作。
2.1.1 基础map传参
@test
public void testinsertcarbymap() {
sqlsession sqlsession = sqlsessionutil.opensession();
// 使用map封装前端传递的数据
map<string, object> map = new hashmap<>();
map.put("carnum", "11111");
map.put("brand", "比亚迪汉");
map.put("guideprice", 10.0);
map.put("producetime", "2020-11-11");
map.put("cartype", "电车");
// 执行sql插入操作
int count = sqlsession.insert("insertcar", map);
system.out.println("插入记录数:" + count);
sqlsession.commit();
sqlsession.close();
}
2.1.2 mapper xml配置
<!-- carmapper.xml -->
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!doctype mapper
public "-//mybatis.org//dtd mapper 3.0//en"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.example.mapper.carmapper">
<insert id="insertcar">
insert into t_car(id, car_num, brand, guide_price, produce_time, car_type)
values(null, #{carnum}, #{brand}, #{guideprice}, #{producetime}, #{cartype})
</insert>
</mapper>2.1.3 注意事项
- 键名匹配原则:
#{}中的名称必须与map中的key完全一致 - 空值处理:如果key不存在,对应的值将为null
- 命名规范:建议使用有意义的key名称,提高代码可读性
2.2 使用map进行数据查询
@test
public void testselectbymap() {
sqlsession sqlsession = sqlsessionutil.opensession();
map<string, object> parammap = new hashmap<>();
parammap.put("minprice", 10.0);
parammap.put("brand", "宝马");
list<map<string, object>> result = sqlsession.selectlist("selectcarbycondition", parammap);
for (map<string, object> car : result) {
system.out.println(car);
}
sqlsession.close();
}三、mybatis中使用pojo类实现crud
3.1 pojo类定义
// car.java
public class car {
private long id;
private string carnum;
private string brand;
private double guideprice;
private string producetime;
private string cartype;
// 构造方法
public car() {}
public car(long id, string carnum, string brand, double guideprice,
string producetime, string cartype) {
this.id = id;
this.carnum = carnum;
this.brand = brand;
this.guideprice = guideprice;
this.producetime = producetime;
this.cartype = cartype;
}
// getter和setter方法
public long getid() { return id; }
public void setid(long id) { this.id = id; }
public string getcarnum() { return carnum; }
public void setcarnum(string carnum) { this.carnum = carnum; }
// ... 其他getter和setter
}3.2 使用pojo进行数据插入
@test
public void testinsertcarbypojo() {
sqlsession sqlsession = sqlsessionutil.opensession();
// 使用pojo对象封装数据
car car = new car(null, "3333", "比亚迪秦", 30.0, "2020-11-11", "新能源");
// 执行sql
int count = sqlsession.insert("insertcar", car);
system.out.println("插入记录数:" + count);
sqlsession.commit();
sqlsession.close();
}3.3 pojo传参原理
重要规则:#{}占位符中的名称对应的是pojo类的getter方法名去掉"get"并将首字母小写后的名称。
例如:
getcarnum()→#{carnum}getguideprice()→#{guideprice}getusername()→#{username}
3.4 使用pojo进行数据查询
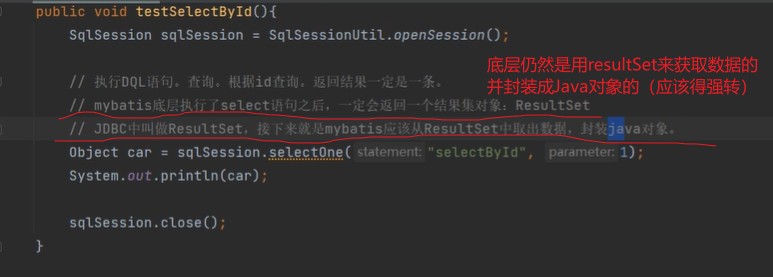
3.4.1 查询单个对象
<!-- 根据id查询汽车信息 -->
<select id="selectbyid" resulttype="com.example.pojo.car">
select * from t_car where id = #{id}
</select>@test
public void testselectbyid() {
sqlsession sqlsession = sqlsessionutil.opensession();
// 查询单个对象
car car = sqlsession.selectone("selectbyid", 1);
system.out.println(car);
sqlsession.close();
}
3.4.2 查询所有记录
<!-- 查询所有汽车信息 -->
<select id="selectall" resulttype="com.example.pojo.car">
select
id,
car_num as carnum,
brand,
guide_price as guideprice,
produce_time as producetime,
car_type as cartype
from t_car
</select>@test
public void testselectall() {
sqlsession sqlsession = sqlsessionutil.opensession();
// 查询所有记录,返回list集合
list<car> carlist = sqlsession.selectlist("selectall");
for (car car : carlist) {
system.out.println(car);
}
sqlsession.close();
}四、解决字段名与属性名映射问题
4.1 问题现象
当数据库字段名与java类属性名不一致时,会出现属性值为null的情况:
-- 数据库表结构 +----+----------+------------+--------------+---------------+----------+ | id | car_num | brand | guide_price | produce_time | car_type | +----+----------+------------+--------------+---------------+----------+ | 1 | 1001 | 宝马520li | 10.00 | 2020-10-11 | 燃油车 | +----+----------+------------+--------------+---------------+----------+ -- 直接查询会导致car对象的carnum、guideprice等属性为null -- 因为数据库字段是car_num,而java属性是carnum
4.2 解决方案
方案一:sql中使用as别名(推荐)
<select id="selectbyid" resulttype="com.example.pojo.car">
select
id,
car_num as carnum, -- 起别名
brand,
guide_price as guideprice, -- 起别名
produce_time as producetime, -- 起别名
car_type as cartype -- 起别名
from t_car
where id = #{id}
</select>方案二:配置驼峰命名自动映射
在mybatis配置文件中开启驼峰命名自动映射:
<!-- mybatis-config.xml -->
<configuration>
<settings>
<!-- 开启驼峰命名自动映射 -->
<setting name="mapunderscoretocamelcase" value="true"/>
</settings>
</configuration>开启后,mybatis会自动将下划线命名的数据库字段映射到驼峰命名的java属性:
car_num→carnumguide_price→guidepriceproduce_time→producetime
方案三:使用resultmap自定义映射
<resultmap id="carresultmap" type="com.example.pojo.car">
<id property="id" column="id"/>
<result property="carnum" column="car_num"/>
<result property="brand" column="brand"/>
<result property="guideprice" column="guide_price"/>
<result property="producetime" column="produce_time"/>
<result property="cartype" column="car_type"/>
</resultmap>
<select id="selectbyid" resultmap="carresultmap">
select * from t_car where id = #{id}
</select>五、map与pojo对比与选择
5.1 使用场景对比
| 特性 | map集合 | pojo类 |
|---|---|---|
| 灵活性 | 高,适合动态参数 | 低,结构固定 |
| 类型安全 | 低,运行时才能发现错误 | 高,编译时检查 |
| 代码可读性 | 低,需要查看map键名 | 高,属性明确 |
| ide支持 | 有限,无法自动提示 | 好,有代码提示 |
| 适合场景 | 临时查询、参数不固定 | 业务实体、固定结构 |
5.2 最佳实践建议
业务实体操作使用pojo
- 用户、订单、商品等核心业务实体
- 需要频繁操作和传递的数据
- 有利于代码维护和重构
临时查询使用map
- 动态条件查询,参数不固定
- 统计报表等临时性数据操作
- 快速原型开发阶段
混合使用策略
// 示例:使用map封装查询条件,返回pojo列表
public list<car> findcars(map<string, object> params) {
return sqlsession.selectlist("findcarsbycondition", params);
}六、完整示例与总结
6.1 完整mapper示例
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!doctype mapper
public "-//mybatis.org//dtd mapper 3.0//en"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.example.mapper.carmapper">
<!-- 插入操作 -->
<insert id="insertcar">
insert into t_car(id, car_num, brand, guide_price, produce_time, car_type)
values(null, #{carnum}, #{brand}, #{guideprice}, #{producetime}, #{cartype})
</insert>
<!-- 根据id查询 -->
<select id="selectbyid" resulttype="com.example.pojo.car">
select
id,
car_num as carnum,
brand,
guide_price as guideprice,
produce_time as producetime,
car_type as cartype
from t_car
where id = #{id}
</select>
<!-- 查询所有 -->
<select id="selectall" resulttype="com.example.pojo.car">
select
id,
car_num as carnum,
brand,
guide_price as guideprice,
produce_time as producetime,
car_type as cartype
from t_car
</select>
<!-- 更新操作 -->
<update id="updatecar">
update t_car
set car_num = #{carnum},
brand = #{brand},
guide_price = #{guideprice},
produce_time = #{producetime},
car_type = #{cartype}
where id = #{id}
</update>
<!-- 删除操作 -->
<delete id="deletebyid">
delete from t_car where id = #{id}
</delete>
</mapper>6.2 关键点总结
#{}与${}的区别:
#{}是预编译处理,防止sql注入${}是字符串替换,有sql注入风险
resulttype与resultmap:
resulttype:自动映射,要求字段名与属性名一致或配置别名resultmap:自定义映射,处理复杂映射关系
占位符命名规则:
- map传参:
#{}中写map的key - pojo传参:
#{}中写getter方法对应的属性名
性能优化建议:
- 尽量使用pojo,享受编译时检查的好处
- 复杂查询考虑使用resultmap提高可读性
- 批量操作使用批量api提高性能
通过本文的学习,你应该掌握了mybatis中使用map和pojo实现crud操作的核心技术。在实际开发中,根据具体场景选择合适的方式,既能提高开发效率,又能保证代码质量。
以上就是mybatis使用map与pojo类实现crud操作的步骤详解的详细内容,更多关于mybatis map与pojo类实现crud的资料请关注代码网其它相关文章!




发表评论