前言:
前面学习了表的增删查改之后,今天我们重点来讲解一下有关查询的复杂问题——复合查询
一、复合查询基础概念
1.1 什么是复合查询
复合查询是指将多个简单查询通过特定的sql语法组合起来,形成一个功能更加强大的查询语句。与简单查询相比,复合查询能够:
- 处理更复杂的数据关系
- 减少应用程序中的数据处理逻辑
- 提高数据检索效率(当正确使用时)
- 实现跨表的数据关联和分析
1.2 复合查询的主要类型
mysql中常见的复合查询包括:
- 子查询(subqueries)
- 连接查询(join operations)
- 联合查询(union queries)
- 派生表(derived tables)
- 公用表表达式(common table expressions,cte)
二、示例数据库结构详解
在进行讲解我们的查询之前,我们先看一下名为需要用到的表,以及往表里添加几组示例数据,以方便我们查询后看到查询的效果
2.1 完整的表结构设计
-- 部门表
create table departments (
dept_id int primary key auto_increment,
dept_name varchar(50) not null,
location varchar(50) not null,
established_date date,
budget decimal(12,2)
);
-- 员工表
create table employees (
emp_id int primary key auto_increment,
emp_name varchar(50) not null,
dept_id int,
salary decimal(10,2) not null,
hire_date date not null,
manager_id int,
email varchar(100),
constraint fk_dept foreign key (dept_id) references departments(dept_id),
constraint fk_manager foreign key (manager_id) references employees(emp_id)
);
-- 项目表
create table projects (
project_id int primary key auto_increment,
project_name varchar(100) not null,
budget decimal(12,2),
start_date date,
end_date date,
dept_id int,
status enum('planning', 'in progress', 'completed', 'on hold') default 'planning',
constraint fk_project_dept foreign key (dept_id) references departments(dept_id)
);
-- 员工项目关联表
create table emp_projects (
emp_id int,
project_id int,
role varchar(50),
join_date date,
hours_allocated int,
primary key (emp_id, project_id),
constraint fk_emp foreign key (emp_id) references employees(emp_id),
constraint fk_project foreign key (project_id) references projects(project_id)
);2.2 示例数据填充
-- 部门数据 insert into departments values (1, '技术研发部', '北京总部', '2015-06-01', 2000000.00), (2, '市场营销部', '上海分公司', '2016-03-15', 1500000.00), (3, '人力资源部', '广州办事处', '2017-01-10', 800000.00), (4, '财务部', '北京总部', '2015-06-01', 1200000.00); -- 员工数据 insert into employees values (1, '张伟', 1, 25000.00, '2016-03-10', null, 'zhangwei@company.com'), (2, '李娜', 1, 18000.00, '2017-05-15', 1, 'lina@company.com'), (3, '王芳', 2, 22000.00, '2016-11-20', null, 'wangfang@company.com'), (4, '赵刚', 2, 16000.00, '2018-02-28', 3, 'zhaogang@company.com'), (5, '钱强', 3, 19000.00, '2017-08-05', null, 'qianqiang@company.com'), (6, '孙丽', 3, 14000.00, '2019-06-15', 5, 'sunli@company.com'), (7, '周明', 4, 21000.00, '2016-07-22', null, 'zhouming@company.com'); -- 项目数据 insert into projects values (1, '新一代电商平台开发', 800000.00, '2023-01-10', '2023-09-30', 1, 'in progress'), (2, '全球市场推广计划', 500000.00, '2023-02-15', '2023-08-15', 2, 'in progress'), (3, '员工技能提升计划', 200000.00, '2023-03-01', '2023-12-31', 3, 'planning'), (4, '财务系统云迁移', 350000.00, '2023-04-01', null, 4, 'in progress'), (5, '移动端应用优化', 300000.00, '2023-05-15', '2023-11-30', 1, 'planning'); -- 员工项目关联 insert into emp_projects values (1, 1, '技术负责人', '2023-01-05', 30), (2, 1, '开发工程师', '2023-01-10', 40), (1, 5, '架构师', '2023-05-10', 20), (3, 2, '市场总监', '2023-02-10', 25), (4, 2, '市场专员', '2023-02-15', 35), (5, 3, '培训经理', '2023-03-01', 30), (6, 3, '培训助理', '2023-03-05', 20), (7, 4, '项目经理', '2023-04-01', 40);
三、子查询深度解析
3.1 子查询分类与语法
3.1.1 按子查询位置分类
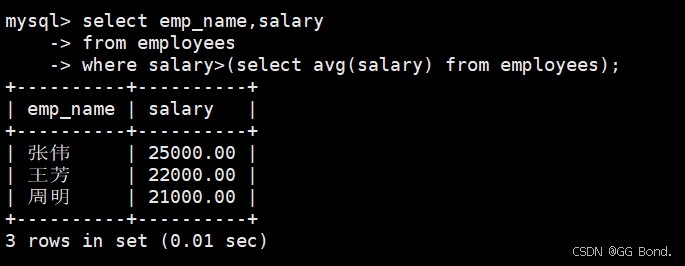
where子句子查询
select emp_name, salary from employees where salary > (select avg(salary) from employees);
from子句子查询(派生表)
select d.dept_name, avg_sal.avg_salary from departments d join (select dept_id, avg(salary) as avg_salary from employees group by dept_id) avg_sal on d.dept_id = avg_sal.dept_id;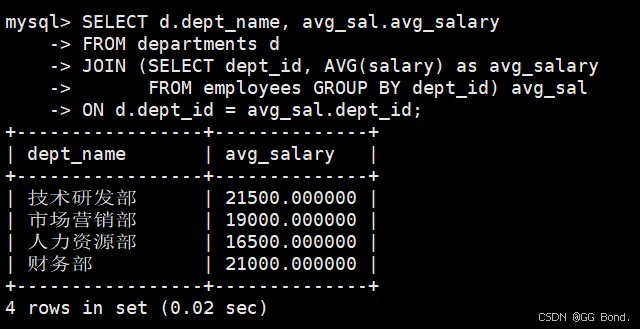
select子句子查询
select emp_name, salary, (select avg(salary) from employees) as company_avg from employees;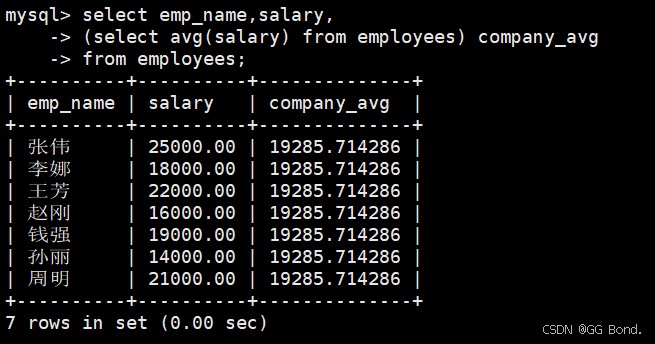
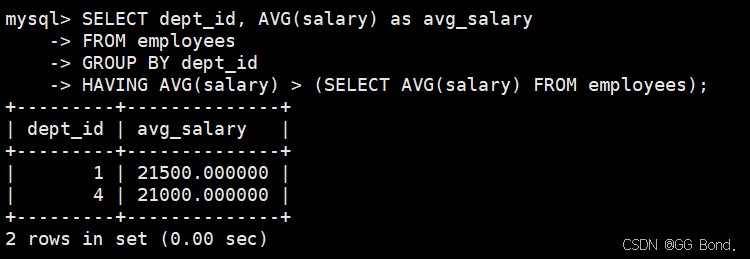
having子句子查询
select dept_id, avg(salary) as avg_salary from employees group by dept_id having avg(salary) > (select avg(salary) from employees);
3.1.2 按子查询相关性分类
非相关子查询
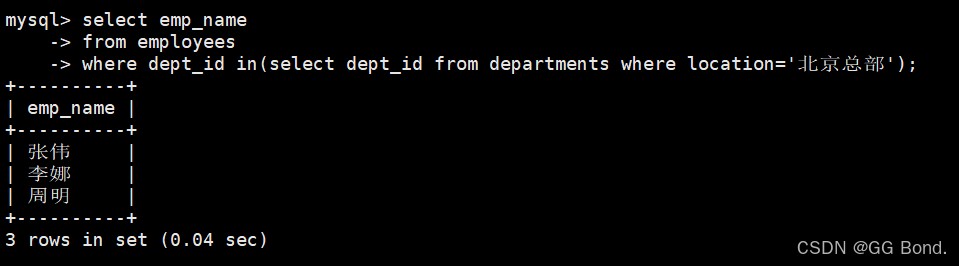
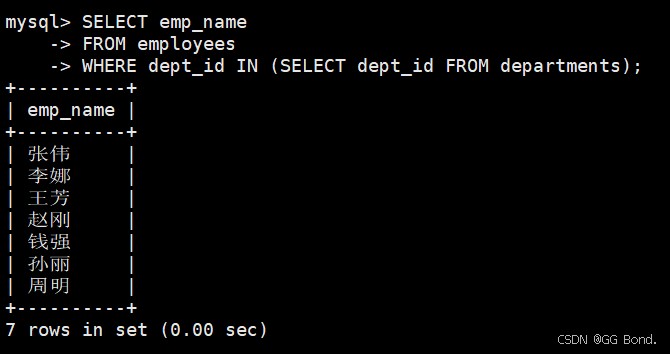
select emp_name from employees where dept_id in (select dept_id from departments where location = '北京总部');
相关子查询
select e1.emp_name, e1.salary
from employees e1
where salary > (select avg(salary)
from employees e2
where e2.dept_id = e1.dept_id);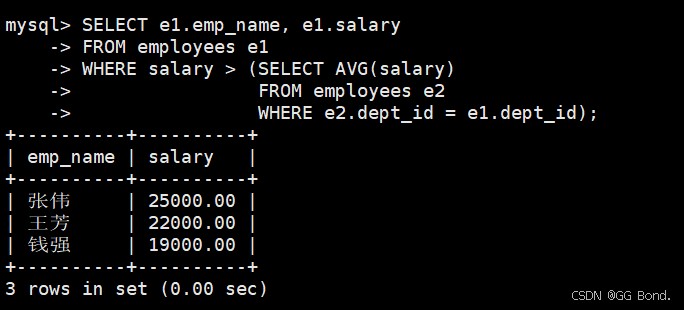
3.2 子查询操作符详解
in操作符
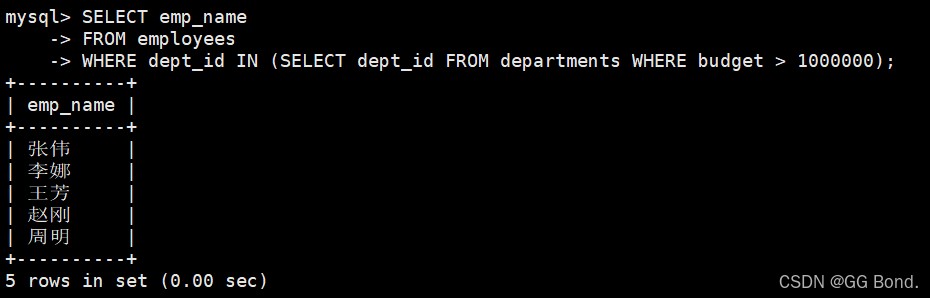
select emp_name from employees where dept_id in (select dept_id from departments where budget > 1000000);
not in操作符
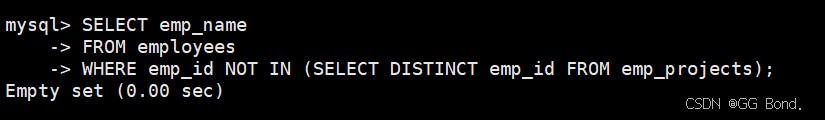
select emp_name from employees where emp_id not in (select distinct emp_id from emp_projects);
exists操作符
select d.dept_name
from departments d
where exists (select 1 from projects p
where p.dept_id = d.dept_id and p.status = 'in progress');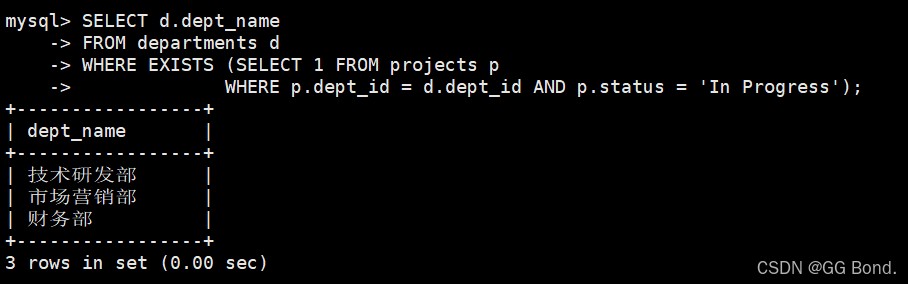
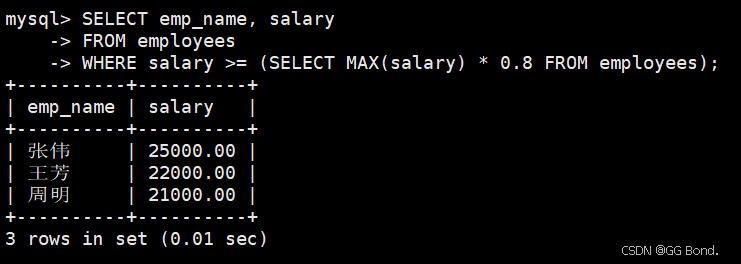
比较运算符子查询
select emp_name, salary from employees where salary >= (select max(salary) * 0.8 from employees);
3.3 子查询性能优化
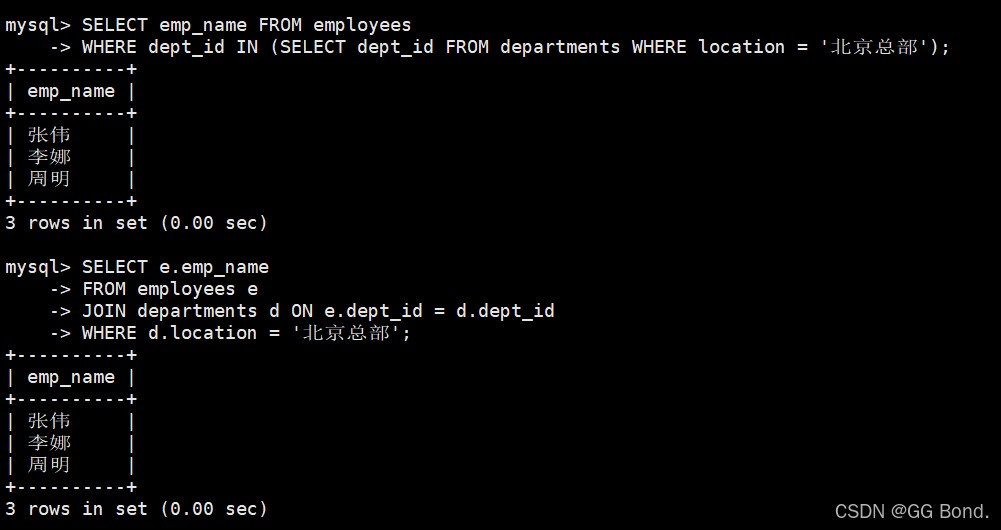
使用join替代子查询
-- 不推荐 select emp_name from employees where dept_id in (select dept_id from departments where location = '北京总部'); -- 推荐 select e.emp_name from employees e join departments d on e.dept_id = d.dept_id where d.location = '北京总部';
使用exists替代in
-- 当子查询结果集大时更高效
select d.dept_name
from departments d
where exists (select 1 from projects p
where p.dept_id = d.dept_id);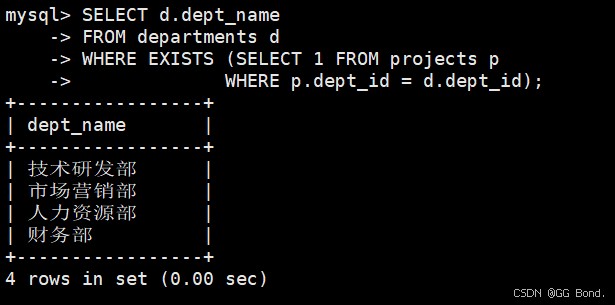
限制子查询返回的列数
-- 只选择必要的列 select emp_name from employees where dept_id in (select dept_id from departments); -- 而不是 select *
四、连接查询全面讲解
4.1 连接类型详解
4.1.1 内连接(inner join)
-- 基本内连接 select e.emp_name, d.dept_name from employees e inner join departments d on e.dept_id = d.dept_id; -- 带条件的内连接 select e.emp_name, p.project_name, ep.role from employees e inner join emp_projects ep on e.emp_id = ep.emp_id inner join projects p on ep.project_id = p.project_id where p.status = 'in progress';
4.1.2 外连接(outer join)
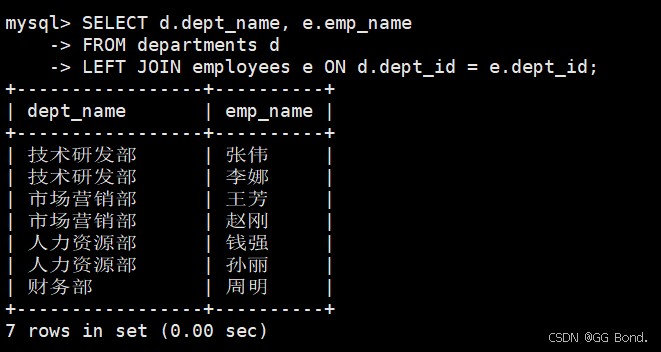
左外连接(left join)
-- 查询所有部门及其员工(包括没有员工的部门) select d.dept_name, e.emp_name from departments d left join employees e on d.dept_id = e.dept_id;
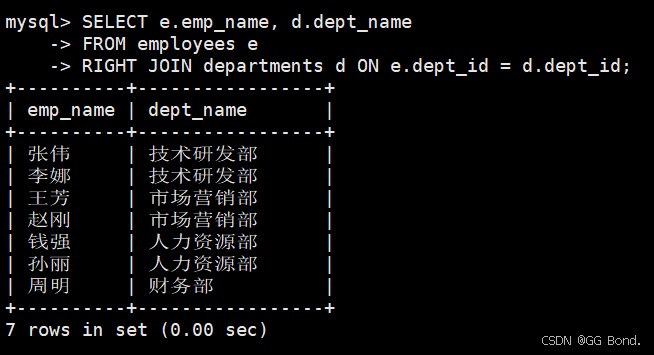
右外连接(right join)
-- 查询所有员工及其部门(包括没有部门的员工) select e.emp_name, d.dept_name from employees e right join departments d on e.dept_id = d.dept_id;
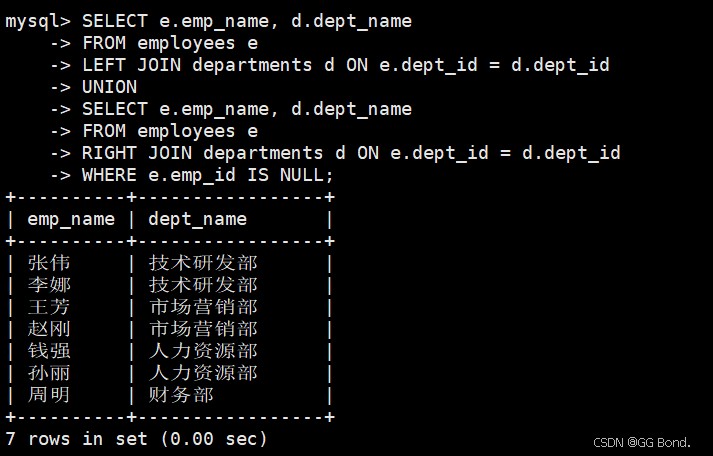
全外连接(full outer join) - mysql通过union实现
-- 查询所有员工和所有部门的组合 select e.emp_name, d.dept_name from employees e left join departments d on e.dept_id = d.dept_id union select e.emp_name, d.dept_name from employees e right join departments d on e.dept_id = d.dept_id where e.emp_id is null;
4.1.3 交叉连接(cross join)
-- 生成员工和项目的所有可能组合 select e.emp_name, p.project_name from employees e cross join projects p;
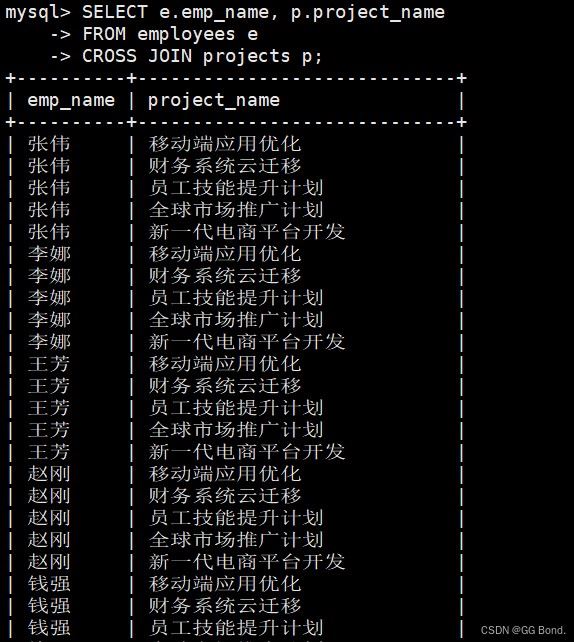
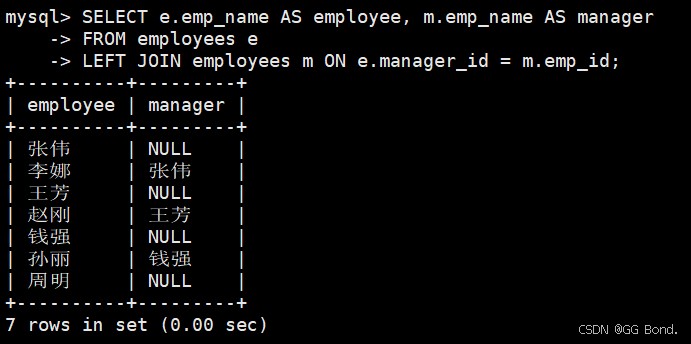
4.1.4 自连接(self join)
-- 查询员工及其经理信息 select e.emp_name as employee, m.emp_name as manager from employees e left join employees m on e.manager_id = m.emp_id;
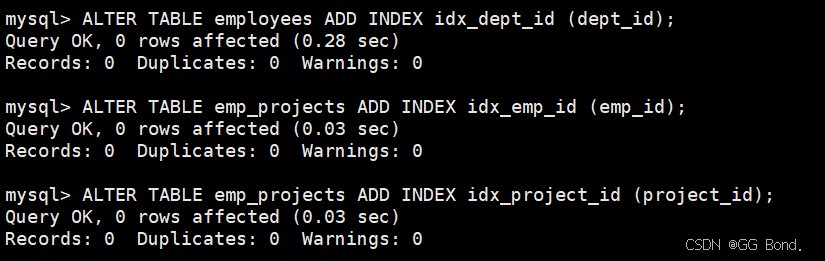
4.2 连接查询优化策略
下面关于索引和视图的知识后面还会详细讲解
确保连接条件有索引
alter table employees add index idx_dept_id (dept_id); alter table emp_projects add index idx_emp_id (emp_id); alter table emp_projects add index idx_project_id (project_id);
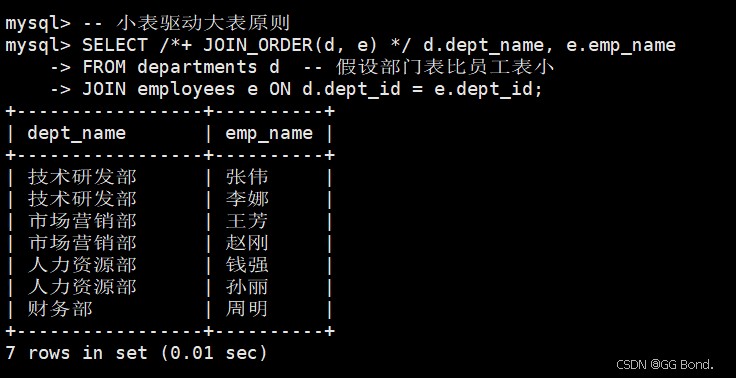
选择适当的连接顺序
-- 小表驱动大表原则 select /*+ join_order(d, e) */ d.dept_name, e.emp_name from departments d -- 假设部门表比员工表小 join employees e on d.dept_id = e.dept_id;
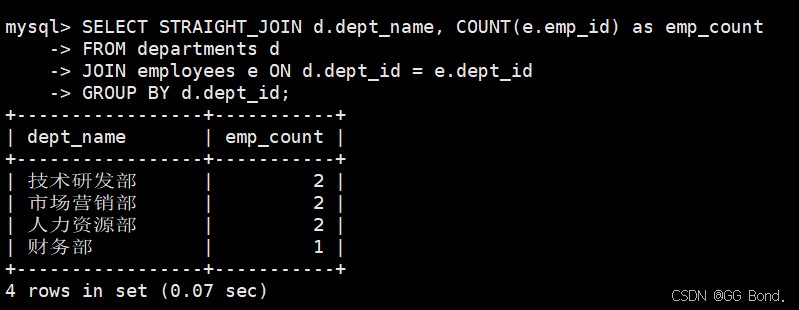
使用straight_join强制连接顺序
select straight_join d.dept_name, count(e.emp_id) as emp_count from departments d join employees e on d.dept_id = e.dept_id group by d.dept_id;
五、union查询高级应用
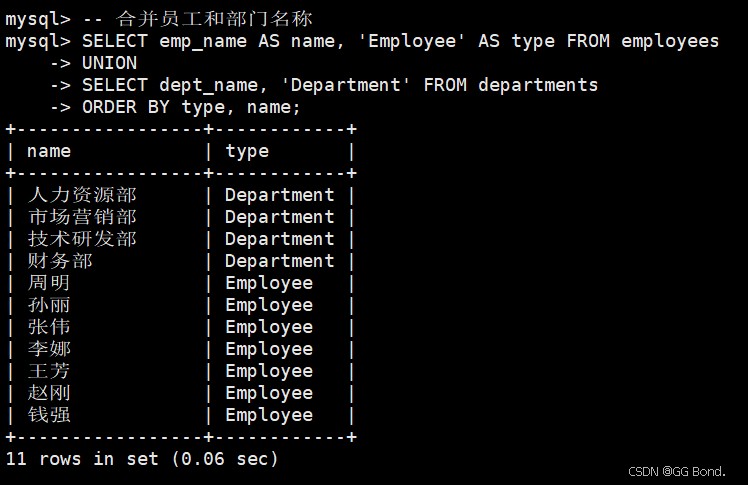
5.1 union基础用法
-- 合并员工和部门名称 select emp_name as name, 'employee' as type from employees union select dept_name, 'department' from departments order by type, name;
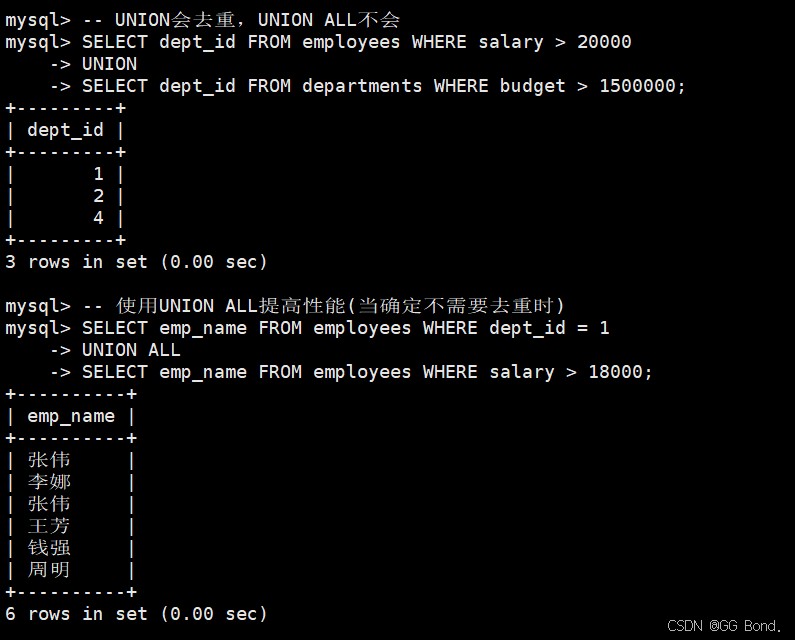
5.2 union all与union的区别
-- union会去重,union all不会 select dept_id from employees where salary > 20000 union select dept_id from departments where budget > 1500000; -- 使用union all提高性能(当确定不需要去重时) select emp_name from employees where dept_id = 1 union all select emp_name from employees where salary > 18000;
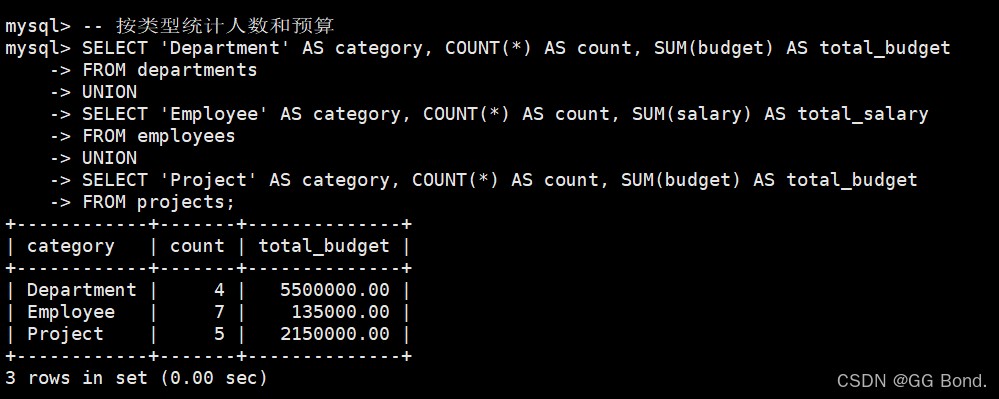
5.3 复杂union查询示例
-- 按类型统计人数和预算 select 'department' as category, count(*) as count, sum(budget) as total_budget from departments union select 'employee' as category, count(*) as count, sum(salary) as total_salary from employees union select 'project' as category, count(*) as count, sum(budget) as total_budget from projects;
六、派生表与cte高级用法
6.1 派生表(mysql 5.7+)
-- 计算各部门薪资统计信息
select d.dept_name,
stats.emp_count,
stats.avg_salary,
stats.max_salary
from departments d
join (
select dept_id,
count(*) as emp_count,
avg(salary) as avg_salary,
max(salary) as max_salary
from employees
group by dept_id
) stats on d.dept_id = stats.dept_id;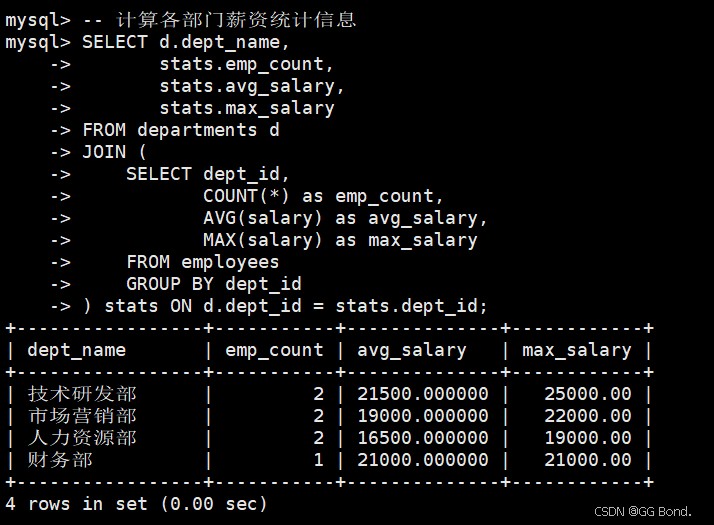
6.2 公用表表达式(cte, mysql 8.0+)
6.2.1 基本cte
-- 查询参与项目的员工信息
with project_emps as (
select distinct emp_id from emp_projects
)
select e.emp_name, e.salary
from employees e
join project_emps pe on e.emp_id = pe.emp_id;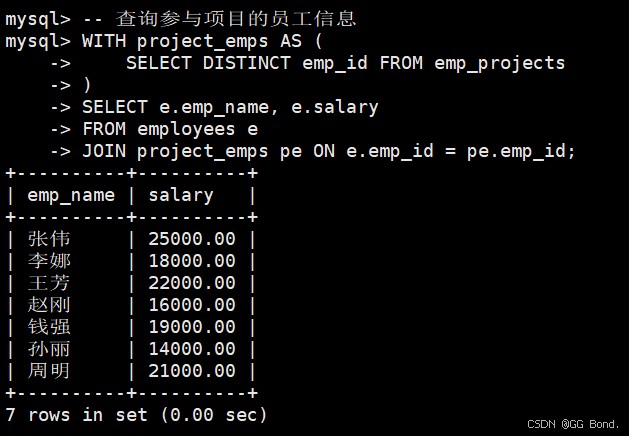
6.2.2 递归cte
-- 组织结构层级查询
with recursive org_hierarchy as (
-- 基础查询:找出所有没有经理的员工(顶层管理者)
select emp_id, emp_name, manager_id, 1 as level
from employees
where manager_id is null
union all
-- 递归查询:找出每个员工的下属
select e.emp_id, e.emp_name, e.manager_id, oh.level + 1
from employees e
join org_hierarchy oh on e.manager_id = oh.emp_id
)
select emp_id, emp_name, level
from org_hierarchy
order by level, emp_name;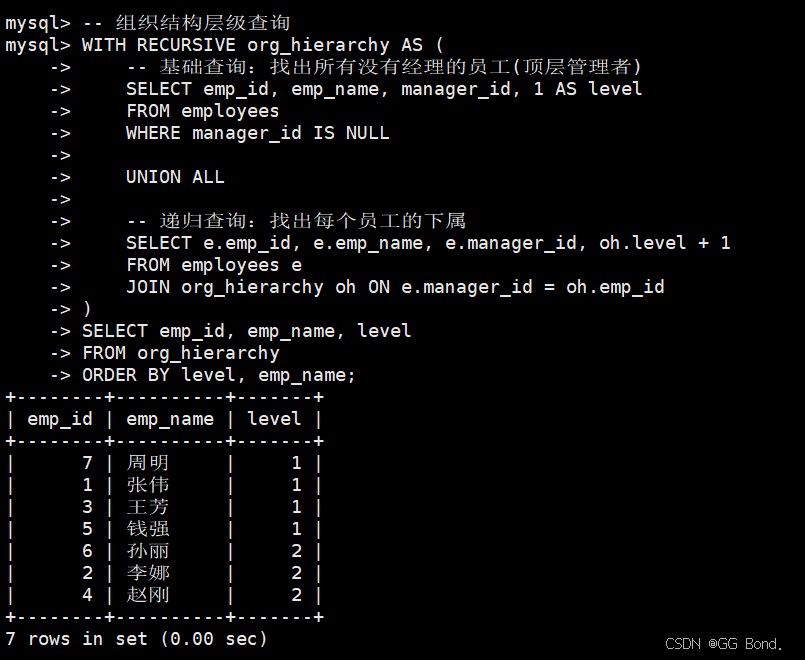
七、复合查询实战案例
7.1 多层级数据分析
-- 分析各部门项目参与情况
with dept_stats as (
select d.dept_id, d.dept_name,
count(distinct e.emp_id) as total_emps,
count(distinct ep.emp_id) as project_emps,
count(distinct p.project_id) as project_count
from departments d
left join employees e on d.dept_id = e.dept_id
left join emp_projects ep on e.emp_id = ep.emp_id
left join projects p on d.dept_id = p.dept_id
group by d.dept_id, d.dept_name
)
select dept_name,
total_emps,
project_emps,
project_count,
concat(round(project_emps/total_emps*100, 2), '%') as participation_rate
from dept_stats
order by participation_rate desc;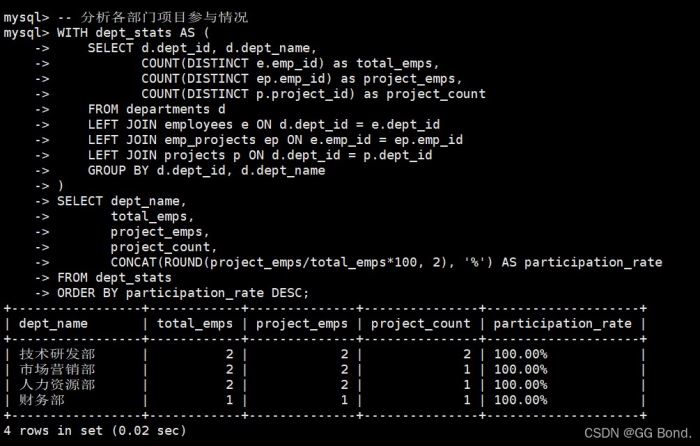
7.2 复杂业务逻辑实现
-- 找出每个部门薪资高于部门平均且参与项目的员工
with dept_avg_salary as (
select dept_id, avg(salary) as avg_salary
from employees
group by dept_id
),
project_employees as (
select distinct emp_id
from emp_projects
)
select e.emp_name, e.salary, d.dept_name, das.avg_salary
from employees e
join departments d on e.dept_id = d.dept_id
join dept_avg_salary das on e.dept_id = das.dept_id
join project_employees pe on e.emp_id = pe.emp_id
where e.salary > das.avg_salary
order by e.dept_id, e.salary desc;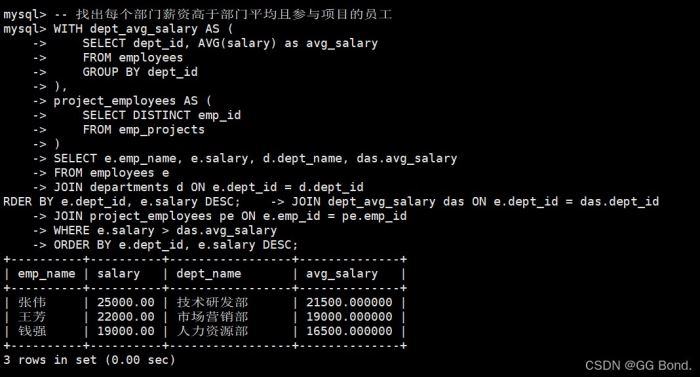
八、性能优化与最佳实践
8.1 复合查询性能优化
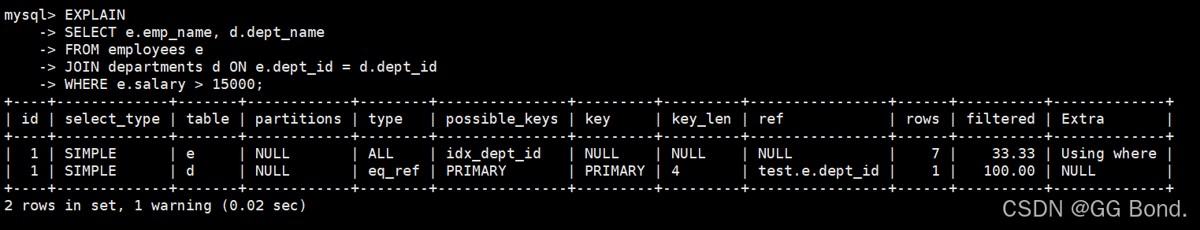
explain分析工具
explain select e.emp_name, d.dept_name from employees e join departments d on e.dept_id = d.dept_id where e.salary > 15000;
- 索引优化建议
- 为所有连接条件创建索引
- 为where子句中的条件列创建索引
- 考虑复合索引的顺序
查询重写技巧
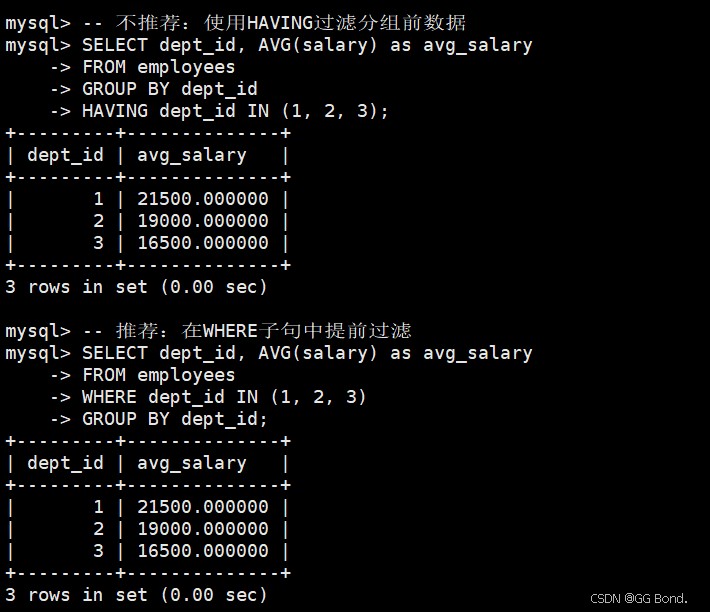
-- 不推荐:使用having过滤分组前数据 select dept_id, avg(salary) as avg_salary from employees group by dept_id having dept_id in (1, 2, 3); -- 推荐:在where子句中提前过滤 select dept_id, avg(salary) as avg_salary from employees where dept_id in (1, 2, 3) group by dept_id;
8.2 复合查询最佳实践
- 保持查询简洁:避免过度复杂的嵌套
- 合理使用注释:解释复杂查询的逻辑
- 分步构建查询:先测试子查询再组合
- 考虑使用视图:对常用复杂查询创建视图
create view dept_project_stats as
select d.dept_id, d.dept_name,
count(distinct e.emp_id) as emp_count,
count(distinct p.project_id) as project_count
from departments d
left join employees e on d.dept_id = e.dept_id
left join projects p on d.dept_id = p.dept_id
group by d.dept_id, d.dept_name;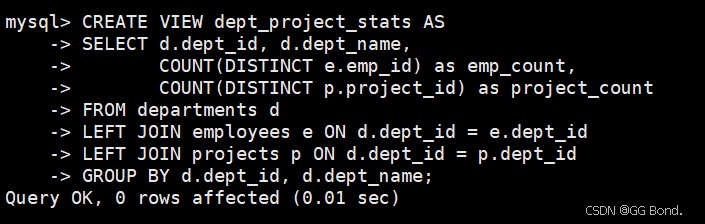
九、常见问题与解决方案
9.1 性能问题排查
问题:复合查询执行缓慢
解决方案:
- 使用explain分析执行计划
- 检查是否使用了适当的索引
- 考虑将复杂查询拆分为多个简单查询
- 评估是否可以使用临时表存储中间结果
9.2 结果不符合预期
问题:查询返回的行数多于或少于预期
解决方案:
- 检查连接条件是否正确
- 确认使用正确的join类型(inner/left/right)
- 验证where条件逻辑
- 检查null值的处理方式
9.3 语法错误处理
常见错误:
- 子查询返回多行但使用了比较运算符
- 在group by或having中引用了不存在的列
- union查询的列数或类型不匹配
解决方案:
-- 错误示例:子查询返回多行 select emp_name from employees where salary = (select salary from employees where dept_id = 1); -- 正确修改: select emp_name from employees where salary in (select salary from employees where dept_id = 1);

十、总结与进阶学习建议
10.1 复合查询核心要点总结
- 子查询适合解决分步查询问题,但要注意性能
- 连接查询是处理表关系的强大工具
- union提供了垂直合并结果集的能力
- cte提高了复杂查询的可读性和可维护性
10.2 进阶学习建议
- 深入学习执行计划:掌握explain输出解读
- 了解查询优化器原理:学习mysql如何优化查询
- 研究分区表查询:大数据量下的查询优化
- 学习窗口函数:mysql 8.0+的高级分析功能
以上就是关于mysql查询中的所有相关知识点,除了前面常用的外,后面的有些时候并不一定能用到,但都是有必要掌握的,由于篇幅原因,有些问题并不能全面刨析到,建议大家看到不理解的地方可以再去找一些教学视频看一下






发表评论