一、什么是 mybatis
通过 mybatis中文网站我们了解到 “mybatis 是一款优秀的持久层框架 ” ,用于简化jdbc的开发,而此处 “ 持久层 ” :指的是持久化操作的层,通常指数据访问层(dao),用来操作数据库
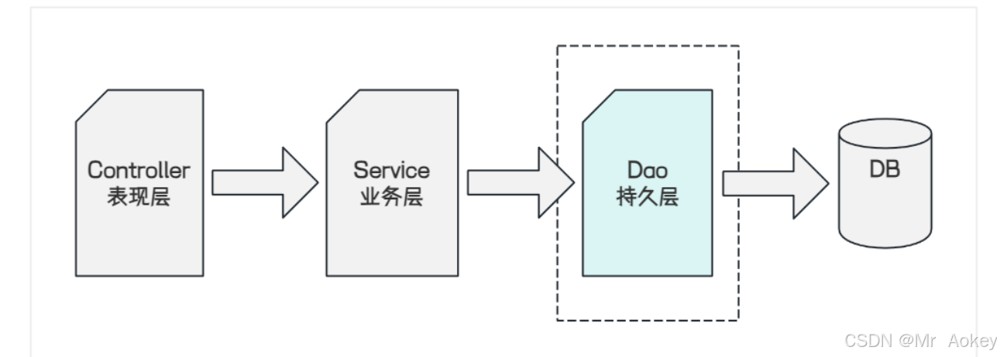
换句话说,mybatis 是更简单的完成程序与数据库交互的框架,即更简单方便地操作和读取数据库工具
二、 mybatis 入门
2.1、创建项目
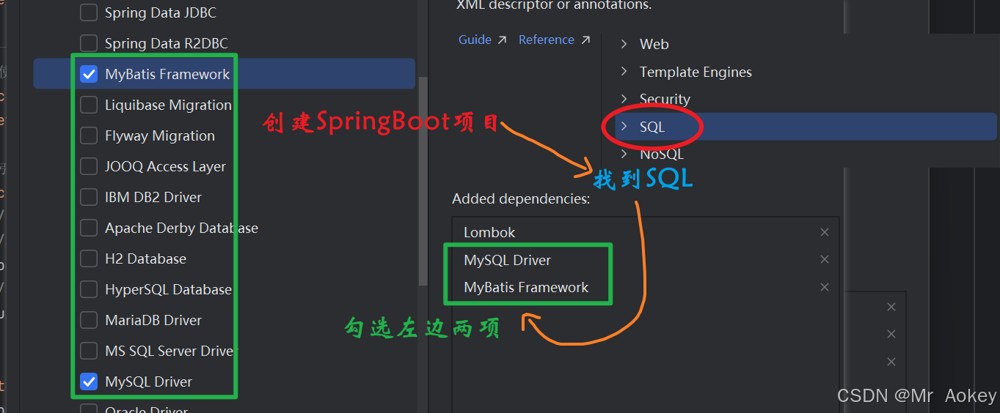
创建 spring boot 项目,并导入 mybatis 启动依赖和 mysql 驱动包
创建用户表,并创建对对应的实体类 userinfo
@data
public class userinfo {
private integer id;
private string username;
private string password;
private integer age;
private integer gender;
private string phone;
private integer deleteflag;
private date createtime;
private date updatetime;
}
数据库规范:全部小写,单词之间用下划线分割( _ )
java规范: 属性使用小驼峰来表示
注意:我们创建表和实体类中,要把数据库字段和java属性一一对应起来
2.2、配置数据库连接字符串
在 application.yml 配置文件中配置如下:
2.3、入门操作
mybatis 采用 “ 接口+xml/注解 ” 的方式实现数据访问层,实现了接口与实现的分离,其核心机制为:在运行时为接口生成动态代理对象,即自动创建它的实现类,能够轻松创建mock实现进行单元测试
mybatis 在运行时通过 动态代理(dynamic proxy) 机制自动生成了接口的实现类
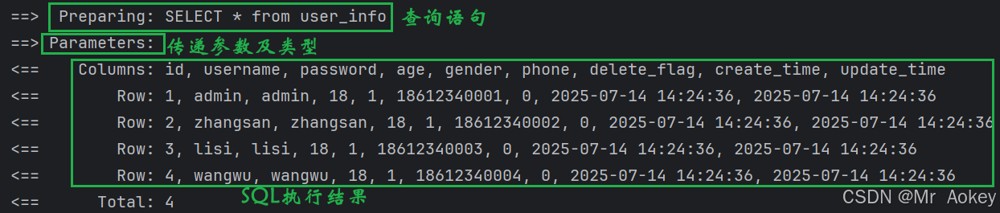
我们接下来查询所有用户
@mapper
public interface userinfomapper {
@select("select * from user_info")
list<userinfo> selectall();
}@mapper注解:标识该接口为 mybatis 的 mapper 接口
• 运行时框架会自动生成接口代理对象,并交由 spring ioc 容器管理
• @select 注解:用于标记查询方法,定义对应 sql 查询语句
2.4、单元测试
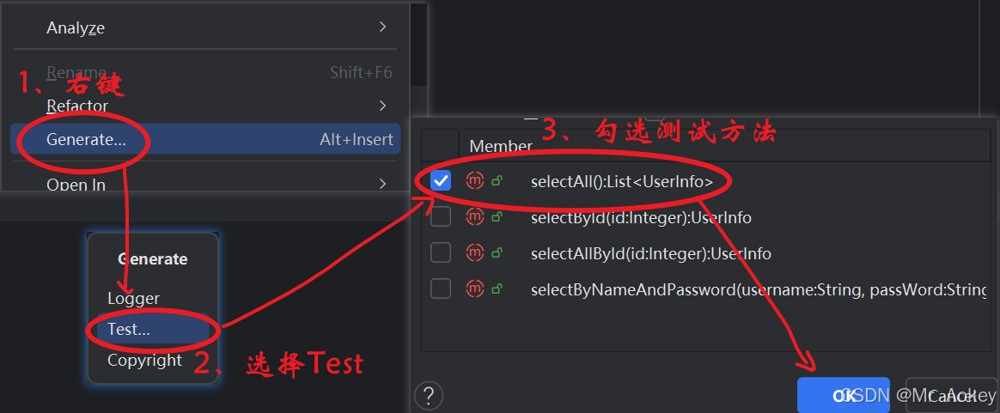
测试类已在 src/test 目录下自动生成,可直接用于测试
@springboottest
class userinfomappertest {
@autowired
private userinfomapper userinfomapper;
@test
void selectall() {
list<userinfo> userinfos = userinfomapper.selectall();
system.out.println(userinfos);
}
}在该测试类上添加了 @springboottest 注解后,运行时将自动加载 spring 运行环境;方法加上@test 注解后,该方法即可单独运行;通过@autowired 注解注入待测试的类后,即可开始进行测试
运行结果:成功查询了所有用户的信息
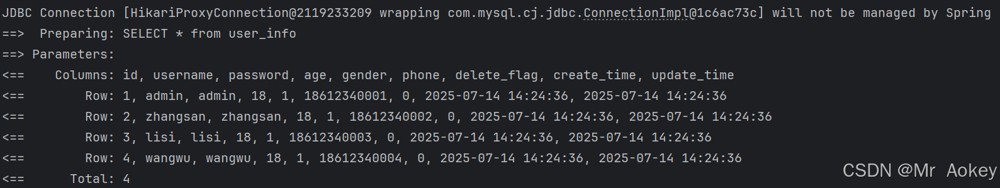
三、mybatis基础操作(增删改查)
3.1、配置日志
在mybatis中我们可以借助日志,查看sql语句的执行,传递的参数以及执行的结果,在application.yml 配置文件中配置(properties文件配置查阅前篇)
mybatis:
configuration: # 配置打印 mybatis⽇志
log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.stdoutimpl配置后可以看到

3.2、参数传递
查询 id 为 3 的用户
@mapper
public interface userinfomapper {
@select("select username,password,age,gender,phone from user_info where id = #{id}")
userinfo selectbyid(integer id);
}当 mapper 接口方法的形参仅有一个普通类型参数时,# {...} 中的属性名称可以任意指定,但是如果形参有多个普通类型的参数时,属性名称必须对应(见3.3例中代码)
生成测试用例:#{id}
@test
void selectbyid() {
userinfo userinfo = userinfomapper.selectbyid(3);
system.out.println(userinfo);
}查询结果:
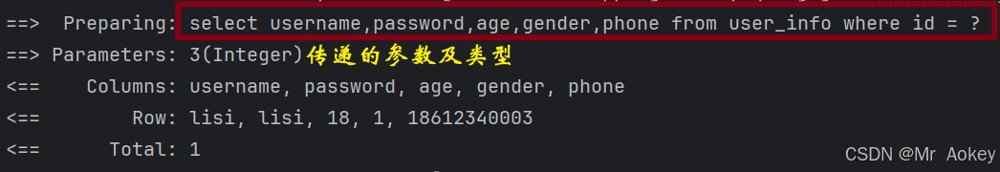
可通过@param 注解设置参数别名。若使用 @param 设置别名,#{...} 中的属性名必须与 @param 指定的别名保持一致
@select("select username,password,age,gender,phone from user_info where id = #{userid}")
userinfo selectbyid(@param("userid") integer id);
⚠️注意:
@select("select * from user_info")
list<userinfo> selectall();
@select("select username,password,age,gender,phone from user_info where id = #{userid}")
userinfo selectbyid(@param("userid") integer id);
@select("select username,password,age,gender,phone from user_info where age = #{age}")
list<userinfo> selectallbyage(integer age);
3.3、增(insert)
目标sql语句:

插入另一条数据,并将sql中的常量替换成动态的参数:
@insert("insert into user_info (username, password, age, gender, phone) values (#{username}, #{password}, #{age}, #{gender}, #{phone})")
integer insert(userinfo userinfo); @test
void insert() {
userinfo userinfo = new userinfo();
userinfo.setusername("楚子航");
userinfo.setpassword("123456");
userinfo.setgender(1);
userinfo.setage(19);
userinfo.setphone("122222222222");
int result=userinfomapper.insert(userinfo);
system.out.println("影响的行数"+result);
}在 mybatis 中,insert() 方法返回的结果和在mysql中返回的结果是一样的,都是返回影响的行数,观察测试结果:
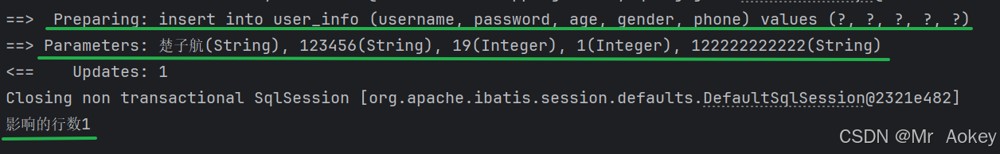
返回主键
我们想在插入之后,拿到刚刚插入的数据id
@options(usegeneratedkeys = true,keyproperty = "id")
@insert("insert into user_info (username, password, age, gender, phone) values (#{username}, #{password}, #{age}, #{gender}, #{phone})")
integer insert(userinfo userinfo); @test
void insert() {
userinfo userinfo = new userinfo();
userinfo.setusername("路鸣泽");
userinfo.setpassword("123456");
userinfo.setgender(1);
userinfo.setage(16);
userinfo.setphone("11111111111");
int result=userinfomapper.insert(userinfo);
system.out.println("影响的行数"+result+" id:"+userinfo.getid());
}• usegeneratedkeys:启用后,mybatis 将调用 jdbc 的 getgeneratedkeys 方法来获取数据库自动生成的主键(如 mysql 和 sql server 中的自增字段),默认值为 false
• keyproperty:指定用于标识对象的唯一属性,mybatis 会通过 getgeneratedkeys 的返回值或 insert 语句的 selectkey 子元素为其赋值
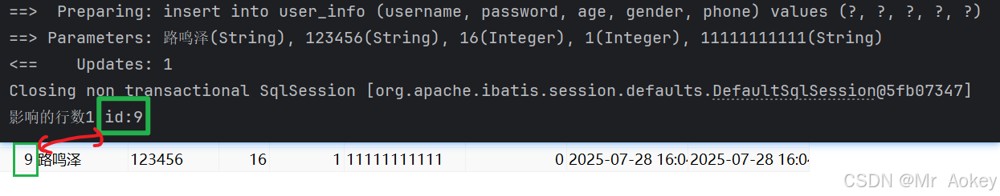
注意:
设置 usegeneratedkeys=true 后,方法返回值仍是受影响的行数,自增 id 会被自动赋给 keyproperty 指定的属性
3.4、删(delete)
 将上述
将上述
sql中的常量替换为动态参数
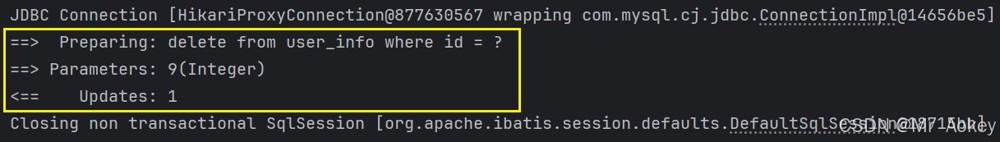
@delete("delete from user_info where id = #{id}")
void deletebyid(integer id); @test
void deletebyid() {
userinfomapper.deletebyid(9);
}观察运行结果发现id为 9 的数据已被删除
3.5、改(update)

将上述sql中的常量替换为动态参数
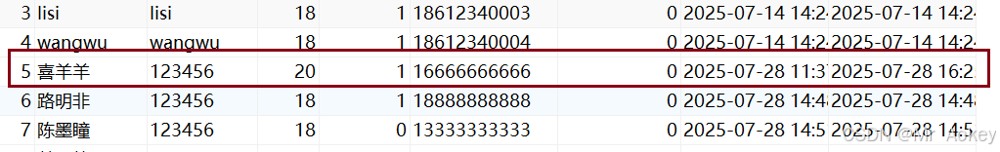
@update("update user_info set username = #{username} where id = #{id}")
void updatebyid(userinfo userinfo); @test
void updatebyid() {
userinfo userinfo = new userinfo();
userinfo.setid(5);
userinfo.setusername("喜羊羊");
userinfomapper.updatebyid(userinfo);
}观察运行结果发现id为 5 的数据名称已经更改为喜羊羊了
3.6、查(select)
我们再次查询所有信息
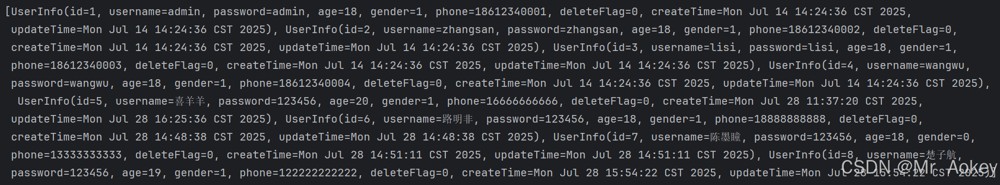
@select("select id,username,password,age,gender,phone,delete_flag,create_time,update_time from user_info")
list<userinfo> selectbyid(); @test
void selectbyid() {
list<userinfo> userinfolist = userinfomapper.selectbyid();
system.out.println(userinfolist);
}从运行结果可以看出,sql语句中查询了 delete_flag、create_time 和 update_time 字段,但这些字段并未被赋值
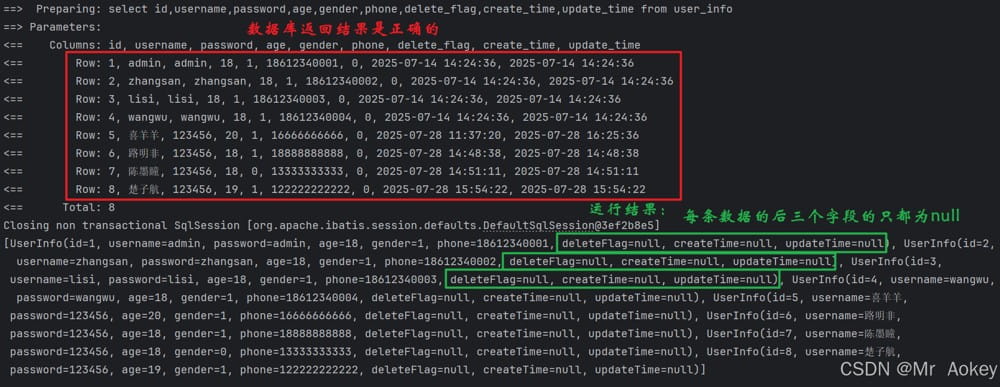
为什么呢? 这时我们会想到是不是 java 属性和数据库字段对应的名称不一致造成的原因呢?
@select("select id,username,password,age,gender,phone," +
"delete_flag as deleteflag,create_time as createtime,update_time as updatetime " +
"from user_info")
list<userinfo> selectbyid();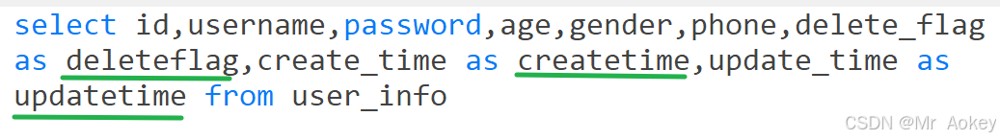
运行结果:
mybatis在自动映射查询结果时,会按以下步骤处理:
- 获取查询结果返回的列名
- 在目标java类中查找名称匹配的属性(不区分大小写)
- 当列名与属性名匹配时(例如数据库列"id"对应java属性"id"),自动将列值映射到对应属性
解决方法
3.6.1、起别名
如上猜测,将数据库字段名称通过起别名的方法与java属性名称保持一致,另外我们从下方代码可见sql语句可以用 + 连接
@select("select id,username,password,age,gender,phone," +
"delete_flag as deleteflag,create_time as createtime,update_time as updatetime " +
"from user_info")
list<userinfo> selectbyid();3.6.2、结果映射
@results 注解用于建立数据库字段与 java 对象属性之间的映射关系,它包含一个由 @result 元素组成的数组,其中每个元素通过 column 指定数据库列名,property 指定对应的 java 属性名,从而实现二者之间的映射关联
@results({
@result(column = "delete_flag",property = "deleteflag"),
@result(column = "create_time",property = "createtime"),
@result(column = "update_time",property = "updatetime")
})
@select("select id,username,password,age,gender,phone,delete_flag,create_time,update_time from user_info")
list<userinfo> selectresult();现在的问题是:我们上述代码实现了众多增删改查方法,每个方法进行结果映射都需要字段复制操作,如果其他方法涉及不同的数据库字段,来回修改会非常不便。在aokey看来,这并不比使用别名便利
针对这种情况,我们可以通过 id 属性为 results 定义别名,然后使用 @resultmap 注解来复用其他已经定义的 resultmap 配置
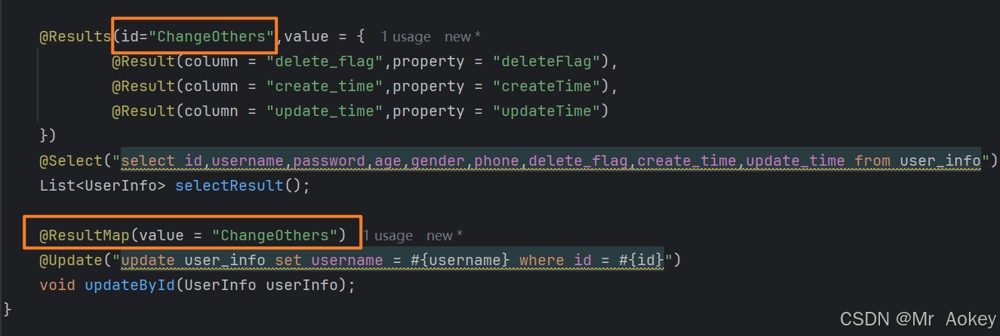
3.6.3、 配置驼峰自动转换
在 application.yml 配置文件中配置如下:
mybatis:
configuration:
map-underscore-to-camel-case: true #配置驼峰⾃动转换 @select("select id,username,password,age,gender,phone,delete_flag,create_time,update_time from user_info where age = #{age}")
list<userinfo> selectallbyage(integer age);查询结果:

到此这篇关于破茧 jdbc:mybatis 在 spring boot 中的轻量实践指南的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关mybatis springboot使用内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!




发表评论