arrays.fill()相关用法
int arr[] = new int[5];
//所有元素赋值为5
arrays.fill(arr,5);
//从索引[1,3)赋值为1
arrays.fill(arr,1,3,1);
//从索引[2,4)赋值为2
arrays.fill(arr,2,4,2);arrays.tostring()
//将数组元素放入字符串中,可以方便快速打印数组元素
//底层实现
//使用stringbuilder拼接字符串
stringbuilder b = new stringbuilder();
//在开头加[
b.append('[');
//遍历数组拼接元素
for (int i = 0; ; i++) {
b.append(string.valueof(a[i]));
if (i == imax)
//末尾拼接]并转为string类型
return b.append(']').tostring();
b.append(", ");
}arrays.sort()
//排序,默认为升序排序
//[3, 3, 5, 2, 2]
arrays.sort(arr2);
//打印结果:[2, 2, 3, 3, 5]
system.out.println(arrays.tostring(arr2));
//倒序排序,collections.reverseorder()返回一个比较器
arrays.sort(arr2, collections.reverseorder());arrays.equals()
//比较两个数组中元素是否相等
//相同:true,不同:false
system.out.println(arrays.equals(arr1,arr2));arrays.binarysearch()
//二分查找元素是否存在数组
int arr4[] = {1,3,3,3,3};
//返回二分查找第一次匹配到元素的索引值,不保证返回的是第一个出现的位置,如果不存在则返回实际插入索引+1的负数
//2
system.out.println(arrays.binarysearch(arr4,3));
//-6
system.out.println(arrays.binarysearch(arr4,10));
//数组区间查找,[0,3),返回第一次命中的下表
system.out.println(arrays.binarysearch(arr4,0,3,3));arrays.copyof()和arrays.copyofrange()
int arr5[] = {1,2,3,4,5};
//拷贝前三个元素[1,2,3]
int[] arr6 = arrays.copyof(arr5, 3);
//拷贝下标[2,5):[3,4,5]
int[] arr7 = arrays.copyofrange(arr5, 2, 5);
//若超过arr5长度,后面元素补0:[3,4,5,0,0...]
copyofrange(arr5, 2, 9);arrays.aslist()
//将对象数组转为list集合,不能是基本类型的数组
integer arr8[] = {1,2,3,4,5};
list<integer> list = arrays.aslist(arr8);collections.addall()
list<integer> list = new arraylist<>(); //向集合中一次添加多个元素 collections.addall(list,2,4,3,23,43);
collections.sort()
//根据类型中实现的comparable接口的compareto()方法排序,或第二个参数放入自定义的比较器 collections.sort(list);
collections.binarysearch()
//二分查找,获取指定元素的索引,若未查找到,返回应插入的元素位置的负数-(索引+1)
int idx = collections.binarysearch(list, 3);
system.out.println("key 下标为:"+ idx);collections.shuffle()
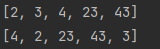
collections.addall(list,2,4,3,23,43);
collections.sort(list);
system.out.println(list);
//打乱顺序
collections.shuffle(list);
system.out.println(list);结果:
collections.reverse()
//翻转元素顺序
collections.reverse(list);
system.out.println(list);collections.min() & collections.max()
//根据元素类型实现的comparable接口中的compareto()方法比较获取最大值和最小值
int max = collections.max(list);
system.out.println("最大值:" + max);
int min = collections.min(list);
system.out.println("最小值:" + min);collections.fill()
//集合中所有元素设置为0 collections.fill(list, 0);
collections.swap()
//交换集合中两个索引的元素 collections.swap(list, 0, 2);
collections.copy()
//拷贝一个集合到另一个集合中
list<integer> list2 = new arraylist<>();
list<integer> list3 = new arraylist<>();
//将list3拷贝到list2中,list3的长度必须小于等于list2
collections.addall(list3,1,2,3,4,5);
collections.addall(list2,0,0,0,0,0);
collections.copy(list2,list3);
system.out.println(list2);collections.replaceall()
//集合中所有元素为2的值替换为100
system.out.println(list2);
collections.replaceall(list2,2,100);到此这篇关于java中arrays类和collections类常用方法的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关java arrays类和collections类内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!




发表评论