前言
细心的朋友们可能已经发现了,先在抖音、知乎、快手、小红书等这些平台已经上线了“网络用户显示 ip 的功能”,境外用户显示的是国家,国内的用户显示的省份,而且此项显示无法关闭,归属地强制显示。
作为一个努力搬砖的码农,我们肯定要来看一下这个功能是如何实现的,今天这篇文章,就来讲述一下这个功能是怎么实现的。
一、获取访问的ip地址
httpservletrequest 获取 ip
首先我们来看一下,在 java 中,是如何获取到 ip 属地的,主要有以下两步:
通过 httpservletrequest 对象,获取用户的 【ip】 地址
通过 ip 地址,获取对应的【省份、城市】
我这里写一个工具类用于获取 ip 地址,因为用户的每次 request 请求都会携带请求的 ip 地址放到请求头中,所以我们可以通过截取请求中的 ip 来获取 ip 地址,代码如下:
package com.test.java.util;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.slf4j;
import org.springframework.http.httpheaders;
import org.springframework.http.server.reactive.serverhttprequest;
import javax.servlet.http.httpservletrequest;
import java.net.inetaddress;
import java.net.networkinterface;
import java.util.objects;
/**
* ip地址util
*/
@slf4j
public class ipaddressutil {
/**
* 获取请求的 ip 地址
*/
public static string getipaddress(httpservletrequest request) {
string ip = request.getheader("x-forwarded-for");
if (ip == null || ip.length() == 0 || "unknown".equalsignorecase(ip)) {
ip = request.getheader("proxy-client-ip");
}
if (ip == null || ip.length() == 0 || "unknown".equalsignorecase(ip)) {
ip = request.getheader("wl-proxy-client-ip");
}
if (ip == null || ip.length() == 0 || "unknown".equalsignorecase(ip)) {
ip = request.getremoteaddr();
if ("127.0.0.1".equals(ip)) {
// 根据网卡取本机配置的 ip
inetaddress inet = null;
try {
inet = inetaddress.getlocalhost();
} catch (exception e) {
e.printstacktrace();
log.error("获取ip地址异常,{}", e.getmessage());
}
if (inet != null) {
ip = inet.gethostaddress();
}
}
}
// 多个代理的情况,第一个ip为客户端真实ip,多个ip按照','分割
if (ip != null && ip.length() > 15) {
if (ip.indexof(",") > 0) {
ip = ip.substring(0, ip.indexof(","));
}
}
// 本机访问
if ("localhost".equalsignorecase(ip) || "127.0.0.1".equalsignorecase(ip) || "0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1".equalsignorecase(ip)) {
// 根据网卡取本机配置的ip
inetaddress inet;
try {
inet = inetaddress.getlocalhost();
ip = inet.gethostaddress();
} catch (exception e) {
e.printstacktrace();
log.error("获取本机ip地址异常,{}", e.getmessage());
}
}
// 如果查找不到 ip,可以返回 127.0.0.1,可以做一定的处理,但是这里不考虑
// if (ip == null) {
// return "127.0.0.1";
// }
return ip;
}
/**
* 获取ip地址
*/
public static string getipaddress(serverhttprequest request) {
httpheaders headers = request.getheaders();
string ipaddress = headers.getfirst("x-forwarded-for");
if (ipaddress == null || ipaddress.length() == 0 || "unknown".equalsignorecase(ipaddress)) {
ipaddress = headers.getfirst("proxy-client-ip");
}
if (ipaddress == null || ipaddress.length() == 0 || "unknown".equalsignorecase(ipaddress)) {
ipaddress = headers.getfirst("wl-proxy-client-ip");
}
if (ipaddress == null || ipaddress.length() == 0 || "unknown".equalsignorecase(ipaddress)) {
ipaddress = objects.requirenonnull(request.getremoteaddress()).getaddress().gethostaddress();
if ("127.0.0.1".equals(ipaddress) || "0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1".equals(ipaddress)) {
// 根据网卡取本机配置的ip
try {
inetaddress inet = inetaddress.getlocalhost();
ipaddress = inet.gethostaddress();
} catch (exception e) {
log.error("获取ip地址异常,{}", e.getmessage());
}
}
}
// 对于通过多个代理的情况,第一个ip为客户端真实ip,多个ip按照','分割
if (ipaddress != null && ipaddress.indexof(",") > 0) {
ipaddress = ipaddress.split(",")[0];
}
return ipaddress;
}
/**
* 获取mac地址
*/
public static string getmacipaddress() {
try {
inetaddress inetaddress = inetaddress.getlocalhost();
byte[] macaddressbytes = networkinterface.getbyinetaddress(inetaddress).gethardwareaddress();
// 将mac地址拼装成string
stringbuilder sb = new stringbuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < macaddressbytes.length; i++) {
if (i != 0) {
sb.append("-");
}
// mac[i] & 0xff 是为了把byte转化为正整数
string s = integer.tohexstring(macaddressbytes[i] & 0xff);
sb.append(s.length() == 1 ? 0 + s : s);
}
return sb.tostring().trim().touppercase();
} catch (exception e) {
log.error("mac获取ip地址异常,{}", e.getmessage());
}
return "";
}
}这里出现了三个名词:
- x-forwarded-for:一个 http 扩展头部,主要是为了让 web 服务器获取访问用户的真实 ip 地址。每个 ip 地址,每个值通过逗号+空格分开,最左边是最原始客户端的 ip 地址,中间如果有多层代理,每⼀层代理会将连接它的客户端 ip 追加在 x-forwarded-for 右边
- x-real-ip:一般只记录真实发出请求的客户端ip
- proxy-client-ip:这个一般是经过 apache http 服务器的请求才会有,用 apache http 做代理时一般会加上 proxy-client-ip 请求头
- wl-proxy-client-ip:也是通过 apache http 服务器,在 weblogic 插件加上的头
二、通过ip地址获取对应的归属地
通过第三方地址库 ip2region,获取ip归属地。
2.1 ip2region
ip2region 是一个 gthub 的开源项目,即 ip2region 开源项目。
github地址:https://github.com/lionsoul2014/ip2region
这个开源库目前已经更新到了 v2 的版本,现在的它是一个强大的离线ip地址定位库和ip定位数据管理框架,其达到了微秒级别的查询效率,还提供了众多主流编程语言的 xdb 数据生成和查询客户端实现,可以说是非常得好用
2.1.1 高达 99.9 % 的查询准确率
数据聚合了一些知名 ip 到地名查询提供商的数据,这些是他们官方的准确率,经测试着实比经典的纯真 ip 定位准确一些。
ip2region 的数据聚合自以下服务商的开放 api 或者数据(升级程序每秒请求次数 2 到 4 次),比例如下:
80%, 淘宝 ip 地址库, ip.taobao.com/
≈10%, geoip, geoip.com/
≈2%, 纯真 ip 库, www.cz88.net/
2.1.2 ip2region v2.0 特性
1.ip 数据管理框架
xdb 支持亿级别的 ip 数据段行数,默认的 region 信息都固定了格式:国家|区域|省份|城市|isp,缺省的地域信息默认是0。
只有中国的数据精确到了城市,其他国家有部分数据只能定位到国家,后前的选项全部是 0,已经包含了全部你能查到的大大小小的国家
生成的数据库文件 ip2region.db 只有几 mb,最小的版本只有 1.5mb,随着数据的详细度增加数据库的大小也慢慢增大,目前还没超过 8mb。
region 信息支持完全自定义,例如:你可以在 region 中追加特定业务需求的数据,例如:gps信息/国际统一地域信息编码/邮编等。也就是你完全可以使用 ip2region 来管理你自己的 ip 定位数据。
2.数据去重和压缩
xdb 格式生成程序会自动去重和压缩部分数据,默认的全部 ip 数据,生成的 ip2region.xdb 数据库是 11mib,随着数据的详细度增加数据库的大小也慢慢增大。
3.极速查询响应
即使是完全基于 xdb 文件的查询,单次查询响应时间在十微秒级别,可通过如下两种方式开启内存加速查询:
- vindex 索引缓存:使用固定的 512kib 的内存空间缓存 vector index 数据,减少一次 io 磁盘操作,保持平均查询效率稳定在10-20微秒之间
- xdb 整个文件缓存:将整个 xdb 文件全部加载到内存,内存占用等同于 xdb 文件大小,无磁盘 io 操作,保持微秒级别的查询效率。
4.内置的三种查询算法
全部的查询客户端单次查询都在 0.x 毫秒级别,内置了三种查询算法:
- memory 算法:整个数据库全部载入内存,单次查询都在0.1x毫秒内,c语言的客户端单次查询在0.00x毫秒级别。
- binary 算法:基于二分查找,基于ip2region.db文件,不需要载入内存,单次查询在0.x毫秒级别。
- b-tree 算法:基于btree算法,基于ip2region.db文件,不需要载入内存,单词查询在0.x毫秒级别,比binary算法更快。
2.1.3 多语言以及查询客户端的支持
已经有的客户端:java、c#、php、c、python、node.js、php 拓展(php 5 和 php 7)等,主要如下:
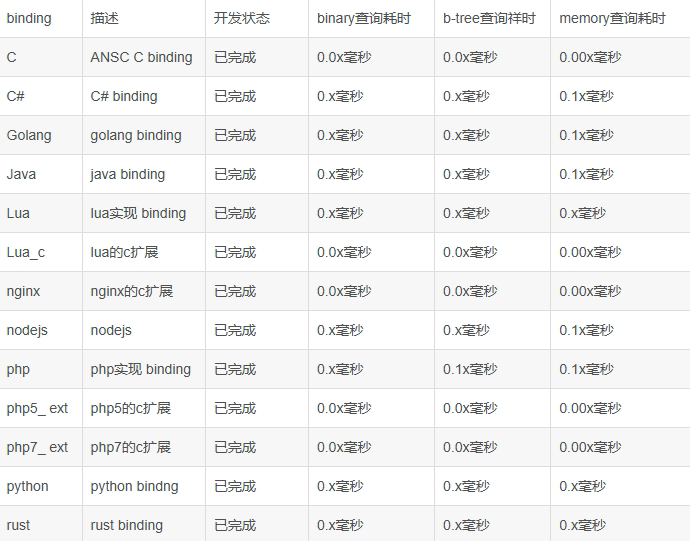
2.2 ip2region xdb java 查询客户端实现
这里简单展示一下 java 的实现,这里使用开发中常用的 maven 实现的方式:
2.2.1 引入 maven 仓库
<!-- ip地址转归属地 --> <dependency> <groupid>org.lionsoul</groupid> <artifactid>ip2region</artifactid> <version>2.6.4</version> </dependency>
2.2.2 ip2region.xdb 文件,放到工程resources目录下
2.2.3 实现方式
基于文件查询
import lombok.extern.slf4j.slf4j;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.stringutils;
import org.lionsoul.ip2region.xdb.searcher;
import java.util.concurrent.timeunit;
/**
* ip地址util
*/
@slf4j
public class ipaddressutil {
// ip2region.xdb 文件地址常量(本地xdb文件路径)
public static string xdb_path = "d:\\idea2022.2.3\\workspace\\java\\src\\main\\resources\\ip\\ip2region.xdb";
/**
* 完全基于ip2region.xdb文件,对用户ip地址进行转换
* 注:并发调用时,每个线程需创建一个独立的searcher对象 单独使用。
*/
public static string getippossessionbyfile(string ip) {
if (stringutils.isnotempty(ip)) {
try {
// 1、创建 searcher 对象
searcher searcher = searcher.newwithfileonly(xdb_path);
// 2、查询
long stime = system.nanotime();
string region = searcher.search(ip);
long cost = timeunit.nanoseconds.tomicros(system.nanotime() - stime);
region = region.replace("|0", "");
log.info("{地区: {}, io操作数: {}, 耗时: {} μs}", region, searcher.getiocount(), cost);
return region;
} catch (exception e) {
log.error("获取ip地址异常:{} ", e.getmessage());
throw new runtimeexception("获取ip地址异常");
}
}
return "未知";
}
}缓存vectorindex索引
我们可以提前从 xdb 文件中加载出来 vectorindex 数据,然后全局缓存,每次创建 searcher 对象的时候使用全局的 vectorindex 缓存可以减少一次固定的 io 操作,从而加速查询,减少 io 压力。
import lombok.extern.slf4j.slf4j;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.stringutils;
import org.lionsoul.ip2region.xdb.searcher;
import java.util.concurrent.timeunit;
/**
* ip地址util
*/
@slf4j
public class ipaddressutil {
// ip2region.xdb 文件地址常量(本地xdb文件路径)
public static string xdb_path = "d:\\idea2022.2.3\\workspace\\java\\src\\main\\resources\\ip\\ip2region.xdb";
/**
* 缓存 vectorindex 索引,对用户ip地址进行转换
* 注:每个线程需要单独创建一个独立的 searcher 对象,但是都共享全局变量 vindex 缓存。
*/
public static string getcityinfobyvectorindex(string ip) {
if (stringutils.isnotempty(ip)) {
try {
// 1、从 xdb_path 中预先加载 vectorindex 缓存,并且作为全局变量,后续反复使用。
byte[] vindex = searcher.loadvectorindexfromfile(xdb_path);
// 2、使用全局的 vindex 创建带 vectorindex 缓存的查询对象。
searcher searcher = searcher.newwithvectorindex(xdb_path, vindex);
// 3、查询
long stime = system.nanotime();
string region = searcher.search(ip);
long cost = timeunit.nanoseconds.tomicros(system.nanotime() - stime);
region = region.replace("|0", "");
log.info("{地区: {}, io操作数: {}, 耗时: {} μs}", region, searcher.getiocount(), cost);
return region;
} catch (exception e) {
log.error("获取ip地址异常:{} ", e.getmessage());
throw new runtimeexception("获取ip地址异常");
}
}
return "未知";
}
}缓存整个 xdb 数据
我们也可以预先加载整个 ip2region.xdb 的数据到内存,然后基于这个数据创建查询对象来实现完全基于文件的查询,类似之前的 memory search。
import lombok.extern.slf4j.slf4j;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.stringutils;
import org.lionsoul.ip2region.xdb.searcher;
import java.util.concurrent.timeunit;
/**
* ip地址util
*/
@slf4j
public class ipaddressutil {
// ip2region.xdb 文件地址常量
public static string xdb_path = "d:\\java\\src\\main\\resources\\ip\\ip2region.xdb";
/**
* 缓存整个 xdb 数据,对用户ip地址进行转换
* 注:并发使用时,用整个 xdb 数据缓存创建的查询对象可以安全的用于并发,也就是你可以把这个 searcher 对象做成全局对象去跨线程访问。
*/
public static string getcityinfobymemorysearch(string ip) {
if (stringutils.isnotempty(ip)) {
try {
// 1、从 xdb_path 加载整个 xdb 到内存。
byte[] cbuff = searcher.loadcontentfromfile(xdb_path);
// 2、使用上述的 cbuff 创建一个完全基于内存的查询对象。
searcher searcher = searcher.newwithbuffer(cbuff);
// 3、查询
long stime = system.nanotime();
string region = searcher.search(ip);
long cost = timeunit.nanoseconds.tomicros(system.nanotime() - stime);
region = region.replace("|0", "");
log.info("{地区: {}, io操作数: {}, 耗时: {} μs}", region, searcher.getiocount(), cost);
return region;
} catch (exception e) {
log.error("获取ip地址异常:{} ", e.getmessage());
throw new runtimeexception("获取ip地址异常");
}
}
return "未知";
}
}通过第三方api查询(在线查询)
前面介绍的3种方法都是离线查询,该方法主要通过第三方提供的官网或api接口去实现在线查询的功能,但有个弊端就是特别依赖对方的服务器,一旦对方的服务器宕机就无法访问了。具体实现效果跟之前介绍的离线查询方法是一样的。
import com.google.gson.gson;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.slf4j;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.stringutils;
import java.io.bufferedreader;
import java.io.inputstream;
import java.io.inputstreamreader;
import java.net.httpurlconnection;
import java.net.url;
import java.nio.charset.standardcharsets;
import java.util.hashmap;
import java.util.map;
/**
* ip地址util
*/
@slf4j
public class ipaddressutil {
/**
* 在线查询ip归属地
*/
public static string getipaddressbyonline(string ip) {
try {
//1、创建 urlconnction
url url = new url("http://ip-api.com/json/" + ip + "?lang=zh-cn");
//2、设置connection的属性
httpurlconnection connection = (httpurlconnection) url.openconnection();
connection.setrequestmethod("get");
connection.setconnecttimeout(20000);
connection.setreadtimeout(20000);
connection.setrequestproperty("content-type", "application/json; charset=utf-8");
//3.连接
connection.connect();
//4.获取内容
inputstream inputstream = connection.getinputstream();
bufferedreader br = new bufferedreader(new inputstreamreader(inputstream, standardcharsets.utf_8));
string line;
stringbuilder sb = new stringbuilder();
while ((line = br.readline()) != null) {
sb.append(line);
}
br.close();
//system.out.println(sb);
string str = sb.tostring();
if (stringutils.isnotempty(str)) {
// string转map
gson gson = new gson();
map<string, object> map = new hashmap<>();
map = gson.fromjson(str, map.getclass());
string country = (string) map.get("country");
string city = (string) map.get("city");
string regionname = (string) map.get("regionname");
system.out.println("国家:" + country);
system.out.println("城市:" + city);
system.out.println("地区:" + regionname);
return country + "|" + city + "|" + regionname;
}
} catch (exception e) {
log.error("在线查询ip地址异常,{}", e.getmessage());
throw new runtimeexception(e.getmessage());
}
return null;
}
}最优方案
其实我推荐可以将方法结合使用。先采用离线查询,如果发现地址为null的话,则调用在线查询方法。这样在一定的程度上能够保证数据的完整性。完整的工具类如下:
import com.google.gson.gson;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.slf4j;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.stringutils;
import org.lionsoul.ip2region.xdb.searcher;
import javax.servlet.http.httpservletrequest;
import java.io.bufferedreader;
import java.io.inputstream;
import java.io.inputstreamreader;
import java.net.httpurlconnection;
import java.net.inetaddress;
import java.net.networkinterface;
import java.net.url;
import java.nio.charset.standardcharsets;
import java.util.hashmap;
import java.util.map;
import java.util.concurrent.timeunit;
/**
* ip地址util
*/
@slf4j
public class ipaddressutil {
// ip2region.xdb 文件地址常量(本地xdb文件路径)
public static string xdb_path = "d:\\idea2022.2.3\\workspace\\java\\src\\main\\resources\\ip\\ip2region.xdb";
/**
* 获取ip地址:
*/
public static string getipaddress(httpservletrequest request) {
string ipaddress = null;
try {
ipaddress = request.getheader("x-forwarded-for");
if (ipaddress != null && ipaddress.length() != 0 && !"unknown".equalsignorecase(ipaddress)) {
// 多次反向代理后会有多个ip值,第一个ip才是真实ip
if (ipaddress.contains(",")) {
ipaddress = ipaddress.split(",")[0];
}
}
if (ipaddress == null || ipaddress.length() == 0 || "unknown".equalsignorecase(ipaddress)) {
ipaddress = request.getheader("proxy-client-ip");
}
if (ipaddress == null || ipaddress.length() == 0 || "unknown".equalsignorecase(ipaddress)) {
ipaddress = request.getheader("wl-proxy-client-ip");
}
if (ipaddress == null || ipaddress.length() == 0 || "unknown".equalsignorecase(ipaddress)) {
ipaddress = request.getheader("http_client_ip");
}
if (ipaddress == null || ipaddress.length() == 0 || "unknown".equalsignorecase(ipaddress)) {
ipaddress = request.getremoteaddr();
}
} catch (exception e) {
log.error("获取ip地址异常,{}", e.getmessage());
}
return ipaddress;
}
/**
* 获取mac地址
*/
public static string getmacipaddress() {
try {
inetaddress inetaddress = inetaddress.getlocalhost();
byte[] macaddressbytes = networkinterface.getbyinetaddress(inetaddress).gethardwareaddress();
// 将mac地址拼装成string
stringbuilder sb = new stringbuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < macaddressbytes.length; i++) {
if (i != 0) {
sb.append("-");
}
// mac[i] & 0xff 是为了把byte转化为正整数
string s = integer.tohexstring(macaddressbytes[i] & 0xff);
sb.append(s.length() == 1 ? 0 + s : s);
}
return sb.tostring().trim().touppercase();
} catch (exception e) {
log.error("mac获取ip地址异常,{}", e.getmessage());
}
return "";
}
/**
* 方法一:完全基于ip2region.xdb文件,对用户ip地址进行转换
* 注:并发调用时,每个线程需创建一个独立的searcher对象 单独使用。
*/
public static string getippossessionbyfile(string ip) {
if (stringutils.isnotempty(ip)) {
try {
// 1、创建 searcher 对象
searcher searcher = searcher.newwithfileonly(xdb_path);
// 2、查询
long stime = system.nanotime();
string region = searcher.search(ip);
long cost = timeunit.nanoseconds.tomicros(system.nanotime() - stime);
region = region.replace("|0", "");
//log.info("{地区: {}, io操作数: {}, 耗时: {} μs}", region, searcher.getiocount(), cost);
return region;
} catch (exception e) {
log.error("获取ip地址异常:{} ", e.getmessage());
throw new runtimeexception("获取ip地址异常");
}
}
return "未知";
}
/**
* 方法二:缓存 vectorindex 索引,对用户ip地址进行转换
* 注:每个线程需要单独创建一个独立的 searcher 对象,但是都共享全局变量 vindex 缓存。
*/
public static string getcityinfobyvectorindex(string ip) {
if (stringutils.isnotempty(ip)) {
try {
// 1、从 xdb_path 中预先加载 vectorindex 缓存,并且作为全局变量,后续反复使用。
byte[] vindex = searcher.loadvectorindexfromfile(xdb_path);
// 2、使用全局的 vindex 创建带 vectorindex 缓存的查询对象。
searcher searcher = searcher.newwithvectorindex(xdb_path, vindex);
// 3、查询
long stime = system.nanotime();
string region = searcher.search(ip);
long cost = timeunit.nanoseconds.tomicros(system.nanotime() - stime);
region = region.replace("|0", "");
//log.info("{地区: {}, io操作数: {}, 耗时: {} μs}", region, searcher.getiocount(), cost);
return region;
} catch (exception e) {
log.error("获取ip地址异常:{} ", e.getmessage());
throw new runtimeexception("获取ip地址异常");
}
}
return "未知";
}
/**
* 方法三:缓存整个 xdb 数据,对用户ip地址进行转换
* 注:并发使用时,用整个 xdb 数据缓存创建的查询对象可以安全的用于并发,也就是你可以把这个 searcher 对象做成全局对象去跨线程访问。
*/
public static string getcityinfobymemorysearch(string ip) {
if (stringutils.isnotempty(ip)) {
try {
// 1、从 xdb_path 加载整个 xdb 到内存。
byte[] cbuff = searcher.loadcontentfromfile(xdb_path);
// 2、使用上述的 cbuff 创建一个完全基于内存的查询对象。
searcher searcher = searcher.newwithbuffer(cbuff);
// 3、查询
long stime = system.nanotime();
string region = searcher.search(ip);
long cost = timeunit.nanoseconds.tomicros(system.nanotime() - stime);
region = region.replace("|0", "");
//log.info("{地区: {}, io操作数: {}, 耗时: {} μs}", region, searcher.getiocount(), cost);
return region;
} catch (exception e) {
log.error("获取ip地址异常:{} ", e.getmessage());
throw new runtimeexception("获取ip地址异常");
}
}
return "未知";
}
/**
* 方法四:在线获取ip地址
* 注:通过别人或者官网提供的api接口去实现查询的功能,弊端就是特别依赖别人的服务器,一旦服务器宕机就无法访问了。
*/
public static string getipaddressbyonline(string ip) {
try {
//1、创建 urlconnction
url url = new url("http://ip-api.com/json/" + ip + "?lang=zh-cn");
//2、设置connection的属性
httpurlconnection connection = (httpurlconnection) url.openconnection();
connection.setrequestmethod("get");
connection.setconnecttimeout(20000);
connection.setreadtimeout(20000);
connection.setrequestproperty("content-type", "application/json; charset=utf-8");
//3.连接
connection.connect();
//4.获取内容
inputstream inputstream = connection.getinputstream();
bufferedreader br = new bufferedreader(new inputstreamreader(inputstream, standardcharsets.utf_8));
string line;
stringbuilder sb = new stringbuilder();
while ((line = br.readline()) != null) {
sb.append(line);
}
br.close();
//system.out.println(sb);
string str = sb.tostring();
if (stringutils.isnotempty(str)) {
// string转map
gson gson = new gson();
map<string, object> map = new hashmap<>();
map = gson.fromjson(str, map.getclass());
string country = (string) map.get("country");
string city = (string) map.get("city");
string regionname = (string) map.get("regionname");
//log.info("【国家】{},【城市】{},【地区】{}", country, city, regionname);
return country + "|" + city + "|" + regionname;
}
} catch (exception e) {
log.error("在线查询ip地址异常,{}", e.getmessage());
throw new runtimeexception("在线查询ip地址异常");
}
return null;
}
/**
* 根据ip地址 获取归属地
*/
public static string getippossession(string ipaddress) {
if (stringutils.isnotempty(ipaddress)) {
ipaddress = ipaddress.replace("|", " ");
string[] citylist = ipaddress.split(" ");
if (citylist.length > 0) {
// 国内的显示到具体的省
if ("中国".equals(citylist[0])) {
if (citylist.length > 1) {
return citylist[1];
}
}
// 国外显示到国家
return citylist[0];
}
}
return "未知";
}
public static void main(string[] args) {
string ip = "183.162.252.0";// 国内ip
string abroadip = "48.119.248.100"; // 国外ip
system.out.println("方法一(国内):" + getippossessionbyfile(ip));
system.out.println("方法二(国内):" + getcityinfobyvectorindex(ip));
system.out.println("方法三(国内):" + getcityinfobymemorysearch(ip));
system.out.println("方法四(国内):" + getipaddressbyonline(ip));
system.out.println("方法一(国外):" + getippossessionbyfile(abroadip));
system.out.println("方法二(国外):" + getcityinfobyvectorindex(abroadip));
system.out.println("方法三(国外):" + getcityinfobymemorysearch(abroadip));
system.out.println("方法四(国外):" + getipaddressbyonline(abroadip));
//system.out.println("归属地(国内):" + getippossession(getcityinfobyvectorindex(ip)));
//system.out.println("归属地(国外):" + getippossession(getcityinfobyvectorindex(abroadip)));
}
}以上就是java获取ip地址及对应的归属地的方法详解的详细内容,更多关于java获取ip地址和归属地的资料请关注代码网其它相关文章!





发表评论