本文介绍bio,nio,aio 及如何使用spring boot集成netty,实现后台向前端推送信息的功能。利用spring boot简化netty的集成和配置。
1.bio,nio,aio
bio、nio和aio是java编程语言中用于处理输入输出(io)操作的三种不同的机制,它们分别代表 同步阻塞i/o,同步非阻塞i/o 和 异步非阻塞i/o。
1.1 bio
bio(blocking io) 是最传统的io模型,也称为同步阻塞io。它实现的是同步阻塞模型,即服务器实现模式为一个连接一个线程,即客户端有连接请求时服务器端就需要启动一个线程进行处理。如果这个连接不做任何事情会造成不必要的线程开销,并且线程在进行io操作期间是被阻塞的,无法进行其他任务。在高并发环境下,bio的性能较差,因为它需要为每个连接创建一个线程,而且线程切换开销较大,不过可以通过线程池机制改善。bio适合一些简单的、低频的、短连接的通信场景,例如http请求。
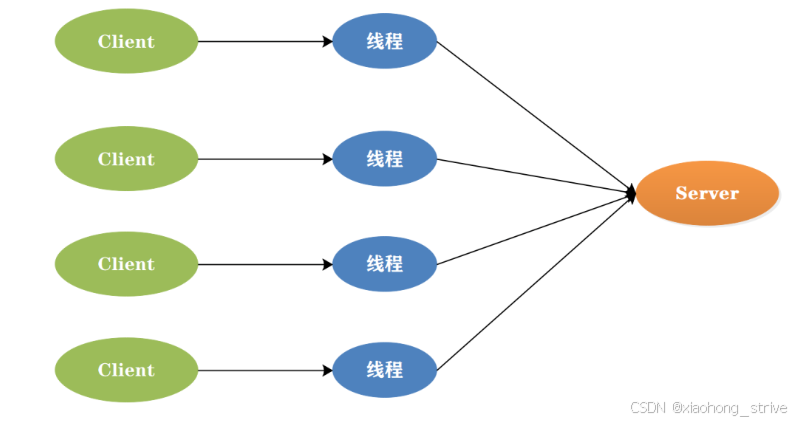
1.2 nio
nio是java 1.4引入的新io模型,也称为同步非阻塞io,它提供了一种基于事件驱动的方式来处理i/o操作。
相比于传统的bio模型,nio采用了channel、buffer和selector等组件,线程可以对某个io事件进行监听,并继续执行其他任务,不需要阻塞等待。当io事件就绪时,线程会得到通知,然后可以进行相应的操作,实现了非阻塞式的高伸缩性网络通信。在nio模型中,数据总是从channel读入buffer,或者从buffer写入channel,这种模式提高了io效率,并且可以充分利用系统资源。
nio主要由三部分组成:选择器(selector)、缓冲区(buffer)和通道(channel)。channel是一个可以进行数据读写的对象,所有的数据都通过buffer来处理,这种方式避免了直接将字节写入通道中,而是将数据写入包含一个或者多个字节的缓冲区。在多线程模式下,一个线程可以处理多个请求,这是通过将客户端的连接请求注册到多路复用器上,然后由多路复用器轮询到连接有i/o请求时进行处理。
对于nio,如果从特性来看,它是非阻塞式io,n是non-blocking的意思;如果从技术角度,nio对于bio来说是一个新技术,n的意思是new的意思。所以nio也常常被称作non-blocking i/o或new i/o。
nio适用于连接数目多且连接比较短(轻操作)的架构,例如聊天服务器、弹幕系统、服务器间通讯等。它通过引入非阻塞通道的概念,提高了系统的伸缩性和并发性能。同时,nio的使用也简化了程序编写,提高了开发效率。
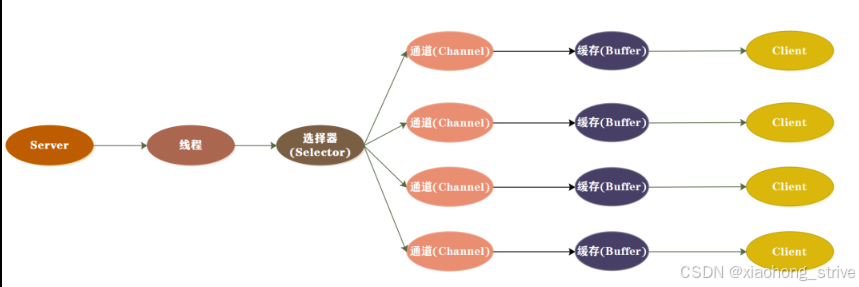
1.3 aio
java aio(asynchronous i/o)是java提供的异步非阻塞io编程模型,从java 7版本开始支持,aio又称nio 2.0。
相比于nio模型,aio模型更进一步地实现了异步非阻塞io,提高了系统的并发性能和伸缩性。在nio模型中,虽然可以通过多路复用器处理多个连接请求,但仍需要在每个连接上进行读写操作,这仍然存在一定的阻塞。而在aio模型中,所有的io操作都是异步的,不会阻塞任何线程,可以更好地利用系统资源。
aio模型有以下特性:
- 异步能力:aio模型的最大特性是异步能力,对于socket和i/o操作都有效。读写操作都是异步的,完成后会自动调用回调函数。
- 回调函数:在aio模型中,当一个异步操作完成后,会通知相关线程进行后续处理,这种处理方式称为“回调”。回调函数可以由开发者自行定义,用于处理异步操作的结果。
- 非阻塞:aio模型实现了完全的异步非阻塞io,不会阻塞任何线程,可以更好地利用系统资源。
- 高性能:由于aio模型的异步能力和非阻塞特性,它可以更好地处理高并发、高伸缩性的网络通信场景,进一步提高系统的性能和效率。
- 操作系统支持:aio模型需要操作系统的支持,因此在不同的操作系统上可能会有不同的表现。在linux内核2.6版本之后增加了对真正异步io的实现
2 netty原理
2.1 netty原理
netty基于java nio(非阻塞io)实现,它采用事件驱动的编程模型,将io操作抽象为事件,通过事件处理器来处理这些事件。netty的主要组件包括:
- bootstrap:用于启动客户端和服务器的引导类
- channel:代表io操作的通道,用于网络读写操作
- channelhandler:用于处理io事件的事件处理器
- eventloopgroup:用于处理io操作的多线程事件循环组
3 spring boot集成netty和websocket
在spring boot应用程序中,我们可以通过集成netty,实现后台向前端推送信息的功能。首先,我们需要添加netty依赖,然后在spring boot应用程序中创建一个nettyserver类,用于初始化websocket通道。
1.引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupid>io.netty</groupid>
<artifactid>netty-all</artifactid>
<version>4.1.111.final</version>
</dependency>2.创建 nettyconfig 配置管理所有管道
import io.netty.channel.channel;
import io.netty.channel.group.channelgroup;
import io.netty.channel.group.defaultchannelgroup;
import io.netty.util.concurrent.globaleventexecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.concurrenthashmap;
@suppresswarnings("all")
public class nettyconfig {
/**
* 定义全局单例channel组 管理所有channel
*/
private static volatile channelgroup channelgroup = null;
/**
* 存放请求id与channel的对应关系
*/
private static volatile concurrenthashmap<string, channel> channelmap = null;
/**
* 定义两把锁
*/
private static final object lock1 = new object();
private static final object lock2 = new object();
public static channelgroup getchannelgroup() {
if (null == channelgroup) {
synchronized (lock1) {
if (null == channelgroup) {
channelgroup = new defaultchannelgroup(globaleventexecutor.instance);
}
}
}
return channelgroup;
}
public static concurrenthashmap<string, channel> getchannelmap() {
if (null == channelmap) {
synchronized (lock2) {
if (null == channelmap) {
channelmap = new concurrenthashmap<>();
}
}
}
return channelmap;
}
public static channel getchannel(string userid) {
if (null == channelmap) {
return getchannelmap().get(userid);
}
return channelmap.get(userid);
}
}3.创建mychannelhandlerpool 通道组池
import io.netty.channel.group.channelgroup;
import io.netty.channel.group.defaultchannelgroup;
import io.netty.util.concurrent.globaleventexecutor;
/**
* mychannelhandlerpool
* 通道组池,管理所有websocket连接
*/
public class mychannelhandlerpool {
private mychannelhandlerpool(){}
public static channelgroup channelgroup = new defaultchannelgroup(globaleventexecutor.instance);
}
4.创建nettyserver 初始化netty
import io.netty.bootstrap.serverbootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.*;
import io.netty.channel.nio.nioeventloopgroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.socketchannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.nioserversocketchannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.httpobjectaggregator;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.httpservercodec;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.websocketx.websocketserverprotocolhandler;
import io.netty.handler.stream.chunkedwritehandler;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.slf4j;
import org.springframework.stereotype.component;
/**
* nettyserver netty服务器配置
*/
@slf4j
@component
@suppresswarnings("all")
public class nettyserver {
private string url = "/admin/socket";
public nettyserver() {}
public void start() throws exception {
// 主事件组
eventloopgroup bossgroup = new nioeventloopgroup();
// 执行事件组
eventloopgroup group = new nioeventloopgroup();
try {
serverbootstrap serverbootstrap = new serverbootstrap();
serverbootstrap.option(channeloption.so_backlog, 1024);
int port = 12345;
serverbootstrap.group(group, bossgroup) // 绑定线程池
.channel(nioserversocketchannel.class) // 指定使用的channel
.localaddress(port)// 绑定监听端口
.childhandler(new channelinitializer<socketchannel>() { // 绑定客户端连接时候触发操作
@override
protected void initchannel(socketchannel ch) throws exception {
// 添加objectencoder和objectdecoder来处理对象的序列化和反序列化
log.info("收到新连接");
//websocket协议本身是基于http协议的,所以这边也要使用http解编码器
ch.pipeline().addlast(new httpservercodec());
//以块的方式来写的处理器
ch.pipeline().addlast(new chunkedwritehandler());
ch.pipeline().addlast(new httpobjectaggregator(8192));
ch.pipeline().addlast(new websockethandler());
ch.pipeline().addlast(new websocketserverprotocolhandler(url, null, true, 65536 * 10));
}
});
// 绑定端口并同步等待直到绑定完成
channelfuture future = serverbootstrap.bind().sync();
log.info(nettyserver.class.getname() + "启动正在监听: " + future.channel().localaddress());
// 等待服务器通道关闭
future.channel().closefuture().sync();
} finally {
// 释放线程池资源
group.shutdowngracefully().sync();
bossgroup.shutdowngracefully().sync();
}
}
}5. 创建 websockethandler 执行任务
@slf4j
@component
@suppresswarnings("all")
public class websockethandler extends simplechannelinboundhandler<textwebsocketframe> {
public static final string netty_start = "netty-start";
public websockethandler() {}
private scheduledfuture<?> senddatatask;
@autowired
private devicelevelfourservice devicelevelfourservice;
@override
public void channelactive(channelhandlercontext ctx) throws exception {
//添加到channelgroup通道组
mychannelhandlerpool.channelgroup.add(ctx.channel());
}
@override
public void channelinactive(channelhandlercontext ctx) throws exception {
log.info("与客户端断开连接,通道关闭!");
//添加到channelgroup 通道组
mychannelhandlerpool.channelgroup.remove(ctx.channel());
}
@override
public void channelread(channelhandlercontext ctx, object msg) throws exception {
// 首次连接是fullhttprequest,处理参数
if (msg instanceof fullhttprequest) {
fullhttprequest request = (fullhttprequest) msg;
string uri = request.uri();
map<string, string> parammap = geturlparams(uri);
log.info("接收到的参数是:" + json.tojsonstring(parammap));
// 如果url包含参数,需要处理
if (uri.contains("?")) {
string newuri = uri.substring(0, uri.indexof("?"));
log.info(newuri);
request.seturi(newuri);
}
// 当连接建立时,启动定时任务
senddatatask = ctx.channel().eventloop().scheduleatfixedrate(new runnable() {
@override
public void run() {
try {
if (devicelevelfourservice == null) {
devicelevelfourservice = springcontextutil.getbean(devicelevelfourserviceimpl.class);
}
// 此处可以接收路径参数 ,直接获取前端传递参数
// "ws://localhost:12345/admin/socket?id=1"
string deviceid = parammap.get("id");
/**
* -------此处为自己的数据---------
*/
// 调用service 得到前端需要的数据,用json工具类转换推送到前端
list<devicenettydata> devicenettydata = devicelevelfourservice.handlerdevicedata(long.parselong(deviceid));
string json = json.tojsonstring(devicenettydata, serializerfeature.writemapnullvalue);
log.info(json);
// 将 json 字符串封装为 textwebsocketframe
textwebsocketframe framenetty = new textwebsocketframe(json);
ctx.writeandflush(framenetty); // 发送 websocket 帧
} catch (exception e) {
log.error(e.getmessage(), e);
}
}
}, 0, 30, timeunit.seconds); // 立即开始,每30秒发送一次
// 调用父类方法,处理下一个handler
super.channelread(ctx, request);
} else if (msg instanceof textwebsocketframe frame) {
// 正常的text消息类型
sendallmessage(frame.text());
// 继续传递给后续handler
super.channelread(ctx, frame);
} else {
// 如果消息类型不匹配,记录警告或处理异常情况
log.error("未处理的消息类型:" + msg.getclass());
super.channelread(ctx, msg); // 仍然传递给后续处理
}
}
@override
protected void channelread0(channelhandlercontext channelhandlercontext, textwebsocketframe textwebsocketframe) throws exception {
log.info(channelhandlercontext.name());
}
//读取完成刷新
@override
public void channelreadcomplete(channelhandlercontext ctx) {
ctx.flush();
}
//异常则关闭channelhandlercontext连接
@override
public void exceptioncaught(channelhandlercontext ctx, throwable cause) {
// close the connection when an exception is raised.
cause.printstacktrace();
ctx.close();
}
private void sendallmessage(string message){
//收到信息后,群发给所有channel
mychannelhandlerpool.channelgroup.writeandflush( new textwebsocketframe(message));
}
private static map<string ,string> geturlparams(string url){
map<string,string> map = new hashmap<>();
url = url.replace("?",";");
if (!url.contains(";")){
return map;
}
if (url.split(";").length > 0){
string[] arr = url.split(";")[1].split("&");
for (string s : arr){
string key = s.split("=")[0];
string value = s.split("=")[1];
map.put(key,value);
}
return map;
}else{
return map;
}
}
}6.创建nettyserverrunner 用来使用新线程调用netterserver
@slf4j
public class nettyserverrunner implements runnable {
@override
public void run() {
try {
new nettyserver().start();
} catch (exception e) {
// 使用logger进行日志记录
log.error(e.getmessage(), e);
}
}
}7. 最后可以在随意注入到spring容器类中,在项目启动时候调用,也可以在其他访问接口事件调用
// 方式一
@postconstruct
public void init(){
// 在新的线程中运行netty服务器
thread thread = new thread(new nettyserverrunner());
thread.start();
}
// 方式二调用
@getmapping("/test/{id}")
public r getdevice(@pathvariable long id){
// 在新的线程中运行netty服务器
thread thread = new thread(new nettyserverrunner());
thread.start();
return deviceservice.getdevicealarmcount(deviceid);
}注意:
使用新线程时候,spring容器注入的对象为空,容易产生空指针异常,可以借鉴websockethandler 类中方法,重新从spring容器中获取需要的对象。
总结
到此这篇关于利用netty+springboot实现定时后端向前端推送数据的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关springboot定时后端向前端推送数据内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!




发表评论