我们这次项目主要从resttemplate 和 feign 进行选型分析。
一、spring cloud feign分析
feign是另外一种客户端负载均衡实现。
我在该模块写了feign client的示例代码。
【1】spring-cloud-web-demo-api为服务的sdk模块
【2】spring-cloud-web-demo-service为提供接口服务的模块
【3】spring-cloud-web-demo-client为模拟调用服务的模块
首先在spring-cloud-web-demo-api模块,定义feign api。spring-cloud-web-demo为spring-cloud-web-demo-service暴露的服务名。
@feignclient(value = "spring-cloud-web-demo")
public interface userfeign {
@getmapping(value = "/user/getuserbyid", produces = "application/json;charset=utf-8")
object getuserbyid(@requestparam(value = "id", required = false) long id);
//省略
}然后通过clientautoconfiguration自动装配。(client直接引入api包就可以使用,不需要再enablefeignclients)
@configuration
@enablefeignclients("net.teaho.demo.spring.cloud.web.api")
public class clientautoconfiguration {
}
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.enableautoconfiguration=\
net.teaho.demo.spring.cloud.web.api.config.clientautoconfiguration在service模块如以往spring mvc般实现api模块接口即可。
@restcontroller
public class usercontroller implements userfeign {
private static final logger logger = loggerfactory.getlogger(usercontroller.class);
@override
public object getuserbyid(long id) {
return "{\"id\":1, \"name\": \"test\"}";
}
//省略
}在client模块,注入bean后直接调用。
@component
@slf4j
public class testservice {
@autowired
private resttemplate resttemplate;
public object getoneuser(){
return usercontroller.getuserbyid(1l);
}
}二、resttemplate分析
写了具有客户端负载均衡能力的resttemplate的请求代码。
类似这样定义:
@bean
@loadbalanced
public resttemplate resttemplate() {
return new resttemplate();
}resttemplate究竟是如何利用注册中心实现客户端负载均衡的呢?
实现方式: 就是将上面所说的loadbalancerinterceptor负载均衡拦截器加到标注了@loadbalanced的resttemplate实例中。 loadbalancerinterceptor拦截器会在执行过程中获取并设置适合的目标请求实例,重新构造请求uri。
// 将配置中标注了@loadbalanced的resttemplate注入到这里
@loadbalanced
@autowired(required = false)
private list<resttemplate> resttemplates = collections.emptylist();
//将注册的resttemplatecustomizer(resttemplate自定义器)集合处理上面的resttemplates集合
@bean
public smartinitializingsingleton loadbalancedresttemplateinitializerdeprecated(
final objectprovider<list<resttemplatecustomizer>> resttemplatecustomizers) {
return () -> resttemplatecustomizers.ifavailable(customizers -> {
for (resttemplate resttemplate : loadbalancerautoconfiguration.this.resttemplates) {
for (resttemplatecustomizer customizer : customizers) {
customizer.customize(resttemplate);
}
}
});
}三、技术选型
最终选择使用openfeign,下面说说原因。
和resttemplate比起来,openfeign显得更适合spring boot微服务。
open feign相当于(http)rpc,相比起resttemplate,它直接显式将api声明以java接口形式标识出来。 并且因为底层用的动态代理,它还可以(无感知地)替换底层实现。比如,github上就有替换底层逻辑的repo – open feign+dubbo的rpc实现。
通过sdk包的形式,方便了调用,不需要像resttemplate一样,客户端自行拼接上一串请求参数。在代码编写上也清晰。
要使用就必须知道openfeign是怎么实现的呢?
四、openfeign 初始化分析
流程图如下:

看看前面例子里我们引入的openfeign的东西
【1】@enablefeignclients(“net.teaho.demo.spring.cloud.web.api”)
【2】@feignclient(value = “spring-cloud-web-demo”) 还有自动装配引入的
【3】feignribbonclientautoconfiguration
【4】feignclientsconfiguration
我们就从这两个注解开始分析源码。
【1】首先看@feignclient注解。
//给接口标注成一个rest调用方
@target(elementtype.type)
@retention(retentionpolicy.runtime)
@documented
public @interface feignclient {
//服务名,可以带协议前缀,也可以用${property.name}关联一个配置值。
@aliasfor("name")
string value() default "";
@deprecated
string serviceid() default "";
//bean name
string contextid() default "";
@aliasfor("value")
string name() default "";
/**
* sets the <code>@qualifier</code> value for the feign client.
*/
string qualifier() default "";
//直接指定一个地址,比如http://localhost:12345,一般用于调试
string url() default "";
boolean decode404() default false;
/**
* a custom <code>@configuration</code> for the feign client. can contain override
* <code>@bean</code> definition for the pieces that make up the client, for instance
* {@link feign.codec.decoder}, {@link feign.codec.encoder}, {@link feign.contract}.
*
* @see feignclientsconfiguration for the defaults
*/
//可用于覆盖feignclient默认设置
class<?>[] configuration() default {};
//回滚类,像我的例子中定义的回滚类必须实现userfeign接口,看https://cloud.spring.io/spring-cloud-static/greenwich.sr5/single/spring-cloud.html#spring-cloud-feign-hystrix-fallback
class<?> fallback() default void.class;
//如果需要对异常做诊断可用此属性,https://cloud.spring.io/spring-cloud-static/greenwich.sr5/single/spring-cloud.html#spring-cloud-feign-hystrix-fallback
class<?> fallbackfactory() default void.class;
//路径前缀
string path() default "";
//标记bean是否为primary
boolean primary() default true;
}【2】接下来重点关注@enablefeignclients注解是如何扫描feignclient接口的。
@retention(retentionpolicy.runtime)
@target(elementtype.type)
@documented
@import(feignclientsregistrar.class)
public @interface enablefeignclients {
//省略
}嗯,发现没有,就是feignclientsregistrar做处理的。来分析下重点方法registerfeignclients和registerfeignclient
class feignclientsregistrar implements importbeandefinitionregistrar,
resourceloaderaware, environmentaware {
public void registerfeignclients(annotationmetadata metadata,
beandefinitionregistry registry) {
//classpath扫描器
classpathscanningcandidatecomponentprovider scanner = getscanner();
scanner.setresourceloader(this.resourceloader);
//classpathscanningcandidatecomponentprovider扫描的basepackage集合
set<string> basepackages;
map<string, object> attrs = metadata
.getannotationattributes(enablefeignclients.class.getname());
//扫描器用于扫描标注了@feignclient类的拦截器
annotationtypefilter annotationtypefilter = new annotationtypefilter(
feignclient.class);
final class<?>[] clients = attrs == null ? null
: (class<?>[]) attrs.get("clients");
//clients属性为空,以@enablefeignclients的value、basepackage等为根包扫描
if (clients == null || clients.length == 0) {
scanner.addincludefilter(annotationtypefilter);
basepackages = getbasepackages(metadata);
}
//@enablefeignclients的clients属性不为空,解析clients的类和根包
else {
final set<string> clientclasses = new hashset<>();
basepackages = new hashset<>();
for (class<?> clazz : clients) {
basepackages.add(classutils.getpackagename(clazz));
clientclasses.add(clazz.getcanonicalname());
}
abstractclasstestingtypefilter filter = new abstractclasstestingtypefilter() {
@override
protected boolean match(classmetadata metadata) {
string cleaned = metadata.getclassname().replaceall("\\$", ".");
return clientclasses.contains(cleaned);
}
};
scanner.addincludefilter(
new alltypefilter(arrays.aslist(filter, annotationtypefilter)));
}
//1.根据basepackage找到目标@feignclient接口
//2.检查是否为接口
//3.将找到的接口注册为feignclientfactorybean
for (string basepackage : basepackages) {
set<beandefinition> candidatecomponents = scanner
.findcandidatecomponents(basepackage);
for (beandefinition candidatecomponent : candidatecomponents) {
if (candidatecomponent instanceof annotatedbeandefinition) {
// verify annotated class is an interface
annotatedbeandefinition beandefinition = (annotatedbeandefinition) candidatecomponent;
annotationmetadata annotationmetadata = beandefinition.getmetadata();
assert.istrue(annotationmetadata.isinterface(),
"@feignclient can only be specified on an interface");
map<string, object> attributes = annotationmetadata
.getannotationattributes(
feignclient.class.getcanonicalname());
string name = getclientname(attributes);
registerclientconfiguration(registry, name,
attributes.get("configuration"));
registerfeignclient(registry, annotationmetadata, attributes);
}
}
}
}
private string getclientname(map<string, object> client) {
if (client == null) {
return null;
}
string value = (string) client.get("contextid");
if (!stringutils.hastext(value)) {
value = (string) client.get("value");
}
if (!stringutils.hastext(value)) {
value = (string) client.get("name");
}
if (!stringutils.hastext(value)) {
value = (string) client.get("serviceid");
}
if (stringutils.hastext(value)) {
return value;
}
throw new illegalstateexception("either 'name' or 'value' must be provided in @"
+ feignclient.class.getsimplename());
}
private void registerfeignclient(beandefinitionregistry registry,
annotationmetadata annotationmetadata, map<string, object> attributes) {
string classname = annotationmetadata.getclassname();
beandefinitionbuilder definition = beandefinitionbuilder
.genericbeandefinition(feignclientfactorybean.class);
validate(attributes);
definition.addpropertyvalue("url", geturl(attributes));
definition.addpropertyvalue("path", getpath(attributes));
string name = getname(attributes);
definition.addpropertyvalue("name", name);
string contextid = getcontextid(attributes);
definition.addpropertyvalue("contextid", contextid);
definition.addpropertyvalue("type", classname);
definition.addpropertyvalue("decode404", attributes.get("decode404"));
definition.addpropertyvalue("fallback", attributes.get("fallback"));
definition.addpropertyvalue("fallbackfactory", attributes.get("fallbackfactory"));
definition.setautowiremode(abstractbeandefinition.autowire_by_type);
string alias = contextid + "feignclient";
abstractbeandefinition beandefinition = definition.getbeandefinition();
boolean primary = (boolean)attributes.get("primary"); // has a default, won't be null
beandefinition.setprimary(primary);
string qualifier = getqualifier(attributes);
if (stringutils.hastext(qualifier)) {
alias = qualifier;
}
beandefinitionholder holder = new beandefinitionholder(beandefinition, classname,
new string[] { alias });
beandefinitionreaderutils.registerbeandefinition(holder, registry);
}
}可以看到最后注册beandefinition时,我们看到注册了feignclientfactorybean这一factorybean。 我们看看工厂bean feignclientfactorybean是如何构造对象的。
class feignclientfactorybean implements factorybean<object>, initializingbean,
applicationcontextaware {
//省略
@override
public object getobject() throws exception {
return gettarget();
}
<t> t gettarget() {
//1.获取feigncontext,在feignautoconfiguration声明
feigncontext context = applicationcontext.getbean(feigncontext.class);
//2.构造feign builder
feign.builder builder = feign(context);
//3.如果没有设置url参数
if (!stringutils.hastext(this.url)) {
if (!this.name.startswith("http")) {
url = "http://" + this.name;
}
else {
url = this.name;
}
//4.设置path
url += cleanpath();
//5.获取client(用于执行最终http/https请求,比如loadbalancerfeignclient),
//构造反射实例
return (t) loadbalance(builder, context, new hardcodedtarget<>(this.type,
this.name, url));
}
//存在url参数,构造非loadbalance的请求实例(target)
if (stringutils.hastext(this.url) && !this.url.startswith("http")) {
this.url = "http://" + this.url;
}
string url = this.url + cleanpath();
client client = getoptional(context, client.class);
if (client != null) {
if (client instanceof loadbalancerfeignclient) {
// not load balancing because we have a url,
// but ribbon is on the classpath, so unwrap
client = ((loadbalancerfeignclient)client).getdelegate();
}
builder.client(client);
}
targeter targeter = get(context, targeter.class);
return (t) targeter.target(this, builder, context, new hardcodedtarget<>(
this.type, this.name, url));
}
//在feigncontext中获取一些在feignclientsconfiguration中声明,feign需要用到的组件
protected feign.builder feign(feigncontext context) {
feignloggerfactory loggerfactory = get(context, feignloggerfactory.class);
logger logger = loggerfactory.create(this.type);
// @formatter:off
feign.builder builder = get(context, feign.builder.class)
// required values
.logger(logger)
.encoder(get(context, encoder.class))
.decoder(get(context, decoder.class))
.contract(get(context, contract.class));
// @formatter:on
configurefeign(context, builder);
return builder;
}
protected <t> t loadbalance(feign.builder builder, feigncontext context,
hardcodedtarget<t> target) {
//获取client
client client = getoptional(context, client.class);
if (client != null) {
builder.client(client);
//从context获取targeter,targeter用于生成最终target实例(对应我的例子是被调用的通过反射生成的userfeign实例)
targeter targeter = get(context, targeter.class);
return targeter.target(this, builder, context, target);
}
throw new illegalstateexception(
"no feign client for loadbalancing defined. did you forget to include spring-cloud-starter-netflix-ribbon?");
}
//省略
}在非调试情况下(即我们没设置url参数), 我们来看看targeter.target(this, builder, context, target)做了什么。
targeter接口是构造被请求的代理bean的类。有两个实现类hystrixtargeter、defaulttargeter。
hystrixtargeter会比默认的多设置一些回滚措施,用到feign的contract属性, 我会先从defaulttargeter说起。
defaulttargeter会通过feign.builder#target(target target)生成实例。我们来看看代码。
public abstract class feign {
//省略
public static class builder {
private final list<requestinterceptor> requestinterceptors =
new arraylist<requestinterceptor>();
private logger.level loglevel = logger.level.none;
private contract contract = new contract.default();
private client client = new client.default(null, null);
private retryer retryer = new retryer.default();
private logger logger = new nooplogger();
private encoder encoder = new encoder.default();
private decoder decoder = new decoder.default();
private querymapencoder querymapencoder = new querymapencoder.default();
private errordecoder errordecoder = new errordecoder.default();
private options options = new options();
private invocationhandlerfactory invocationhandlerfactory =
new invocationhandlerfactory.default();
private boolean decode404;
private boolean closeafterdecode = true;
private exceptionpropagationpolicy propagationpolicy = none;
//省略
public <t> t target(class<t> apitype, string url) {
return target(new hardcodedtarget<t>(apitype, url));
}
public <t> t target(target<t> target) {
return build().newinstance(target);
}
//默认实现就是创建一个reflectivefeign实例
public feign build() {
synchronousmethodhandler.factory synchronousmethodhandlerfactory =
new synchronousmethodhandler.factory(client, retryer, requestinterceptors, logger,
loglevel, decode404, closeafterdecode, propagationpolicy);
parsehandlersbyname handlersbyname =
new parsehandlersbyname(contract, options, encoder, decoder, querymapencoder,
errordecoder, synchronousmethodhandlerfactory);
return new reflectivefeign(handlersbyname, invocationhandlerfactory, querymapencoder);
}
}
//省略
}在解读reflectivefeign前介绍几个概念:
1、invocationhandlerfactory 是控制反射方法分发的接口,create方法返回invocationhandler。
2、invocationhandlerfactory.methodhandler 最终将对代理类方法调用转换成http请求的地方,请看实现类synchronousmethodhandler
3、invocationhandlerfactory.default 默认实现,作为构造参数传入reflectivefeign,create方法创建的是new reflectivefeign.feigninvocationhandler(target, dispatch)。
4、reflectivefeign.parsehandlersbyname 作为构造参数传入reflectivefeign,核心方法apply(target key)先将标注了@feignclient的接口的方法解析出待处理的元数据list, 然后创建出方法名和方法处理器的map映射map<string, methodhandler>string是方法名,方法处理器通过synchronousmethodhandler.factory#create创建。
5、feigninvocationhandler 为处理一般方法的处理器
6、defaultmethodhandler 为处理接口默认方法的处理器
有了以上介绍,接下来简单分析reflectivefeign的newinstance方法。
public class reflectivefeign extends feign {
private final parsehandlersbyname targettohandlersbyname;
private final invocationhandlerfactory factory;
private final querymapencoder querymapencoder;
reflectivefeign(parsehandlersbyname targettohandlersbyname, invocationhandlerfactory factory,
querymapencoder querymapencoder) {
this.targettohandlersbyname = targettohandlersbyname;
this.factory = factory;
this.querymapencoder = querymapencoder;
}
..
/**
* creates an api binding to the {@code target}. as this invokes reflection, care should be taken
* to cache the result.
*/
@suppresswarnings("unchecked")
@override
public <t> t newinstance(target<t> target) {
//创建方法名和方法处理器的map映射
map<string, methodhandler> nametohandler = targettohandlersbyname.apply(target);
map<method, methodhandler> methodtohandler = new linkedhashmap<method, methodhandler>();
list<defaultmethodhandler> defaultmethodhandlers = new linkedlist<defaultmethodhandler>();
for (method method : target.type().getmethods()) {
if (method.getdeclaringclass() == object.class) {
continue;
//判断是否为接口的默认方法,defaultmethodhandler的处理逻辑是直接调用会原接口的default方法
} else if (util.isdefault(method)) {
defaultmethodhandler handler = new defaultmethodhandler(method);
defaultmethodhandlers.add(handler);
methodtohandler.put(method, handler);
} else {
//方法处理map
methodtohandler.put(method, nametohandler.get(feign.configkey(target.type(), method)));
}
}
invocationhandler handler = factory.create(target, methodtohandler);
//jdk动态代理创建对象
t proxy = (t) proxy.newproxyinstance(target.type().getclassloader(),
new class<?>[] {target.type()}, handler);
//将默认方法处理器也绑定到代理对象上
for (defaultmethodhandler defaultmethodhandler : defaultmethodhandlers) {
defaultmethodhandler.bindto(proxy);
}
return proxy;
}
static class feigninvocationhandler implements invocationhandler {
private final target target;
private final map<method, methodhandler> dispatch;
//省略
@override
public object invoke(object proxy, method method, object[] args) throws throwable {
//自定义的equals、hashcode和tostring的处理
if ("equals".equals(method.getname())) {
try {
object otherhandler =
args.length > 0 && args[0] != null ? proxy.getinvocationhandler(args[0]) : null;
return equals(otherhandler);
} catch (illegalargumentexception e) {
return false;
}
} else if ("hashcode".equals(method.getname())) {
return hashcode();
} else if ("tostring".equals(method.getname())) {
return tostring();
}
//分发调用到对应方法的invocationhandlerfactory.methodhandler
return dispatch.get(method).invoke(args);
}
//省略
}初始化完成。
五、openfeign 执行分析
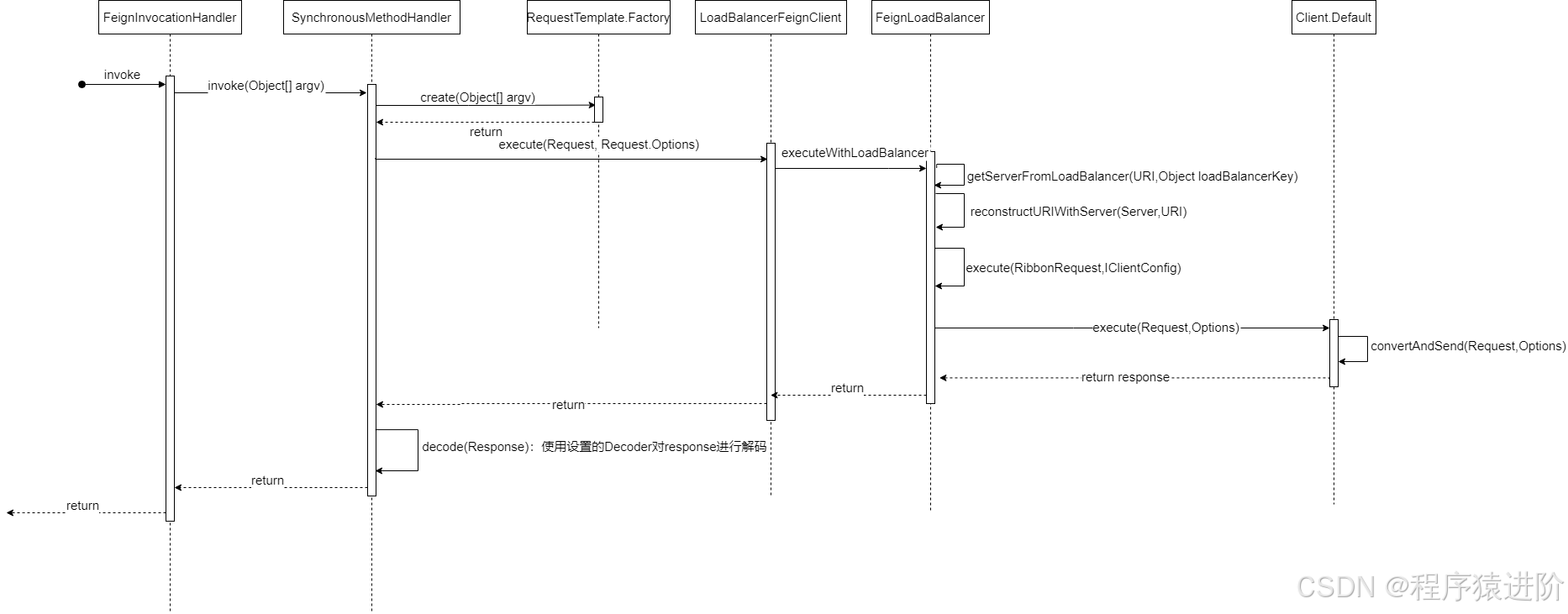
上图是openfeign构造的代理对象被调用时的时序图。
1、代理对象被执行
2、找到对应synchronousmethodhandler进行方法调用。
3、构造requesttemplate
4、loadbalancerfeignclient执行负载请求
5、feignloadbalancer通过iloadbalancer选择合适server,通过server重组uri,通过ribbonrequest持有的client执行实际http请求包装成response。
6、synchronousmethodhandler通过decoder将请求响应用decoder解码成最终结果。
下面介绍执行过程中涉及到源码中的部分组件。
1、requesttemplate 是一个http请求内容的抽象。
2、requesttemplate.factory 将方法参数解析成requesttemplate。
3、retryer 我在上面的时序图没有标注出来,实际上它在synchronousmethodhandler的执行中控制重试逻辑。
4、requestinterceptor 在synchronousmethodhandler发起执行中,会使用该拦截器对requesttemplate进行处理。这是一个拓展点。
5、logger 执行请求时打日志(在debug时打)。默认为logger.level.none即不打日志,可以增加bean覆盖。
- logger.level.none 不打印信息
- logger.level.basic 打印请求url和响应码。
- logger.level.headers 打印basic信息外加header信息
- logger.level.full 打印所有
6、loadbalancerfeignclient client接口的实现类,是具有负载均衡能力的client。client接口为执行http的接口,client.default是最终发出http请求的类。
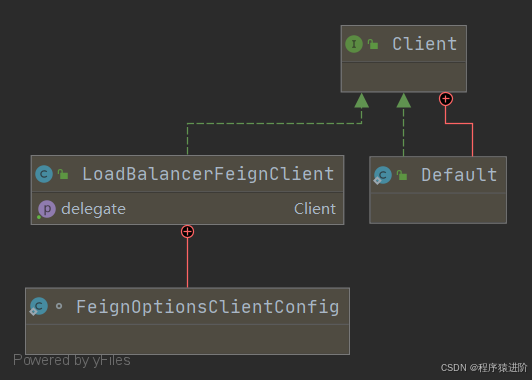
7、feignloadbalancer feignloadbalancer通过iloadbalancer选择合适server,通过server重组uri,通过ribbonrequest持有的client执行实际http请求包装成response。
8、loadbalancercommand ribbon的rxjava实现,执行负载流程逻辑的组件。
9、iloadbalancer ribbon的负载均衡器抽象。
熔断: 在feignclientsconfiguration中, 当配置了feign.hystrix.enabled,feign builder使用hystrixfeign.builder()。
所以build的时候新建hystrixinvocationhandler和hystrixdelegatingcontract实例。
feign build(final fallbackfactory<?> nullablefallbackfactory) {
super.invocationhandlerfactory(new invocationhandlerfactory() {
@override
public invocationhandler create(target target,
map<method, methodhandler> dispatch) {
return new hystrixinvocationhandler(target, dispatch, setterfactory,
nullablefallbackfactory);
}
});
super.contract(new hystrixdelegatingcontract(contract));
return super.build();
}来看看hystrixinvocationhandler的hystrix调用代码
final class hystrixinvocationhandler implements invocationhandler {
//省略
@override
public object invoke(final object proxy, final method method, final object[] args)
throws throwable {
//省略
hystrixcommand<object> hystrixcommand =
new hystrixcommand<object>(settermethodmap.get(method)) {
//实际执行
@override
protected object run() throws exception {
try {
return hystrixinvocationhandler.this.dispatch.get(method).invoke(args);
} catch (exception e) {
throw e;
} catch (throwable t) {
throw (error) t;
}
}
@override
protected object getfallback() {
if (fallbackfactory == null) {
return super.getfallback();
}
try {
//用配置的fallbackfactory创建fallback实例
object fallback = fallbackfactory.create(getexecutionexception());
object result = fallbackmethodmap.get(method).invoke(fallback, args);
//根据fallback对象的returntype解析包装内的结果返回
if (isreturnshystrixcommand(method)) {
return ((hystrixcommand) result).execute();
} else if (isreturnsobservable(method)) {
// create a cold observable
return ((observable) result).toblocking().first();
} else if (isreturnssingle(method)) {
// create a cold observable as a single
return ((single) result).toobservable().toblocking().first();
} else if (isreturnscompletable(method)) {
((completable) result).await();
return null;
} else {
return result;
}
} catch (illegalaccessexception e) {
// shouldn't happen as method is public due to being an interface
throw new assertionerror(e);
} catch (invocationtargetexception e) {
// exceptions on fallback are tossed by hystrix
throw new assertionerror(e.getcause());
}
}
};
//根据方法的return去返回结果
if (util.isdefault(method)) {
return hystrixcommand.execute();
} else if (isreturnshystrixcommand(method)) {
return hystrixcommand;
} else if (isreturnsobservable(method)) {
// create a cold observable
return hystrixcommand.toobservable();
} else if (isreturnssingle(method)) {
// create a cold observable as a single
return hystrixcommand.toobservable().tosingle();
} else if (isreturnscompletable(method)) {
return hystrixcommand.toobservable().tocompletable();
}
return hystrixcommand.execute();
}
//省略
}到此这篇关于spring cloud 负载均衡器架构选型的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关spring cloud 负载均衡内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!




发表评论