一、spring boot应用启动
一个spring boot应用的启动通常如下:
@springbootapplication
@slf4j
public class applicationmain {
public static void main(string[] args) {
configurableapplicationcontext ctx = springapplication.run(applicationmain.class, args);
}
}执行如上代码,spring boot程序启动成功。事实上启动spring boot应用离不开springapplication。
所以,我们跟随springapplication的脚步,开始从源码角度分析spring boot的初始化过程。
btw,可参看例子一节,我对spring boot启动的拓展点都做了demo,可参照下面源码分析进行理解。
文档有一句话说了springapplication做了什么(目的):
create an appropriate applicationcontext instance (depending on your classpath) register a commandlinepropertysource to expose command line arguments as spring properties refresh the application context, loading all singleton beans trigger any commandlinerunner beans
二、springapplication构造函数
启动代码先创建springapplication示例,在执行run方法:
public static configurableapplicationcontext run(class<?>[] primarysources,
string[] args) {
return new springapplication(primarysources).run(args);
}如下是springapplication的构造函数代码分析。
this.resourceloader = resourceloader; assert.notnull(primarysources, "primarysources must not be null"); this.primarysources = new linkedhashset<>(arrays.aslist(primarysources)); //通过classloader探测不同web应用核心类是否存在,进而设置web应用类型 this.webapplicationtype = webapplicationtype.deducefromclasspath(); //找出所有spring.factories中声明的applicationcontextinitializer并设置, //applicationcontextinitializer定义了回调接口,在refresh()前初始化调用(即在preparecontext的applyinitializers方法中调用) setinitializers((collection) getspringfactoriesinstances( applicationcontextinitializer.class)); //找出所有spring.factories中声明的applicationlistener(细节往后再叙),applicationlistener继承了 //java.util.eventlistener,实现了类似观察者模式的形式,通过实现applicationlistener、smartapplicationlistener,能够监听spring上下文的refresh、prepared等事件或者是自定义事件 setlisteners((collection) getspringfactoriesinstances(applicationlistener.class)); //找出主启动类(有趣的是,是通过new一个runtime异常然后在异常栈里面找出来的) this.mainapplicationclass = deducemainapplicationclass();
在构造期间,主要做了:
1、判定应用类型,为后面创建不同类型的spring context做准备。
2、初始化applicationcontextinitializer和applicationlistener。
3、找出启动类。
三、run()源码解析
介绍run()方法前,先说说贯穿run方法的applicationrunlistener,它有助于理解整个run()的运行周期。
写在这里:spring application事件机制
run()方法分析如下:
//java.awt.headless,是j2se的一种模式,用于在缺失显示屏、鼠标或者键盘时的系统配置。
configureheadlessproperty();
//将spring.factories中的springapplicationrunlistener接口实现类拖出来,塞到springapplicationrunlisteners(一个集合)中,统一批量执行
springapplicationrunlisteners listeners = getrunlisteners(args);
//触发runlistener的starting
listeners.starting();
try {
applicationarguments applicationarguments = new defaultapplicationarguments(
args);
configurableenvironment environment = prepareenvironment(listeners,
applicationarguments);
//spring.beaninfo.ignore如果没有设置值,则把它设为true,具体情况具体设置,
//如果没用的话,把它设为true可以ignore掉classloader对于不存在的beaninfo的扫描,提高性能。
configureignorebeaninfo(environment);
//banner打印。自定义banner挺好玩的
banner printedbanner = printbanner(environment);
//根据webapplicationtype(一开始推断的应用类型)去新建applicationcontext
context = createapplicationcontext();
//获取springbootexceptionreporter,回调接口类,提供启动时的异常报告
exceptionreporters = getspringfactoriesinstances(
springbootexceptionreporter.class,
new class[] { configurableapplicationcontext.class }, context);
//下面会说
preparecontext(context, environment, listeners, applicationarguments,
printedbanner);
refreshcontext(context);
//do nothing
afterrefresh(context, applicationarguments);
//计时停止
stopwatch.stop();
//打日志
if (this.logstartupinfo) {
new startupinfologger(this.mainapplicationclass)
.logstarted(getapplicationlog(), stopwatch);
}
//启动
listeners.started(context);
//找出context的applicationrunner和commandlinerunner,用annotationawareordercomparator排序,并执行
callrunners(context, applicationarguments);下面再分别说说两个方法(prepareenvironment、refreshcontext)的代码。
四、prepareenvironment
private configurableenvironment prepareenvironment(
springapplicationrunlisteners listeners,
applicationarguments applicationarguments) {
// create and configure the environment
configurableenvironment environment = getorcreateenvironment();
configureenvironment(environment, applicationarguments.getsourceargs());
//发布environment prepared事件
listeners.environmentprepared(environment);
//将获取到的environment中的spring.main配置绑定到springapplication中,
//使用的是binder这个spring boot2.0开始有的类
bindtospringapplication(environment);
if (!this.iscustomenvironment) {
environment = new environmentconverter(getclassloader())
.convertenvironmentifnecessary(environment, deduceenvironmentclass());
}
//附加的解析器将动态跟踪底层 environment 属性源的任何添加或删除,
//关于configurationpropertysourcespropertysource和mutablepropertiysource
//将在environment中作进一步讲解
configurationpropertysources.attach(environment);
return environment;
}五、preparecontext
private void preparecontext(configurableapplicationcontext context,
configurableenvironment environment, springapplicationrunlisteners listeners,
applicationarguments applicationarguments, banner printedbanner) {
//为上下文设置environment(配置、profile)
context.setenvironment(environment);
//对application做一些处理,设置一些组件,
//比如beannamegenerator,applicationconversionservice(包含一些默认的converter和formatter)
postprocessapplicationcontext(context);
// 加载并运行applicationcontextinitializer
applyinitializers(context);
listeners.contextprepared(context);
if (this.logstartupinfo) {
logstartupinfo(context.getparent() == null);
logstartupprofileinfo(context);
}
// add boot specific singleton beans
configurablelistablebeanfactory beanfactory = context.getbeanfactory();
beanfactory.registersingleton("springapplicationarguments", applicationarguments);
if (printedbanner != null) {
beanfactory.registersingleton("springbootbanner", printedbanner);
}
if (beanfactory instanceof defaultlistablebeanfactory) {
((defaultlistablebeanfactory) beanfactory)
.setallowbeandefinitionoverriding(this.allowbeandefinitionoverriding);
}
// load the sources
set<object> sources = getallsources();
assert.notempty(sources, "sources must not be empty");
//load beans(其实是由sources构建beandefinition) into the application context.
//构建beandefinitionloader并执行beandefinitionloader.load()
load(context, sources.toarray(new object[0]));
//执行contextloaded事件
listeners.contextloaded(context);
}六、容器refresh(refreshcontext)
private void refreshcontext(configurableapplicationcontext context) {
refresh(context);
if (this.registershutdownhook) {
try {
context.registershutdownhook();
}
catch (accesscontrolexception ex) {
// not allowed in some environments.
}
}
}refreshcontext会做两件事,
1、应用上下文刷新
2、注册shutdown钩子
我们来看看servletwebserver的刷新。
// servletwebserverapplicationcontext
public final void refresh() throws beansexception, illegalstateexception {
try {
super.refresh();
}
catch (runtimeexception ex) {
//停止webserver
stopandreleasewebserver();
throw ex;
}
}
org.springframework.context.support.abstractapplicationcontext refresh()
public void refresh() throws beansexception, illegalstateexception {
// 单线程执行
synchronized (this.startupshutdownmonitor) {
// prepare this context for refreshing.
// 1、设置spring容器的启动时间,撤销关闭状态,开启活跃状态。2、初始化属性源信息(property)3、验证环境信息里一些必须存在的属性
preparerefresh();
// tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
// 如果是refreshtableapplicationcontext会做了很多事情:
// 1、让子类刷新内部beanfactory ,创建ioc容器(defaultlistablebeanfactory--configurablelistablebeanfactory 的实现类)
// 2、加载解析xml文件(最终存储到document对象中)
// 3、读取document对象,并完成beandefinition的加载和注册工作
configurablelistablebeanfactory beanfactory = obtainfreshbeanfactory();
// prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
//从spring容器获取beanfactory(spring bean容器)并进行相关的设置为后续的使用做准备:
//1、设置classloader(用于加载bean),设置表达式解析器(解析bean定义中的一些表达式),添加属性编辑注册器(注册属性编辑器)
//2、添加applicationcontextawareprocessor这个beanpostprocessor。取消resourceloaderaware、applicationeventpublisheraware、messagesourceaware、applicationcontextaware、environmentaware这5个接口的自动注入。因为applicationcontextawareprocessor把这5个接口的实现工作做了
//3、设置特殊的类型对应的bean。beanfactory对应刚刚获取的beanfactory;resourceloader、applicationeventpublisher、applicationcontext这3个接口对应的bean都设置为当前的spring容器
//4、注入一些其它信息的bean,比如environment、systemproperties等
preparebeanfactory(beanfactory);
try {
// allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postprocessbeanfactory(beanfactory);
// invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context. 执行beanfactorypostprocessor
invokebeanfactorypostprocessors(beanfactory);
// register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
// 注册beanpostprocessor
registerbeanpostprocessors(beanfactory);
// initialize message source for this context. 初始化messagesource
initmessagesource();
// initialize event multicaster for this context.
initapplicationeventmulticaster();
// initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onrefresh();
// check for listener beans and register them.
registerlisteners();
// instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishbeanfactoryinitialization(beanfactory);
// last step: publish corresponding event.
finishrefresh();
} catch (beansexception ex) {
if (logger.iswarnenabled()) {
logger.warn("exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroybeans();
// reset 'active' flag.
cancelrefresh(ex);
// propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// reset common introspection caches in spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetcommoncaches();
}
}
}七、postprocessbeanfactory()
设置beanfactory之后再进行后续的一些beanfactory操作。
不同的context会进行不同的操作。 比如,annotationconfigservletwebserverapplicationcontext
protected void postprocessbeanfactory(configurablelistablebeanfactory beanfactory) {
// 父类实现,会注册web应用特有的factory scope,
super.postprocessbeanfactory(beanfactory);
//查看basepackages属性,如果设置了会使用classpathbeandefinitionscanner去扫描basepackages包下的bean并注
if (this.basepackages != null && this.basepackages.length > 0) {
this.scanner.scan(this.basepackages);
}
// 查看annotatedclasses属性,如果设置了会使用annotatedbeandefinitionreader去注册这些bean
if (!this.annotatedclasses.isempty()) {
this.reader.register(classutils.toclassarray(this.annotatedclasses));
}
}八、invokebeanfactorypostprocessors()
/**
* instantiate and invoke all registered beanfactorypostprocessor beans,
* respecting explicit order if given.
* <p>must be called before singleton instantiation.
*/
protected void invokebeanfactorypostprocessors(configurablelistablebeanfactory beanfactory) {
//执行abstractcontext持有的beanfactory后置处理器
//这些处理器是之前contextinitializer
postprocessorregistrationdelegate.invokebeanfactorypostprocessors(beanfactory, getbeanfactorypostprocessors());
// detect a loadtimeweaver and prepare for weaving, if found in the meantime
// (e.g. through an @bean method registered by configurationclasspostprocessor)
// 如果通过-javaagent参数设置了ltw的织入器类包,那么增加ltw的beanprocessor。
if (beanfactory.gettempclassloader() == null && beanfactory.containsbean(load_time_weaver_bean_name)) {
beanfactory.addbeanpostprocessor(new loadtimeweaverawareprocessor(beanfactory));
beanfactory.settempclassloader(new contexttypematchclassloader(beanfactory.getbeanclassloader()));
}
}从容器中找出beandefinitionregistrypostprocessor、beanfactorypostprocessor(二者的区别是,一个使用beandefinitionregistry作处理,一个使用beanfactory做处理), 并按一定的规则顺序执行。
configurationclasspostprocessor的优先级为最高,它会对项目中的@configuration注解修饰的类(@component、@componentscan、@import、@importresource修饰的类也会被处理)进行解析,解析完成之后把这些bean注册到beanfactory中。 需要注意的是这个时候注册进来的bean还没有实例化。
configurationclasspostprocessor的流程之后会独立进行分析。
九、registerbeanpostprocessors(configurablelistablebeanfactory beanfactory)方法
···java
/**
instantiate and invoke all registered beanpostprocessor beans,respecting explicit order if given.
must be called before any instantiation of application beans.
*/
protected void registerbeanpostprocessors(configurablelistablebeanfactory beanfactory) {
//委派postprocessorregistrationdelegate去做
postprocessorregistrationdelegate.registerbeanpostprocessors(beanfactory, this);
}从spring容器中按一定顺序(priorityordered、ordered、非priorityordered非ordered)找出实现了beanpostprocessor接口的bean,并设置到beanfactory的属性中。之后bean被实例化的时候会调用这个beanpostprocessor。 ## 十、initmessagesource() 初始化一些国际化相关的属性。 spring boot的国际化配置可阅读messagesourceautoconfiguration。 默认情况会设置一个delegatingmessagesource,是一个空实现,因为applicationcontext接口拓展了messagesource接口,所以spring容器都有getmessage方法, 可是,在实现上又允许空messagesource,所以,通过一个delegatingmessagesource去适配。 ## 十一、initapplicationeventmulticaster() initialize event multicaster for this context. 初始化事件广播器。默认实现是simpleapplicationeventmulticaster。 onrefresh() 模板方法,给不同的spring应用容器去实例化一些特殊的类。 比如,annotationconfigservletwebserverapplicationcontext、annotationconfigreactivewebserverapplicationcontext会去创建web server(createwebserver())。 spring boot的mvc内置支持有tomcat、undertow、jetty三种server,而reactive web server则内置支持tomcat、jetty、netty三种。 java // unlike jetty, all tomcat threads are daemon threads. we create a // blocking non-daemon to stop immediate shutdown startdaemonawaitthread();
btw,如果是tomcat server的话,spring boot会启动多一个线程防止退出。
十二、registerlisteners()
把beanfactory的applicationlistener拿出来塞到事件广播器里。
如果applicationcontext的earlyapplicationevents属性有值,则广播该属性持有的early事件。
十三、finishbeanfactoryinitialization(beanfactory)
实例化beanfactory中已经被注册但是未实例化的所有实例(懒加载的不需要实例化)。
比如invokebeanfactorypostprocessors方法中根据各种注解解析出来的类,在这个时候都会被初始化。
十四、finishrefresh()
// reactivewebserverapplicationcontext
@override
protected void finishrefresh() {
super.finishrefresh();
webserver webserver = startreactivewebserver();
if (webserver != null) {
publishevent(new reactivewebserverinitializedevent(webserver, this));
}
}
// abstractapplicationcontext
/**
* finish the refresh of this context, invoking the lifecycleprocessor's
* onrefresh() method and publishing the
* {@link org.springframework.context.event.contextrefreshedevent}.
*/
protected void finishrefresh() {
// clear context-level resource caches (such as asm metadata from scanning).
// 容器完成刷新,清除资源缓存
clearresourcecaches();
// initialize lifecycle processor for this context.
// 初始化lifecycleprocessor, 默认实现是defaultlifecycleprocessor,实现了beanfactoryaware接口,通过beanfactory找出lifecycle bean
// 可通过自定义实现lifecycle接口的bean,来监听容器的生命周期。
initlifecycleprocessor();
// propagate refresh to lifecycle processor first.
//粗发生命周期处理器的onrefresh方法,顺带一说,在程序正常退出时,会粗发shutdownhook,那时会粗发生命周期处理器的onclose方法
getlifecycleprocessor().onrefresh();
// publish the final event.
// 广播contextrefreshed事件
publishevent(new contextrefreshedevent(this));
// participate in livebeansview mbean, if active.
// 将applicationcontext注册到spring tool suite里
livebeansview.registerapplicationcontext(this);
}十五、resetcommoncaches()
// reset common introspection caches in spring's core, since we // might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore... resetcommoncaches();
最后会在finally执行resetcommoncaches(),清除一些spring core、beans加载和解析的bean信息缓存(因为对于singleton bean来说已经不需要了)。
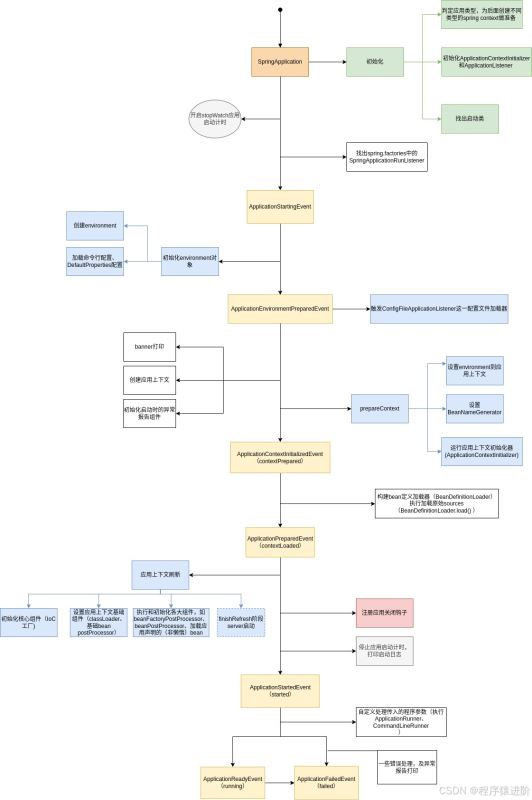
十六、流程整理
最后,按照启动阶段整理一幅全景图。
十七、例子
在github里,我把spring boot应用启动的拓展组件(自定义的应用初始器、监听器、事件、applicationrunner)都写了例子,可参照阅读。 代码在这 | spring-boot-none-startup
日志如下:
2020-05-20 18:30:11.625 info 81568 --- [ main] n.t.d.s.b.s.n.s.r.simplerunlistener : environmentprepared, env:standardenvironment {activeprofiles=[dev], defaultprofiles=[default], propertysources=[mappropertysource {name='systemproperties'}, originawaresystemenvironmentpropertysource {name='systemenvironment'}, randomvaluepropertysource {name='random'}, origintrackedmappropertysource {name='applicationconfig: [classpath:/application-dev.yml]'}, origintrackedmappropertysource {name='applicationconfig: [classpath:/application.yml]'}]}
. ____ _ __ _ _
/\\ / ___'_ __ _ _(_)_ __ __ _ \ \ \ \
( ( )\___ | '_ | '_| | '_ \/ _` | \ \ \ \
\\/ ___)| |_)| | | | | || (_| | ) ) ) )
' |____| .__|_| |_|_| |_\__, | / / / /
=========|_|==============|___/=/_/_/_/
:: spring boot :: (v2.1.3.release)2020-05-20 18:30:11.832 info 81568 --- [ main] n.t.d.s.b.s.n.s.r.simplerunlistener : contextprepared, ctx:org.springframework.context.annotation.annotationconfigapplicationcontext@1d730606, started on thu may 01 08:00:00 cst 1970
2020-05-20 18:30:11.838 info 81568 --- [ main] n.t.d.s.b.startup.none.applicationmain : starting applicationmain on desktop-oldghc1 with pid 81568 ( started by teash in )
2020-05-20 18:30:11.838 info 81568 --- [ main] n.t.d.s.b.startup.none.applicationmain : the following profiles are active: dev
2020-05-20 18:30:11.894 info 81568 --- [ main] n.t.d.s.b.s.n.s.r.simplerunlistener : contextloaded, context: org.springframework.context.annotation.annotationconfigapplicationcontext@1d730606, started on thu may 01 08:00:00 cst 1970
2020-05-20 18:30:12.404 info 81568 --- [ main] .s.b.s.n.s.simpleapplicationcontextaware : simpleapplicationcontextaware and send simpleappevent
2020-05-20 18:30:12.441 info 81568 --- [ main] n.t.d.s.b.s.n.s.e.simpleeventlistener : event: net.teaho.demo.spring.boot.startup.none.spring.event.simpleappevent[source=event source], source: event source
2020-05-20 18:30:12.444 info 81568 --- [ main] n.t.d.s.b.s.n.config.beanconfiguration : [net.teaho.demo.spring.boot.startup.none.spring.spi.demospringloaderimpl@c96a4ea]
2020-05-20 18:30:12.484 info 81568 --- [ main] n.t.d.s.b.s.n.s.l.logginglifecycle : in life cycle bean start().
2020-05-20 18:30:12.496 info 81568 --- [ main] n.t.d.s.b.startup.none.applicationmain : started applicationmain in 1.573 seconds (jvm running for 3.195)
2020-05-20 18:30:12.496 info 81568 --- [ main] n.t.d.s.b.s.n.s.r.simplerunlistener : started, context: org.springframework.context.annotation.annotationconfigapplicationcontext@1d730606, started on mon may 25 18:30:11 cst 2020
2020-05-20 18:30:12.497 info 81568 --- [ main] n.t.d.s.b.s.n.s.r.echoapplicationrunner : echoapplicationrunner running, args:org.springframework.boot.defaultapplicationarguments@45673f68
2020-05-20 18:30:12.497 info 81568 --- [ main] n.t.d.s.b.s.n.s.r.echocommandlinerunner : echocommandlinerunner running
2020-05-20 18:30:12.497 info 81568 --- [ main] n.t.d.s.b.s.n.s.r.simplerunlistener : running, context: org.springframework.context.annotation.annotationconfigapplicationcontext@1d730606, started on mon may 25 18:30:11 cst 2020
2020-05-20 18:30:12.500 info 81568 --- [ thread-3] n.t.d.s.b.s.n.s.l.logginglifecycle : in life cycle bean stop().
到此这篇关于spring boot启动原理及相关组件的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关spring boot启动原理内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!





发表评论