当我们长期在电脑面前坐太久后,会产生一系列健康风险,包括干眼症,颈椎,腰椎,肌肉僵硬等等。解决方案是在一定的时间间隔内我们需要have a break, 远眺可以缓解干眼症等眼部症状,站起来走动两步,或者做一些舒展动作,可以让我们身体肌肉放松。microsoft store的一些第三方免费定时提醒程序,如breaktimer, 常常难以在约定的时间内唤起。其他一些有着类似功能且有更丰富特性的第三方程序需要注册缴费才能使用很多功能。这触发了我自己写一个程序来实现该功能。
因为python的功能强大,且开发程序的门槛低,所以我选择它,我电脑安装的版本是3.10. 第一步,开发一个可以显示在底部工具栏右边隐藏托盘的图标,当我们有鼠标放上去时,可以显示当前离下一次休息还剩下的时间,以分钟和秒计。点击鼠标右键时,可以弹出菜单显示当前剩余时间和退出按钮。
要实现以上功能,需要安装第三方库 pystray 和 pillow。代码如下:
import threading
from pystray import icon, menuitem, menu
from pil import image, imagedraw
def create_image():
# load an existing image for the tray icon
icon_path = r"c:\technical learning\python\take-break-icon.png" # path to your image file (e.g., .png or .ico)
return image.open(icon_path)
def stop_program(icon, item):
# stop the video playback and exit the program
global keep_run
icon.stop()
keep_run=false
def start_tray_icon(icon):
# create the system tray icon with a menu
icon.run()
myicon = icon("videoplayer", create_image())
# start the tray icon in a separate thread
tray_thread = threading.thread(target=start_tray_icon, args=[myicon],daemon=true)
tray_thread.start()
def update_tray_menu(icon):
# update the menu with the remaining time
global time_left
#the tray menu has three items, time left, set timer, and stop
menu = menu(
menuitem(f"time left: {time_left[0]} minutes {time_left[1]} seconds", lambda icon,item:none),
menuitem('set timer', set_timer), # add the new menu option here
menuitem('stop', action=stop_program)
)
icon.menu = menu
#the title will show when you mouse over the icon
icon.title = f"{time_left}"
首先通过已有的图片创建一个icon object,并创建一个线程来运行该object。因为要实时显示剩余时间,所以有一个update函数来对menu内容进行更新。
第二步,实现每隔预设的时间, 启动vlc播放器,播放一段指定的视频。同时计时器重新开始倒计时。
import subprocess
import time
# path to vlc and your video file
vlc_path = r"d:\program files (x86)\videolan\vlc\vlc.exe" # update if needed
video_path = r"c:\technical learning\python\health_song_fxx.mp4"
#the minutes and seconds to pass to have a break periodically,default is 60 minutes
time_set = (59,60)
# global variable to track time left
time_left = list(time_set)
keep_run = true
def start_play_video():
subprocess.run([vlc_path, video_path])
while keep_run:
update_tray_menu(myicon) #you can see the update of time_left instantly
if time_left[0]==-1: #it's the time for a break
video_play_thread = threading.thread(target=start_play_video)
video_play_thread.start()
time_left = list(time_set) # reset time left
time.sleep(1)
if time_left[1]==0:
time_left[1]=60
time_left[0]-=1
time_left[1] -= 1
主线程是一个while loop,每隔1s更新time_left,当time out,启动一个线程来通过subprocess来调用vlc播放器来播放视频,之所以用subprocess是这样一般可以带来前台窗体播放的效果,更好的提醒作用。当icon点击了stop后,keep_run为false,循环退出,程序结束。
最简单功能的桌面定时提醒程序这时候可以告一段落了,但是在你使用电脑的过程中,你可能本身会中途离开,比方说中午午餐,去开会,或者去做运动了。这时候电脑进入休眠状态。当你回来后,计时器还是会按照计算机休眠前剩余的时间继续计时,这个不太合理。因为这个时候你其实已经眼睛和身体已经得到了一些放松,起码没有一直盯着屏幕。所以应该重新开始计时。
要实现windows计算机从休眠中醒来重新计数,需要安装第三方库pywin32,别被名字糊弄,因为历史原因,它后续的版本也包括了64 bit windows.
import win32api
import win32gui
import win32con
#the class used to handle event of computer waking up from hibernation
class powereventhandler:
def __init__(self):
self.internal_variable = 0
def handle_event(self, hwnd, msg, wparam, lparam):
global time_left
if msg == win32con.wm_powerbroadcast and wparam == win32con.pbt_apmresumeautomatic:
#print("laptop woke up from hibernation!")
time_left = [59,60]
list(time_set)
return true
'''creates a custom windows message handling window'''
handler = powereventhandler()
wc = win32gui.wndclass()
wc.lpszclassname = 'powerhandler'
wc.hinstance = win32api.getmodulehandle(none)
wc.lpfnwndproc = handler.handle_event
class_atom = win32gui.registerclass(wc)
#create a window of the registered class with no size and invisible
hwnd = win32gui.createwindow(class_atom, 'powerhandler', 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, wc.hinstance, none)创建一个不可见窗体来接受windows系统的消息,当接收到从休眠中醒来的消息时,重置剩下的时间为预设值。同时你需要在while loop里不断地处理pending的windows系统消息。
win32gui.pumpwaitingmessages()
第四步,目前为止,隔多少时间休息的时间段是在程序里写死的,默认是60分钟。用户可能需要根据自己的偏好进行修改。那么需要在icon的menu里增加一个选项,点击后弹框进行时间段设置。
这里就要用到tkinter lib,这个默认在pythond的安装包里,无需另外安装。
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import simpledialog
#a pop up dialog to set the time_set
def set_timer(icon, item):
#after the user clicking the set button
def validate_and_set_time():
nonlocal root, error_label
try:
minutes = int(minute_input.get())
seconds = int(second_input.get())
#print(minutes,seconds)
# validate range [0, 60]
if 0 <= minutes <= 60 and 0 <= seconds <= 60:
with time_left_lock:
global time_set,time_left
time_set=(minutes,seconds)
time_left=list(time_set) #each time_set is set, time_let needs to update accordingly
#print(time_left)
root.destroy() # close dialog if input is valid
else:
error_label.config(text="minutes and seconds must be between 0 and 60!")
except valueerror:
error_label.config(text="please enter valid integers!")
#create the dialog
root = tk.tk()
root.title("set timer")
root.geometry("300x200")
# get screen width and height
screen_width = root.winfo_screenwidth()
screen_height = root.winfo_screenheight()
# calculate position x and y to center the window
window_width = 300
window_height = 200
position_x = (screen_width // 2) - (window_width // 2)
position_y = (screen_height // 2) - (window_height // 2)
# set the geometry to center the window
root.geometry(f"{window_width}x{window_height}+{position_x}+{position_y}")
tk.label(root, text="set timer").pack(pady=5)
tk.label(root, text="minutes (0-60):").pack()
minute_input = tk.entry(root)
minute_input.pack()
tk.label(root, text="seconds (0-60):").pack()
second_input = tk.entry(root)
second_input.pack()
error_label = tk.label(root, text="", fg="red") # label for error messages
error_label.pack(pady=5)
#set the button call-back method to validate_and_set_time
tk.button(root, text="set", command=validate_and_set_time).pack(pady=10)
root.mainloop()上面的代码就包括了弹窗设计,用户输入数据校验,间隔时间段设置,以及剩余时间重置等。
另外,在icon的menu里需增加一栏,用于设置间隔时间段。
menuitem('set timer', set_timer), # add the new menu option here
最后一步,为了让用户设置的时间段间隔永久生效,需要用一个文件来存储。 启动这个程序的时候,从这个文件读数据,退出程序的时候,把数据存入到该文件。
这是鼠标移到icon上,点击右键出现的menu:
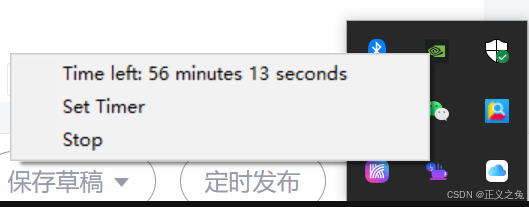
下面是点击set timer后的弹框。
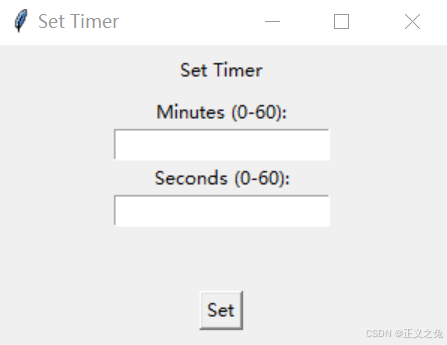
到此这篇关于基于python实现windows桌面定时提醒休息程序的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关python定时提醒内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!







发表评论