简介
反射,反射,程序员的快乐。
前期绑定与后期绑定
在.net中,前期绑定(early binding)是指在编译时就确定了对象的类型和方法,而后期绑定(late binding)或动态绑定是在运行时确定对象的类型和方法。
前置知识:c#类型系统结构
c#作为c++++ ,在类型系统上沿用c++的类型系统
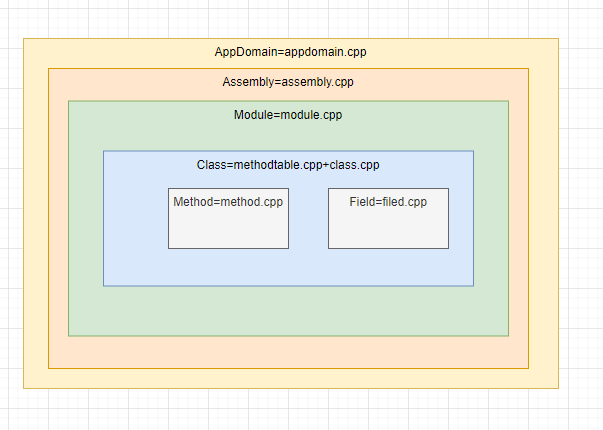
前期绑定
在代码能执行之前,将代码中依赖的assembly,module,class,method,field等类型系统的元素提前构建好。
前期绑定的优点是编译时类型检查,提高了类型安全性和性能。缺点是如果需要更换类型,需要重新编译代码。灵活性不够
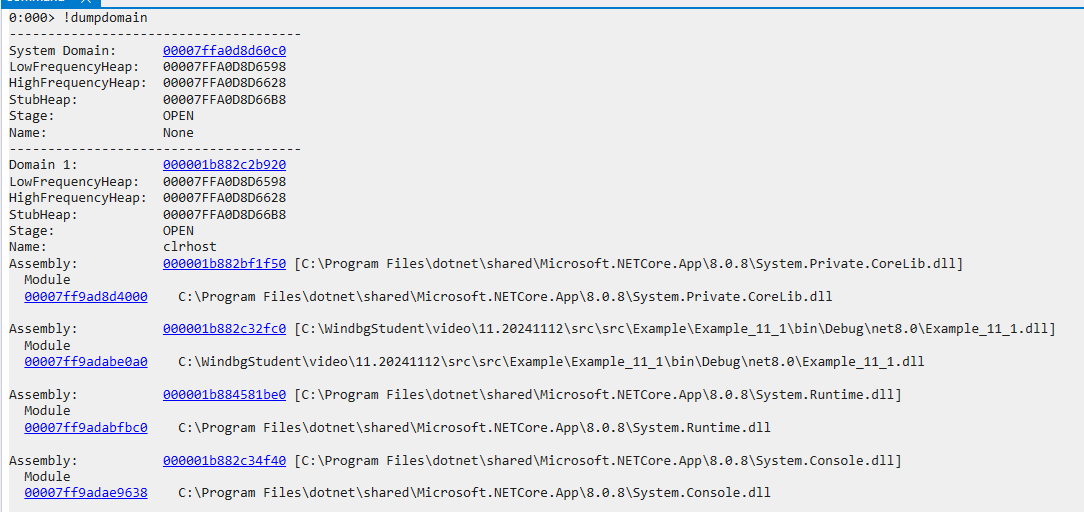
比如一个简单的的控制台,就自动提前加载了各种需要的dll文件。完成前期绑定。
后期绑定
后期绑定的优点是可以在运行时更改类型,无需重新编译代码。缺点是在编译时不进行类型检查,可能导致运行时错误。
几个常用的场景,比如dynamic ,多态,system.reflection等
举个例子,使用reflection下的“元数据查询api”,动态加载dll
var dllpath = "xxx.dll";
assembly assembly = assembly.loadfrom(dllpath);//构建assembly+module
type dataaccesstype = assembly.gettype("xxxxx");//构建class(methodtable+eeclass)
object dataaccess = activator.createinstance(dataaccesstype);//在托管堆中创建mt实例
methodinfo addmethod = dataaccesstype.getmethod("add");//构建methoddesc
addmethod.invoke(dataaccess, new object[] { "hello world" });//调用方法反射
反射的本质就是“操作元数据”
什么是元数据?
metadata,本是上就是存储在dll中的一个信息数据库,记录了这个assembled中有哪些方法,哪些类,哪些属性等等信息
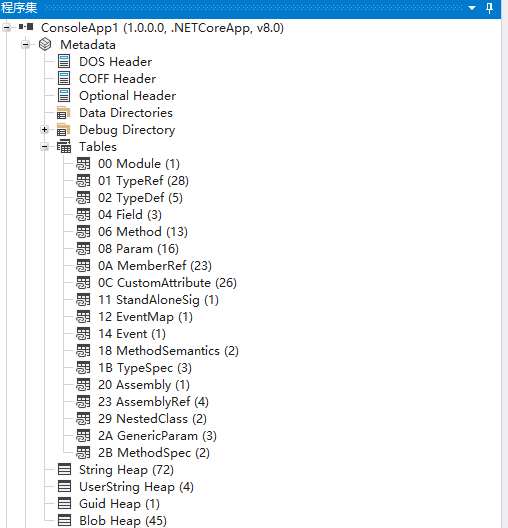
可以看到,各种table组成的信息,是不是类似一个数据库?
举个例子:
执行type.gettype("int"),反射会在metadata寻找"int"的类型。但在运行时会返回null.因为metadata中只有"system.int32"这个字符串。
反射如何查询metadata?
通过reflection xxxinfo系列api 查询所有细节
type t = typeof(system.io.filestream); fieldinfo[] fi = t.getfields(bindingflags.static | bindingflags.nonpublic | bindingflags.public); propertyinfo[] pi = t.getproperties(bindingflags.static | bindingflags.nonpublic | bindingflags.public); eventinfo[] ei = t.getevents(bindingflags.static | bindingflags.nonpublic | bindingflags.public); ......
反射如何构建类型系统
通过reflection xxxbuilder系列api 构建一个全新的类型
assemblybuilder ab = assemblybuilder.definedynamicassembly(new assemblyname("myassembly"), assemblybuilderaccess.runandcollect);//创建assembly
modulebuilder mob = ab.definedynamicmodule("mymodule");//创建module
typebuilder tb = mob.definetype("mytype", typeattributes.public | typeattributes.class);//创建class
methodbuilder mb = tb.definemethod("summethod", methodattributes.public | methodattributes.static, typeof(int), new type[] { typeof(int), typeof(int) });//创建methodtable
ilgenerator il = mb.getilgenerator();//通过il api 动态构建methoddesc
il.emit(opcodes.ldarg_0);
il.emit(opcodes.ldarg_1);
il.emit(opcodes.add);
il.emit(opcodes.ret);
type type = tb.createtype(); //mt + eeclass
methodinfo method = type.getmethod("summethod");
console.writeline(method.invoke(null, new object[] { 5, 10 }));反射底层调用
c#的类型系统,与c++的类型系统是一一对应的。因此其底层必定是调用c++的方法。
示意图如下,有兴趣的小伙伴可以去参考coreclr的源码
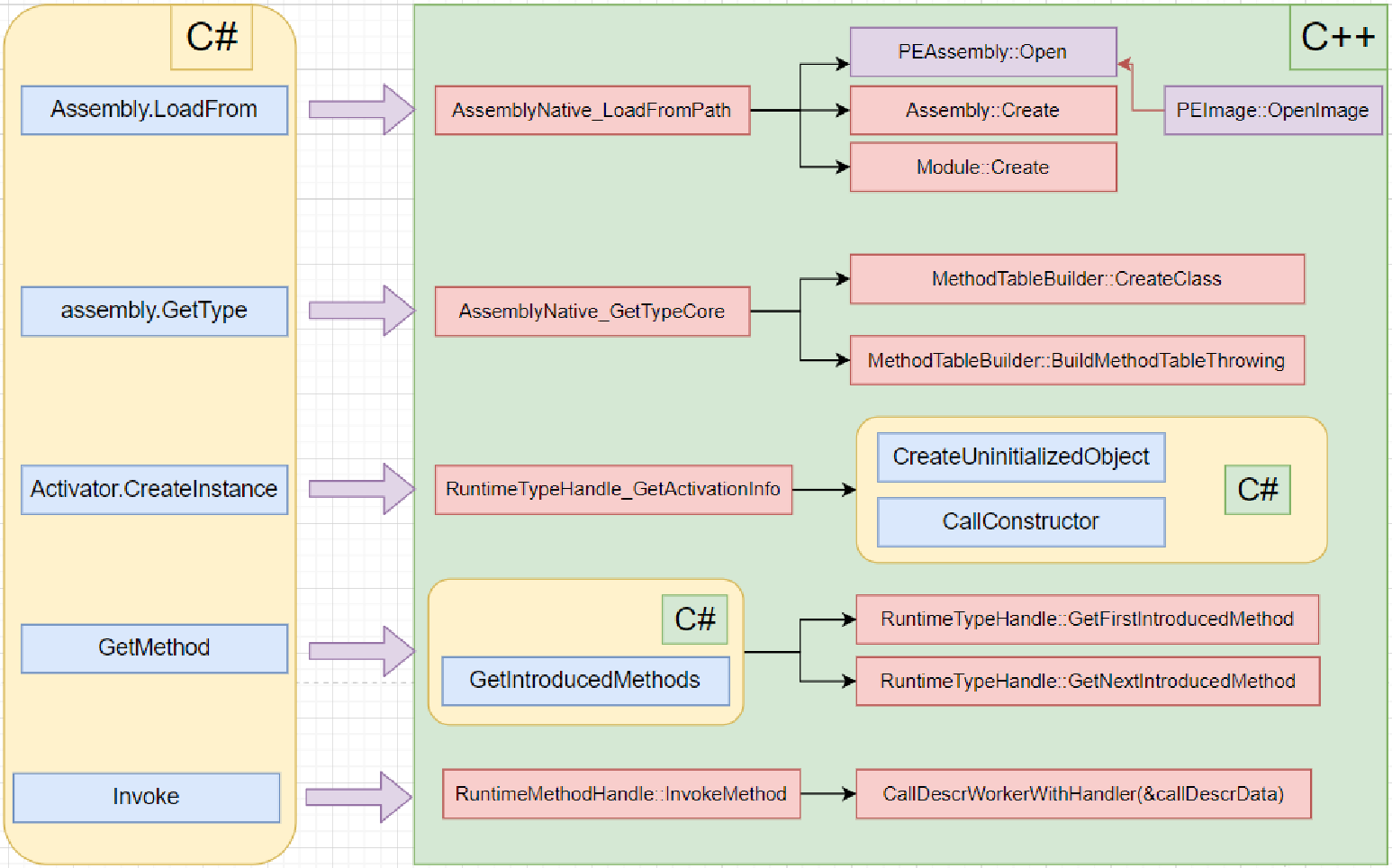
眼见为实,以invoke为例
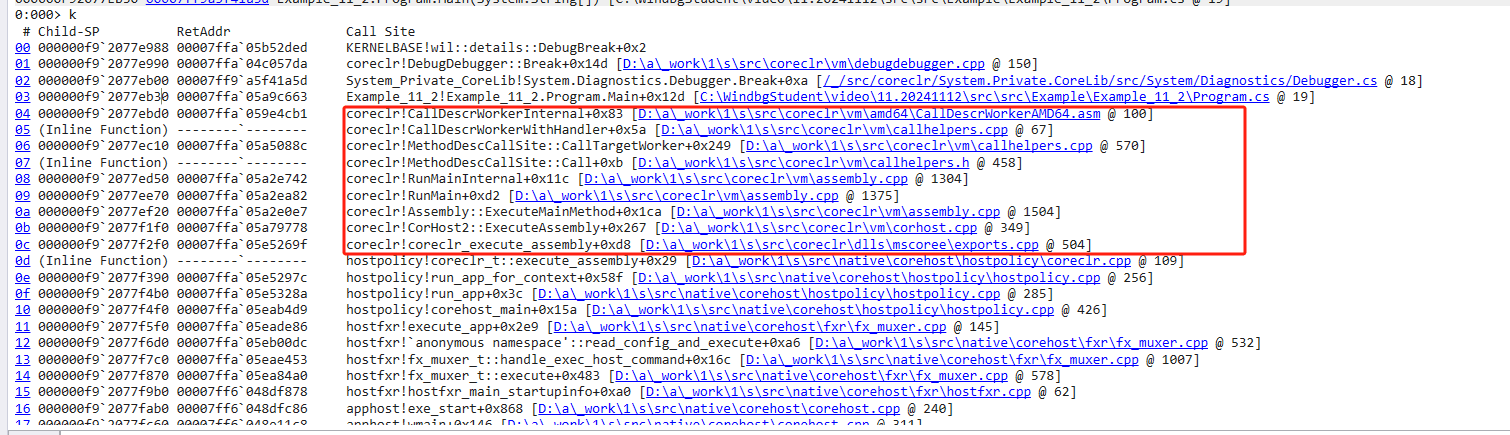
反射到底慢在哪?
- 动态解析
从上面可知道,反射作为后期绑定,在runtime中要根据metadata查询出信息,严重依赖字符串匹配,这本身就增加了额外的操作 - 动态调用
使用反射调用方法时,先要将参数打包成数组,再解包到线程栈上。又是额外操作。 - 无法在编译时优化
反射是动态的临时调用,jit无法优化。只能根据代码一步一步执行。 - 额外的安全检查
反射会涉及到访问和修改只读字段等操作,运行时需要进行额外的安全性检查,这也会增加一定的开销 - 缓存易失效
反射如果参数发生变化,那么缓存的汇编就会失效。又需要重新查找与解析。
总之,千言万语汇成一句话。最好的反射就是不要用反射。除非你能保证对性能要求不高/缓存高命中率
clr的对反射的优化
除了缓存反射的汇编,.net 中提供了一系列新特性来尽可能的绕开“反射”
emit
emit 是 .net 提供的一种动态生成和编译代码的技术。通过 emit,我们可以动态生成一个新的方法,这个方法可以直接访问私有成员,这对于一些特殊场景非常有用,比如动态代理、代码生成器、aop(面向切面编程)等.
public class person
{
private int _age;
public override string tostring()
{
return _age.tostring();
}
}
static void emittest(person person)
{
// 获取person类的类型对象
type persontype = typeof(person);
// 获取私有字段_age的fieldinfo,无法避免部分使用反射
fieldinfo agefield = persontype.getfield("_age", bindingflags.instance | bindingflags.nonpublic);
if (agefield == null)
{
throw new argumentexception("未找到指定的私有字段");
}
// 创建一个动态方法
dynamicmethod dynamicmethod = new dynamicmethod("setagevalue", null, new type[] { typeof(person), typeof(int) }, persontype);
// 获取il生成器
ilgenerator ilgenerator = dynamicmethod.getilgenerator();
// 将传入的person对象加载到计算栈上(this指针)
ilgenerator.emit(opcodes.ldarg_0);
// 将传入的新值加载到计算栈上
ilgenerator.emit(opcodes.ldarg_1);
// 将新值存储到对应的私有字段中
ilgenerator.emit(opcodes.stfld, agefield);
// 返回(因为方法无返回值,这里只是结束方法执行)
ilgenerator.emit(opcodes.ret);
// 创建委托类型,其签名与动态方法匹配
action<person, int> setageaction = (action<person, int>)dynamicmethod.createdelegate(typeof(action<person, int>));
// 通过委托调用动态生成的方法来修改私有字段的值
setageaction(person, 100);
}切构建代码又臭又长。
expression
expression 是 .net 提供的一种表达式树的技术。通过 expression,我们可以创建一个表达式树,然后编译这个表达式树,生成一个可以访问私有成员的方法
static void expressiontest(person person)
{
// 获取person类的类型对象
type persontype = typeof(person);
// 获取私有字段_age的fieldinfo,无法避免部分使用反射
fieldinfo agefield = persontype.getfield("_age", bindingflags.instance | bindingflags.nonpublic);
if (agefield == null)
{
throw new argumentexception("未找到指定的私有字段");
}
// 创建参数表达式,对应传入的person对象实例
parameterexpression instanceparam = expression.parameter(persontype, "instance");
// 创建参数表达式,对应传入的新值
parameterexpression newvalueparam = expression.parameter(typeof(int), "newvalue");
// 创建一个赋值表达式,将新值赋给私有字段
binaryexpression assignexpression = expression.assign(expression.field(instanceparam, agefield), newvalueparam);
// 创建一个包含赋值表达式的表达式块,这里因为只有一个赋值操作,所以块里就这一个表达式
blockexpression blockexpression = expression.block(assignexpression);
// 创建一个可执行的委托,其类型与表达式块的逻辑匹配
action<person, int> setageaction = expression.lambda<action<person, int>>(blockexpression, instanceparam, newvalueparam).compile();
// 通过委托调用表达式树生成的逻辑来修改私有字段的值
setageaction(person, 100);
}切构建代码又臭又长。
unsafeaccessorattribute
.net 8中引入了新特性unsafeaccessorattribute 。
使用该特性,来提供对私有字段的快速修改
static void new()
{
var person = new person();
getagefield(person) = 100;
}
[unsafeaccessor(unsafeaccessorkind.field, name = "_age")]
static extern ref int getagefield(person counter);为什么它这么快?
对于c#来说,私有类型是oop语言的定义。它定义了什么是私有类型,它的行为是什么。
但对于程序本身来说,代码和数据都只是一段内存,实际上你的指针想访问哪就访问哪。哪管你什么私有类型。换一个指向地址不就得了。因此clr开放了这么一个口子,利用外部访问直接操作内存。看它的命名unsafeaccessor就能猜到意图了
3,2,1. 上汇编!!!
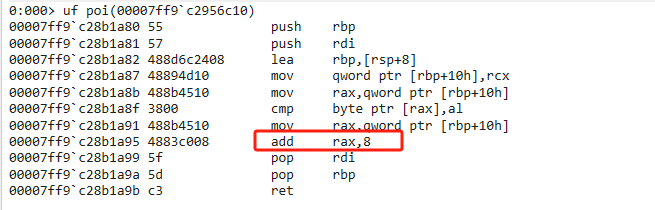
直接将rax寄存器偏移量+8,直接返回int(占用4字节,偏移量8)类型的_age。 没有emit,expression的弯弯绕绕,丝毫不拖泥带水。
.net 9中的改进
参考资料
到此这篇关于.net core 反射底层原理浅谈的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关.net core 反射底层原理内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!



发表评论