java线程池带返回值的方式方法
在java中,线程池是一种重要的多线程处理方式,可以有效管理和重用线程,提高程序的性能和效率。有时候我们需要在多线程处理中获取线程的返回值,本文将介绍如何使用线程池实现带返回值的方式方法。
使用callable和future
java中的callable接口是一种带返回值的多线程处理方式,结合future接口可以实现获取线程返回值的功能。下面是一个示例代码:
import java.util.concurrent.callable;
import java.util.concurrent.executorservice;
import java.util.concurrent.executors;
import java.util.concurrent.future;
public class threadpoolwithreturnvalueexample {
public static void main(string[] args) {
executorservice executor = executors.newfixedthreadpool(1);
callable<integer> task = new callable<integer>() {
@override
public integer call() throws exception {
// 在这里编写具体的任务逻辑
return 42; // 返回一个整数结果
}
};
future<integer> future = executor.submit(task);
try {
integer result = future.get();
system.out.println("线程返回值为:" + result);
} catch (exception e) {
e.printstacktrace();
}
executor.shutdown();
}
}在上面的示例中,我们创建了一个callable匿名类来实现具体的任务逻辑,然后将其提交给线程池进行处理。通过future的get()方法可以获取到线程的返回值。
使用completionservice
除了上面的方法,还可以使用completionservice来更加灵活地实现带返回值的线程处理,下面是一个示例代码:
import java.util.concurrent.callable;
import java.util.concurrent.completionservice;
import java.util.concurrent.executorservice;
import java.util.concurrent.executors;
import java.util.concurrent.future;
public class threadpoolwithreturnvalueexample {
public static void main(string[] args) throws exception {
executorservice executor = executors.newfixedthreadpool(1);
completionservice<integer> completionservice = new executorcompletionservice<>(executor);
callable<integer> task = new callable<integer>() {
@override
public integer call() throws exception {
// 在这里编写具体的任务逻辑
return 42; // 返回一个整数结果
}
};
completionservice.submit(task);
future<integer> future = completionservice.take();
integer result = future.get();
system.out.println("线程返回值为:" + result);
executor.shutdown();
}
}在这个示例中,我们使用了completionservice来管理任务的执行和获取返回值,通过take()方法获取最先完成的任务结果。 通过以上方法,我们可以实现在java中使用线程池带返回值的方式方法,更好地控制和处理多线程任务,并获取线程处理的结果。希望本文对您有所帮助。
会遇到需要处理大量数据的情况,使用线程池可以提高数据处理的效率。下面是一个示例场景:假设我们有一个包含大量任务的列表,每个任务需要处理一条数据,并返回处理结果。我们可以利用线程池来同时处理这些任务,最后获取结果并进行统计。
import java.util.arraylist;
import java.util.list;
import java.util.random;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class threadpoolbatchdataprocessing {
public static void main(string[] args) {
// 模拟生成大量任务数据
list<string> datalist = generatedatalist(100);
// 创建线程池
executorservice executor = executors.newfixedthreadpool(5);
// 定义任务列表
list<callable<integer>> tasks = new arraylist<>();
for (string data : datalist) {
tasks.add(() -> {
// 模拟数据处理,这里使用随机数表示处理结果
random random = new random();
return random.nextint(100);
});
}
// 批量提交任务
list<future<integer>> futures;
try {
futures = executor.invokeall(tasks);
} catch (interruptedexception e) {
e.printstacktrace();
return;
}
int totalresult = 0;
for (future<integer> future : futures) {
try {
totalresult += future.get();
} catch (interruptedexception | executionexception e) {
e.printstacktrace();
}
}
system.out.println("所有任务处理完成,结果总和为:" + totalresult);
// 关闭线程池
executor.shutdown();
}
// 模拟生成大量数据的方法
private static list<string> generatedatalist(int size) {
list<string> datalist = new arraylist<>();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
datalist.add("data-" + i);
}
return datalist;
}
}在上述示例中,我们模拟了一个需要处理大量数据的场景,使用线程池并行处理任务并获取处理结果,在最后统计所有任务的处理结果。这种场景可以帮助提高数据处理的效率,特别是对于大规模数据的处理。
线程池是一种管理和复用线程的机制,它可以在程序运行时创建一定数量的线程,并且在有任务到来时分配线程执行任务,执行完毕后将线程返回线程池以备重用,从而避免频繁地创建和销毁线程,提高了线程的利用率和系统的性能。 下面是线程池的一些重要特点和优点:
- 重用线程: 线程池会在内部维护一定数量的线程,这些线程可以被重复利用,而不是每次执行任务都要创建新线程,减少了线程创建和销毁的开销。
- 控制最大并发数: 线程池可以限制可以同时执行的线程数量,可以避免因为线程过多导致系统资源耗尽的问题。
- 管理线程: 线程池可以对线程的生命周期进行管理,包括线程的创建、重用、销毁等操作,让线程的操作更加可控。
- 提高响应速度: 线程池可以让任务立即执行,而不需要等待线程的创建,提高了任务的响应速度。
- 降低系统开销: 使用线程池可以有效控制系统中线程的数量,避免线程爆炸式增长,从而减少了系统资源的开销。 常见的线程池类型包括:fixedthreadpool(固定大小线程池)、cachedthreadpool(缓存线程池)、singlethreadpool(单线程池)和 scheduledthreadpool(定时任务线程池)等。
拓展:java多线程带返回值的方式方法
java利用线程池带有返回值的方式,大体逻辑批量处理大量数据,启用线程池,处理完成后将所有的返回内容进行组装拼接
废话不多说开始看代码,重点敲黑板:
1.threadpoolexecutor 线程池创建
2.countdownlatch 同步工具类,让主线程一直等待,直到子线程执行完后再执行

3.listret 用于接收多线程返回值
方式一
使用线程池
// 创建线程池
threadpoolexecutor executor = new threadpoolexecutor(coresnumber * 2, coresnumber * 2 + 1, 1000, timeunit.minutes, new linkedblockingdeque<>());
/*创建list用来接收多线程返回的内容,泛型里面可以自定义,string或者对象亦或者其他类型*/
list<map<string, object>> listret = new arraylist<>();
// 同步工具类,让主线程一直等待,直到子线程执行完后再执行
countdownlatch downlatch = new countdownlatch(partition.size());
// 循环任务的list
for (list<string> stringlist : partition) {
// 启用开启多个线程
executor.execute(new runnable() {
@override
public void run() {
try {
// 开始调用具体业务代码
map<string, object> mapret = pmptargetpriceservice.targetpricethreadtask(stringlist, initiatetasktype, username);
listret.add(mapret);
} catch (exception e) {
logger.error("循环开启线多线程报错,调用下游系统出现错误,异常:" + e);
} finally {
// 业务逻辑处理完毕,计数器减一【当前线程处理任务完毕,线程释放进入线程池,等待处理下一个任务】
downlatch.countdown();
}
}
});
}
// 主线程需要等待子任务线程执行完,结果汇总之后,主线程继续往下执行
try {
downlatch.await();
} catch (exception e) {
logger.error("等待超时", e);
throw new runtimeexception("系统处理超时,请稍后再试");
}
// 对返回组装的list进循环处理业务逻辑
for (map<string, object> esbresultplm1 : listret) {
// 从future对象上获取任务的返回值,并输出到控制台
// map esbresultplm1 = (map) f.get();
// todo 对我返回的多个map进行拼接
if (esbresultplm1.get("status").equals("fail")) {
failurenum = (int) esbresultplm1.get("failurenum");
failuremsg.append(esbresultplm1.get("msg"));
map.put("msg", failuremsg.tostring());
failurenumcount += failurenum;
} else {
successnum = (int) esbresultplm1.get("successnum");
successmsg.append(esbresultplm1.get("msg"));
map.put("msg", successmsg.tostring());
successnumcount += successnum;
}
}
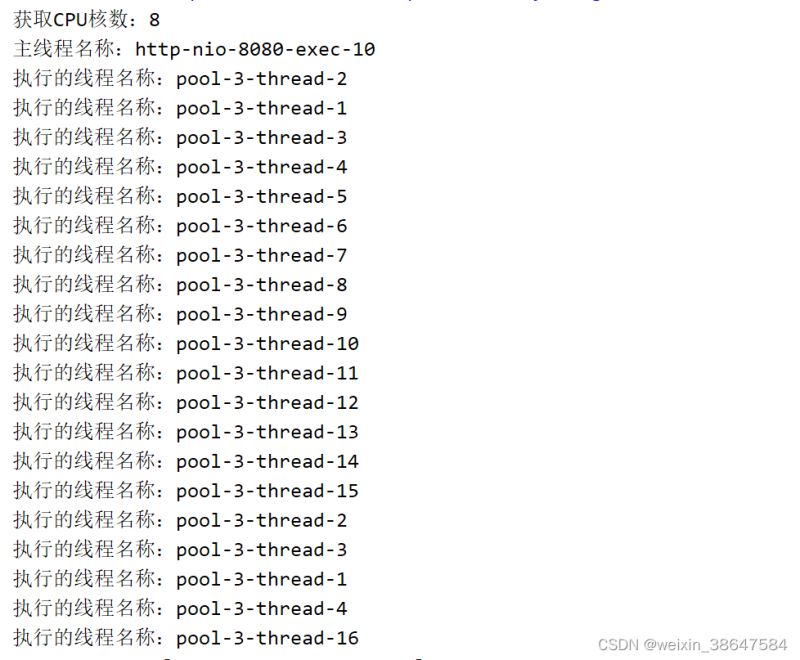
方法一得到的结果如下,使用线程池我这里是核数乘以2是核心线程16,最大17,所以这里最多是16个线程,而且他是无序的随机分配的

方式二
重点不用线程池使用@async注解,但是策略得有所调整,大体逻辑比如你待处理的数据有100条,你可以将这个list按10条为一个新的list,循环这个集合,在调用的实际方法上加@async注解,从而实现多线程加快循环也是可以的
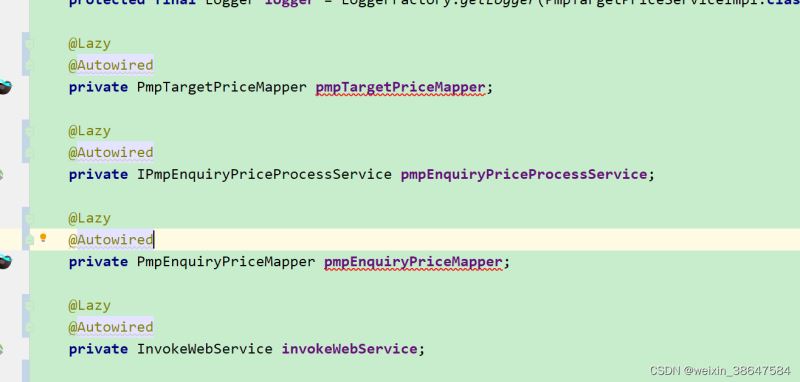
@async注意点,加了该注解的方法不能再同一个类,否则无效,其次有可能存在启动过程@async unsatisfieddependencyexception导致 springboot 无法启动问题解决,我这里是在报错的类里有注入service或者mapper的注解上加了@lazy注解就可以
// 将要发送的集合按10个一组进行重新组装
list<list<string>> partition = lists.partition(list, 10);
/*创建list用来接收多线程返回的内容,泛型里面可以自定义,string或者对象亦或者其他类型*/
list<map<string, object>> listret = new arraylist<>();
// 循环任务的list
for (list<string> stringlist : partition) {
// 开始调用具体业务代码
map<string, object> mapret = pmptargetpriceservice.targetpricethreadtask(stringlist, initiatetasktype, username);
listret.add(mapret);
}
// 对返回组装的list进循环处理业务逻辑
for (map<string, object> esbresultplm1 : listret) {
//对返回的内容进行业务处理
}
// 调用的方法,返回map
@async
public map<string, object> targetpricethreadtask(list<string> idlist, string initiatetasktype, string username) throws exception {
//具体的逻辑代码
map<string, object> map = new hashmap();
return map;
}
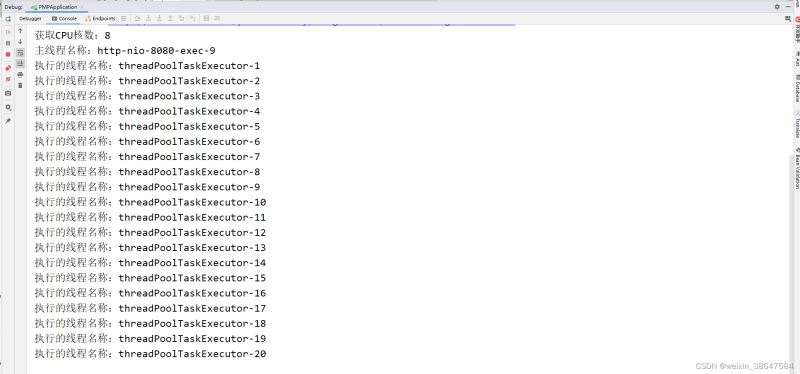
方法二的执行结果,循环多少次就启动了多少个子线程,所以这里的想法是先将原生数组按自定义个进行分配,如有200个任务,分给20个人,每人10个大概就是这样的思路

我的完整代码仅供参考,里面很多类都是我自己业务用到的,大家可以借鉴
public map<string, object> initiatetargetpricetask(pmptargetpricedto pmptargetpricedto) throws exception {
string username = securityutils.getusername();
map map = new hashmap();
list<string> list = arrays.aslist(pmptargetpricedto.getids());
// 将要发送的集合按10个一组进行重新组装
list<list<string>> partition = lists.partition(list, 10);
// 创建一个线程池
// 获取cpu核数
int coresnumber = runtime.getruntime().availableprocessors();
system.out.println("获取cpu核数:" + coresnumber);
// 创建线程池
threadpoolexecutor executor = new threadpoolexecutor(coresnumber * 2, coresnumber * 2 + 1, 1000, timeunit.minutes, new linkedblockingdeque<>());
// 获取任务发起类型字段
string initiatetasktype = pmptargetpricedto.getinitiatetasktype();
/*创建list用来接收多线程返回的内容,泛型里面可以自定义,string或者对象亦或者其他类型*/
list<map<string, object>> listret = new arraylist<>();
// 同步工具类,让主线程一直等待,直到子线程执行完后再执行
countdownlatch downlatch = new countdownlatch(partition.size());
// 循环任务的list
for (list<string> stringlist : partition) {
// 启用开启多个线程
executor.execute(new runnable() {
@override
public void run() {
try {
// 开始调用具体业务代码
map<string, object> mapret = pmptargetpriceservice.targetpricethreadtask(stringlist, initiatetasktype, username);
listret.add(mapret);
} catch (exception e) {
logger.error("循环开启线多线程报错,调用下游系统出现错误,异常:" + e);
} finally {
// 业务逻辑处理完毕,计数器减一【当前线程处理任务完毕,线程释放进入线程池,等待处理下一个任务】
downlatch.countdown();
}
}
});
}
// 主线程需要等待子任务线程执行完,结果汇总之后,主线程继续往下执行
try {
downlatch.await();
} catch (exception e) {
logger.error("等待超时", e);
throw new runtimeexception("系统处理超时,请稍后再试");
}
// 关闭线程池
executor.shutdown();
// 获取所有并发任务的运行结果
stringbuilder successmsg = new stringbuilder();
stringbuilder failuremsg = new stringbuilder();
int failurenum;
int successnum;
int failurenumcount = 0;
int successnumcount = 0;
for (map<string, object> esbresultplm1 : listret) {
// 从future对象上获取任务的返回值,并输出到控制台
// map esbresultplm1 = (map) f.get();
// todo 对我返回的多个map进行拼接
if (esbresultplm1.get("status").equals("fail")) {
failurenum = (int) esbresultplm1.get("failurenum");
failuremsg.append(esbresultplm1.get("msg"));
map.put("msg", failuremsg.tostring());
failurenumcount += failurenum;
} else {
successnum = (int) esbresultplm1.get("successnum");
successmsg.append(esbresultplm1.get("msg"));
map.put("msg", successmsg.tostring());
successnumcount += successnum;
}
}
// todo 对最终的结果进行组装
if (failurenumcount > 0) {
failuremsg.insert(0, "很抱歉,发起任务存在失败!共发起 " + list.size() + "条数据,其中有" + failurenumcount + " 条数据格式不正确,错误如下:");
map.put("status", "fail");
map.put("msg", failuremsg.tostring());
} else {
successmsg.insert(0, "恭喜您,数据已全部发起成功!共 " + successnumcount + " 条");
map.put("status", "success");
map.put("msg", successmsg.tostring());
}
return map;
}
// 调用的逻辑处理方法
public map<string, object> targetpricethreadtask(list<string> idlist, string initiatetasktype, string username) throws exception {
// 发起目标价任务
int successnum = 0;
int failurenum = 0;
stringbuilder successmsg = new stringbuilder();
stringbuilder failuremsg = new stringbuilder();
stringbuffer nosubunitmaterialcode = new stringbuffer(); // 子组不存在的物料号合集
stringbuffer nosubunit = new stringbuffer(); // 没有子组的子组号合集
map<string, object> map = new hashmap();
for (string id : idlist) {
pmptargetprice pmptargetprice = pmptargetpricemapper.selectpmptargetpricebyid(id);
sysapirequestlog sysapirequestlog = new sysapirequestlog();
sysapirequestlog.setrequestmethod("手动发起目标价任务");
sysapirequestlog.setrequestdata("物料号:" + pmptargetprice.getmaterialcode());
//查询是否发起流程,
if (pmptargetprice.getisfqlc().equals("1")) {
failurenum++;
string msg = "<br/>物料号:" + pmptargetprice.getmaterialcode() + "、此物料已经发起过流程,请核实!";
failuremsg.append(msg);
continue;
}
pmptargetpriceprocess targetpriceprocess = new pmptargetpriceprocess();
// 请求plm接口
map invokegetplm = invokewebservice.getinvokegetplm(pmptargetprice.getmaterialcode());
targetpriceprocess.setsouce("手动发起"); // 来源(手动发起)
targetpriceprocess.settasksponsor(username); // 设置发起人
targetpriceprocess.setmaterialstatus("0"); // 状态
targetpriceprocess.setinitiatetasktype(initiatetasktype); // 设置手工发起任务类型
if (null != invokegetplm.get("number").tostring()) {
targetpriceprocess.setmaterialcode(invokegetplm.get("number").tostring()); // 物料编号
}
if (null != invokegetplm.get("name").tostring()) {
targetpriceprocess.setmaterialname(invokegetplm.get("name").tostring()); // 物料名称
}
if (null != invokegetplm.get("phase").tostring()) {
targetpriceprocess.setstage(invokegetplm.get("phase").tostring());//阶段
}
if (null != invokegetplm.get("version").tostring()) {
targetpriceprocess.setversionno(invokegetplm.get("version").tostring()); // 大版本
}
if (null != invokegetplm.get("state").tostring()) {
targetpriceprocess.setmaterialstatus(invokegetplm.get("state").tostring()); // 状态
}
// 请求bom接口获取数据
map materialcode = invokewebservice.getesbbommaterialinfo(pmptargetprice.getmaterialcode());
// 截取物料编码为子组号
string substring = pmptargetpriceprocessservice.getblockcode(pmptargetprice.getmaterialcode());
pmptargetrule targetrule = new pmptargetrule();
pmptargetrule pmptargetrule;
string usercode = "";
// 判断bom是否有返回,有返回表示有路线,无返回表示无路线
if (null != materialcode) {
//根据物料编号截取的子组取目标规则表pmp_target_rule中查
targetrule.setsongroup(substring);
targetrule.setisroute("1");
pmptargetrule = pmptargetruleservice.selectpmptargetrulebysongroup(targetrule);
// 判断<pmptargetrule>子组配置是否存在,如根据子组查询不存在则设置为特殊子组
if (!optional.ofnullable(pmptargetrule).ispresent()) {
targetrule.setsongroup("特殊件无法获取");
targetrule.setisroute("1");
pmptargetrule = pmptargetruleservice.selectpmptargetrulebysongroup(targetrule);
}
/**
* 1.一级制造、一级装配和采购制造均为空时生成任务;
* 2.一级制造、一级装配和采购制造均有值时生成任务;
* 3.一级制造、一级装配有值,采购制造为空时,不生成任务。但要判定一级制造和一级装配均不含cg时为自制件,
* 不生成任务,但返回plm为s,提示“一级制造和一级装配均不含cg,为自制件,不生成任务”,
* 其他情况返回plm为e并提示“非自制件,bom采购制造路线待维护,请稍后发起定价任务”。
*/
string mfmrtg = ""; // 一级制造
string mfartg = ""; // 一级装配
if (stringutils.isnotblank(materialcode.get("mfmrtg").tostring())
&& stringutils.isnotblank(materialcode.get("mfartg").tostring())
) {
mfmrtg = materialcode.get("mfmrtg").tostring(); // 一级制造
mfartg = materialcode.get("mfartg").tostring(); // 一级装配
} else {
failurenum++;
logger.error("物料号:" + pmptargetprice.getmaterialcode() + "获取bom信息,一级制造或一级装配为null,发起任务失败!");
string msg = "<br/>物料号:" + pmptargetprice.getmaterialcode() + "、获取bom信息,一级制造或一级装配为null,发起任务失败! ";
failuremsg.append(msg);
sysapirequestlog.setresponsestatus(esbresult.ret_status_error);
sysapirequestlog.seterrorlog("手动发起目标价任务,失败原因:根据物料号获取bom信息,一级制造或一级装配为null,发起任务失败");
apirequestlogservice.insertsysapirequestlog(sysapirequestlog);
continue;
}
// if (stringutils.isnotblank(materialcode.get("mfmrtg").tostring())) {
// targetpriceprocess.setonelevelmake(materialcode.get("mfmrtg").tostring()); // 一级制造
// }
// if (stringutils.isnotblank(materialcode.get("mfartg").tostring())) {
// targetpriceprocess.setonelevelassembling(materialcode.get("mfartg").tostring()); // 一级装配
// }
targetpriceprocess.setonelevelmake(mfmrtg); // 一级制造
targetpriceprocess.setonelevelassembling(mfartg); // 一级装配
if (stringutils.isnotblank(materialcode.get("cfmrtg").tostring())) {
targetpriceprocess.setpurchasemake(materialcode.get("cfmrtg").tostring()); // 采购制造
//根据bom接口返回采购制造,如果是pt为研究院,否则为财务部
if (targetpriceprocess.getpurchasemake().equals("pt")) {
if (!stringutils.isempty(pmptargetrule.getyjydirectorcode())) {
targetpriceprocess.settaskpurchase(pmptargetrule.getyjydirectorcode()); // 指定填写目标价人:研究院
// 设置审核人
string[] splityjycode = pmptargetrule.getyjydirectorcode().split("/");
usercode = splityjycode[0];
} else {
failurenum++;
string msg = "<br/>物料号:" + pmptargetprice.getmaterialcode() + "、未获取到研究院相关人员,请核对! ";
failuremsg.append(msg);
logger.error("手动发起目标价任务-物料号-pt-yjy:" + pmptargetprice.getmaterialcode() + "设置目标价录入人时配置有误,路线为pt,根据子组查询但是研究院人员code是未维护发起任务失败!");
sysapirequestlog.setresponsestatus(esbresult.ret_status_error);
sysapirequestlog.seterrorlog("手动发起目标价任务失败,失败原因:路线为pt,根据子组查询但是研究院人员code是未维护发起任务失败");
apirequestlogservice.insertsysapirequestlog(sysapirequestlog);
nosubunitmaterialcode.append("物料号-pt-yjy:" + pmptargetprice.getmaterialcode() + "/");
nosubunit.append("子组号-pt-yjy:" + substring + "/");
continue;
}
} else {
if (!stringutils.isempty(pmptargetrule.getcwdirectorcode())) {
targetpriceprocess.settaskpurchase(pmptargetrule.getcwdirectorcode()); // 指定填写目标价人:财务部
// 设置审核人
string[] splitcwcode = pmptargetrule.getcwdirectorcode().split("/");
usercode = splitcwcode[0];
} else {
failurenum++;
string msg = "<br/>物料号:" + pmptargetprice.getmaterialcode() + "、未获取到财务部相关人员,请核对! ";
failuremsg.append(msg);
logger.error("手动发起目标价任务-物料号-非pt-cw:" + pmptargetprice.getmaterialcode() + "设置目标价录入人时配置有误,路线非pt,根据子组查询财务人员code是null发起任务失败!");
sysapirequestlog.setresponsestatus(esbresult.ret_status_error);
sysapirequestlog.seterrorlog("手动发起目标价任务,失败原因:根据子组查询财务人员code是null发起任务失败");
apirequestlogservice.insertsysapirequestlog(sysapirequestlog);
nosubunitmaterialcode.append("物料号-非pt-cw:" + pmptargetprice.getmaterialcode() + "/");
nosubunit.append("子组号-非pt-cw:" + substring + "/");
continue;
}
}
} else {
if (!mfmrtg.equals("cg") || !mfartg.equals("cg")) {
logger.error("物料号:" + pmptargetprice.getmaterialcode() + "一级制造和一级装配均不含cg,为自制件,不生成任务!");
failurenum++;
string msg = "<br/>物料号:" + pmptargetprice.getmaterialcode() + "、一级制造和一级装配均不含cg,为自制件,不生成任务! ";
failuremsg.append(msg);
sysapirequestlog.setresponsestatus(esbresult.ret_status_error);
sysapirequestlog.seterrorlog("手动发起目标价任务,失败原因:一级制造和一级装配均不含cg,为自制件,不生成任务!");
continue;
} else {
failurenum++;
string msg = "<br/>物料号:" + pmptargetprice.getmaterialcode() + "、bom采购制造路线待维护,请稍后发起定价任务!";
failuremsg.append(msg);
sysapirequestlog.setresponsestatus(esbresult.ret_status_error);
sysapirequestlog.seterrorlog("手动发起目标价任务,失败原因:bom采购制造路线待维护,请稍后发起定价任务!");
continue;
}
}
} else {
// 无路线
targetrule.setsongroup(substring);
targetrule.setisroute("0");
pmptargetrule = pmptargetruleservice.selectpmptargetrulebysongroup(targetrule);
/**
* 其他特殊件,无法获取子组,
* pt或无路线由研究院郑宇处理,
* 非pt的由财务部苏战波和赵伟处理
*/
if (!optional.ofnullable(pmptargetrule).ispresent()) {
targetrule.setsongroup("特殊件无法获取");
targetrule.setisroute("1");
pmptargetrule = pmptargetruleservice.selectpmptargetrulebysongroup(targetrule);
}
if (null != pmptargetrule && stringutils.isnotblank(pmptargetrule.getyjydirectorcode())) {
targetpriceprocess.settaskpurchase(pmptargetrule.getyjydirectorcode()); // 指定填写目标价人:研究院
string[] splityjycode = pmptargetrule.getyjydirectorcode().split("/");
usercode = splityjycode[0];
} else {
failurenum++;
string msg = "<br/>物料号:" + pmptargetprice.getmaterialcode() + "、未获取到研究院相关人员(无路线),请核对! ";
failuremsg.append(msg);
continue;
}
}
// todo 判断任务是研究院或者财务,设置审核人
// 查询研究院,财务或者无路线任务办理人,并获取他们的部门编码,向上寻找审核人
if (!usercode.equals("")) {
sysuser sysuser = userservice.selectuserbyusername(usercode);
if (stringutils.isnotnull(sysuser)) {
// 截取部门code
string deptcode = "";
if (sysuser.getdeptid().length() > 9) {
deptcode = sysuser.getdeptid().substring(0, 9);
} else {
deptcode = sysuser.getdeptid();
}
//查询审核配置表,查到审核人,插入目标价
pmptargetauditconfig pmptargetauditconfig = pmptargetauditconfigservice.selectpmptargetauditconfigbydeptcode(deptcode);
targetpriceprocess.setcheckname(pmptargetauditconfig.getauditor());
}
}
//已发起流程
pmptargetprice.setisfqlc("1");
targetpriceprocess.setstatus("0"); // 任务状态 0待定级发起
targetpriceprocess.setquejiatype("目标价"); // 缺价类型默认目标价
//添加任务发起人
targetpriceprocess.settasksponsor(username);
targetpriceprocess.setcreateby(username);
pmptargetpricemapper.updatepmptargetprice(pmptargetprice);
if (stringutils.isempty(targetpriceprocess.getmaterialname())) {
targetpriceprocess.setmaterialname(pmptargetprice.getmaterialname());
}
/**
* 查看当前物料号在目标价任务表中是否存在,最后的检查
*/
pmptargetpriceprocess priceprocess = new pmptargetpriceprocess();
priceprocess.setmaterialcode(targetpriceprocess.getmaterialcode());
priceprocess.setstatus("0,1,2,4");
pmptargetpriceprocess pmptargetpriceprocess = targetpriceprocessservice.selectpmptargetpriceprocessbyentity(priceprocess);
if (null != pmptargetpriceprocess) {
continue;
}
// 设置任务号
string newsno = dateutils.parsedatetostr("yyyymmdd", new date());
int count = targetpriceprocessservice.getfindtaskcount();
string format = string.format("%05d", count);
// 任务编号 mbjrw+年月日+流水号
targetpriceprocess.settasknumber("mbjrw" + newsno + format);
targetpriceprocessservice.insertpmptargetpriceprocess(targetpriceprocess);
successnum++;
}
if (failurenum > 0) {
// failuremsg.insert(0, "很抱歉,发起任务存在失败!共 " + failurenum + " 条数据格式不正确,错误如下:");
map.put("status", "fail");
map.put("msg", failuremsg.tostring());
map.put("failurenum", failurenum);
} else {
// successmsg.insert(0, "恭喜您,数据已全部发起成功!共 " + successnum + " 条");
map.put("status", "success");
map.put("msg", successmsg.tostring());
map.put("successnum", successnum);
}
logger.info("手动发起目标价任务结束!");
logger.info("手动发起目标价-物料号查找子组有误的物料统计:" + nosubunitmaterialcode.tostring());
logger.info("手动发起目标价-物料号查找子组有误的子组号统计:" + nosubunit.tostring());
return map;
}
总结方式一和方式二都能解决加快任务处理,处理时间都差不读多,大家可以挑选自己适合的方式,如有更好的方式或不对的点请指正,欢迎大家沟通交流,共同成长进步
到此这篇关于java线程池实现带返回值的方式方法的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关java线程池带返回值内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!






发表评论