我们在查询mysql数据时,查询某个字段的数剧是我们经常接触的,直接使用sql语句或者更方便的直接使用数据库的orm语句查询。但是如果需要查询某个json字段里面的某些数据,orm模型可能都无法达到效果,还不如直接使用sql语句进行查询来的直观。下面总结了一些sql语句查询json字段里面的值。
mysql版本是5.7,使用fastapi和tortoise-orm接口的方式返回查询到的响应结果。
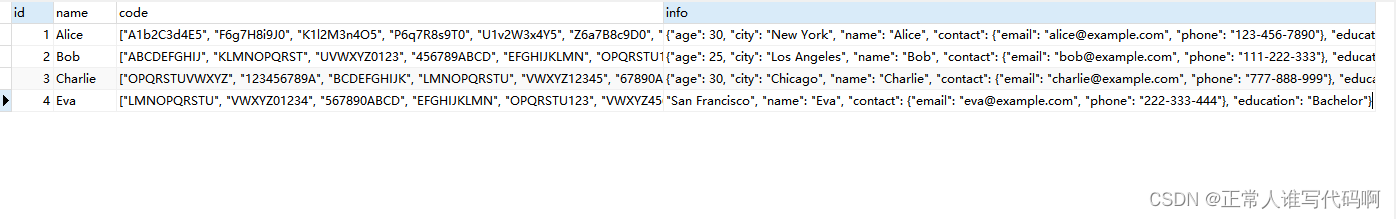
下面创建了一个用于测试的数据表。包括主键id,varchar类型的name,json类型的code(数组)和info(映射)。
例如:code数据结构:["a1b2c3d4e5", "f6g7h8i9j0", "k1l2m3n4o5", "p6q7r8s9t0", "u1v2w3x4y5", "z6a7b8c9d0", "e1f2g3h4i5", "j6k7l8m9n0", "o1p2q3r4s5", "t6u7v8w9x0", "y1z2a3b4c5", "d6e7f8g9h0", "i1j2k3l4m5", "n6o7p8q9r0", "s1t2u3v4w5", "x6y7z8a9b0"]
info数据结构:{"age": 30, "city": "new york", "name": "alice", "contact": {"email": "alice@example.com", "phone": "123-456-7890"}, "education": "bachelor"}
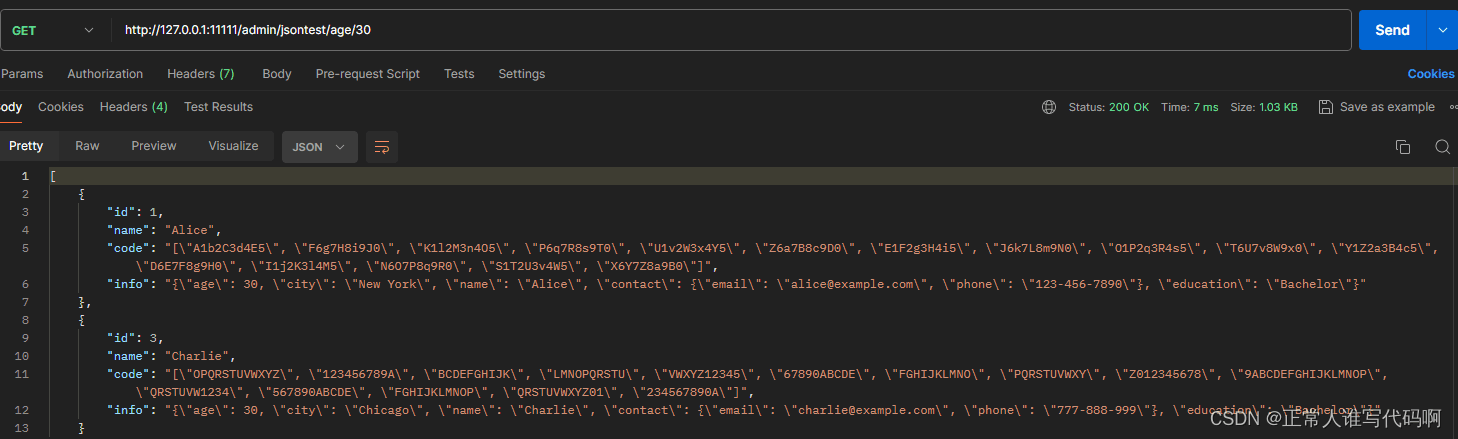
1、查询info中age=30的数据
@router.get('/jsontest/{keyword}/{value}', description="获取mysql的json值测试")
async def search_(keyword: str, value: str):
query = f"select * from jsontest where json_contains(info->'$.{keyword}','{value}')"
conn = tortoise.tortoise.get_connection("default")
try:
_, index_result = await conn.execute_query(query)
except exception as ex:
error_msg = f"error:{ex.__class__.__name__}-{str(ex)}"
log_it(error_msg, level=logging.error)
return jsonresponse(status_code=status.http_500_internal_server_error, content=error_msg)
finally:
await conn.close()
return jsonresponse(
status_code=status.http_200_ok,
content=index_result
)select * from jsontest where json_contains(info->'$.age','30')
查询结果
为了避免重复代码冗余,后续的查询直接写sql语句了。可以通过更改api接口传参,构造query语句达到一样的效果。
2、查询code数组中包含"anopqrstu8"的数据
select * from jsontest where json_contains(code,'"anopqrstu8"')
3、查询info中city是new york并且code中包含awxyz01239的数据
select * from jsontest where json_contains(info->'$.city','"new york"') and json_contains(code,'"awxyz01239"')
4、查询info中包含city和age的数据,指定的是"one"表示只需包含任何一个路径即可,"all"表示需要包含所有指定路径
select * from jsontest where json_contains_path(info, 'one', '$.city', '$.age'); select * from jsontest where json_contains_path(info, 'all', '$.city', '$.contact.email');
5、查询alice info数据中的city,age,以及contact里面的email。下面两种效果是一样的,只不过使用json_extract返回的是一个字段,而->这种方法返回的是拆分开的字段
select json_extract(info, '$.city','$.age','$.contact.email') as name from jsontest where name = 'alice'; select info->'$.city',info->'$.age',info->'$.contact.email' from jsontest where name = 'alice'
6、查询alice code数组中前三个数据。数组类型的json只能通过索引获取值,如果想获取全部则改成'$[*]'即可。下面两种效果是一样的,只不过使用json_extract返回的是一个字段,而->这种方法返回的是拆分开的字段
select json_extract(code, '$[0]','$[1]','$[2]') as res from jsontest where name = 'alice'; select code->'$[0]',code->'$[1]',code->'$[2]' from jsontest where name = 'alice'; # 获取数组里面的所有数据 select json_extract(code, '$[*]') as res from jsontest where name = 'alice'; select code->'$[*]' from jsontest where name = 'alice';
7、使用json_unquote去除 json 字符串的引号。上面返回的数据带有原始json的引号,这一点有时对结果处理特别不友好,可以使用json_unquote进行处理
select json_unquote(json_extract(info, '$.contact.email')) as email from jsontest where name = 'alice';
8、提取info映射里面的所有key,也可以查询嵌套字典里面的所有key
select json_keys(info) as k from jsontest where name = 'alice'; #查询嵌套字典的key select json_keys(info->'$.contact') as k from jsontest where name = 'alice';
9、获取code数组和字典info的长度
select json_length(code, '$') as count from jsontest where name = 'alice' select json_length(info, '$') as count from jsontest where name = 'alice' # 获取嵌套字典的长度 select json_length(info->'$.contact') as count from jsontest where name = 'alice'
10、搜索数组和字典里面的值
# 搜索字典中的value,one_or_all: 指定搜索所有匹配项还是仅找到的第一个匹配项 select json_search(info, 'all', "new york") as search_result from jsontest # 搜索数组中的值,%a%模糊搜索含有a的数据 select json_search(code, 'all', '%a%') as search_result from jsontest
到此这篇关于mysql中json字段的值的实现示例的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关mysql json字段值内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!





发表评论