问题描述
线上环境异步任务全部未执行,代码没有抛出任何异常和提示,cpu、内存都很正常,基本没有波动,gc也没啥异常的。
问题原因
经定位是异步由于嵌套异步任务使用了future.get()方法导致的程序阻塞
手动使用线程池示例
public class futureblocktest {
public static void main(string[] args) {
// 为了模拟我这里只存创建一个工作线程
executorservice fixedthreadpool = executors.newfixedthreadpool(1);
// 第一层异步任务
runnable runnable = () -> {
system.out.println(thread.currentthread().getname() + "-main-thread");
// 第二层异步任务(嵌套任务)
futuretask<long> futuretask = new futuretask<>(() -> {
system.out.println(thread.currentthread().getname() + "-child-thread");
return 10l;
});
fixedthreadpool.execute(futuretask);
system.out.println("子任务提交完毕");
// 获取子线程的返回值
try {
system.out.println(futuretask.get());
} catch (exception e) {
e.printstacktrace();
}
};
// 提交主线
fixedthreadpool.submit(runnable);
}
}
执行上诉示例后输出
pool-1-thread-1-main-thread
子任务提交完毕
然后程序假死。
使用@async示例
// 程序入口
@controller
public class asynccontroller {
@autowired
private mainthreadservice mainthreadservice;
@getmapping("/")
public string helloworld() throws exception {
mainthreadservice.asyncmethod();
return "hello world";
}
}
// 主任务代码
@service
public class mainthreadservice {
@autowired
private childthreadservice childthreadservice;
@async("asyncthreadpool")
public void asyncmethod() throws exception {
// 主任务开始
// todo
// 开启子任务
future<long> longfuture = childthreadservice.asyncmethod();
// 子任务阻塞子任务
longfuture.get();
// todo
}
}
// 子任务示例
@service
public class childthreadservice {
@async("asyncthreadpool")
public future<long> asyncmethod() throws exception {
// 子任务执行
thread.sleep(1000);
// 返回异步结果
return new asyncresult<>(10l);
}
}定位
1.通过jps和 jstack命令定位
jstack 81173 | grep 'waiting' -a 15
admin@wangyuhao spring-boot-student % jstack 81173 | grep 'waiting' -a 15
java.lang.thread.state: waiting (parking)
at sun.misc.unsafe.park(native method)
- parking to wait for <0x000000076b541b38> (a java.util.concurrent.futuretask)
at java.util.concurrent.locks.locksupport.park(locksupport.java:175)
at java.util.concurrent.futuretask.awaitdone(futuretask.java:429)
at java.util.concurrent.futuretask.get(futuretask.java:191)
at com.xiaolyuh.futureblocktest.lambda$main$1(futureblocktest.java:28)
at com.xiaolyuh.futureblocktest$$lambda$1/885951223.run(unknown source)
at java.util.concurrent.executors$runnableadapter.call(executors.java:511)
at java.util.concurrent.futuretask.run$$$capture(futuretask.java:266)
at java.util.concurrent.futuretask.run(futuretask.java)
at java.util.concurrent.threadpoolexecutor.runworker(threadpoolexecutor.java:1149)
at java.util.concurrent.threadpoolexecutor$worker.run(threadpoolexecutor.java:624)
at java.lang.thread.run(thread.java:748)
可以定位到是futuretask.get()发生了阻塞。
2.也可以使用 arthas定位

| 状态 | 场景 | 原因 |
|---|---|---|
| blocked | 线程处于blocked状态的场景 | 1.当前线程在等待一个monitor lock,比如synchronizedhuo或者lock。 |
| waiting | 线程处于waiting状态的场景 | 1. 调用object对象的wait方法,但没有指定超时值。 2. 调用thread对象的join方法,但没有指定超时值。 3. 调用locksupport对象的park方法。 |
| timed_waiting | 线程处于timed_waiting状态的场景 | 1. 调用thread.sleep方法。 2. 调用object对象的wait方法,指定超时值。 3. 调用thread对象的join方法,指定超时值。 4. 调用locksupport对象的parknanos方法。 5. 调用locksupport对象的parkuntil方法。 |
问题分析
线程池内部结构
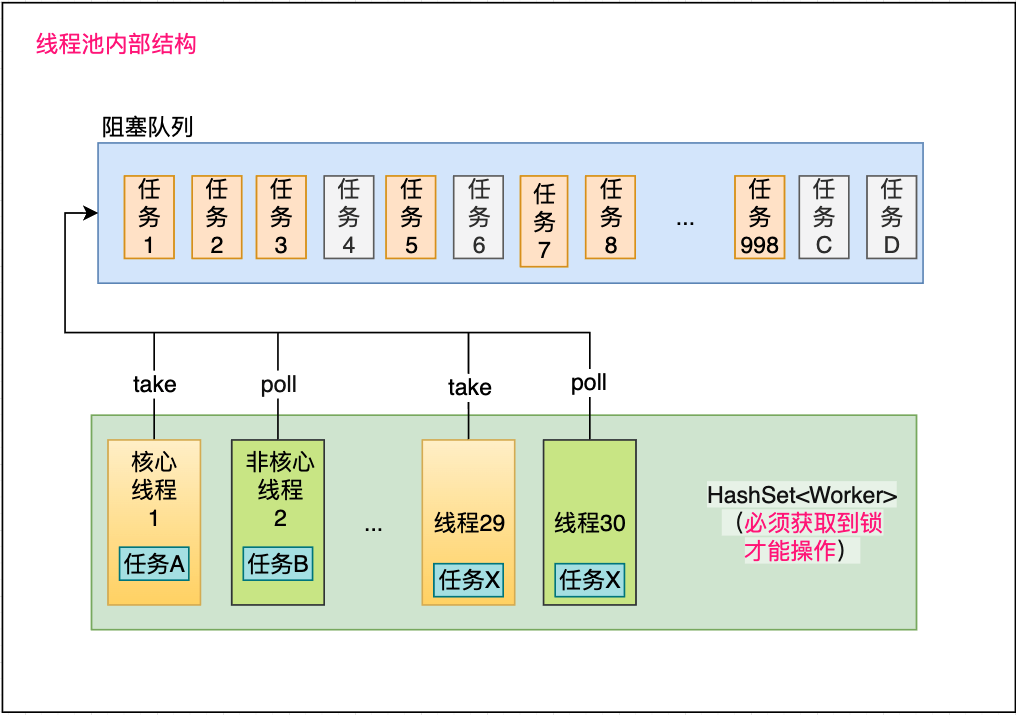
当线程1中的任务a嵌套了任务c后,任务c被放到了阻塞队列,这时线程1就被柱塞了,必须等到任务c执行完毕。
这时如果其他线程也发生相同清空,如线程2的任务b,他的嵌套任务d也被放入阻塞队列,这是线程2也会被阻塞。
如果这类任务比较多时就会将所有线程池的线程阻塞住。最后导致线程池假死,所有异步任务无法执行。
解决办法
- futuretask.get()必须加上超时时间,这样至少不会导致程序一直假死
- 不要使用嵌套的异步任务,或者嵌套任务不要获取子任务结果,不要阻塞主任务
- 将主任务和子任务的线程池拆分成两个线程池池,不要使用同一个线程池(推荐)
思考
我们程序代码使用的@async注解,也就是示例二的代码。使用注解默认配置,那么spring会给所有任务分配单独线程,且线程不能重用,源码如下:
获取executor源码
org.springframework.aop.interceptor.asyncexecutioninterceptor#getdefaultexecutor
/**
* this implementation searches for a unique {@link org.springframework.core.task.taskexecutor}
* bean in the context, or for an {@link executor} bean named "taskexecutor" otherwise.
* if neither of the two is resolvable (e.g. if no {@code beanfactory} was configured at all),
* this implementation falls back to a newly created {@link simpleasynctaskexecutor} instance
* for local use if no default could be found.
* @see #default_task_executor_bean_name
*/
@override
protected executor getdefaultexecutor(beanfactory beanfactory) {
executor defaultexecutor = super.getdefaultexecutor(beanfactory);
return (defaultexecutor != null ? defaultexecutor : new simpleasynctaskexecutor());
}获取执行任务源码
org.springframework.core.task.simpleasynctaskexecutor#doexecute
/**
* template method for the actual execution of a task.
* <p>the default implementation creates a new thread and starts it.
* @param task the runnable to execute
* @see #setthreadfactory
* @see #createthread
* @see java.lang.thread#start()
*/
protected void doexecute(runnable task) {
thread thread = (this.threadfactory != null ? this.threadfactory.newthread(task) : createthread(task));
thread.start();
}我们可以发现默认执行@async注解的异步线程池,内部其实就没用线程池,它会给每一个任务创建一个新的线程,线程使用过后会销毁掉,线程不会重用。
- 那它将会带来一个问题,那就是异步任务过多就会不断创建线程,最终将系统资源耗尽。
- 这也是网络上大部分文章不推荐直接使用@async注解默认配置的原因。
我们需要思考的是,spring的设计这为什么要这样设计,这里有这么明显的问题,难道他们不知道吗,我理解这样设计的初衷可能就是为了避免上诉我们发现的任务嵌套问题,因为每个任务单独线程执行是不会发生上诉程序假死的情况的。
总结
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持代码网。




发表评论