这几天在自学socket网络编程时突然要用到文件和文本同时传输到服务器,
但是在网上找了半天页找不到具体的结局办法,最后在不断琢磨之下终于解决了这个问题,
在传输数据时使用的是java中的objectinputstream 和 objectoutputstream对象流,
这个流可以封装复杂的数据在网络中进行传输,
发送涉及到的类需要实现serializable接口,是一个标志接口,用于序列化的,没有任何的方法需要实现。
废话不多说,直接上代码
第一种方案
student类,用于封装数据进行传输和解析
public class student implements serializable {
private string username;
private string sex;
private byte[] file;
private string filename;
public string getusername() {
return username;
}
public void setusername(string username) {
this.username = username;
}
public string getsex() {
return sex;
}
public void setsex(string sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
public byte[] getfile() {
return file;
}
public void setfile(byte[] file) {
this.file = file;
}
public string getfilename() {
return filename;
}
public void setfilename(string filename) {
this.filename = filename;
}
@override
public string tostring() {
return "student{" +
"username='" + username + '\'' +
", sex='" + sex + '\'' +
", filename='" + filename + '\'' +
'}';
}
}客户端
public class clientsocket {
public static void main(string[] args) throws ioexception {
socket socket = new socket("127.0.0.1",9999);
// 获得socket输出字节流
outputstream os = socket.getoutputstream();
student student = new student();
student.setusername("765652244");
student.setsex("男");
// 获取文件地址
file file = new file("c:\\users\\网络杀手\\desktop\\image\\soft\\bg.png");
// 将文件名保存到student中
student.setfilename(file.getname());
// 获得文件字节输入流
fileinputstream fis = new fileinputstream(file);
// 将文件字节流保存至字节输出缓冲流
bytearrayoutputstream bos = new bytearrayoutputstream(fis.available());
byte[] b = new byte[1024];
int len = -1;
while((len = fis.read(b)) != -1) {
bos.write(b, 0, len);
}
// 将得到的文件字节转换为字节数组
student.setfile(bos.tobytearray());
// 将socket输出流进行转换
objectoutputstream oos =new objectoutputstream(os);
// 将对象输出流发送到服务器
oos.writeobject(student);
fis.close();
bos.close();
oos.flush();
oos.close();
system.out.println("发送成功");
}
}服务器
public class serversocketdome {
public static void main(string[] args) throws ioexception, classnotfoundexception {
serversocket serversocket = new serversocket(9999);
// 监听9999端口,等待客户端连接,如果没有连接,将会一直阻塞
socket accept = serversocket.accept();
// 获得数据输入流,
inputstream is = accept.getinputstream();
// 对数据输入流进行转换
objectinputstream ois = new objectinputstream(is);
// 将获得的数据转换为studen类
student o = (student)ois.readobject();
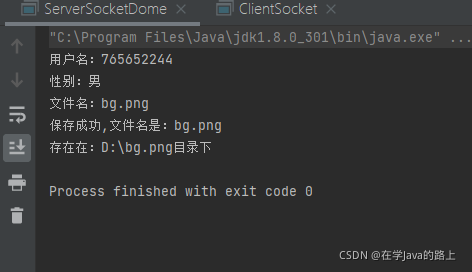
system.out.println("用户名:"+o.getusername()+"\n"+"性别:"+o.getsex());
system.out.println("文件名:"+o.getfilename());
// 将获得的文件保存至磁盘中
file file = new file("d:\\"+o.getfilename());
// 获得输出流,准备将内存中的数据写到磁盘
fileoutputstream fos = new fileoutputstream(file);
// 将student类中或的文件字节写入磁盘
fos.write(o.getfile());
fos.close();
serversocket.close();
accept.close();
is.close();
ois.close();
system.out.println("保存成功,文件名是:"+o.getfilename()+"\n存在在:"+file+"目录下");
}
}结果
第二种方案
不需要封装类,也不需要实现serializable接口
服务端
public class serversocketdome1 {
public static void main(string[] args) {
try {
serversocket serversocket = new serversocket(9999);
socket socket = serversocket.accept();
// 对象流
objectinputstream ois = new objectinputstream(socket.getinputstream());
// 读取文件名
string str = ois.readutf();
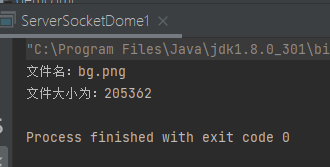
system.out.println("文件名:"+str);
// 读取文件大小
long l = ois.readlong();
system.out.println("文件大小为:"+l);
// 这是使用的是缓冲流,避免了文件大时内存溢出
bufferedoutputstream bos = new bufferedoutputstream(new fileoutputstream(new file("d:\\"+str)));
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024*1024];
int len = -1 ;
while ((len=ois.read(buffer))!=-1){
bos.write(buffer,0,len);
}
ois.close();
bos.close();
socket.close();
serversocket.close();
} catch (ioexception e) {
e.printstacktrace();
}
}
}
客户端
public class client1 {
public static void main(string[] args) {
try {
socket socket = new socket("127.0.0.1",9999);
outputstream os = socket.getoutputstream();
objectoutputstream oos = new objectoutputstream(os);
file file = new file("c:\\users\\网络杀手\\desktop\\image\\soft\\bg.png");
fileinputstream fis = new fileinputstream(file);
bufferedinputstream bis = new bufferedinputstream(fis);
// 写入文件名
oos.writeutf(file.getname());
// 获得文件大小
oos.writelong(file.length());
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024*1024];
int len =-1;
while ((len=bis.read(buffer))!=-1){
oos.write(buffer,0,len);
}
oos.flush();
os.close();
oos.close();
fis.close();
bis.close();
socket.close();
} catch (ioexception e) {
e.printstacktrace();
}
}
}结果
两种方案中明显是方案二要简便些,但是各有个的优点:
方案一中发送的数据需要封装,解析时候方便(可以将bytearrayoutputstream换成bufferedinputstream)如果是多个文件,对student类中的属性进行一下变更,就能够实现
第二种方案中需要使用gson数据封装之后发送和解析,对于负杂的数据时还是要进行封装之后才能发送,否则服务器不好解析。
总结
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持代码网。






发表评论