2023年还没有学习elasticsearch?,那么您将错过最强大、最通用的编程语言之一。
本文将介绍在elasticsearch对文档分别使用dsl语句和java high level rest clientapi来对文档进行操作。获取更多信息查看官网帮助文档

运行环境:
linux,docker
简介
elasticsearch是一个分布式的restful搜索和分析引擎。它是建立在lucene之上的,lucene是一个强大的全文搜索引擎。elasticsearch被设计为可伸缩、容错和易于使用。它被各种各样的组织使用,包括ebay、思cisco和spotify。
1.安装和启动elasticsearch和所需组件kibana
在docker中安装和配置elasticsearch和kibana版本控制在7.12.1,
相关配置的操作文档参考我另外一篇如何使用elasticsearch构建强大的搜索和分析应用程序(2023年最新es新手教程)目录1.2.1
1.1.docker中运行成功

1.2.访问linux的ip地址对应kibana的端口号5601
访问网页“linux的ip地址:5601/app/dev_tools#/console,kibana提供的可以控制es的控制台
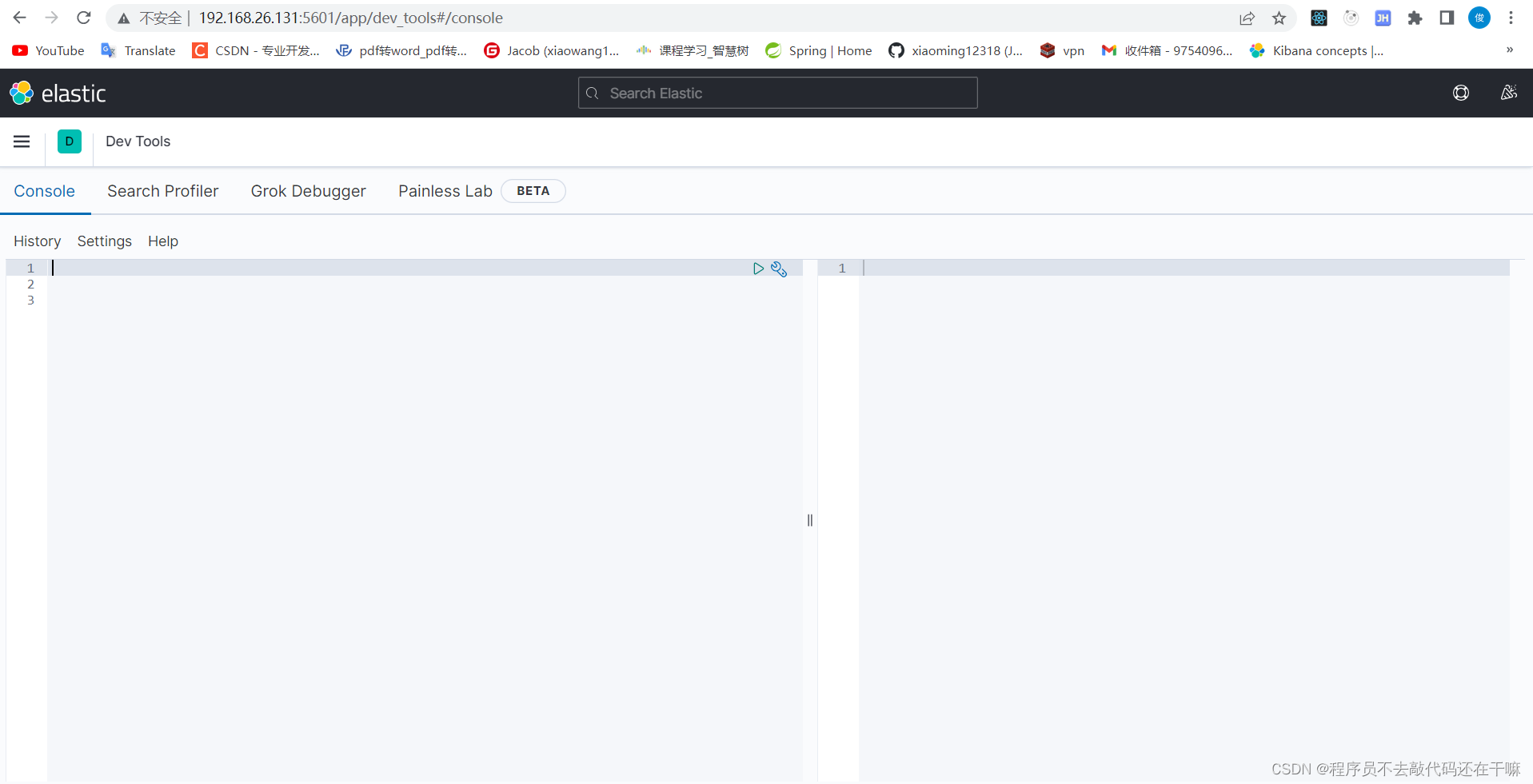
get /
get测试运行的到的信息和访问端口9200得到结果相同,则之前的配置文件生效,运行成功。
2.快速入门dsl语句和rest api的编写
在此之前也可以参考如何使用elasticsearch构建强大的搜索和分析应用程序(2023年最新es新手教程) 目录1.1.3 ,了解什么是索引?,什么是文档。
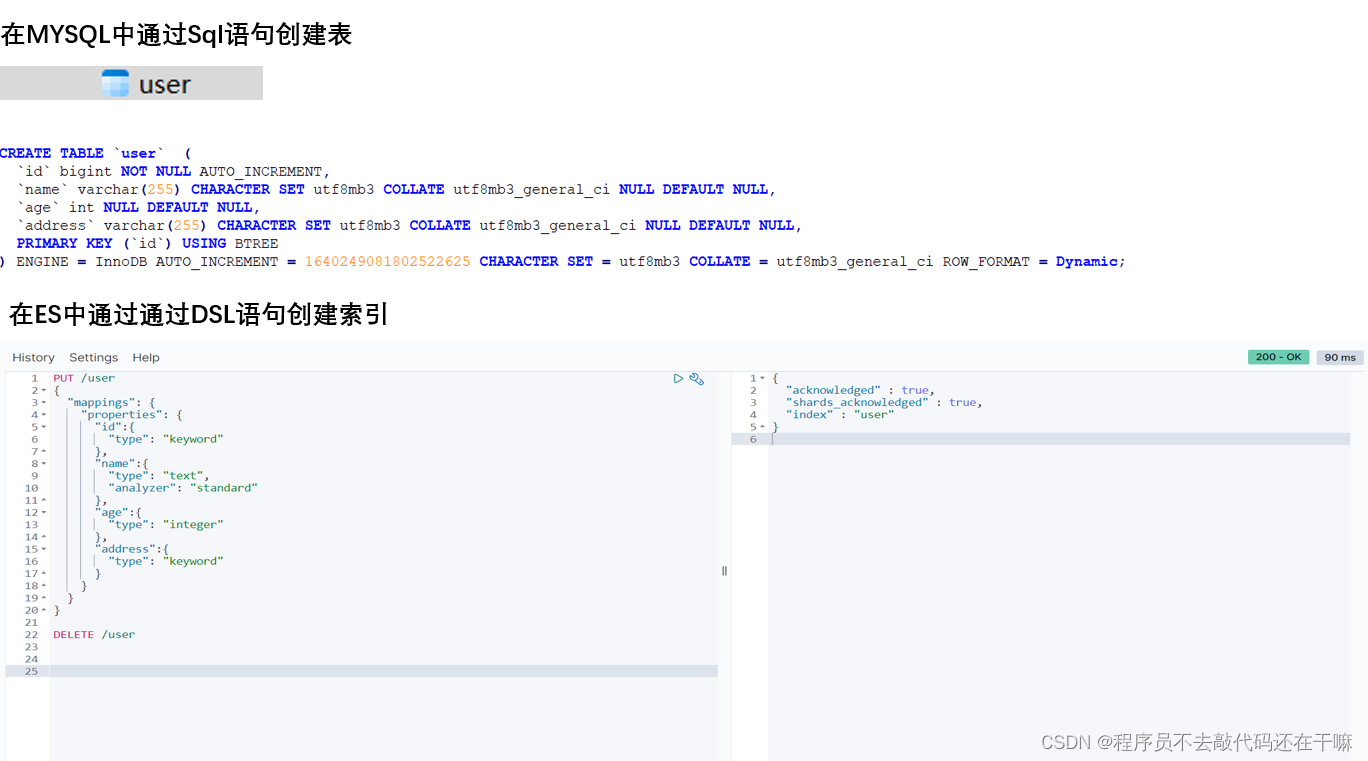
2.1.创建索引
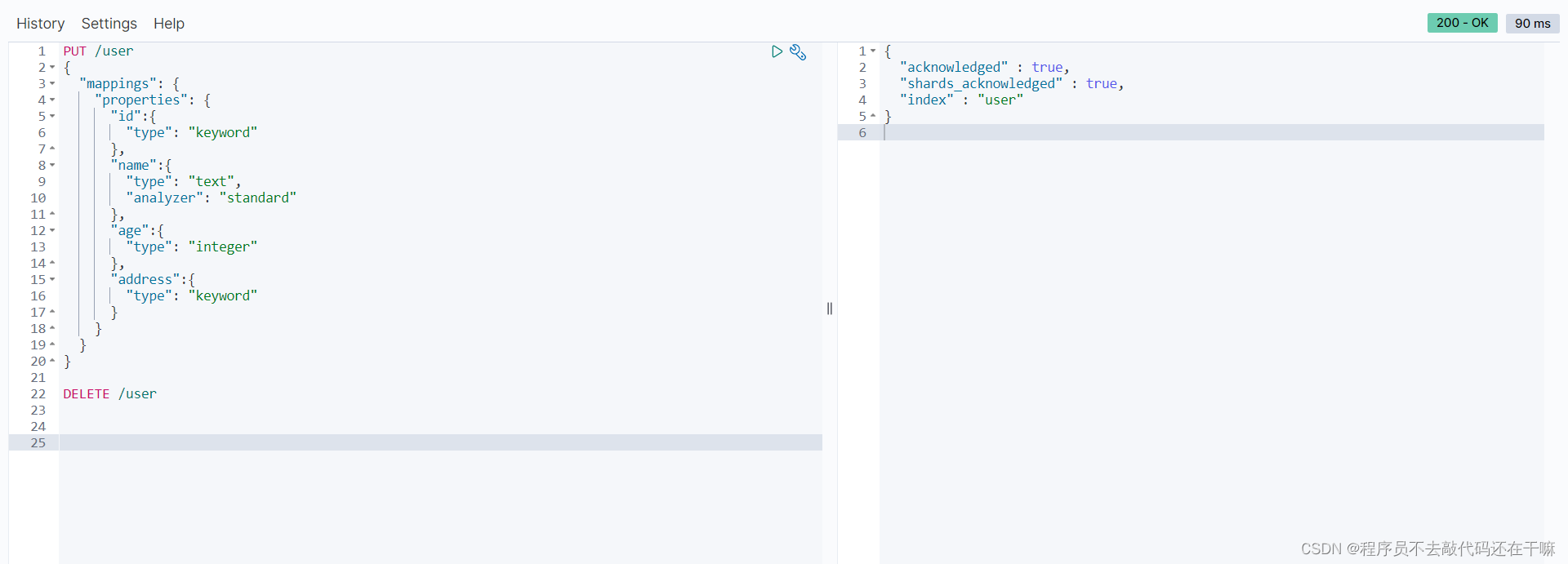
put /user
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"id":{
"type": "keyword"
},
"name":{
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "standard"
},
"age":{
"type": "integer"
},
"address":{
"type": "keyword"
}
}
}
}
得到以下结果
以数据库为例,一个表有数据结构,和字段。elasticsearch同样也有索引和文档,下表方便理解es的索引结构,当然本身这两个技术并没有什么关系,这里只是用mysql做例子方便理解。
| mysql | elasticsearch | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| table(table structure) | index | 索引,就是文档的集合,类似数据库的表 |
| row | document | 文档,就是一条条的数据,类似数据库中的行(row),文档都是json格式 |
| column | field(字段) | 字段,就是json文档中的字段,类似数据库的列 |
| schema | mapping | mapping是索引中文档的约束,列如字段类型约束。类似数据库的表结构 |
| sql | dsl | dsl是elasticsearch提供的json风格的请求语句,用来操作elasticsearch,实现crud |
2.2.dsl语句实现crud
dsl是elasticsearch提供的json风格的请求语句,用来操作elasticsearch,实现crud,dsl代表领域特定语言。在elasticsearch上下文中,dsl指的是一组工具和技术,这些工具和技术可以用一种更简洁、更富有表现力的方式与elasticsearch交互。
2.2.1.dsl_新增文档
给指定的数据流或索引添加json文档使其可搜索,如果索引和文档已经存在,则会更新文档。
| 请求方式 | 用法 |
|---|---|
| post | 创建文档 |
| put | 重写和创建文档 |
post /user/_doc/1
{
"id":1,
"name":"王五",
"age":19,
"address":"北京市海淀区颐和园路5号"
}
或者
put /user/_doc/1
{
"id":1,
"name":"王五",
"age":19,
"address":"北京市海淀区颐和园路5号"
}
结果图
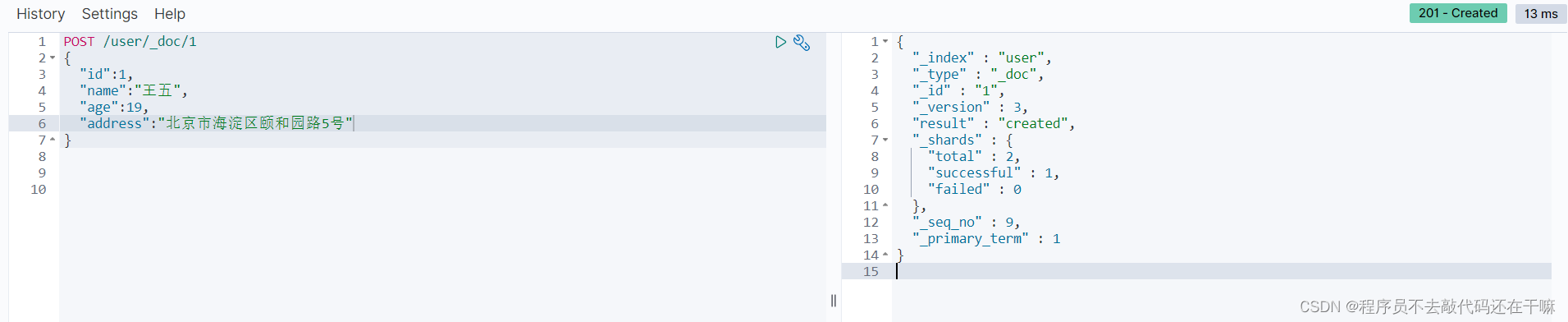
put效果相同
2.2.1.dsl_新增文档扩展
| 请求参数 | 在post中的用法 | 在put中的用法 |
|---|---|---|
| _doc | 在添加一个索引(index)不存在的文档时,es会自动创建索引并且当请求方式为post的时候文档允许省略id,es自动生成id的同时生成索引。2.2.1.演示1 | 在添加一个索引(index)不存在的文档时,es会自动创建索引并且当请求方式为put创建文档须指定id,es才会自动生成索引 |
| _create | 在添加一个索引(index)不存在的文档(document)时,es也会自动创建索引,但是两种都不允许省略id。2.2.1.演示2 |
post+_doc的请求格式,无id的情况下,可以看到创建es自动生成一个很复杂的id并且索引自动创建
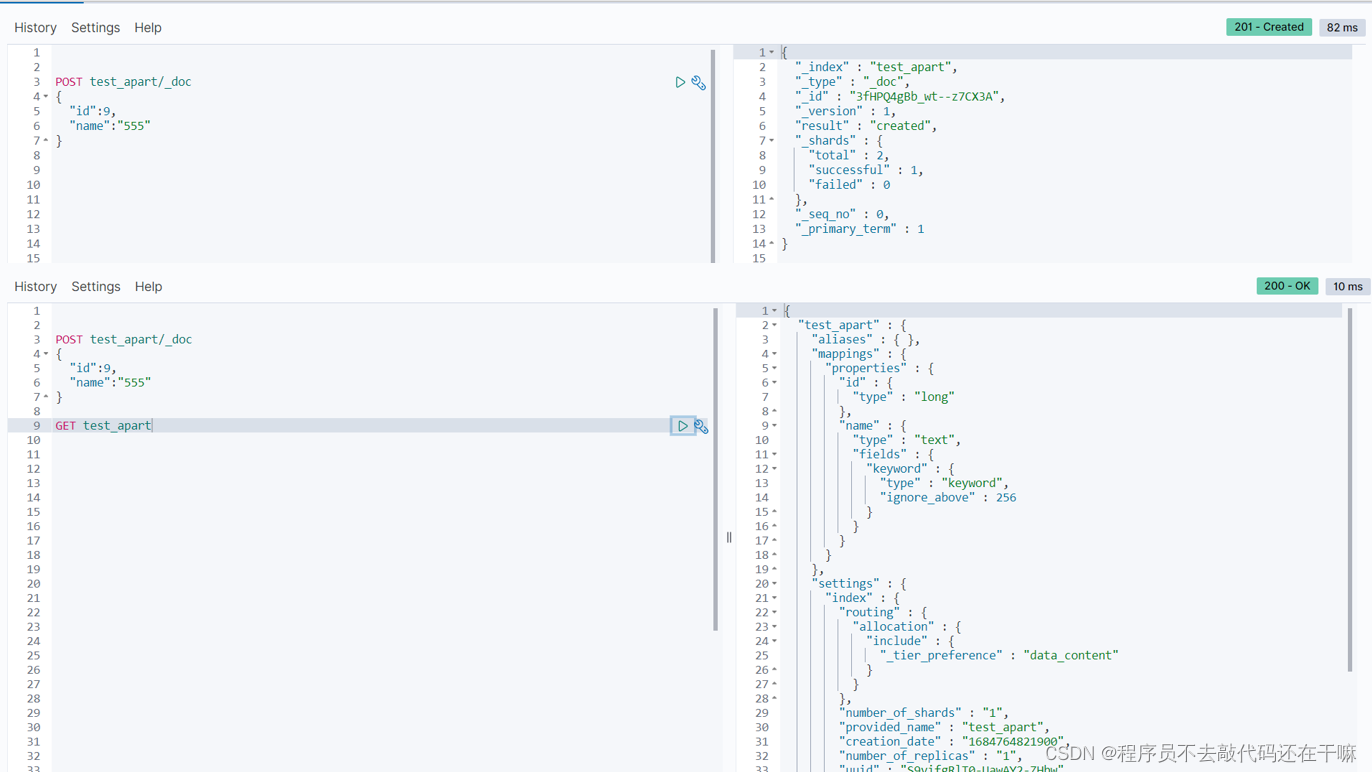
加上id之后响应的id为自定义的id,索引也是自动创建
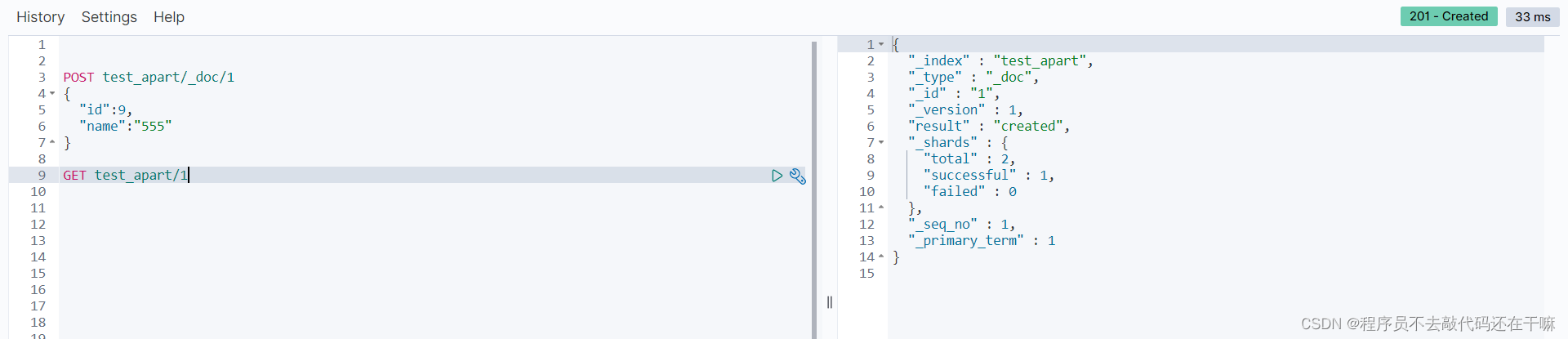
put+_doc的请求格式,无id的情况下,
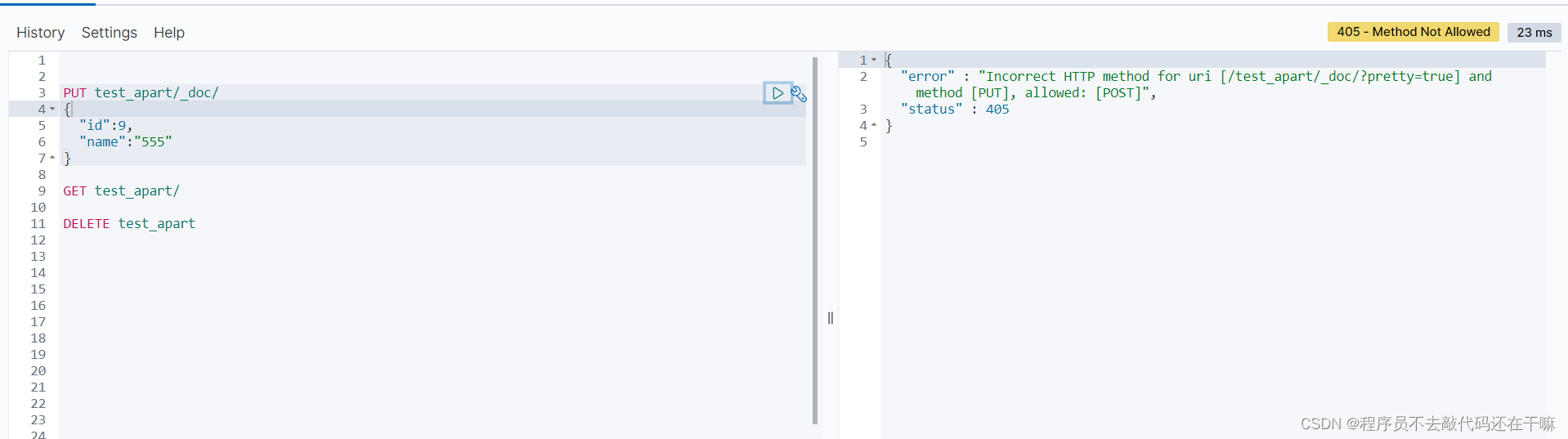
测试结果报错
当put携带id的时候,添加成功并且自动创建对应的索引结构
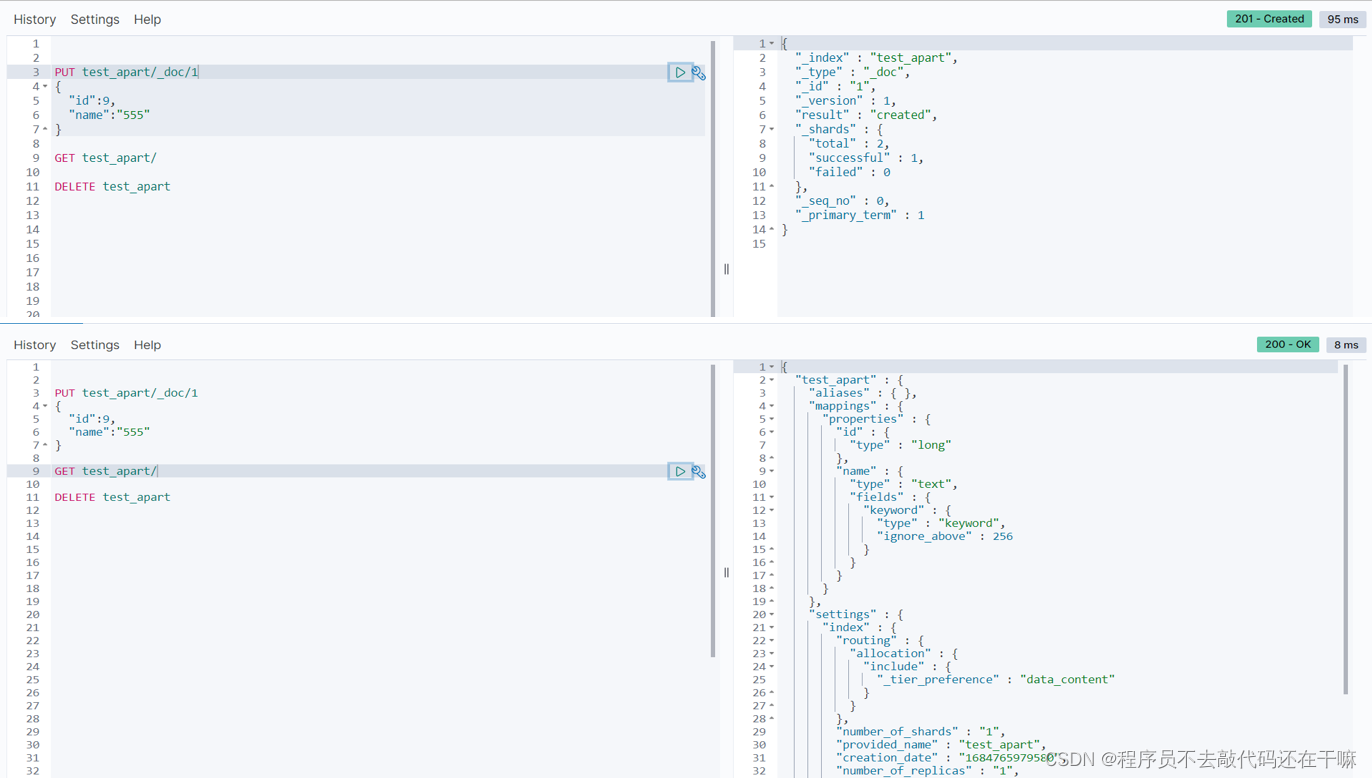
警告:索引名不能有大写字母
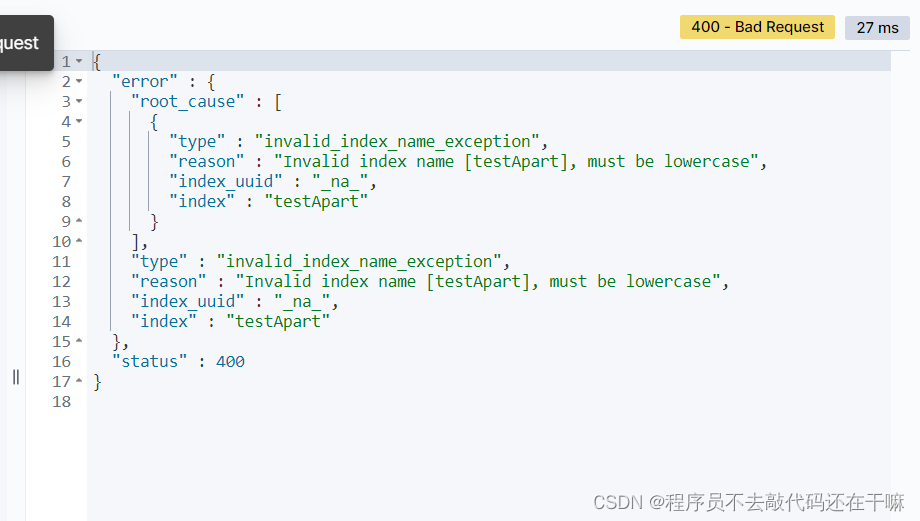
非法索引名[testapart],必须小写,es支持下划线的写法test_apart
**警告:**在默认情况下新建使用post ,并且需要指定id,并且创建文档必须建立在已经创建了索引的基础上,es自动生成不能保证索引结构能达到预期的结果。
2.2.2.dsl_删除文档
使用delete从索引中删除文档。必须指定索引名称和文档id。
delete /索引名/_doc/id
2.2.3.dsl_更新文档
使用指定的脚本更新文档,修改有两种方法
-
局部修改
更新文档(优先用于更新)
post /索引名/_update/文档id { "doc":{ "字段名":"新的值" } } -
全局修改
删除旧文档,添加新文档
put /索引名/_doc/id { "字段1":xxx, "字段2":xxx, }
2.2.4.dsl_查看文档
-
get api
从索引中检索指定的json文档。
-
请求类型
get <index>/_doc/<_id> get <index>/_source/<_id> head <index>/_doc/<_id> head <index>/_source/<_id> -
描述
使用get从特定索引中检索文档和文档源或存储字段。使用head验证文档是否存在。也可以使用_source资源只检索文档源或验证是否存在。
-
测试
-
get

-
head
head查到数据左图,查无数据右图
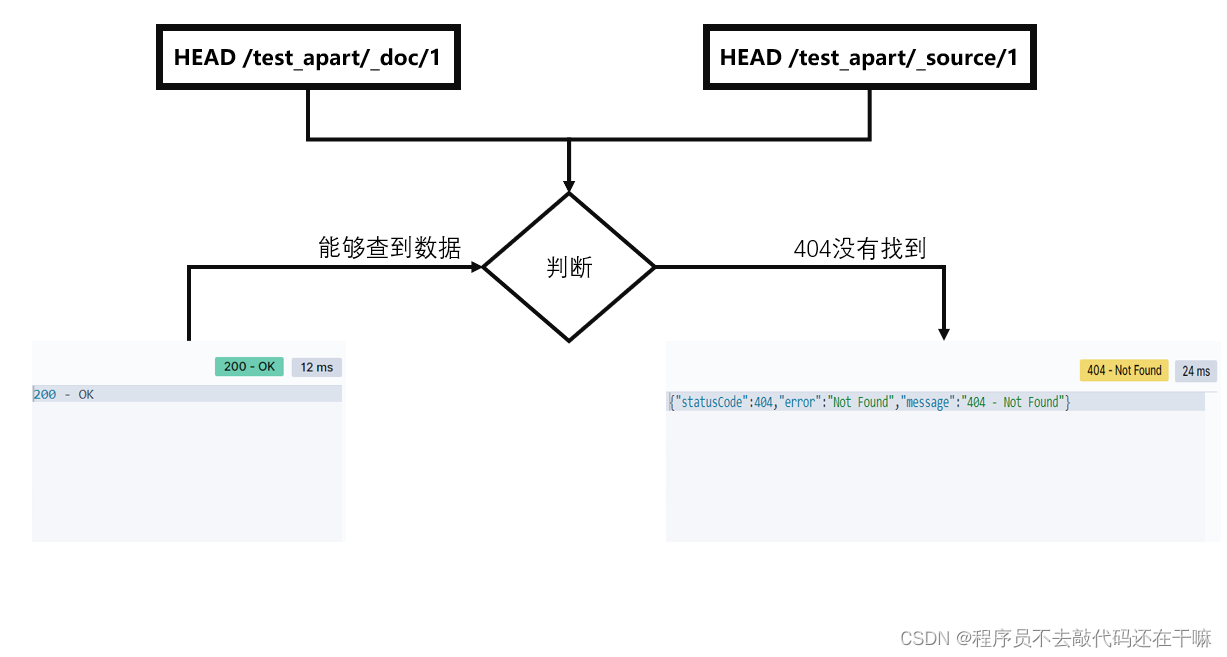
-
2.3.restapi中java语言实现crud
java高级rest客户端工作在java低级rest客户端之上。它的主要目标是公开特定于api的方法,这些方法接受请求对象作为参数并返回响应对象,这样请求编组和响应反编组就由客户机自己处理了。
2.3.1.配置maven依赖
<!--引入es的依赖,这个版本要和自己的es版本对应-->
<dependency>
<groupid>org.elasticsearch.client</groupid>
<artifactid>elasticsearch-rest-high-level-client</artifactid>
</dependency>
设定与docker中启动的es版本一致,以7.12.1版本为例
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
<elasticsearch.version>7.12.1</elasticsearch.version>
</properties>
2.3.2.建立与es的连接
-
在springboot启动类中编写一个方法通过@bean注入springfactory,推荐
@bean public resthighlevelclient client(){ //ip服务器的地址 9200是elasticsearch的端口 return new resthighlevelclient(restclient.builder(httphost.create("192.168.26.131:9200"))); }需要时自动注入
@autowired private resthighlevelclient client; -
在类中编写一个方法。
private resthighlevelclient client; public void setup(){ client=new resthighlevelclient(restclient.builder(httphost.create("192.168.26.131:9200"))); }
2.3.3.restapi_新增文档
新增总的来说有两种生成方式,一种是由字符串提供的文档源,另外是由map提供的文档源
-
由字符串(string)提供的文档源的新增
package com.cn; import org.apache.http.httphost; import org.elasticsearch.action.index.indexrequest; import org.elasticsearch.client.requestoptions; import org.elasticsearch.client.restclient; import org.elasticsearch.client.resthighlevelclient; import org.elasticsearch.common.xcontent.xcontenttype; import org.junit.jupiter.api.aftereach; import org.junit.jupiter.api.beforeeach; import org.junit.jupiter.api.test; import org.springframework.boot.test.context.springboottest; import java.io.ioexception; import java.util.hashmap; import java.util.map; @springboottest class testforrestapiapplicationtests { private resthighlevelclient client; @beforeeach void startup(){ client=new resthighlevelclient(restclient.builder(httphost.create("192.168.26.131:9200"))); } @aftereach void teardown() throws ioexception { client.close(); } @test void contextloads() { system.out.println(client); } @test void add1() throws ioexception { indexrequest request=new indexrequest("user").id("1"); string jsonstring="" + "{\n" + " \"id\":1,\n" + " \"name\":\"张三\",\n" + " \"age\":18,\n" + " \"address\":\"北京市朝阳区\"\n" + "}"; request.source(jsonstring,xcontenttype.json); client.index(request,requestoptions.default); } }下图剖析执行流程与dsl语句的对应关系

-
由map提供的文档源的新增,在官方文档中说明了map可以自动转换为json格式
package com.cn; import org.apache.http.httphost; import org.elasticsearch.action.index.indexrequest; import org.elasticsearch.client.requestoptions; import org.elasticsearch.client.restclient; import org.elasticsearch.client.resthighlevelclient; import org.junit.jupiter.api.aftereach; import org.junit.jupiter.api.beforeeach; import org.junit.jupiter.api.test; import org.springframework.boot.test.context.springboottest; import java.io.ioexception; import java.util.hashmap; import java.util.map; @springboottest class testforrestapiapplicationtests { private resthighlevelclient client; @beforeeach void startup(){ client=new resthighlevelclient(restclient.builder(httphost.create("192.168.26.131:9200"))); } @aftereach void teardown() throws ioexception { client.close(); } @test void contextloads() { system.out.println(client); } @test void add2() throws ioexception { map<string,object> map=new hashmap<>(); map.put("id",2); map.put("name","小赵"); map.put("age",10); map.put("address","成都市武侯区"); //作为map提供的文档源会自动转换为json格式 indexrequest request=new indexrequest("user").source(map); client.index(request,requestoptions.default); } }剖析关系图
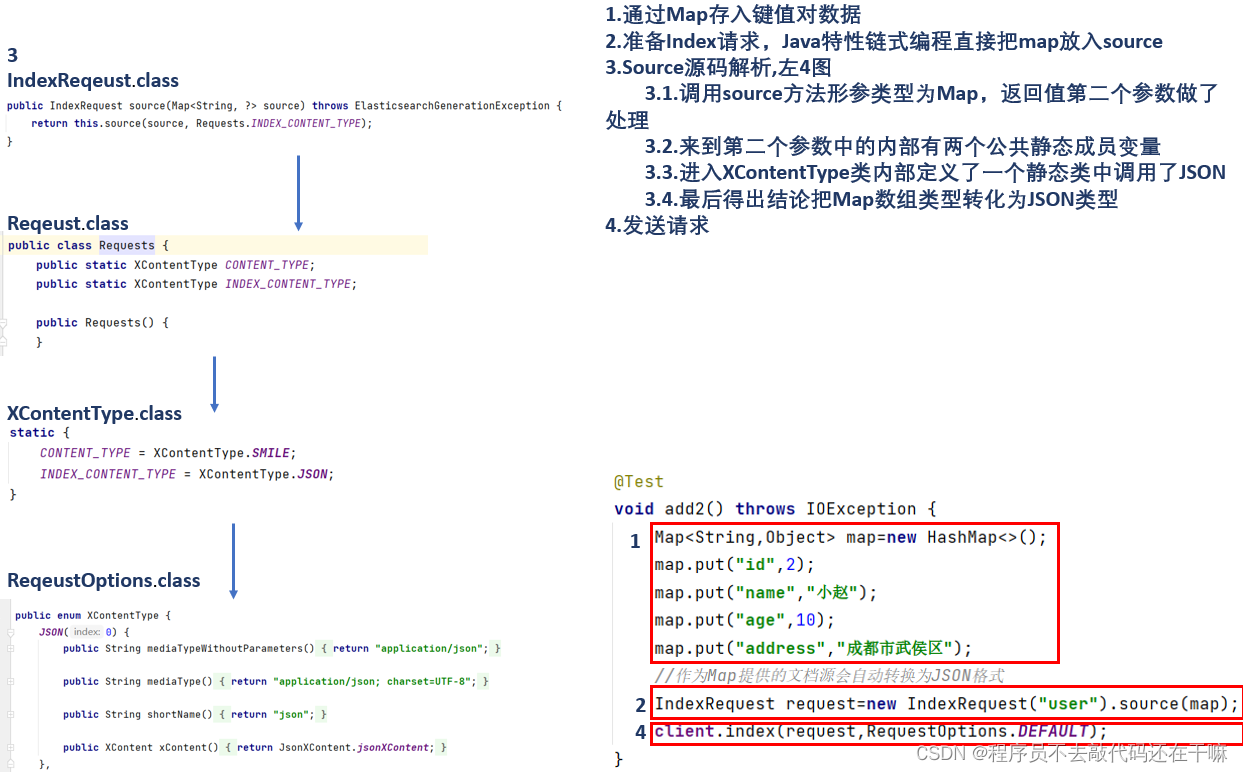
总结:在开发中一般会定义一个与es索引结构相同的实体类(user.java),封装所需参数,返回值类型为user.java
2.3.4.restapi_删除文档
删除比较简单
@test
void delete() throws ioexception {
//准备deleterequest方法,指定索引名,和文档id
deleterequest request=new deleterequest("user").id("1");
//发送删除请求
client.delete(request,requestoptions.default);
}
2.3.5.restapi_更新文档
-
使用部分文档更新
-
string字符串的更新
和新增逻辑相同,只不过请求参数变成updaterequest
@test void update() throws ioexception { //准备request updaterequest request=new updaterequest("user","1"); //准备json数据 string jsonstring="" + "{\n" + " \"id\":3,\n" + " \"name\":\"张胜男\",\n" + " \"age\":12,\n" + " \"address\":\"武汉市\"\n" + " }"; request.doc(jsonstring,xcontenttype.json); client.update(request,requestoptions.default); }代码分析图

-
map数组的更新
@test void update2() throws ioexception { map<string,object> map=new hashmap<>(); map.put("name","小赵"); map.put("age",10); //准备request updaterequest request=new updaterequest("user","1").doc(map); //准备json数据 client.update(request,requestoptions.default); }这里就和使用map新增的方法大同小异了
-
-
使用脚本更新
这里先引用一下官方的例子,等有空了在做详细的脚本更新
//1 map<string, object> parameters = singletonmap("user", "张三"); //2 script inline = new script(scripttype.inline, "painless","ctx._source.field += params.count", parameters); //3 request.script(inline);这段代码来自官方文档,可以看出
- 作为对象映射提供的脚本参数
- 使用简单的语言和前面的参数创建内联脚本
- 将脚本设置为更新请求
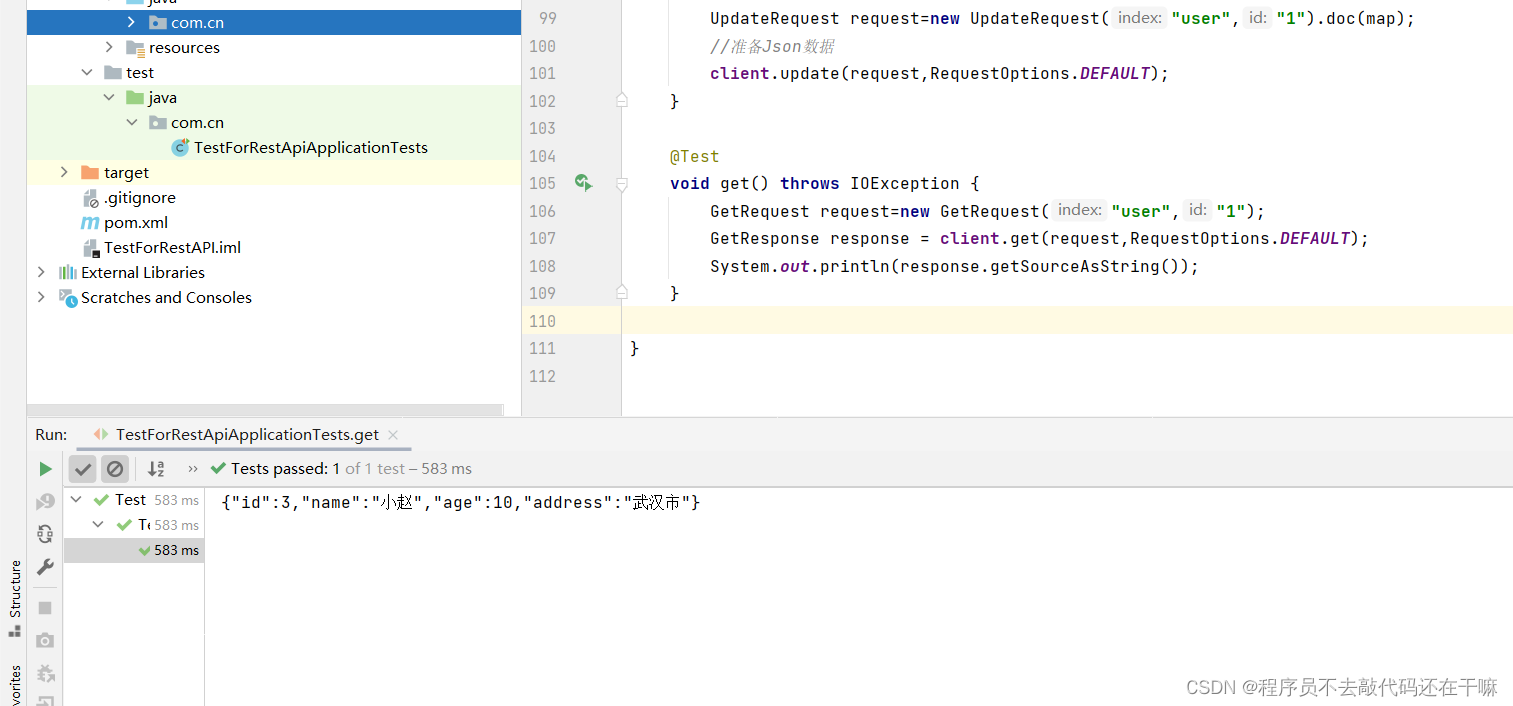
2.3.6.restapi_查看文档
@test
void get() throws ioexception {
getrequest request=new getrequest("user","1");
getresponse response = client.get(request,requestoptions.default);
system.out.println(response.getsourceasstring());
}
以上是查看的代码
3.总结
本文提供了在es中的分别使用原始dsl语句和javarestclient实现的crud的概述。最后,本文概述了elasticsearch如何分别使用dsl语句和resthighlevelclient处理文档。elasticsearch是一个强大的工具,可以用来存储和搜索大量的数据。在dsl语句和resthighlevelclient的帮助下,可以以各种方式与文档进行交互。如果你有兴趣学习更多关于elasticsearch的知识.关注我,更新更多有用的免费的知识。



发表评论