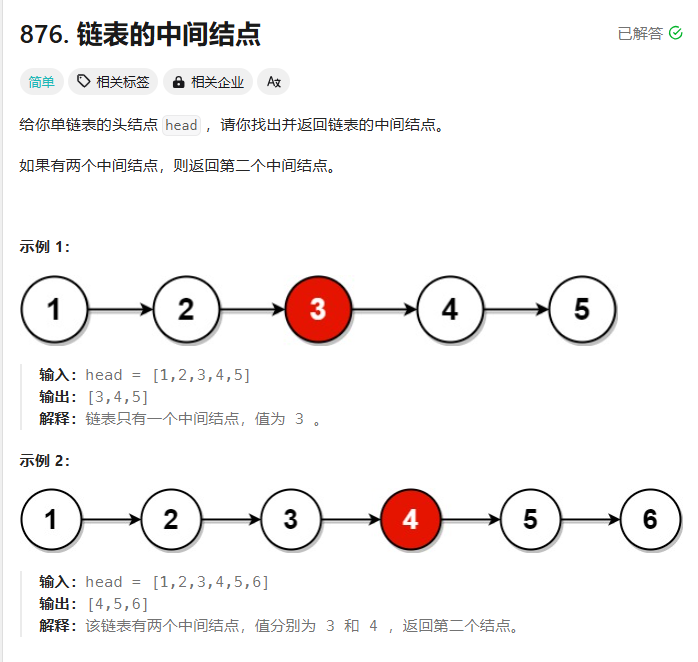
链表的回文结构
要解决链表的回文结构:首先需要求中间节点,其次是会反转链表。
一.链表的中间节点
思路1:暴力求解
- 求出链表的长度。
- 求出要返回的中间节点的位置(除2+1),遍历链表返回节点指针即可。
- 注意:兼容奇数个节点与偶数个节点。
typedef struct listnode listnode;
struct listnode* middlenode(struct listnode* head)
{
listnode* cur = head;
int listlength = 0;
while(cur)
{
//求链表的长度
listlength++;
cur = cur->next;
}
//链表中间节点的位置
int middle = listlength / 2 + 1;
int i = 1; //注意:非i=0
cur = head;
while(i < middle)
{
i++;
cur = cur->next;
}
return cur;
}
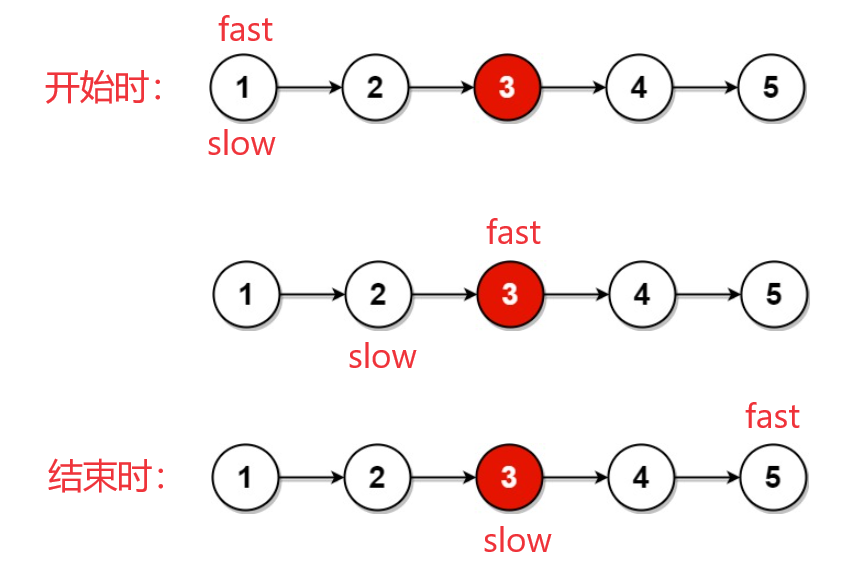
思路2:快慢指针
- 定义两个指针fast、slow保存链表头节点的地址。
- 进入循环,fast指针一次走
两个节点,slow指针一次走一个节点,当fast != null && fast->next != null时循环继续,否则循环结束。
情况1.含有奇数个节点
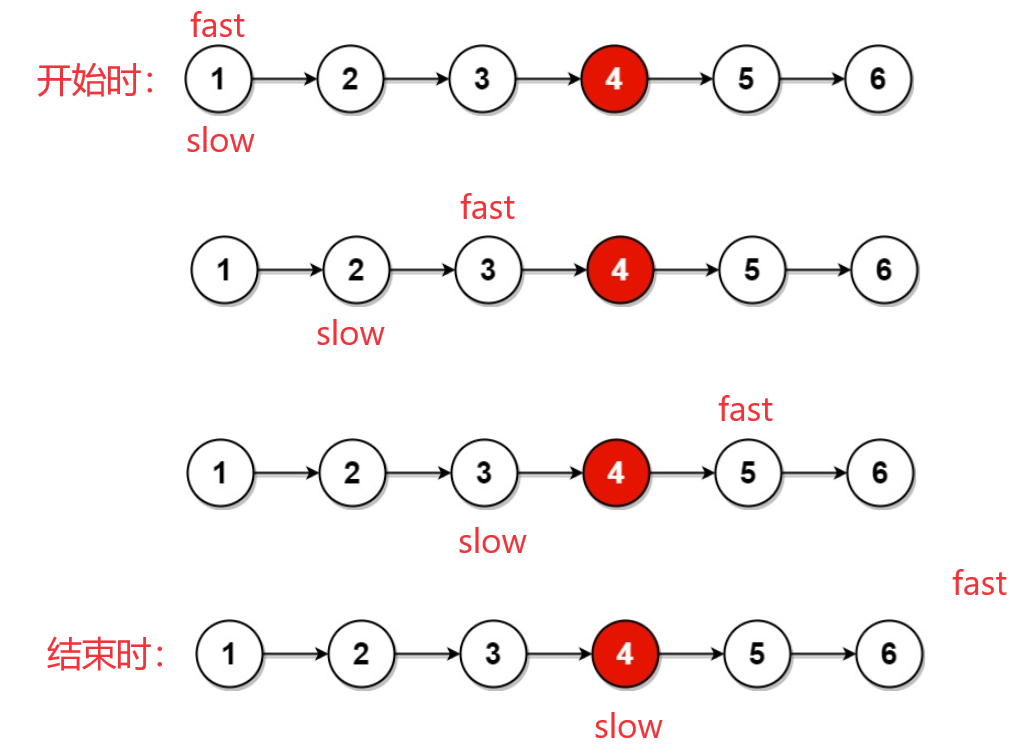
情况2.含有偶数个节点
typedef struct listnode listnode;
struct listnode* middlenode(struct listnode* head)
{
//快慢指针:慢指针一次走一步,快指针一次走两步
listnode* fast = head;
listnode* slow = head;
//注意循环继续的条件是&&而不是||,且fast与fast->next的位置不能交换
while (fast != null && fast->next != null)
{
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
return slow;
}
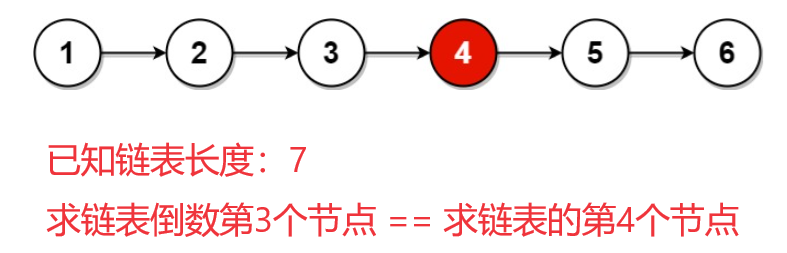
二.返回倒数第k个节点

思路1:暴力求解
- 遍历链表求链表的长度
length。 - 倒数第k个节点,等价于从前往后的第
length - k个节点。 - 再次遍历链表找到第
length - k个节点,返回节点指针即可。
typedef struct listnode listnode;
int kthtolast(struct listnode* head, int k)
{
//1.遍历链表求出链表长度,再遍历一次链表,找到返回值
int size = 0;
listnode* cur = head;
while(cur)
{
size++;
cur = cur->next;
}
int i = 0;
cur = head;
while(i < size - k)
{
cur = cur->next;
i++;
}
return cur->val;
}
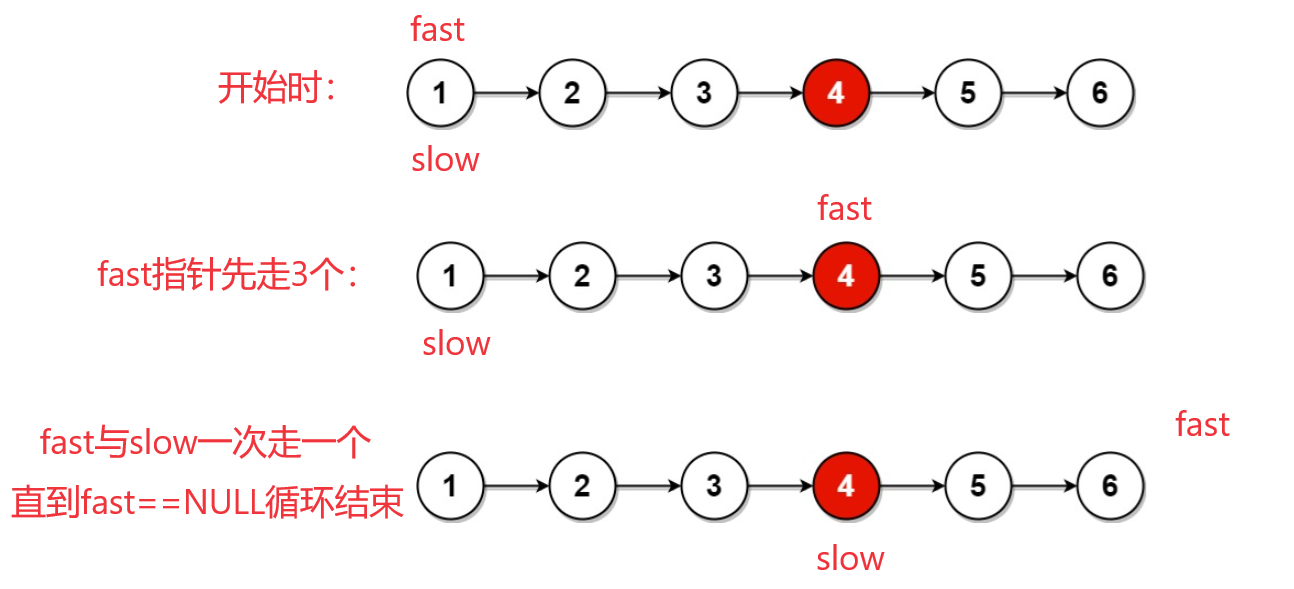
思路2:快慢指针
- 定义两个指针fast、slow保存链表头节点的地址。
- fast指针先走
k个节点。 - 进入循环,fast与slow指针各自每次走一个节点,当
fast != null时循环继续,否则循环结束。
typedef struct listnode listnode;
int kthtolast(struct listnode* head, int k)
{
//2.快慢指针:快指针先走k步,然后快指针一次走一步,慢指针一次走一步
listnode* fast = head;
listnode* slow = head;
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++)
{
fast = fast->next;
}
while (fast != null)
{
fast = fast->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
return slow->val;
}
三.反转链表
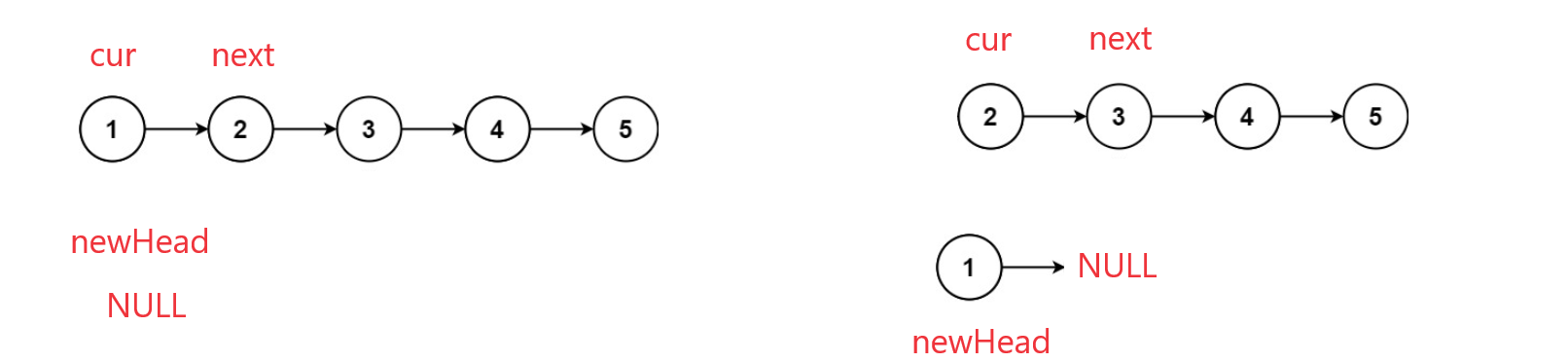
思路1:头插法
- 创建新链表 newhead = null。
- 遍历原链表,逐个节点头插倒新链表中。
typedef struct listnode listnode;
struct listnode* reverselist(struct listnode* head)
{
//1.创建新链表,遍历原链表,逐个头插
listnode* newhead = null, *cur = head;
while(cur)
{
//头插
listnode* next = cur->next;
cur->next = newhead;
newhead = cur;
cur = next;
}
return newhead;
}
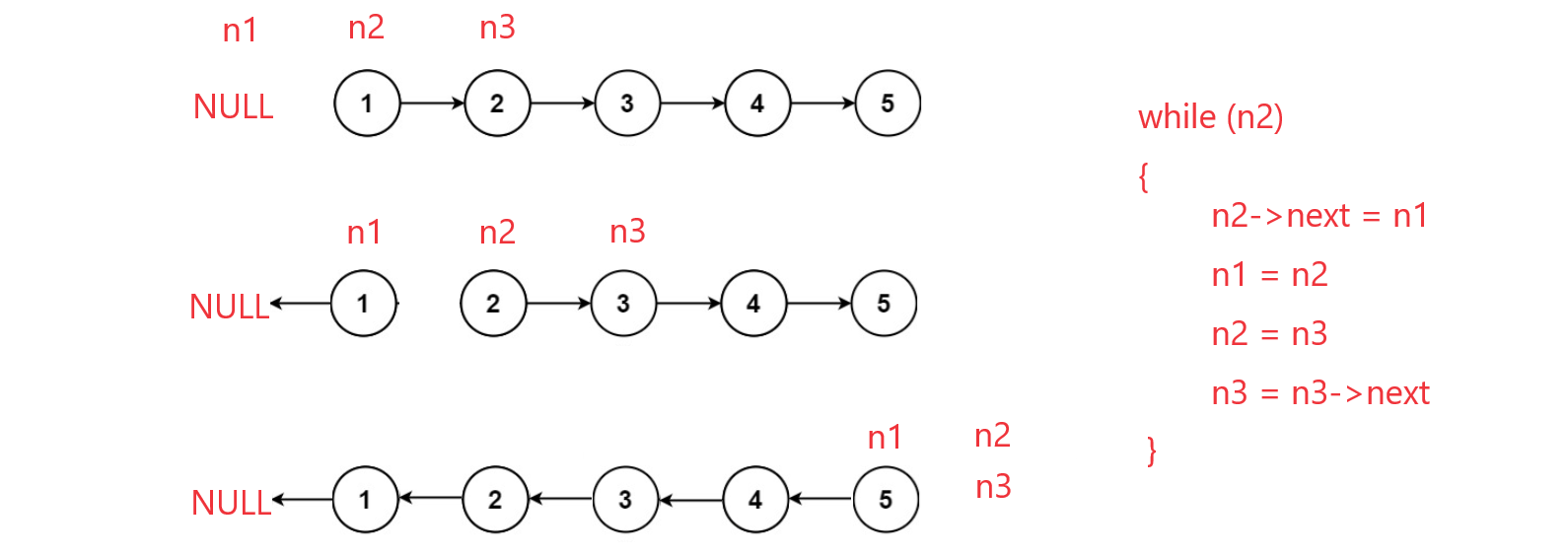
思路2:反转指针的指向
typedef struct listnode listnode;
struct listnode* reverselist(struct listnode* head)
{
//2.创建三个指针,反转指针的指向
if(head == null)
{
return null;
}
listnode* n1 = null, *n2 = head, *n3 = n2->next;
while(n2)
{
n2->next = n1;
n1 = n2;
n2 = n3;
if(n3 != null)
{
n3 = n3->next;
}
}
return n1;
}
四.链表的回文结构
思路1:利用数组,判断是否回文
class palindromelist {
public:
//判断数组是否满足回文结构
bool isreverse(int arr[], int left, int right)
{
while(left < right)
{
if(arr[left] != arr[right])
{
return false;
}
left++;
right--;
}
return true;
}
bool chkpalindrome(listnode* a)
{
int arr[900];
listnode* cur = a;
int i = 0, listlength = 0;
while(cur)
{
arr[i++] = cur->val;//将链表中的值保存到数组中
cur = cur->next;
listlength++;//求链表的长度
}
return isreverse(arr, 0, listlength - 1);
}
};
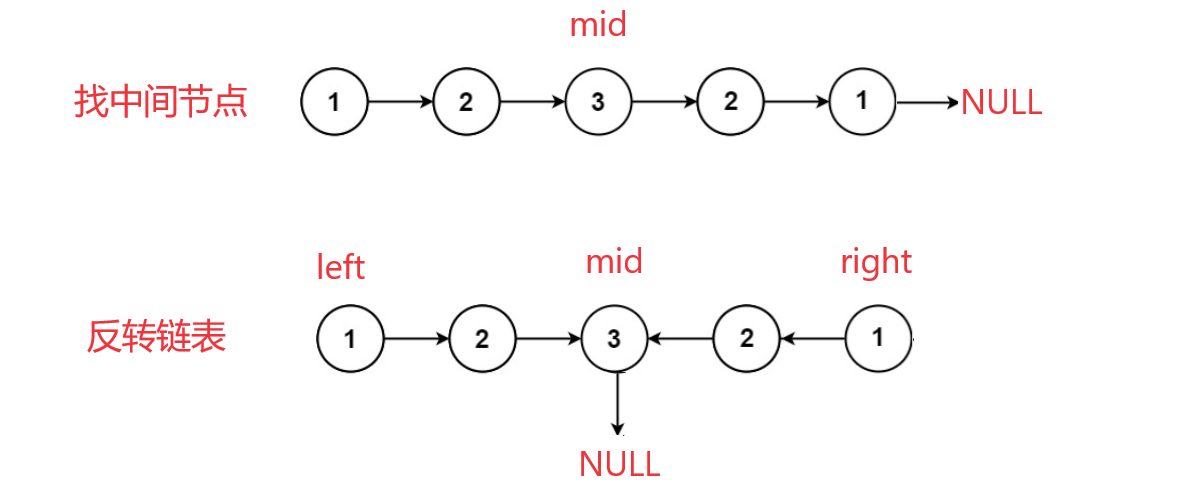
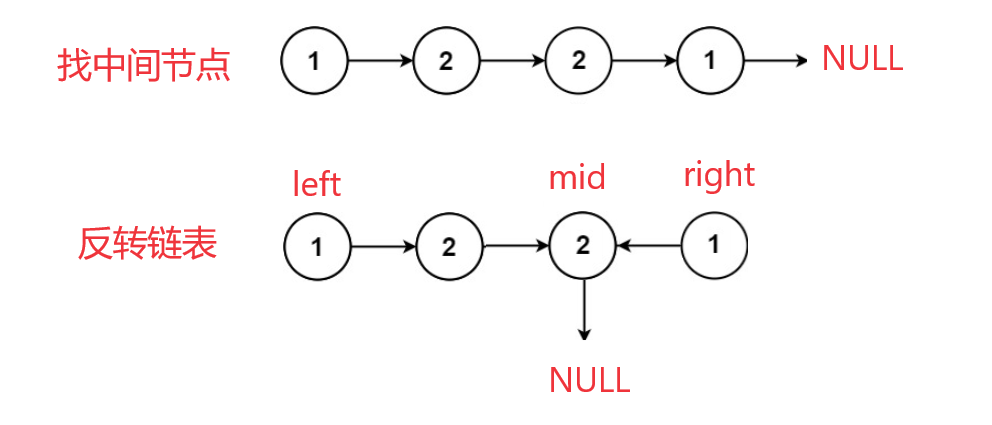
思路2:求链表的中间节点+反转链表
- 寻找链表的中间节点 mid。
- 将中间节点 mid 以及之后的节点组成的链表反转。
- 遍历反转后的链表,当一个一个与原链表的数据域对比,若相同则是回文结构。
情况1.含有奇数个节点:
情况2.含有偶数个节点:
class palindromelist {
public:
listnode* findmidnode(listnode* phead)
{
listnode* fast = phead;
listnode* slow = phead;
while(fast && fast->next)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
return slow;
}
listnode* reverselist(listnode* phead)
{
listnode* n1, *n2, *n3;
n1 = null, n2 = phead, n3 = n2->next;
while(n2)
{
n2->next = n1;
n1 = n2;
n2 = n3;
if(n3 != null)
{
n3 = n3->next;
}
}
return n1;
}
bool chkpalindrome(listnode* a)
{
//1.找链表的中间节点
listnode* mid = findmidnode(a);
//2.反转中间节点以及之后的节点组成的链表
listnode* right = reverselist(mid);
//3.遍历反转链表,与原链表进制值的比较
listnode* left = a;
while(right)
{
if(right->val != left->val)
{
return false;
}
right = right->next;
left = left->next;
}
return true;
}
};


发表评论