目录
1、人体姿态估计简介
人体姿态估计(human posture estimation),是通过将图片中已检测到的人体关键点正确的联系起来,从而估计人体姿态。
人体关键点通常对应人体上有一定自由度的关节,比如颈、肩、肘、腕、腰、膝、踝等,如下图。
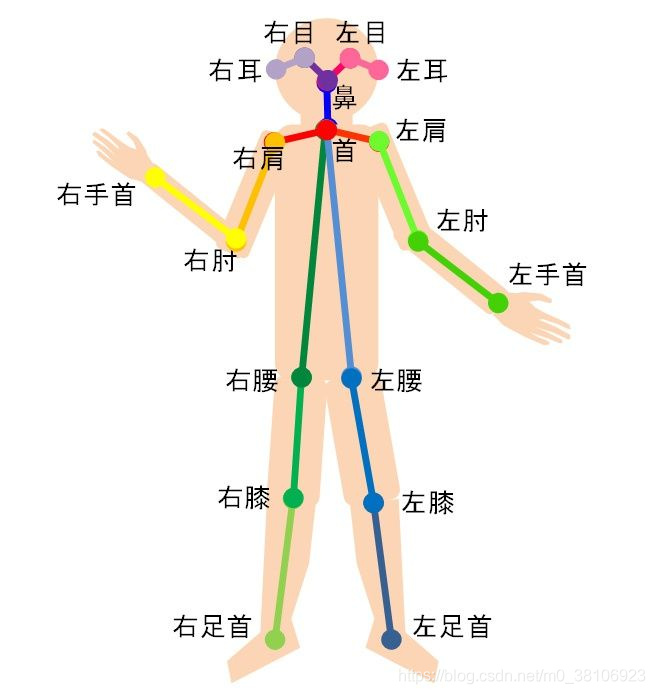

通过对人体关键点在三维空间相对位置的计算,来估计人体当前的姿态。
进一步,增加时间序列,看一段时间范围内人体关键点的位置变化,可以更加准确的检测姿态,估计目标未来时刻姿态,以及做更抽象的人体行为分析,例如判断一个人是否在打电话等。
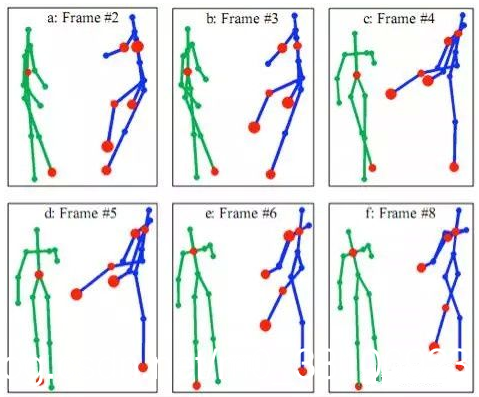
人体姿态检测的挑战:
- 每张图片中包含的人的数量是未知的。
- 人与人之间的相互作用是非常复杂的,比如接触、遮挡等,这使得联合各个肢体,即确定一个人有哪些部分变得困难。
- 图像中人越多,计算复杂度越大(计算量与人的数量正相关),这使得实时检测变得困难。
2、人体姿态估计数据集
由于缺乏高质量的数据集,在人体姿势估计方面进展缓慢。在近几年中,一些具有挑战性的数据集已经发布,这使得研究人员进行研发工作。人体姿态估计常用数据集:
3、openpose库
openpose人体姿态识别项目是美国卡耐基梅隆大学(cmu)基于卷积神经网络和监督学习并以caffe为框架开发的开源库。可以实现人体动作、面部表情、手指运动等姿态估计。适用于单人和多人,具有极好的鲁棒性。是世界上首个基于深度学习的实时多人二维姿态估计应用,基于它的实例如雨后春笋般涌现。
其理论基础来自realtime multi-person 2d pose estimation using part affinity fields ,是cvpr 2017的一篇论文,作者是来自cmu感知计算实验室的曹哲(http://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/\~zhecao/#top),tomas simon,shih-en wei,yaser sheikh 。
人体姿态估计技术在体育健身、动作采集、3d试衣、舆情监测等领域具有广阔的应用前景,人们更加熟悉的应用就是抖音尬舞机。
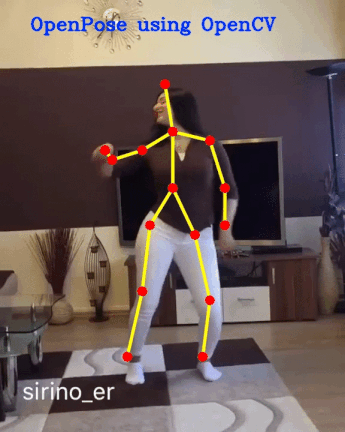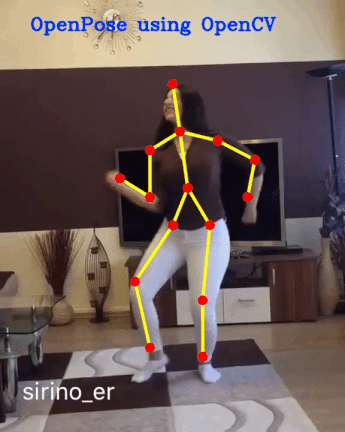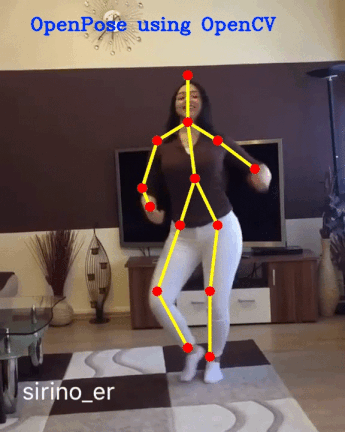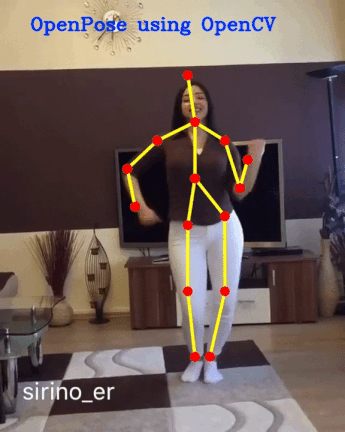
openpose项目github链接:https://github.com/cmu-perceptual-computing-lab/openpose
4、实现原理
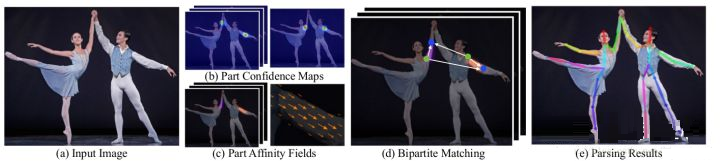
- 输入一幅图像,经过卷积网络提取特征,得到一组特征图,然后分成两个岔路,分别使用 cnn网络提取part confidence maps 和 part affinity fields;
- 得到这两个信息后,我们使用图论中的 bipartite matching(偶匹配) 求出part association,将同一个人的关节点连接起来,由于paf自身的矢量性,使得生成的偶匹配很正确,最终合并为一个人的整体骨架;
- 最后基于pafs求multi-person parsing—>把multi-person parsing问题转换成graphs问题—>hungarian algorithm(匈牙利算法)
(匈牙利算法是部图匹配最常见的算法,该算法的核心就是寻找增广路径,它是一种用增广路径求二分图最大匹配的算法。)
5、实现神经网络
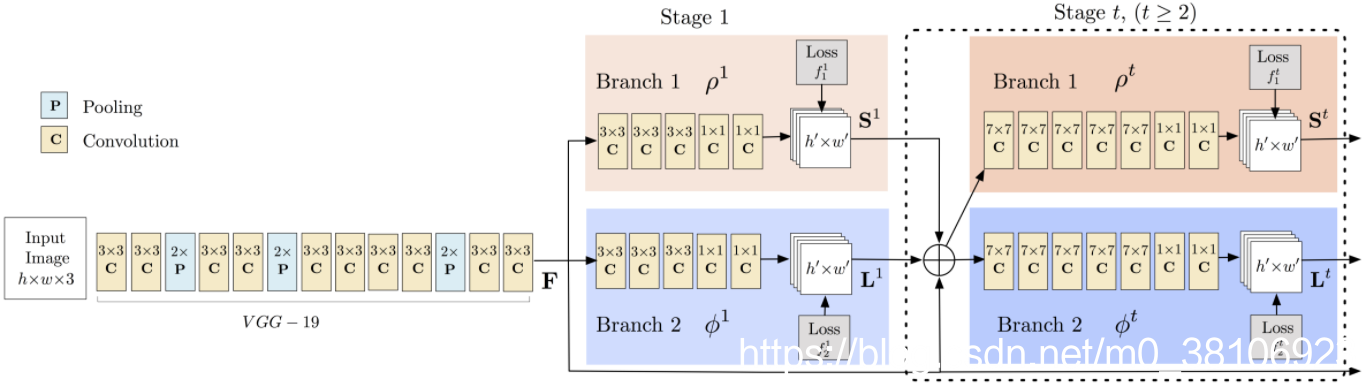
阶段一:vggnet的前10层用于为输入图像创建特征映射。
阶段二:使用2分支多阶段cnn,其中第一分支预测身体部位位置(例如肘部,膝部等)的一组2d置信度图(s)。 如下图所示,给出关键点的置信度图和亲和力图 - 左肩。

第二分支预测一组部分亲和度的2d矢量场(l),其编码部分之间的关联度。 如下图所示,显示颈部和左肩之间的部分亲和力。

阶段三: 通过贪心推理解析置信度和亲和力图,对图像中的所有人生成2d关键点。
6、实现代码
```python import cv2 as cv import numpy as np import argparse
parser = argparse.argumentparser() parser.addargument('--input', help='path to image or video. skip to capture frames from camera') parser.addargument('--thr', default=0.2, type=float, help='threshold value for pose parts heat map') parser.addargument('--width', default=368, type=int, help='resize input to specific width.') parser.addargument('--height', default=368, type=int, help='resize input to specific height.')
args = parser.parse_args()
body_parts = { "nose": 0, "neck": 1, "rshoulder": 2, "relbow": 3, "rwrist": 4, "lshoulder": 5, "lelbow": 6, "lwrist": 7, "rhip": 8, "rknee": 9, "rankle": 10, "lhip": 11, "lknee": 12, "lankle": 13, "reye": 14, "leye": 15, "rear": 16, "lear": 17, "background": 18 }
pose_pairs = [ ["neck", "rshoulder"], ["neck", "lshoulder"], ["rshoulder", "relbow"], ["relbow", "rwrist"], ["lshoulder", "lelbow"], ["lelbow", "lwrist"], ["neck", "rhip"], ["rhip", "rknee"], ["rknee", "rankle"], ["neck", "lhip"], ["lhip", "lknee"], ["lknee", "lankle"], ["neck", "nose"], ["nose", "reye"], ["reye", "rear"], ["nose", "leye"], ["leye", "lear"] ]
inwidth = args.width inheight = args.height
net = cv.dnn.readnetfromtensorflow("graph_opt.pb")
cap = cv.videocapture(args.input if args.input else 0)
while cv.waitkey(1) < 0: hasframe, frame = cap.read() if not hasframe: cv.waitkey() break
framewidth = frame.shape[1]
frameheight = frame.shape[0]
net.setinput(cv.dnn.blobfromimage(frame, 1.0, (inwidth, inheight), (127.5, 127.5, 127.5), swaprb=true, crop=false))
out = net.forward()
out = out[:, :19, :, :] # mobilenet output [1, 57, -1, -1], we only need the first 19 elements
assert(len(body_parts) == out.shape[1])
points = []
for i in range(len(body_parts)):
# slice heatmap of corresponging body's part.
heatmap = out[0, i, :, :]
# originally, we try to find all the local maximums. to simplify a sample
# we just find a global one. however only a single pose at the same time
# could be detected this way.
_, conf, _, point = cv.minmaxloc(heatmap)
x = (framewidth * point[0]) / out.shape[3]
y = (frameheight * point[1]) / out.shape[2]
# add a point if it's confidence is higher than threshold.
points.append((int(x), int(y)) if conf > args.thr else none)
for pair in pose_pairs:
partfrom = pair[0]
partto = pair[1]
assert(partfrom in body_parts)
assert(partto in body_parts)
idfrom = body_parts[partfrom]
idto = body_parts[partto]
if points[idfrom] and points[idto]:
cv.line(frame, points[idfrom], points[idto], (0, 255, 0), 3)
cv.ellipse(frame, points[idfrom], (3, 3), 0, 0, 360, (0, 0, 255), cv.filled)
cv.ellipse(frame, points[idto], (3, 3), 0, 0, 360, (0, 0, 255), cv.filled)
t, _ = net.getperfprofile()
freq = cv.gettickfrequency() / 1000
cv.puttext(frame, '%.2fms' % (t / freq), (10, 20), cv.font_hershey_simplex, 0.5, (0, 0, 0))
cv.imshow('openpose using opencv', frame)```
本项目实现代码及模型参见网址:
关注公众号,发送关键字:关键点检测,获取资源。

发表评论