多线程基础
线程:一个程序内部的一条执行流程,只有一条执行流程就是单线程
java.lang.thread代表线程
主线程退出,子线程存在,进程不会退出
可以使用jconsole查看
创建线程
有多个方法可以创建线程
-
继承thread类
- 优点:编码简单
- 缺点:无法继承其他类,不利于功能的扩展
-
实现runnable接口
- 优点:任务类只是实现了接口,可以继续继承其他类、实现其他接口,扩展性强
- 缺点:需要多创建一个runnable对象
-
实现callable接口和futuretask类
- 优点:可以返回线程执行结束之后的结果
- 缺点:编码复杂
执行为什么是start()?
使用run不是多线程, 相当于直接调用方法 还是单线程
start->start0(本地方法 jvm调用 c/c++实现的)
方法一
public class demo1 {
public static void main(string[] args) throws exception {
//main是主线程执行的
//新建了一个t线程
thread t = new primethread();
//启动线程 start自动调用run方法 必须要调用start方法
//如果是t.run() 相当于直接调用方法 还是单线程
t.start();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
system.out.println("主线程");
thread.sleep(500);
}
}
}
class primethread extends thread{
public primethread(){
}
@override
public void run() {
//描述线程的执行的任务
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
system.out.println("子线程");
try {
thread.sleep(500);
} catch (exception e) {
e.printstacktrace();
}
}
}
}
方法二
public class demo2 {
public static void main(string[] args) throws exception {
//runnable只是一个任务对象
runnable target = new prime1thread();
//需要线程对象接受任务对象 开辟新的线程
new thread(target).start();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
system.out.println("主线程");
thread.sleep(500);
}
}
}
class prime1thread implements runnable{
@override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
system.out.println("子线程");
try {
thread.sleep(500);
} catch (exception e) {
e.printstacktrace();
}
}
}
}
//可以使用匿名内部类
public class demo2 {
public static void main(string[] args) throws exception {
//需要线程对象进行调用任务对象开辟新的线程
new thread(()-> {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
system.out.println("子线程");
try {
thread.sleep(500);
} catch (interruptedexception e) {
throw new runtimeexception(e);
}
}
}).start();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
system.out.println("主线程");
thread.sleep(500);
}
}
}
方法三
import java.util.concurrent.callable;
import java.util.concurrent.executionexception;
import java.util.concurrent.futuretask;
public class demo3 {
public static void main(string[] args) throws executionexception, interruptedexception {
//创建一个callable对象
callable<string> mycallable = new mycallable(100);
// 把callable的对象封装成一个futuretask对象(任务对象)
// 未来任务对象的作用?
// 1、是一个任务对象,实现下runnable对象
// 2、可以在线程执行完毕之后,用未来任务对象调用get方法获取线程执行完毕的结果
//也可以使用匿名内部类
futuretask<string> stringfuturetask = new futuretask<>(mycallable);
new thread(stringfuturetask).start();
//获取结果会阻塞线程
system.out.println(stringfuturetask.get());
}
}
//泛型
class mycallable implements callable<string>{
private int n;
public mycallable(int n) {
this.n = n;
}
@override
public string call() throws exception {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
sum+=i;
}
return sum+"";
}
}
线程方法
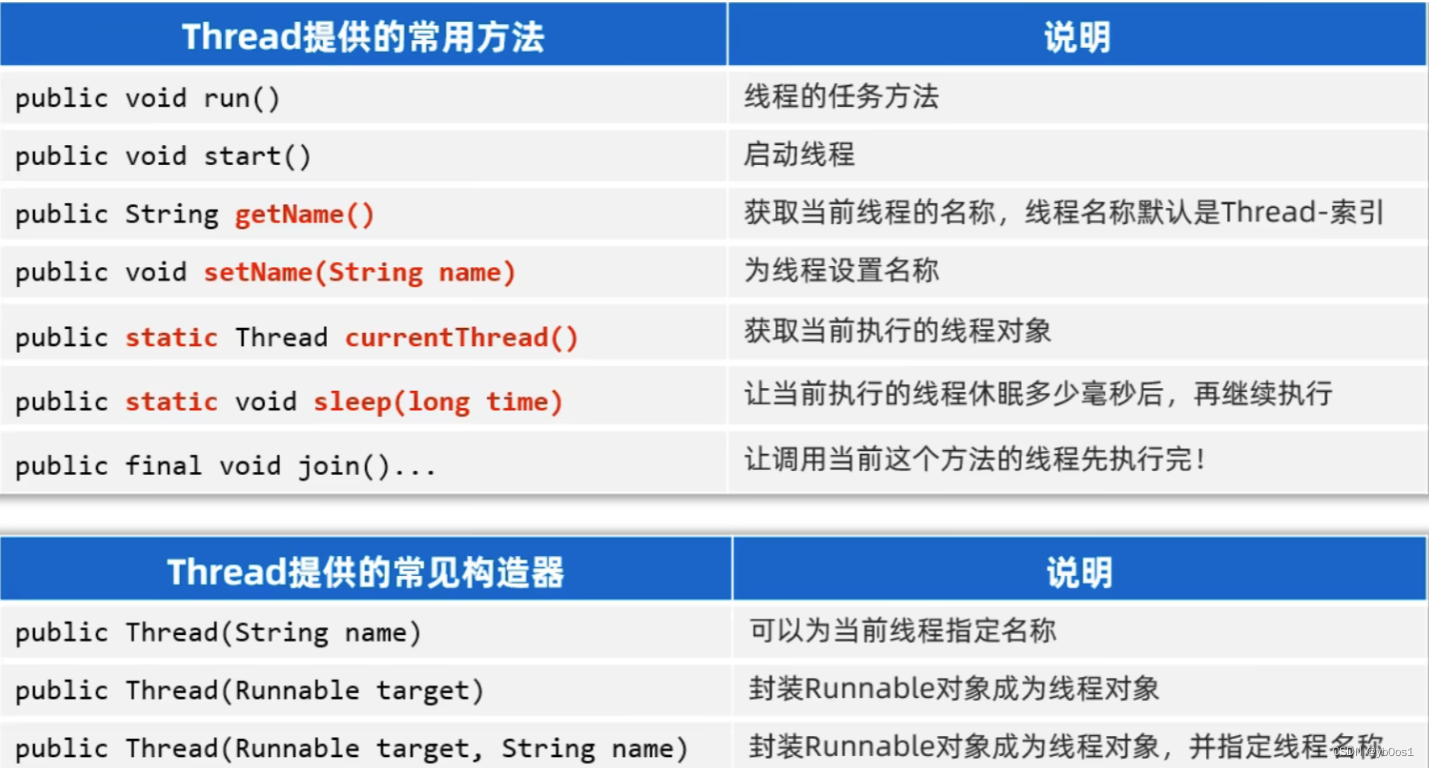
setpriority()更改线程的优先级getpriority()获取线程的优先级interrupt中断线程,并不是真正的结束线程 所以一般用于中断正在休眠的线程yield线程的礼让,不一定礼让成功(和join相反,线程的插队)
public class demo4 {
public static void main(string[] args) throws interruptedexception {
thread t1 = new thread1("1号线程");
// t1.setname("1号线程");//启动之前取名字
t1.start();
t1.join();
// system.out.println(t1.getname());
thread t2 = new thread1("2号线程");
// t2.setname("2号线程");//启动之前取名字
t2.start();
t2.join();//t2线程执行完成之后才能继续往下执行
// system.out.println(t2.getname());
thread t3 = new thread1("3号线程");
t3.start();
t3.join();
thread m = thread.currentthread();
m.setname("最牛逼的名字");
// system.out.println(m.getname());
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
system.out.println(m.getname()+"输出"+(i+1));
}
}
}
class thread1 extends thread{
public thread1(string name) {
super(name);
}
@override
public void run() {
thread t= thread.currentthread();
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
system.out.println("子线程"+t.getname()+"输出:"+(i+1));
}
}
}
线程终止
- 当线程执行完成时,自动退出
- 使用变量来控制run方法退出的方式停止线程
守护线程
当所有的用户线程都退出时,守护线程自动退出
垃圾回收机制
public class test {
public static void main(string[] args) {
//子线程设置为守护线程
mydaemonthread mydaemonthread = new mydaemonthread();
mydaemonthread.setdaemon(true);
mydaemonthread.start();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
system.out.println(thread.currentthread().getname() + " 执行");
try {
thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (interruptedexception e) {
throw new runtimeexception(e);
}
}
}
}
/*
守护线程:
当用户线程退出后 子线程也自动退出
*/
class mydaemonthread extends thread {
@override
public void run() {
while (true) {
system.out.println(thread.currentthread().getname() + " 正在执行");
try {
thread.sleep(500);
} catch (interruptedexception e) {
throw new runtimeexception(e);
}
}
}
}
线程安全
概念
多个线程同时操作同一个共享资源的时候可能出现业务安全问题
模拟线程安全问题
package thread_;
public class demo5 {
public static void main(string[] args) {
thread xiaohong = new drawthread("小红");
thread xiaoming = new drawthread("小明");
xiaoming.start();
xiaohong.start();
}
}
class account{
private static double moneys = 100000;
private account(){}
public static double getmoneys() {
return moneys;
}
public static void setmoneys(double moneys) {
account.moneys = moneys;
}
public static boolean drawmoneys(double moneys){
string name = thread.currentthread().getname();
if (moneys>account.getmoneys()){
system.out.println(name+"来取钱,钱不够");
return false;
}
account.moneys-=moneys;
system.out.println(name+"来取钱,取钱成功,剩余"+account.moneys);
return true;
}
}
class drawthread extends thread{
public drawthread(string name) {
super(name);
}
@override
public void run() {
account.drawmoneys(100000.0);
}
}
线程同步
认识线程同步
多个线程实现先后依次访问共享资源
**加锁:**每次只允许一个线程加锁,加锁之后才能访问,访问完毕之后自动解锁,然后其他线程才能再加锁继续
方法一:同步代码块
把访问共享资源的核心代码给上锁,保证线程安全
synchronized(同步锁){
访问共享资源的核心代码
}
对于当前同时执行的线程来说,同步锁必须是同一把(同一对象)
锁对象的选择:
- 实例对象:使用
this - 静态对象:使用
类型.class
public class demo5 {
public static void main(string[] args) throws interruptedexception {
account acc1 = new account(100000);
thread xiaohong = new drawthread("小红",acc1);
thread xiaoming = new drawthread("小明",acc1);
xiaoming.start();
xiaohong.start();
account acc2 = new account(100000);
thread dagang = new drawthread("大纲",acc2);
thread dali = new drawthread("大力",acc2);
dagang.start();
dali.start();
}
}
class account {
private double moneys;
public account() {
}
public account(double moneys) {
this.moneys = moneys;
}
public double getmoneys() {
return moneys;
}
public void setmoneys(double moneys) {
this.moneys = moneys;
}
public void drawmoneys(double moneys) throws interruptedexception {
string name = thread.currentthread().getname();
/*
* 两个人同时竞争lock这个对象(这把锁),只有一个人能够得到
* 上锁之后另外一个人要等待开锁
*
* 但是这个lock对于所有的对象是一个锁
* 一个对象上锁的时候 和该对象无关的对象也无法进入核心代码
* 非static建议使用 this
* static建议使用 classname.class
* */
synchronized (this) {
// thread.sleep(5000); 测试
if (moneys > this.getmoneys()) {
system.out.println(name + "来取钱,钱不够");
} else {
this.moneys -= moneys;
system.out.println(name + "来取钱,取钱" + moneys + "成功,剩余" + this.moneys);
}
}
}
}
class drawthread extends thread {
private account acc;
public drawthread(string name,account acc) {
super(name);
this.acc = acc;
}
@override
public void run() {
try {
acc.drawmoneys(100000);
} catch (interruptedexception e) {
throw new runtimeexception(e);
}
}
}
方法二:同步方法
访问共享资源的核心方法给上锁
修饰符 synchronized 返回值类型 方法名称(形参列表){
操作共享资源的代码
}
public class demo5 {
public static void main(string[] args) throws interruptedexception {
account acc1 = new account(100000);
thread xiaohong = new drawthread("小红", acc1);
thread xiaoming = new drawthread("小明", acc1);
xiaoming.start();
xiaohong.start();
account acc2 = new account(100000);
thread dagang = new drawthread("大纲", acc2);
thread dali = new drawthread("大力", acc2);
dagang.start();
dali.start();
}
}
class account {
private double moneys;
public account() {
}
public account(double moneys) {
this.moneys = moneys;
}
public double getmoneys() {
return moneys;
}
public void setmoneys(double moneys) {
this.moneys = moneys;
}
/*
有一个隐含的锁 实例方法是 this 静态方法是 类型.class
*/
public synchronized void drawmoneys(double moneys) throws interruptedexception {
string name = thread.currentthread().getname();
if (moneys > this.getmoneys()) {
system.out.println(name + "来取钱,钱不够");
} else {
this.moneys -= moneys;
system.out.println(name + "来取钱,取钱" + moneys + "成功,剩余" + this.moneys);
}
}
}
class drawthread extends thread {
private account acc;
public drawthread(string name, account acc) {
super(name);
this.acc = acc;
}
@override
public void run() {
try {
acc.drawmoneys(100000);
} catch (interruptedexception e) {
throw new runtimeexception(e);
}
}
}

方法三:lock锁
lock锁是idk5开始提供的一个新的锁定操作,通过它可以创建出锁对象进行加锁和解锁,更灵活、更方便、更强大
lock是接口,不能直接实例化,可以采用它的实现类**reentrantlock**来构建lock锁对象。
package thread_;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.reentrantlock;
public class demo5 {
public static void main(string[] args) throws interruptedexception {
account acc1 = new account(100000);
thread xiaohong = new drawthread("小红", acc1);
thread xiaoming = new drawthread("小明", acc1);
xiaoming.start();
xiaohong.start();
account acc2 = new account(100000);
thread dagang = new drawthread("大纲", acc2);
thread dali = new drawthread("大力", acc2);
dagang.start();
dali.start();
}
}
class account {
/*
创建了一个锁对象 每一个账户都有一个自己的锁对象
不允许二次赋值
*/
private final lock lk = new reentrantlock();
private double moneys;
public account() {
}
public account(double moneys) {
this.moneys = moneys;
}
public double getmoneys() {
return moneys;
}
public void setmoneys(double moneys) {
this.moneys = moneys;
}
public void drawmoneys(double moneys) throws interruptedexception {
string name = thread.currentthread().getname();
try {
lk.lock();
if (moneys > this.getmoneys()) {
system.out.println(name + "来取钱,钱不够");
} else {
this.moneys -= moneys;
system.out.println(name + "来取钱,取钱" + moneys + "成功,剩余" + this.moneys);
}
} catch (exception e) {
throw new runtimeexception(e);
} finally {
lk.unlock();//无论try中代码是否有错误 都会解锁
}
}
}
class drawthread extends thread {
private account acc;
public drawthread(string name, account acc) {
super(name);
this.acc = acc;
}
@override
public void run() {
try {
acc.drawmoneys(100000);
} catch (interruptedexception e) {
throw new runtimeexception(e);
}
}
}
释放锁的时机
- 当前线程的同步方法、同步代码块执行结束
- 当前线程在同步方法、同步代码块中遇到
break、return - 当前线程在同步方法、同步代码块中出现了未处理的
error或者exception,导致异常结束 - 当前线程在同步方法、同步代码块中执行了线程对象的
wait()方法,当前线程暂停 释放锁,等待唤醒
不释放锁
thread.sleep()、thread.yeild不会释放锁suspend()挂起方法,也不会释放锁suspend、resume控制线程,不推荐使用
线程死锁
多个线程都占用了对方的锁资源,但是不肯相让,导致了死锁
public class demo {
public static void main(string[] args) {
new thread(new mydeadthread(false)).start();
new thread(new mydeadthread(true)).start();
}
}
class mydeadthread implements runnable{
private boolean flag;
private static object o1 = new object();
private static object o2 = new object();
public mydeadthread() {
}
public mydeadthread(boolean flag) {
this.flag = flag;
}
@override
public void run() {
while (true){
/*
flag=true 占用o1锁 抢夺o2锁
flag=false 占用o2锁 抢夺o1锁
如果两个线程 一个占用o1 一个占用o2 那么就造成死锁
*/
if (flag){
synchronized (o1){
system.out.println("o1");
synchronized (o2){
system.out.println("o2");
}
}
}else {
synchronized (o2){
system.out.println("o2");
synchronized (o1){
system.out.println("o1");
}
}
}
}
}
}
线程通信
当多个线程共同操作共享资源的时候,线程间通过某种方式相互告知自己的状态,相互协调,避免无效的资源争夺
生产者消费者模型
- 生产者线程负责生产数据
- 消费者线程负责消费生产者生产的数据
- 生产者生产完数据应该等待,通知消费者消费;消费者消费完数据也应该等待,通知生产者生产

public class threadtest {
public static void main(string[] args) {
desk desk = new desk();
//3个生产者
new thread(()-> {while (true){desk.put();}},"厨师1").start();
new thread(()-> {while (true){desk.put();}},"厨师2").start();
new thread(()-> {while (true){desk.put();}},"厨师3").start();
//2个消费者
new thread(()-> {while (true){desk.get();}},"吃货1").start();
new thread(()-> {while (true){desk.get();}},"吃货2").start();
}
}
import java.util.arraylist;
import java.util.list;
public class desk {
private final list<string>list = new arraylist<>();
//这个五个人是同一把锁
public synchronized void put(){
try {
string name = thread.currentthread().getname();
if (list.isempty()){
list.add(name+"做的肉包子");
system.out.println(name+"做的肉包子");
thread.sleep(500);
}
//等待自己 唤醒别人 先唤醒后等待
//只能线程对象调用
this.notify();
this.wait();
} catch (exception e) {
throw new runtimeexception(e);
}
}
public synchronized void get(){
try {
string name = thread.currentthread().getname();
if (!list.isempty()){
system.out.println(name + "吃了"+list.remove(0));
thread.sleep(500);
}
//等待自己 唤醒别人 先唤醒后等待
//只能线程对象调用
this.notify();
this.wait();
} catch (exception e) {
throw new runtimeexception(e);
}
}
}
线程池
概念
可以复用线程的技术
**不使用线程池:**用户每发起一个请求,后台就需要创建一个新线程来处理,下次新任务来了肯定又要创建新线程处理的,而创建新线程的开销是很大的,并且请求过多时,肯定会产生大量的线程出来,这样会严重影响系统的性能。
使用executorservice创建线程池
使用executorservice的实现类threadpoolexecutor创建一个线程池对象(jdk5.0之后提供代表线程池的接口:executorservice)

corepoolsize:指定线程池的核心线程的数量maximumpoolsize:指定线程池的最大线程的数量keepalicetime:指定临时线程的存活时间unit:指定临时线程存货时间的单位(秒、分、时、天)workqueue:指定线程池的任务队列threadfactory:指定线程池的线程工厂handler:指定线程池的任务拒绝策略(线程都在忙,任务队列也满了的时候,新任务来了该怎么处理)
/*
threadpoolexecutor(int corepoolsize,
int maximumpoolsize,
long keepalivetime,
timeunit unit,
blockingqueue<runnable> workqueue,
threadfactory threadfactory,
rejectedexecutionhandler handler)
*/
executorservice poolexecutor = new threadpoolexecutor(3, 5, 8, timeunit.seconds, new arrayblockingqueue<>(4), executors.defaultthreadfactory(), new threadpoolexecutor.abortpolicy());
什么时候创建临时对象?
新任务提交时发现核心线程都在忙,任务队列也满了,并且还可以创建临时线程,才会创建
什么时候会开始拒绝新任务?
核心线程和临时线程都在忙,任务队列也满了
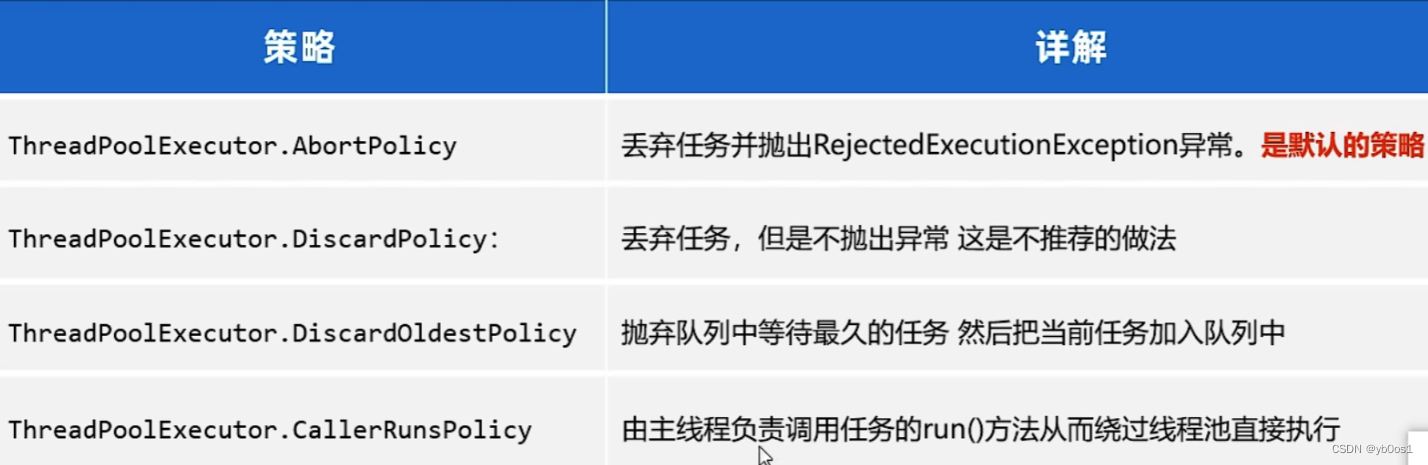
新任务拒绝策略
处理runnable任务

import java.util.concurrent.arrayblockingqueue;
import java.util.concurrent.blockingqueue;
import java.util.concurrent.executorservice;
import java.util.concurrent.executors;
import java.util.concurrent.rejectedexecutionhandler;
import java.util.concurrent.threadfactory;
import java.util.concurrent.threadpoolexecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.timeunit;
public class _threadpool {
public static void main(string[] args) {
/*
threadpoolexecutor(int corepoolsize,
int maximumpoolsize,
long keepalivetime,
timeunit unit,
blockingqueue<runnable> workqueue,
threadfactory threadfactory,
rejectedexecutionhandler handler)
*/
executorservice poolexecutor = new threadpoolexecutor(3, 5,
8, timeunit.seconds, new arrayblockingqueue<>(4),
executors.defaultthreadfactory(), new threadpoolexecutor.callerrunspolicy());
myrunnable myrunnable1 = new myrunnable();
myrunnable myrunnable2 = new myrunnable();
myrunnable myrunnable3 = new myrunnable();
//三个核心线程在忙
poolexecutor.execute(myrunnable1);
poolexecutor.execute(myrunnable2);
poolexecutor.execute(myrunnable3);
//任务队列占满
poolexecutor.execute(myrunnable3);
poolexecutor.execute(myrunnable3);
poolexecutor.execute(myrunnable3);
poolexecutor.execute(myrunnable3);
//可以创建两个临时线程
poolexecutor.execute(myrunnable3);
poolexecutor.execute(myrunnable3);
//拒绝新任务
poolexecutor.execute(myrunnable3);
// poolexecutor.shutdown();//等任务执行完后关闭线程池
// poolexecutor.shutdownnow();//立刻关闭线程池
}
}
class myrunnable implements runnable {
@override
public void run() {
string name = thread.currentthread().getname();
system.out.println(name + "666");
try {
thread.sleep(100000);
} catch (interruptedexception e) {
throw new runtimeexception(e);
}
}
}
处理callable任务

import java.util.concurrent.arrayblockingqueue;
import java.util.concurrent.callable;
import java.util.concurrent.executorservice;
import java.util.concurrent.executors;
import java.util.concurrent.future;
import java.util.concurrent.threadpoolexecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.timeunit;
public class _threadpool {
public static void main(string[] args) throws exception {
/*
threadpoolexecutor(int corepoolsize,
int maximumpoolsize,
long keepalivetime,
timeunit unit,
blockingqueue<runnable> workqueue,
threadfactory threadfactory,
rejectedexecutionhandler handler)
*/
executorservice poolexecutor = new threadpoolexecutor(3, 5,
8, timeunit.seconds, new arrayblockingqueue<>(4),
executors.defaultthreadfactory(), new threadpoolexecutor.callerrunspolicy());
future<string>f1 = poolexecutor.submit(new mycallable(100));
future<string>f2 = poolexecutor.submit(new mycallable(200));
future<string>f3 = poolexecutor.submit(new mycallable(300));
future<string>f4 = poolexecutor.submit(new mycallable(400));
system.out.println(f1.get());
system.out.println(f2.get());
system.out.println(f3.get());
system.out.println(f4.get());
}
}
class mycallable implements callable<string> {
private int n;
public mycallable(int n) {
this.n = n;
}
@override
public string call() throws exception {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
sum+=i;
}
return thread.currentthread().getname()+"计算出1-"+n+"的和为"+sum;
}
}
使用executors创建线程池(大型并发系统不建议)
(线程池的工具类)调用方法返回不同特点的线程池对象
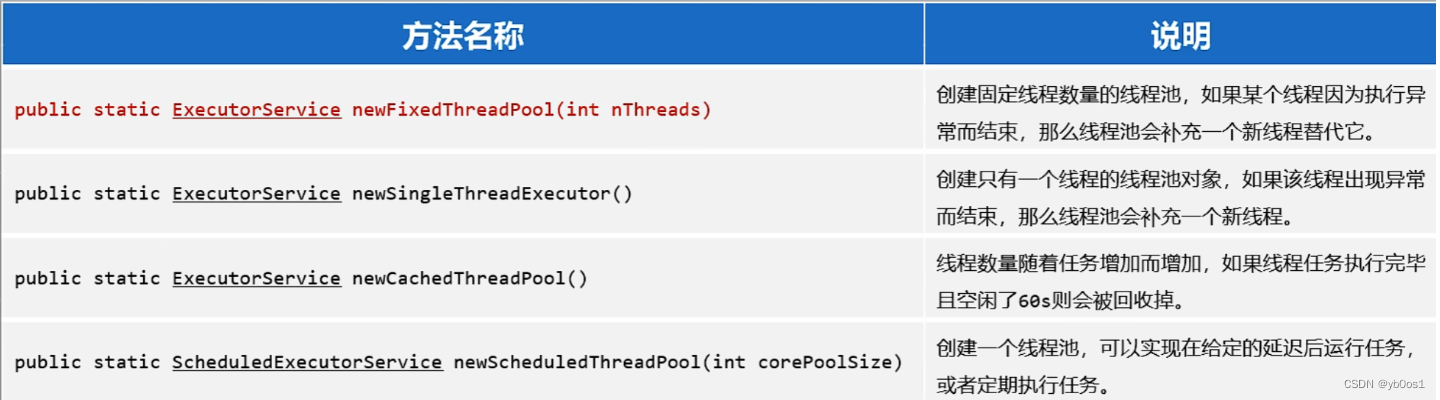
- fixedthreadpool、singlethreadexecutor允许请求队列长度为integer.max_value
- cachedthreadpool允许创建线程数量为integer.max_value
这些方法的底层,都是通过线程池的实现类threadpoolexecutor创建的线程池对象
executorservice pool = executors.newfixedthreadpool(3);
核心线程配置数量
- 计算密集型的任务:cpu核数+1
- io密集型的任务:cpu核数*2
并发和并行
并发的含义
进程中的线程是由cpu负责调度执行的,但是cpu能同时处理线程的数量是有限的。
为了保证全部线程都能往前执行,cpu会轮询为系统的每个线程服务,由于cpu切换速度很快,给我们的感觉就是这些线程在同时执行,这就是并发
并行的含义
同一时刻上,同时有多个线程在被cpu调度执行
线程生命周期
也就是线程从生到死的过程,经历的各种状态以及状态转换
理解线程这些状态有利于提高并发编程的理解能力
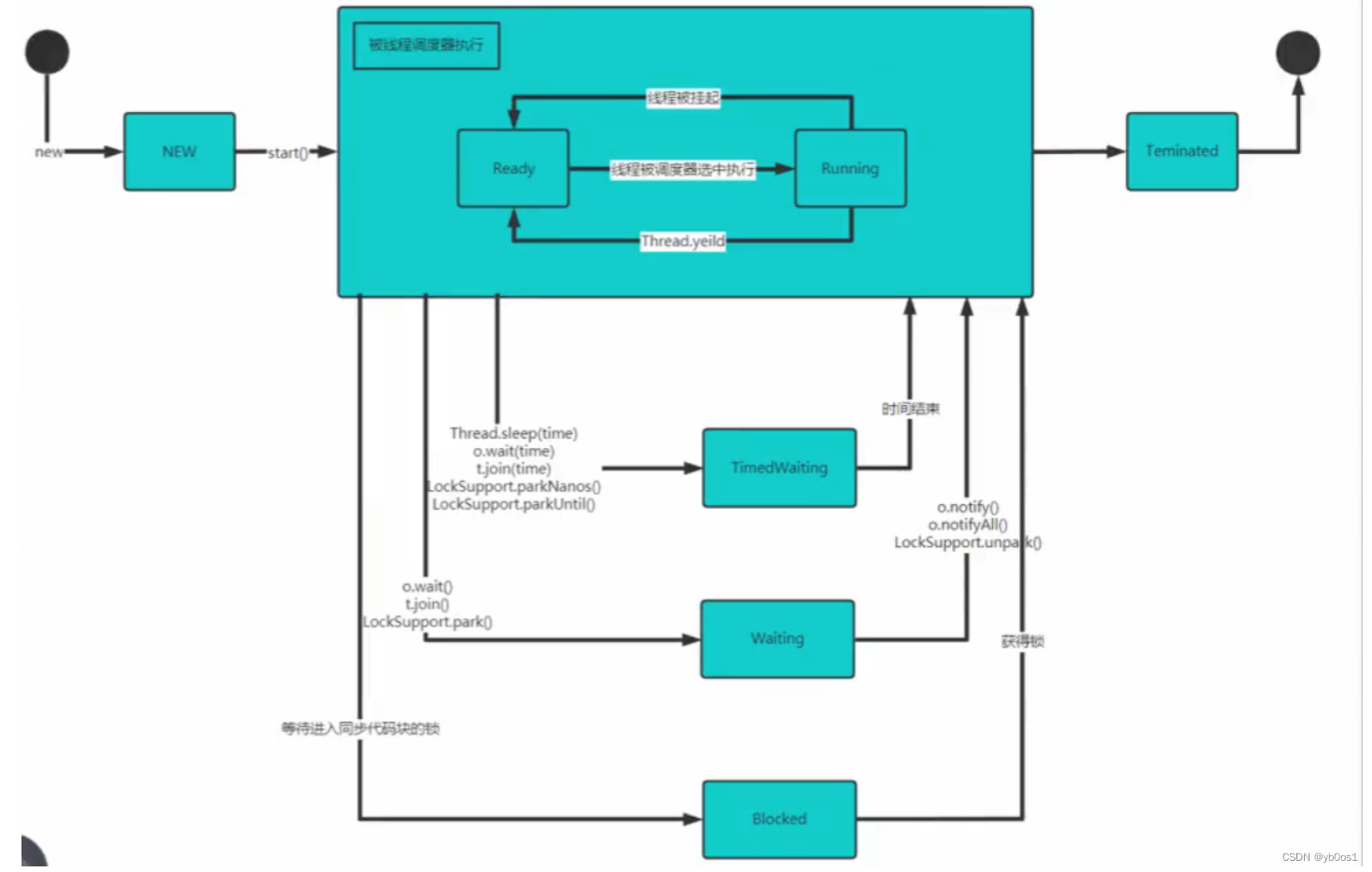

扩展:悲观锁和乐观锁
悲观锁:一开始就加锁,没有安全感,每次只能一个线程进入,访问完毕后再解锁。线程安全 性能较差
乐观锁:一开始不上锁,认为没问题,等出现线程安全的时候才开始控制。线程安全 性能较好
//乐观锁
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.atomicinteger;
public class demo7 {
//一个静态变量,100个线程,每个线程对其加100次
public static void main(string[] args) {
runnable mrunnable = new mrunnable2();
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
//100个线程执行相同的任务
new thread(mrunnable).start();
}
}
}
class mrunnable2 implements runnable {
// private int count;
//整数修改的乐观锁:原子类,
private atomicinteger count = new atomicinteger();
@override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
system.out.println("count====>" + (count.incrementandget()));
}
}
}
多线程练习
import java.util.arraylist;
import java.util.arrays;
import java.util.random;
public class test1 {
public static void main(string[] args) throws interruptedexception {
/**
* 目标:有100份礼品,小红,小明两人同时发送,当剩下的礼品小于10份的时候则不再送出,
* 利用多线程模拟该过程并将线程的名称打印出来。并最后在控制台分别打印小红,小明各自送出多少分礼物。
*/
arraylist<string> gifts = new arraylist<>();
string[] names = {"口红", "包包", "腰带", "剃须刀", "香水", "衣服"};
random r = new random();
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
gifts.add(names[r.nextint(names.length)] + (i + 1));
}
sendthread xm = new sendthread(gifts, "小明");
sendthread xh = new sendthread(gifts, "小红");
xm.start();
xh.start();
xm.join();
xh.join();
system.out.println("小明送出去" + xm.getcount());
system.out.println("小红送出去" + xh.getcount());
}
}
class sendthread extends thread {
private arraylist<string> gifts;
private int count;
public int getcount() {
return count;
}
public void setcount(int count) {
this.count = count;
}
public sendthread() {
}
public sendthread(arraylist<string> gifts, string name) {
super(name);
this.gifts = gifts;
}
@override
public void run() {
random r = new random();
string name = thread.currentthread().getname();
while (true) {
synchronized (gifts) {
int length = gifts.size();
if (length < 10)
break;
string s = gifts.remove(r.nextint(length));
system.out.println(name + "送出礼物" + s);
++count;
}
}
}
}
网络编程基础
可以让设备中的程序与网络上其他设备中的程序进行数据交互(实现网络通信的)
java.net.*的包下
网络通信三要素
- ip地址:设备在网络中的地址,是唯一的标识
- 端口号:应用程序在设备中唯一的标识
- 协议:连接和数据在网络中传输的规则
java获取ip地址:inetaddress
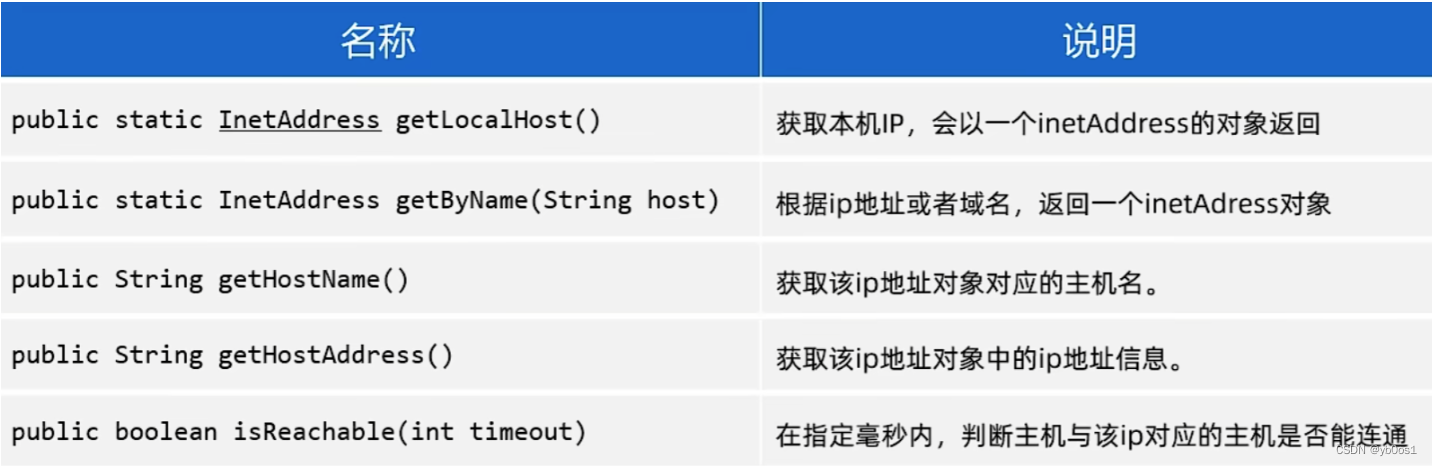
import java.net.inetaddress;
import java.net.unknownhostexception;
public class getip {
public static void main(string[] args) throws exception {
//本机
inetaddress ip = inetaddress.getlocalhost();
system.out.println(ip.gethostname());
system.out.println(ip.gethostaddress());
//指定
inetaddress ipbaidu = inetaddress.getbyname("www.baidu.com");
system.out.println(ipbaidu.gethostname());
system.out.println(ipbaidu.gethostaddress());
//本机ping 百度
system.out.println(ipbaidu.isreachable(6000));
}
}
udp通信
java.net.datagramsocket实现udp通信
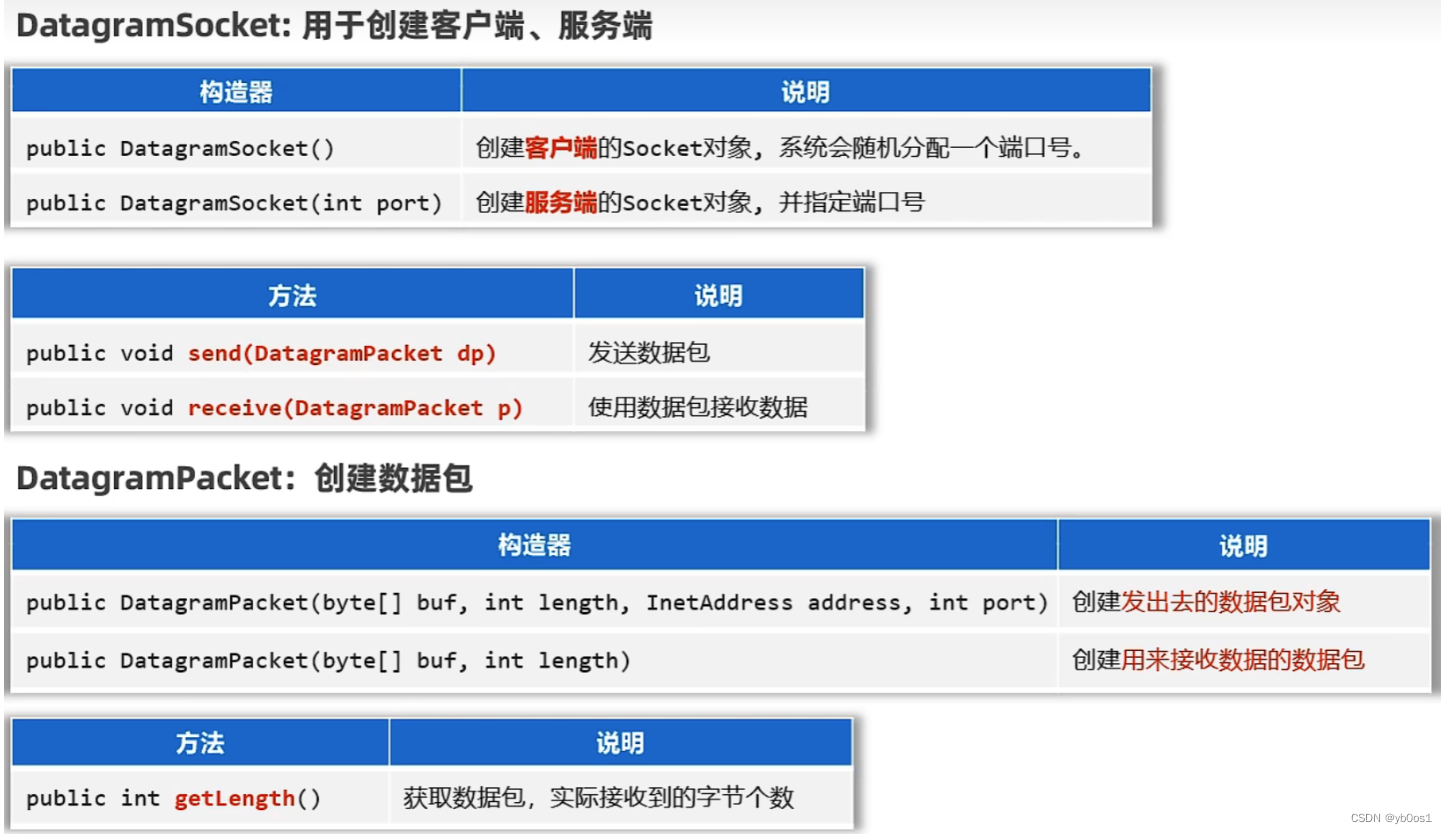
一发一收
client
import java.net.datagrampacket;
import java.net.datagramsocket;
import java.net.inetaddress;
public class client {
public static void main(string[] args) throws exception {
//创建客户端 以及客户端端口
datagramsocket socket = new datagramsocket(6666);
string data = "我是客户端,哈哈哈";
byte[]bytes = data.getbytes();
//创建数据包
datagrampacket packet = new datagrampacket(bytes,bytes.length, inetaddress.getlocalhost(),5555);
//发送数据
socket.send(packet);
system.out.println("客户端数据发送完毕");
//释放资源
socket.close();
}
}
serve
import java.net.datagrampacket;
import java.net.datagramsocket;
public class serve {
public static void main(string[] args) throws exception {
system.out.println("===服务端启动===");
//创建服务端 注册服务端端口
datagramsocket socket = new datagramsocket(5555);
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024*64];//64kb udp一个数据包最大为64kb
//创建一个用来接收数据的数据包对象
datagrampacket packet = new datagrampacket(buffer, buffer.length);
//接受数据
socket.receive(packet);
//从字节数组中获取接受的数据
int len = packet.getlength();
string data = new string(buffer,0,len);
system.out.println(data);
//获取客户端的ip 端口
system.out.println(packet.getaddress().gethostaddress());
system.out.println(packet.getport());
//释放资源
socket.close();
}
}
多发多收
可以多个用户同时发送
client
import java.net.datagrampacket;
import java.net.datagramsocket;
import java.net.inetaddress;
import java.util.scanner;
public class client {
public static void main(string[] args) throws exception {
//创建客户端 以及客户端端口(默认随机分配)
datagramsocket socket = new datagramsocket();
scanner sc = new scanner(system.in);
while (true) {
system.out.println("请输入消息://exit是退出");
string msg = sc.nextline();
if (msg.equals("exit")){
system.out.println("欢迎下次光临");
break;
}
byte[]bytes = msg.getbytes();
//创建数据包
datagrampacket packet = new datagrampacket(bytes,bytes.length, inetaddress.getlocalhost(),5555);
//发送数据
socket.send(packet);
}
socket.close();
}
}
serve
import java.net.datagrampacket;
import java.net.datagramsocket;
public class serve {
public static void main(string[] args) throws exception {
system.out.println("===服务端启动===");
//创建服务端 注册服务端端口
datagramsocket socket = new datagramsocket(5555);
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024*64];//64kb udp一个数据包最大为64kb
//创建一个用来接收数据的数据包对象
datagrampacket packet = new datagrampacket(buffer, buffer.length);
while (true) {
//接受数据
socket.receive(packet);
//从字节数组中获取接受的数据
int len = packet.getlength();
string data = new string(buffer,0,len);
system.out.println(data);
//获取客户端的ip 端口
system.out.println(packet.getaddress().gethostaddress());
system.out.println(packet.getport());
system.out.println("----------------");
}
}
}
tcp通信
客户端:java.net.socket
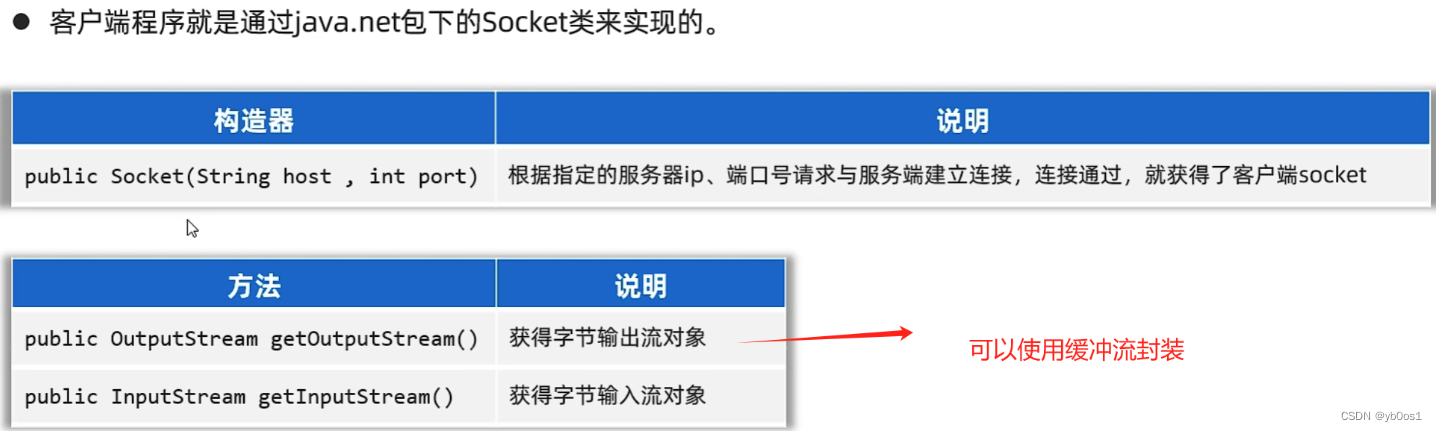
一发一收
client
import java.io.dataoutputstream;
import java.io.outputstream;
import java.net.inetaddress;
import java.net.socket;
public class clienttcp {
public static void main(string[] args) throws exception {
//创建socket对象
socket socket = new socket(inetaddress.getlocalhost(), 5555);
//从socket通信管道中得到一个字节输出流
outputstream os = socket.getoutputstream();
//封装成数据输出流
dataoutputstream dataoutputstream = new dataoutputstream(os);
//写入数据
dataoutputstream.writeutf("你好呀!");
//关闭数据流
dataoutputstream.close();
//关闭socket
socket.close();
}
}
serve
import java.io.datainputstream;
import java.io.inputstream;
import java.net.serversocket;
import java.net.socket;
public class servetcp {
public static void main(string[] args) throws exception{
system.out.println("--服务端启动--");
//创建服务端对象 绑定端口
serversocket serversocket = new serversocket(5555);
//等待连接
socket socket = serversocket.accept();
//接受数据
inputstream ds = socket.getinputstream();
//封装
datainputstream datainputstream = new datainputstream(ds);
//接受数据
string s = datainputstream.readutf();
system.out.println(s);
//客户端ip地址
system.out.println(socket.getremotesocketaddress());
datainputstream.close();
socket.close();
}
}
多发多收
client
import java.io.dataoutputstream;
import java.io.outputstream;
import java.net.inetaddress;
import java.net.socket;
import java.util.objects;
import java.util.scanner;
public class clienttcp {
public static void main(string[] args) throws exception {
//创建socket对象
socket socket = new socket(inetaddress.getlocalhost(), 5555);
//从socket通信管道中得到一个字节输出流
outputstream os = socket.getoutputstream();
//封装成数据输出流
dataoutputstream dataoutputstream = new dataoutputstream(os);
scanner sc = new scanner(system.in);
while (true) {
//写入数据
system.out.println("请说:");
string s = sc.nextline();
if (objects.equals(s, "exit")){
system.out.println("欢迎下次光临");
break;
}
dataoutputstream.writeutf(s);
dataoutputstream.flush();
}
//关闭数据流
dataoutputstream.close();
//关闭socket
socket.close();
}
}
serve
import java.io.datainputstream;
import java.io.ioexception;
import java.io.inputstream;
import java.net.serversocket;
import java.net.socket;
public class servetcp {
public static void main(string[] args) throws exception{
system.out.println("--服务端启动--");
//创建服务端对象 绑定端口
serversocket serversocket = new serversocket(5555);
//等待连接
socket socket = serversocket.accept();
//接受数据
inputstream ds = socket.getinputstream();
//封装
datainputstream datainputstream = new datainputstream(ds);
//接受数据
while (true) {
try {
string s = datainputstream.readutf();
system.out.println(s);
//客户端ip地址
// system.out.println(socket.getremotesocketaddress());
} catch (ioexception e) {
system.out.println(socket.getremotesocketaddress()+"离线");
break;
}
}
datainputstream.close();
socket.close();
}
}
多个客户端连接一个服务端
服务端:
- 主线程负责接受客户端连接
- 子线程负责具体每一个客户端
client
import java.io.dataoutputstream;
import java.io.outputstream;
import java.net.socket;
import java.util.scanner;
public class clienttcp {
public static void main(string[] args) throws exception {
socket socket = new socket("127.0.0.1", 8888);
outputstream os = socket.getoutputstream();
dataoutputstream dos = new dataoutputstream(os);
scanner sc = new scanner(system.in);
while (true){
string s = sc.nextline();
if (s.equals("exit")){
system.out.println("欢迎下次光临");
dos.close();
socket.close();
break;
}
dos.writeutf(s);
dos.flush();
}
}
}
serve
import java.io.datainputstream;
import java.io.ioexception;
import java.io.inputstream;
import java.net.serversocket;
import java.net.socket;
import java.net.socketaddress;
public class servetcp {
public static void main(string[] args) throws exception {
system.out.println("服务端开启...");
serversocket serversocket = new serversocket(8888);
while (true) {
socket socket = serversocket.accept();
system.out.println(socket.getremotesocketaddress()+"上线了");
new thread(new socketthread(socket)).start();
}
}
}
class socketthread implements runnable{
private socket socket;
public socketthread(socket socket){
this.socket = socket;
}
@override
public void run() {
socketaddress remotesocketaddress = socket.getremotesocketaddress();
try {
inputstream is = socket.getinputstream();
datainputstream dis = new datainputstream(is);
while (true) {
try {
string s = dis.readutf();
system.out.println(remotesocketaddress+"发送:"+s);
} catch (exception e) {
system.out.println(remotesocketaddress+"下线了");
socket.close();
dis.close();
break;
}
}
} catch (exception e) {
e.printstacktrace();
}
}
}
案例:群聊
client
import java.io.datainputstream;
import java.io.dataoutputstream;
import java.io.inputstream;
import java.io.outputstream;
import java.net.inetaddress;
import java.net.socket;
import java.util.scanner;
public class clientchat {
public static void main(string[] args) {
try {
socket socket = new socket("127.0.0.1", 8888);
new clientthread(socket).start();
outputstream os = socket.getoutputstream();
dataoutputstream dos = new dataoutputstream(os);
scanner sc = new scanner(system.in);
while (true) {
string s = sc.nextline();
if (s.equals("exit")) {
system.out.println("欢迎下次光临");
socket.close();
dos.close();
break;
}
dos.writeutf(s);
dos.flush();
}
} catch (exception e) {
e.printstacktrace();
}
}
}
class clientthread extends thread {
private socket socket;
public clientthread(socket socket) {
this.socket = socket;
}
@override
public void run() {
try {
inputstream is = socket.getinputstream();
datainputstream dis = new datainputstream(is);
while (true) {
try {
string msg = dis.readutf();
system.out.println(msg);
} catch (exception e) {
dis.close();
socket.close();
break;
}
}
} catch (exception e) {
e.printstacktrace();
}
}
}
serve
import java.io.datainputstream;
import java.io.dataoutputstream;
import java.io.inputstream;
import java.io.outputstream;
import java.net.serversocket;
import java.net.socket;
import java.net.socketaddress;
import java.util.arraylist;
import java.util.list;
import java.util.objects;
public class servechat {
public static final list<socket> onlineusers = new arraylist<>();
public static void main(string[] args) throws exception{
system.out.println("==服务器启动==");
serversocket serversocket = new serversocket(8888);
while (true) {
socket socket = serversocket.accept();
onlineusers.add(socket);
new servereaderthread(socket).start();
}
}
}
class servereaderthread extends thread {
private socket socket;
public servereaderthread(socket socket) {
this.socket = socket;
}
@override
public void run() {
try {
inputstream is = socket.getinputstream();
datainputstream dis = new datainputstream(is);
while (true) {
try {
string msg = dis.readutf();
system.out.println(msg);
sendallonlineusers(socket,msg);
} catch (exception e) {
servechat.onlineusers.remove(socket);
socket.close();
dis.close();
system.out.println(socket.getremotesocketaddress() + "下线");
break;
}
}
} catch (exception e) {
e.printstacktrace();
}
}
private void sendallonlineusers(socket socket,string msg) throws exception {
for (socket onlineuser : servechat.onlineusers) {
socketaddress remotesocketaddress = socket.getremotesocketaddress();
if (objects.equals(onlineuser.getremotesocketaddress(),remotesocketaddress)){
continue;
}
outputstream os = onlineuser.getoutputstream();
dataoutputstream dos = new dataoutputstream(os);
dos.writeutf(remotesocketaddress+"说:"+msg);
dos.flush();
}
}
}
案例:简易bs架构
import java.io.dataoutputstream;
import java.io.ioexception;
import java.io.outputstream;
import java.io.printstream;
import java.net.serversocket;
import java.net.socket;
public class serve {
public static void main(string[] args) throws exception {
serversocket serversocket = new serversocket(8080);
while (true){
socket socket = serversocket.accept();
system.out.println(socket.getremotesocketaddress()+"上线了");
new cthread(socket).start();
}
}
}
class cthread extends thread{
private socket socket;
public cthread(socket socket){
this.socket=socket;
}
@override
public void run() {
try {
outputstream os = socket.getoutputstream();
printstream ps = new printstream(os);
/*
服务器必须给浏览器相应http协议规定的格式
*/
ps.println("http/1.1 200 ok");
ps.println("content-type:text/html;charset=utf-8");
ps.println();//必须换行
ps.println("<div style='color:red;font-size:120px;'>java666</div>");
ps.close();
socket.close();
} catch (exception e) {
e.printstacktrace();
}
}
}
改进:线程池
import java.io.dataoutputstream;
import java.io.ioexception;
import java.io.outputstream;
import java.io.printstream;
import java.net.serversocket;
import java.net.socket;
import java.util.concurrent.arrayblockingqueue;
import java.util.concurrent.executors;
import java.util.concurrent.threadpoolexecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.timeunit;
public class serve {
public static void main(string[] args) throws exception {
serversocket serversocket = new serversocket(8080);
threadpoolexecutor pool = new threadpoolexecutor(16 * 2, 16 * 2, 0, timeunit.seconds, new arrayblockingqueue<>(8), executors.defaultthreadfactory(), new threadpoolexecutor.abortpolicy());
while (true){
socket socket = serversocket.accept();
system.out.println(socket.getremotesocketaddress()+"上线了");
pool.execute(new cthread(socket));
}
}
}
class cthread implements runnable{
private socket socket;
public cthread(socket socket){
this.socket=socket;
}
@override
public void run() {
try {
outputstream os = socket.getoutputstream();
printstream ps = new printstream(os);
/*
服务器必须给浏览器相应http协议规定的格式
*/
ps.println("http/1.1 200 ok");
ps.println("content-type:text/html;charset=utf-8");
ps.println();//必须换行
ps.println("<div style='color:red;font-size:120px;'>java666</div>");
ps.close();
socket.close();
} catch (exception e) {
e.printstacktrace();
}
}
}
案例:多用户即时通信系统
需求分析
- 用户登录
- 拉取在线用户
- 无异常退出
- 私聊
- 群聊
- 发文件
- 服务器推送新闻
java高级
单元测试
就是针对最小的功能单元(方法),编写测试代码对其进行正确性测试
junit单元测试框架
- 可以灵活的编写测试代码,可以针对某个方法执行测试,也支持一键完成对全部的方法自动化测试
- 不需要程序员去分析测试结果,会自动生成测试报告
具体使用
public class demo {
public static void printnumber(string name){
if (name==null)return;
system.out.println("名字长度:"+name.length());
}
public static int getmaxindex(string data){
if (data==null)
return -1;
return data.length();
}
}
import org.junit.after;
import org.junit.afterclass;
import org.junit.assert;
import org.junit.before;
import org.junit.beforeclass;
import org.junit.test;
/*
测试类
*/
public class demotest {
@before
public void test1(){
system.out.println("---------before---------");
}
@after
public void test2(){
system.out.println("---------after---------");
}
@afterclass
public static void test3(){
system.out.println("---------afterclass---------");
}
@beforeclass
public static void test4(){
system.out.println("---------beforeclass---------");
}
/*
公开 无返回值
*/
@test //测试方法
public void testprintnumber(){
demo.printnumber("admin");
demo.printnumber(null);
}
@test //测试方法
public void testgetmaxindex(){
//断言机制:可以通过预测业务方法的结果来测试 bug
system.out.println(demo.getmaxindex("admin"));
system.out.println(demo.getmaxindex(null));
//断言机制:可以通过预测业务方法的结果来测试 bug
assert.assertequals("有bug",4,demo.getmaxindex("admin"));
}
}


以下是学习框架源码的时候会用到,开发几乎不会用
反射
认识反射
加载类,并允许以编程的方式解剖类中的各个成分(成员变量、方法、构造器等)
步骤
- 加载类,获取类的字节码:class对象
- 获取类的构造器:constructor对象
- 获取类成员变量:field对象
- 获取类成员方法:method对象
获取类的字节码
- class c1 = 类名.class
- 调用class提供的方法
public static class forname(string package);全类名 - object的方法 对象.getclass()
获取类的构造器

import java.lang.reflect.constructor;
public class demo1 {
public static void main(string[] args) throws exception {
class c = cat.class;
constructor constructor = c.getdeclaredconstructor();
system.out.println(constructor.getname()+"--"+constructor.getparametercount());
cat o = (cat) constructor.newinstance();
system.out.println(o);
constructor declaredconstructor = c.getdeclaredconstructor(string.class, int.class);
system.out.println(declaredconstructor.getname()+"--"+declaredconstructor.getparametercount());
declaredconstructor.setaccessible(true);//打破修饰符的限制
cat o1 = (cat)declaredconstructor.newinstance("学习", 5);
}
}
class cat{
private string name;
private int age;
public string getname() {
return name;
}
public void setname(string name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getage() {
return age;
}
public void setage(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public cat() {
}
private cat(string name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public cat(string name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
获取类的成员变量

import java.lang.reflect.field;
public class demo1 {
public static void main(string[] args) throws exception {
class c = cat.class;
field[] fields = c.getdeclaredfields();
for (field field : fields) {
system.out.println(field.getname()+"--"+field.gettype());
}
field name = c.getdeclaredfield("name");
system.out.println(name.getname()+"--"+name.gettype());
cat cat = new cat();
name.setaccessible(true);
name.set(cat,"猫猫");
system.out.println(name.get(cat));
}
}
class cat{
public static int a;
public static final string country ="中国";
private string name;
private int age;
public string getname() {
return name;
}
public void setname(string name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getage() {
return age;
}
public void setage(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public cat() {
}
private cat(string name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public cat(string name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
获取类的成员方法

作用、应用场景
基本作用:可以得到一个类全部成分对其操作;可以破坏封装性;适合做java的框架
import java.io.fileoutputstream;
import java.io.printstream;
import java.lang.reflect.field;
public class test {
public static void main(string[] args)throws exception {
student stu = new student("小明", 18, 82.5);
teacher tea = new teacher("大强", 58);
saveobject(stu);
saveobject(tea);
}
public static void saveobject(object obj) throws exception {
class o = obj.getclass();
string cname = o.getsimplename();
printstream ps = new printstream(new fileoutputstream("./out/obj.txt",true));
ps.println("---------"+cname+"---------");
field[] fields = o.getdeclaredfields();
for (field field : fields) {
field.setaccessible(true);
string name = field.getname();
string value = field.get(obj)+"";
ps.println(name+":"+value);
}
ps.close();
}
}
class student{
private string name;
private int age;
private double sorce;
public student(string name, int age, double sorce) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.sorce = sorce;
}
}
class teacher{
private string name;
private int age;
public teacher(string name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
注解
就是java中特殊的标记,比如@override、@test等
作用:让其他程序根据注解信息来决定怎么执行程序
注解可以用在类、方法、构造器、成员变量、参数等等
自定义注解
public @interface 注解名称{
public 属性类型 属性名() default 默认值;
}
只有一个注解 且为 value 可以省略不写value
注解原理
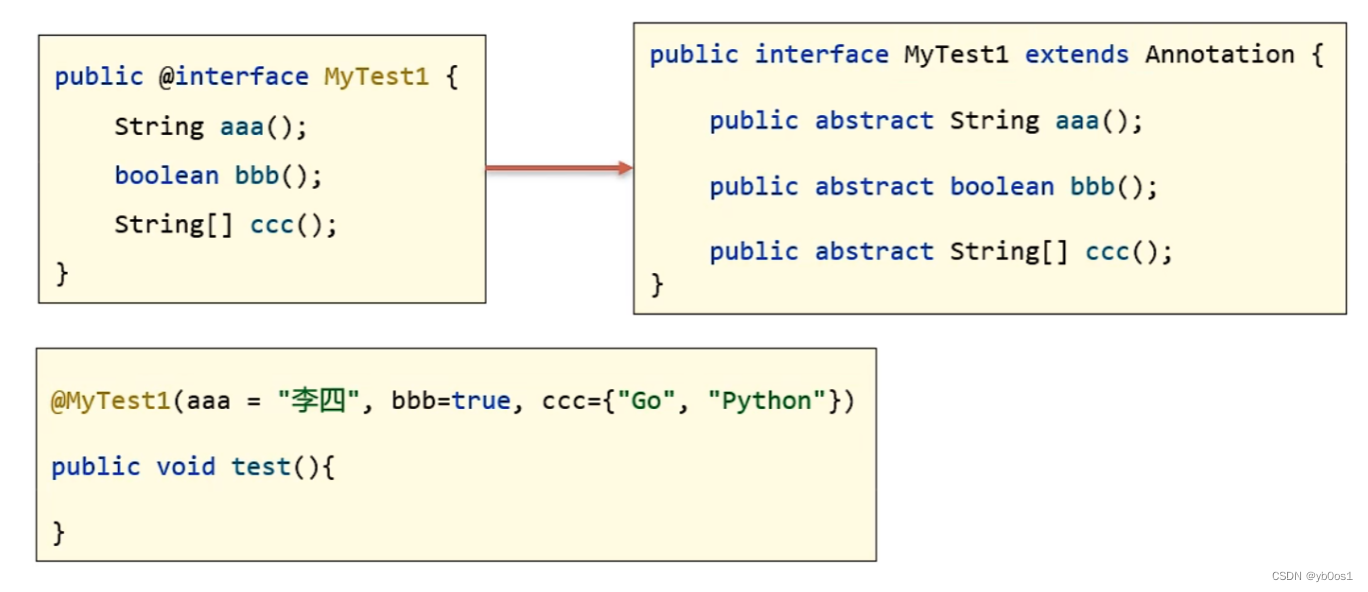
注解本质就是一个接口,java中所有的注解都是继承了annotation的接口
@注解(…)其实就是一个实现类对象,实现了该注解以及annotation的接口
元注解
修饰注解的注解

注解的解析
就是判断类上、方法上、成员变量上是否存在注解,并把注解里的内容给解析出来。
要解析谁的注解,就要先拿到谁
class、method、field,constructor、都实现了annotatedelement接口,它们都拥有解析注解的能力。

package annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.elementtype;
import java.lang.annotation.retention;
import java.lang.annotation.retentionpolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.target;
@target({elementtype.type,elementtype.method})//当前被修饰的注解只能使用在类上
@retention(retentionpolicy.runtime)
public @interface mytest{
string value();
double aaa() default 100;
string[] bbb();
}
package annotation;
@mytest(value = "大强",aaa = 199.9,bbb={"css","java","html"})
public class demo {
@mytest(value = "小明",aaa = 99.9,bbb={"java","html"})
void test(){}
}
package annotation;
import java.lang.reflect.method;
import java.util.arrays;
public class annotationtest {
public static void main(string[] args) throws exception {
class c = demo.class;
method test = c.getdeclaredmethod("test");
if (c.isannotationpresent(mytest.class)) {
mytest mytest = (mytest) c.getdeclaredannotation(mytest.class);
system.out.println(mytest.value());
system.out.println(mytest.aaa());
system.out.println(arrays.tostring(mytest.bbb()));
}
if (test.isannotationpresent(mytest.class)) {
mytest mytest = test.getdeclaredannotation(mytest.class);
system.out.println(mytest.value());
system.out.println(mytest.aaa());
system.out.println(arrays.tostring(mytest.bbb()));
}
}
}
应用场景
模拟junit
package annotation;
import java.lang.reflect.invocationtargetexception;
import java.lang.reflect.method;
public class testtest {
@mytest2
public void test1(){
system.out.println("==test1==");
}
public void test2(){
system.out.println("==test2==");
}
public void test3(){
system.out.println("==test3==");
}
public static void main(string[] args) throws exception {
class c = testtest.class;
method[] methods = c.getdeclaredmethods();
for (method method : methods) {
if (method.isannotationpresent(mytest2.class)){
method.invoke(new testtest());
}
}
}
}
动态代理
概念
对象做的事情太多的话,可以通过代理来转移部分职责

package proxy;
import java.lang.reflect.invocationhandler;
import java.lang.reflect.method;
import java.lang.reflect.proxy;
public class proxyutil {
public static star createproxy(bigstar bigstar) {
/*
参数1:指定一个类加载器
参数2:指定生成的代理是什么样子,也就是有什么方法
参数3:指定生成的代理对象要干什么事情
*/
return (star) proxy.newproxyinstance(proxyutil.class.getclassloader(), new class[]{star.class}, new invocationhandler() {
@override
public object invoke(object proxy, method method, object[] args) throws throwable {
//代理对象要做的事情 会在这里写代码
if (method.getname().equals("sing")){
system.out.println("准备话筒,收钱20w");
}else if (method.getname().equals("dance")){
system.out.println("准备场地,收钱1000w");
}
return method.invoke(bigstar,args);
}
});
}
}
package proxy;
public class bigstar implements star {
private string name;
public bigstar() {
}
public bigstar(string name) {
this.name = name;
}
@override
public string sing(string name) {
system.out.println(this.name+"正在唱"+name+"歌~~~");
return "谢谢!谢谢~";
}
@override
public void dance() {
system.out.println(name+"正在跳舞~~~");
}
}
package proxy;
public interface star {
public string sing(string name);
public void dance();
}
package proxy;
public class test {
public static void main(string[] args) {
bigstar s = new bigstar("杨超越");
star starproxy = proxyutil.createproxy(s);
string rs = starproxy.sing("好日子");
system.out.println(rs);
system.out.println("--------------------------");
starproxy.dance();
}
}
坦克大战
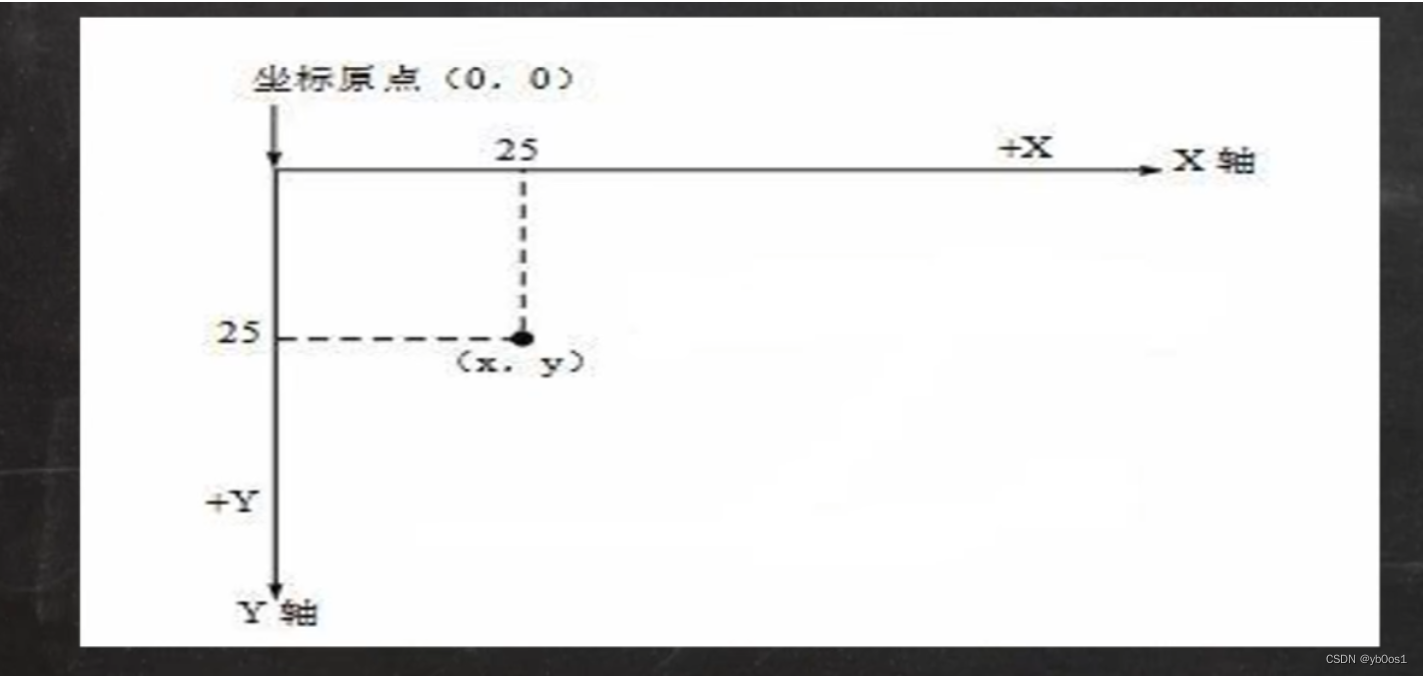
java坐标系
下图说明了java坐标系。坐标原点位于左上角,以像素为单位。在java坐标系中,第一个是x坐标,表示当前位置为水平方向,距离坐标原点x个像素;第二个是y坐标,表示当前位置为垂直方向,距离坐标原点y个像素。
package tankegame;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
public class draw extends jframe {//jframe 对应窗口 可以理解为一个画框
private mypanel mp =null;//定义一个画板
public draw(){
//初始化画板
mp = new mypanel();
//画板放入窗口
this.add(mp);
//设置窗口大小
this.setsize(1000,800);
//可以显示
this.setvisible(true);
//点窗口的× 程序退出
this.setdefaultcloseoperation(jframe.exit_on_close);
}
public static void main(string[] args) {
new draw();
}
}
//1.定义一个mypanel继承jpanel,这个就是画板 画图形
class mypanel extends jpanel{
/*
mypanel:画板(面板)对象
graphics g:画笔
paint调用时机:
1.组件第一次在屏幕中显示的时候,系统自动调用
2.窗口最小化 再最大化
3.窗口大小发生变化
4.repaint函数被调用
*/
@override
public void paint(graphics g) {//绘图的方法
super.paint(g);//调用父类的方法完成初始化
//画一个圆
g.drawoval(10,10,100,100);
//画直线
g.drawline(10,10,60,60);
//画矩形
g.drawrect(10,10,100,100);
//填充矩形
//设置画笔颜色
g.setcolor(color.blue);
g.fillrect(50,50,100,100);
g.filloval(200,200,50,60);
//画图片
//1.加载图片资源
image image = toolkit.getdefaulttoolkit().getimage("d:/shangan.png");
//2.画图片
g.drawimage(image,300,300,300,300,this);
//画字符串
g.setcolor(color.cyan);
g.setfont(new font("隶书",font.bold,50));
//位置是字体的左下角
g.drawstring("yb0os1",500,100);
}
}
事件处理机制
委派事件模型
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.keyevent;
import java.awt.event.keylistener;
//事件控制 键盘控制小球的移动
//画笔
public class ballmove extends jframe {
private drawball ball = null;
public ballmove() {
ball = new drawball();
this.add(ball);
this.setvisible(true);
this.setsize(500, 400);
this.addkeylistener(ball);//jfame对象可以监听ball上面发生的键盘事件
this.setdefaultcloseoperation(jframe.exit_on_close);
}
public static void main(string[] args) {
new ballmove();
}
}
//画板
//keylistener 监听器 监听键盘事件
class drawball extends jpanel implements keylistener {
int x = 10;
int y = 10;
@override//有字符输出时 该方法会触发
public void keytyped(keyevent e) {
}
@override//当某个键被按下时 该方法会触发
public void keypressed(keyevent e) {
// system.out.println((char) e.getkeychar() + "被按下");
//根据用户按下的不同键,来处理小球的移动
//java中给每一个键分配一个值
switch (e.getkeycode()){
case keyevent.vk_down://向下的箭头
++y;break;
case keyevent.vk_up://向上的
--y;break;
case keyevent.vk_left://向左
--x;break;
case keyevent.vk_right://向右
++x;break;
}
//重绘面板
this.repaint();
}
@override//当某个键被松开时 该方法会触发
public void keyreleased(keyevent e) {
}
@override
public void paint(graphics g) {
super.paint(g);
g.filloval(x, y, 20, 20);
}
}



发表评论