24 两两交换链表中的节点
初始思路:
遍历链表,改变每两个之间的pointer关系。实际上需要涉及每对及其前后共4个node,因为它们的顺序与如何连接前后两node相关。因为每对互换,遍历时需要step=2,来保证每次都是相连奇偶index互换;如在末尾一对中只剩一个或本身只有一个node,需要正常遍历step=1。还是使用dummy_head减少特殊处理edge cases。
class solution(object):
def swappairs(self, head):
dummy_head = listnode(0, head)
ptr = dummy_head # ptr指向pre
# 每组四个node分别为 pre -> node1 -> node2 -> post
while ptr.next is not none: # 查看node1是否defined
if ptr.next.next is not none: # 查看node2是否defined
tmp = ptr.next.next.next # 暂存post # tmp = post
ptr.next.next.next = ptr.next # node2 -> node1
# 现在:pre -> node1 <-> node2 # tmp -> post
new_first = ptr.next.next # 暂存node2 # new_first = node2
ptr.next.next = tmp # node1 -> tmp
# 现在:pre -> node1 <- node2; 同时node1 -> tmp (post); # tmp = post # new_first = node2
ptr.next = new_first # pre -> node2
# 现在:pre -> node2 -> node1 -> tmp (post);此时ptr仍然指向pre
# 进行下一轮,需要使ptr指向node1,因为node1是下一组的pre,需要 ptr = ptr.next.next和下面一对中只有node1存在而往前只走一步的情况合并拆分,
ptr = ptr.next
ptr = ptr.next
return dummy_head.next # if [], dummy_head.next = none, not enter while loop, return none
优解与优化
- 方法一: 和自己的版本基本一致,就是在while的判断处进行了优化,意识到如果一对只剩一个就没有必要进行交换下去了。更自然简洁的交换顺序:自己在写的时候思考过最开始的ptr不能随意动,一动一系列next就都变了,所以想要把它放在最后,顺序有些纠结。而优解是存了关键节点防止修改,然后按顺序修改,就清晰很多。
class solution:
def swappairs(self, head: listnode) -> listnode:
dummy_head = listnode(next=head)
current = dummy_head
# 必须有cur的下一个和下下个才能交换,否则说明已经交换结束了
while current.next and current.next.next:
temp = current.next # 防止节点修改
temp1 = current.next.next.next
current.next = current.next.next
current.next.next = temp
temp.next = temp1
current = current.next.next
return dummy_head.next
- 方法二: 更简洁自然的交换顺序。
class solution:
def swappairs(self, head: optional[listnode]) -> optional[listnode]:
if head is none or head.next is none:
return head
# 待翻转的两个node分别是pre和cur
pre = head
cur = head.next
next = head.next.next
cur.next = pre # 交换
pre.next = self.swappairs(next) # 将以next为head的后续链表两两交换
return cur
complexity
time: o(n)
space: o(1)
19 删除链表的倒数第n个节点
初始思路:
用两个指针拉开n个身位的差距,然后一起移动双指针直至后指针变成none,此时前指针指向target的前一个node,可以进行删除操作。
class solution(object):
def removenthfromend(self, head, n):
dummy_head = listnode(0, head)
pre_ptr = dummy_head # 需要让它指向要删除的node的前一个,才能改变pointer删掉目标
ptr = dummy_head # 用来与pre_ptr拉开n个node的差距
# 为什么循环n+1次? 因为倒数第n个target到最后一个last左闭右闭共有n个node,ptr需要检测到自己是none才会停下,也就是n+1的位置。pre又在target之前,即 pre, n个node,ptr。所以停下的时候,从pre作为index 0出发,则ptr应在n+2处。在n+1循环后,让ptr=ptr.next, 则ptr处在n+2的位置。
for i in range(n+1):
if ptr is not none:
ptr = ptr.next
while ptr is not none: # 拉开差距后将后指针正常遍历直至none,就可以让前指针处于target前一个的位置。
ptr = ptr.next
pre_ptr = pre_ptr.next
pre_ptr.next = pre_ptr.next.next # 变换pointer删除target
return dummy_head.next
小结:
双指针+链表:这道题完成得比较容易,主要在于想清楚两个指针需要拉开的距离。
complexity
time: o(n)
space: o(1)
106 链表相交
初始思路:
没有太好的思路,感觉从后往前找的话比较好,但是单链表,从后无法导向前边。分别给两个链表一个指针的话,查看有无相同value然后再检查是否同一个node,但是没想出来应该如何更新指针。最后使用暴力解法,两个while循环,遍历每种可能性,但是超时。
class solution(object):
def getintersectionnode(self, heada, headb):
a = heada
while a is not none:
b = headb
while b is not none:
if a == b:
return a
b = b.next
a = a.next
return none
优解参考
- 方法一:先求长度,对齐后端
class solution(object):
def getintersectionnode(self, heada, headb):
sizea = 0
sizeb = 0
ptra = heada
ptrb = headb
while ptra is not none:
sizea += 1
ptra = ptra.next
while ptrb is not none:
sizeb += 1
ptrb = ptrb.next
ptra = heada
ptrb = headb
if sizea > sizeb:
for i in range(sizea - sizeb):
ptra = ptra.next
if sizeb > sizea:
for i in range(sizeb - sizea):
ptrb = ptrb.next
# same staring
while ptra is not none:
if ptra == ptrb:
return ptra
ptra = ptra.next
ptrb = ptrb.next
return none
- 方法二:a,b长短不一,但a+b的长度等于b+a,以此对齐后端
class solution:
def getintersectionnode(self, heada, headb):
a, b = heada, headb
while (a != b):
a = headb if not a else a.next
b = heada if not b else b.next
return a
complexity
time: o(n+m) 【n,m分别为a链长度和b链长度】
space: o(1)
142 环形列表ii
初始思路:
没有太好的思路。有想到在某个node开始ptr向后遍历,如果距离变近就说明有loop。但是没有能整理成型快慢指针的想法。
代码随想录:
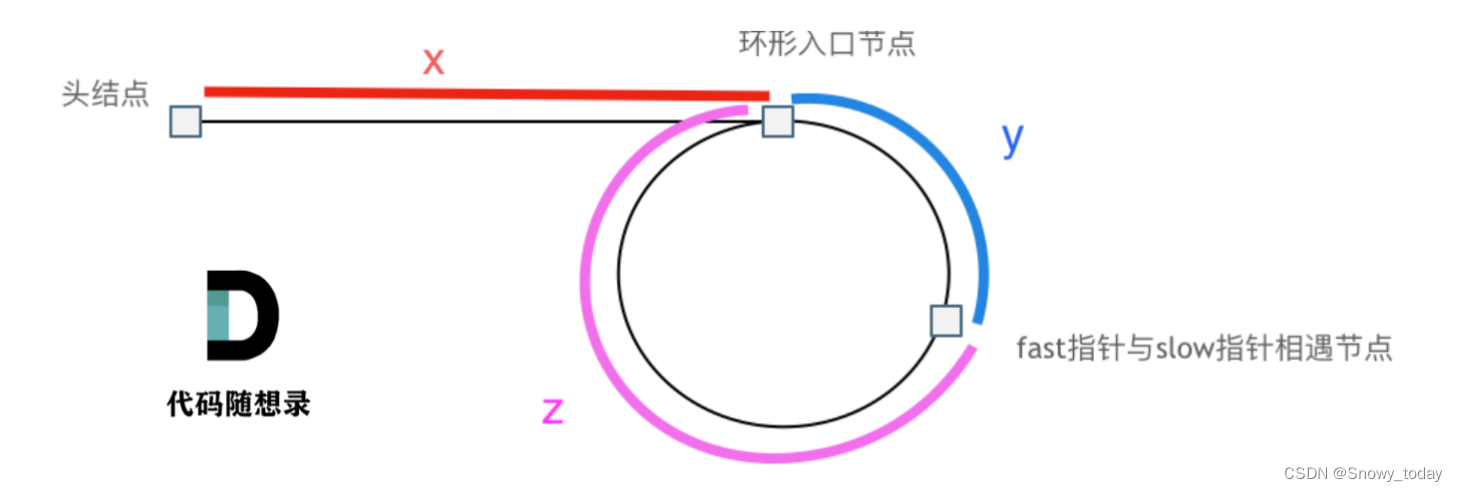
快慢指针:floyd’s cycle-finding algorithm slow
- 判断有环:每次走一步,fast每次走两步,因为步伐差距为1,所以二者一定会遇到
- 找环的入口:
class solution(object):
def detectcycle(self, head):
slow = head
fast = head
while fast and fast.next:
# 两个node是否都defined,如果fast.next不存在,则fast.next.next也不成立
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
if slow == fast:
slow = head
while slow != fast:
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next
return fast
return none
complexity
time: o(n)
space: o(1)
链表总结
- 多数需要dummy_head来节省对head的特殊处理
- 因为单链表的特性,几乎都需要遍历
- 双指针/快慢指针以彼此的间隔距离弥补长度的差距实现同步指向



发表评论