
1 es数据格式
elasticsearch 是面向文档型数据库,一条数据在这里就是一个文档。为了方便大家理解,可以将 elasticsearch 里存储文档数据和关系型数据库 mysql 存储数据的概念进行一个类比。es 里的 index 可以看做一个库,而 types 相当于表,documents 则相当于表的行。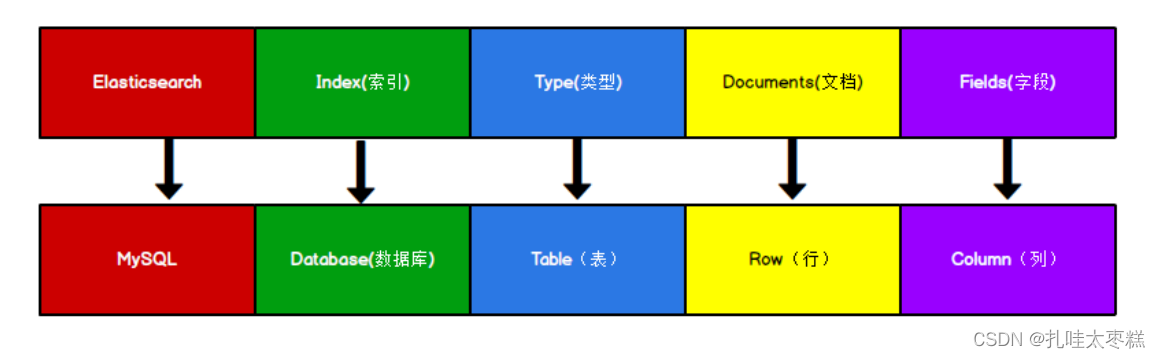
2 es基础操作
2.1 索引的增删查
2.1.1 创建索引
2.1.2 查询索引
查询指定索引
查看所有的索引信息
2.1.3 删除索引
2.2 映射操作
映射就像是mysql数据表中对字段的限制一样,映射可以指定文档的类型以及能否使用索引
2.2.1 创建映射
{
"properties": {
"title": {
"type": "text",
"index": true
},
"category": {
"type": "keyword",
"index": true
},
"images": {
"type": "text",
"index": false
},
"price": {
"type": "long",
"index": true
}
}
}
2.2.2 查看映射
2.3 文档的增删改查
2.3.1 创建文档
向指定索引中添加文档(随机id)
向指定索引中添加文档(指定id)
如果通过以上请求创建文档的话,会对该文档返回一个随机生成的_id,后面需要通过该_id对文档进行查询。显而易见,这个随机生成的_id并不容易记忆,于是我们可以通过加一层请求的方式指定文档的_id进行创建
2.3.2 查询文档
查询指定索引下的指定文档
查询指定索引下的所有文档
2.3.3 修改文档
覆盖性修改(全量更新)
字段修改(局部更新)
2.3.4 删除文档
3 复杂查询
3.1 条件分页查询
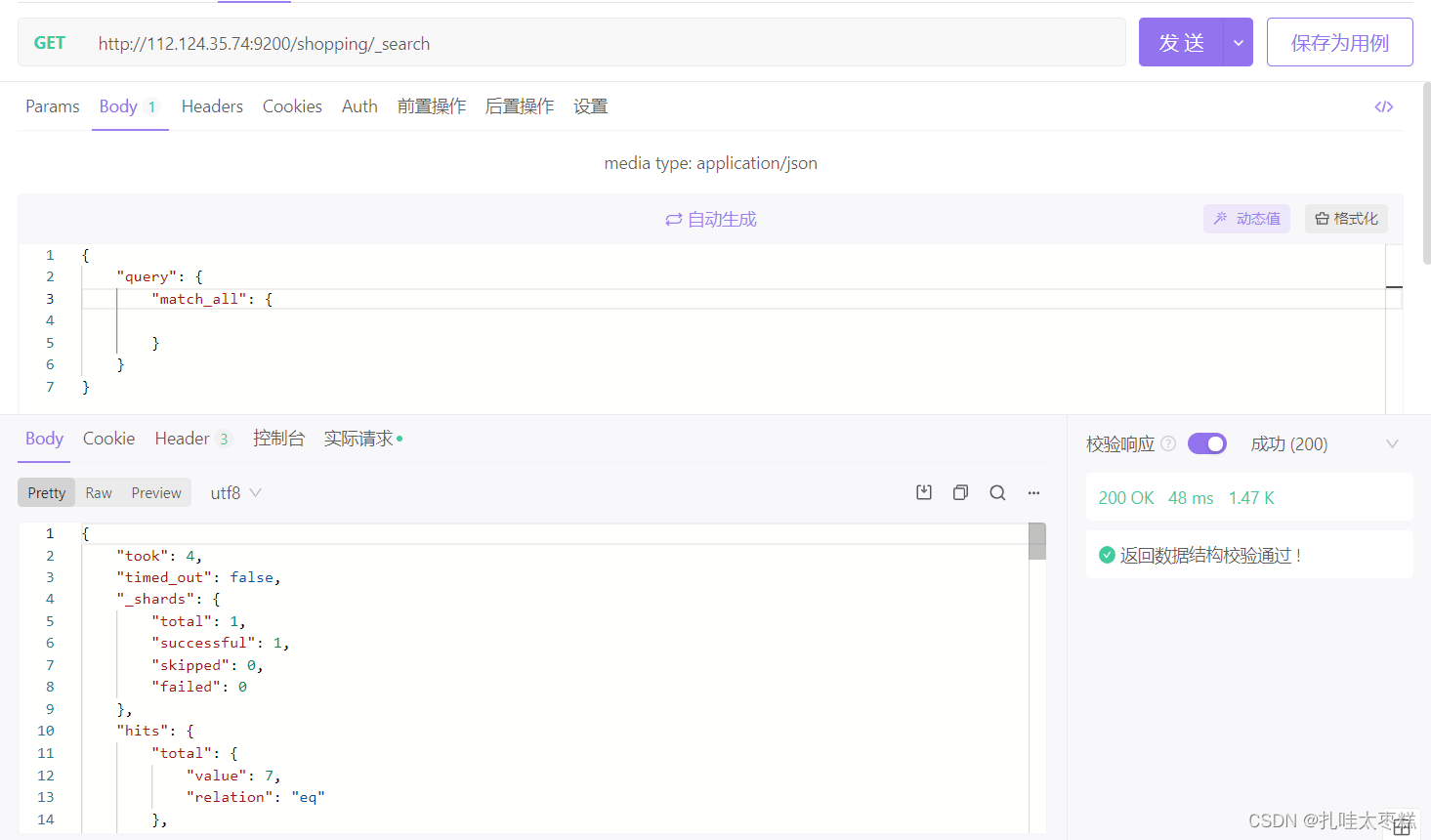
3.1.1 查询所有
{
"query": {
"match_all": {
}
}
}
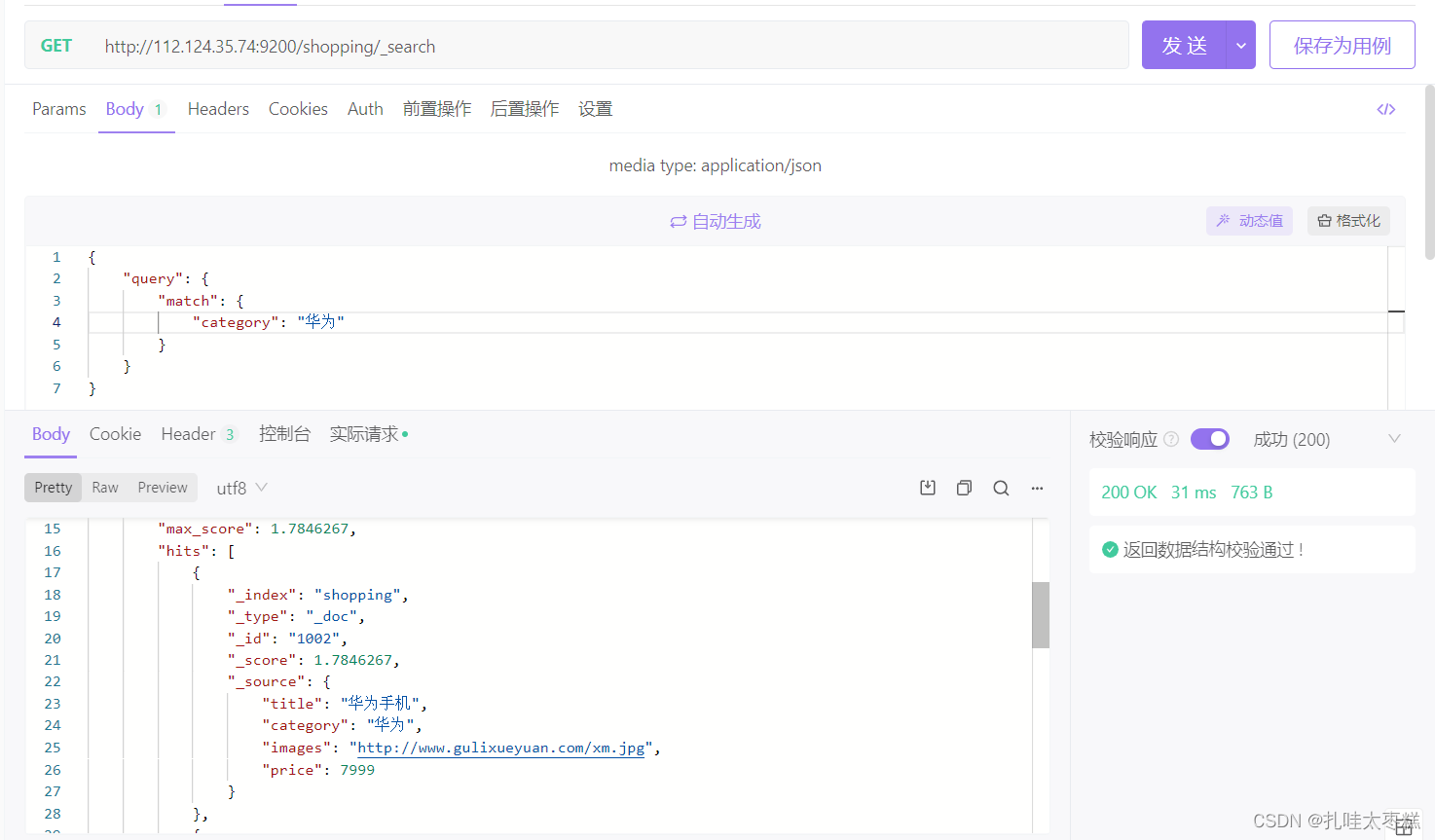
3.1.2 条件查询
{
"query": {
"match": {
"category": "华为"
}
}
}
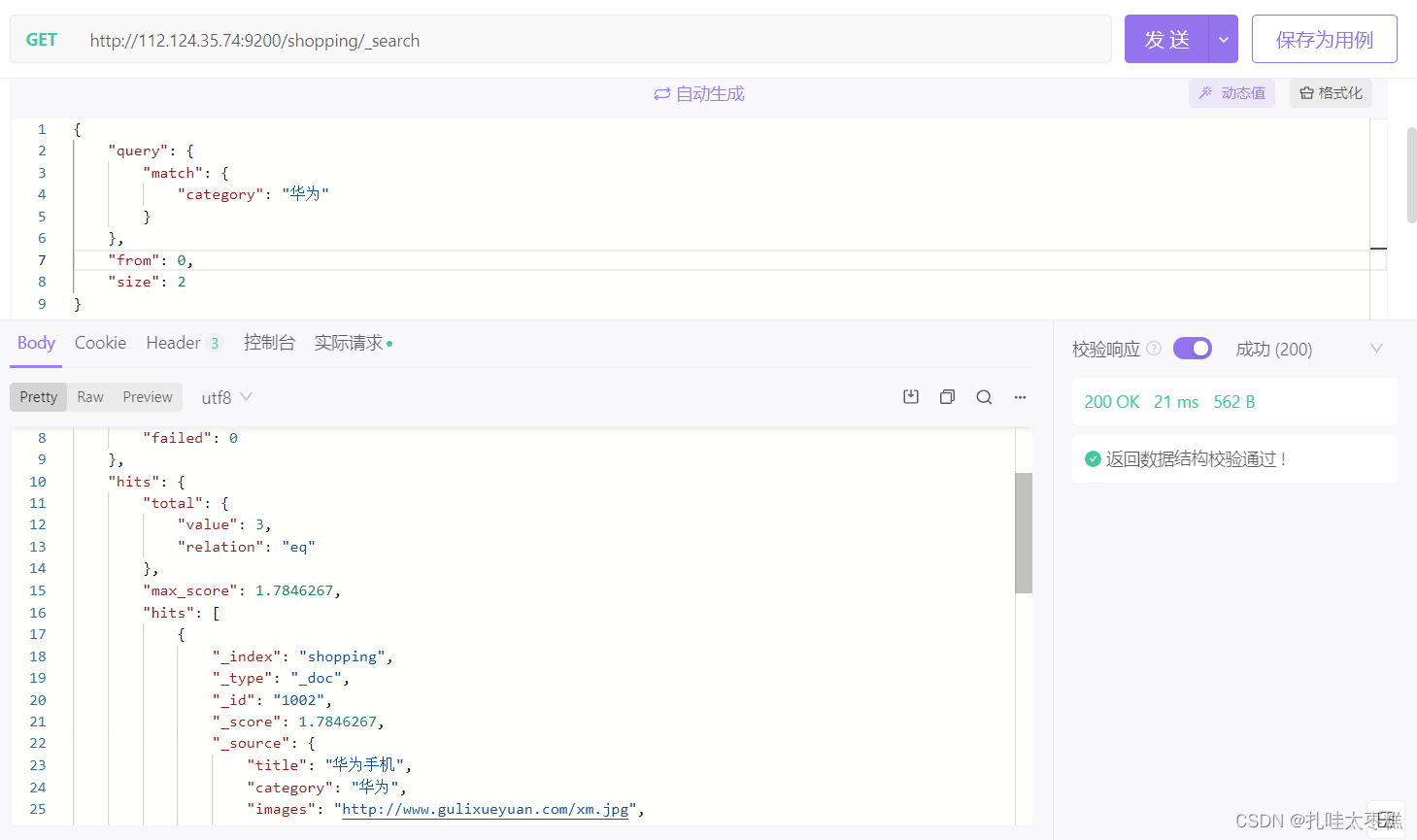
3.1.3 分页条件查询
{
"query": {
"match": {
"category": "华为"
}
},
"from": 0,
"size": 2
}
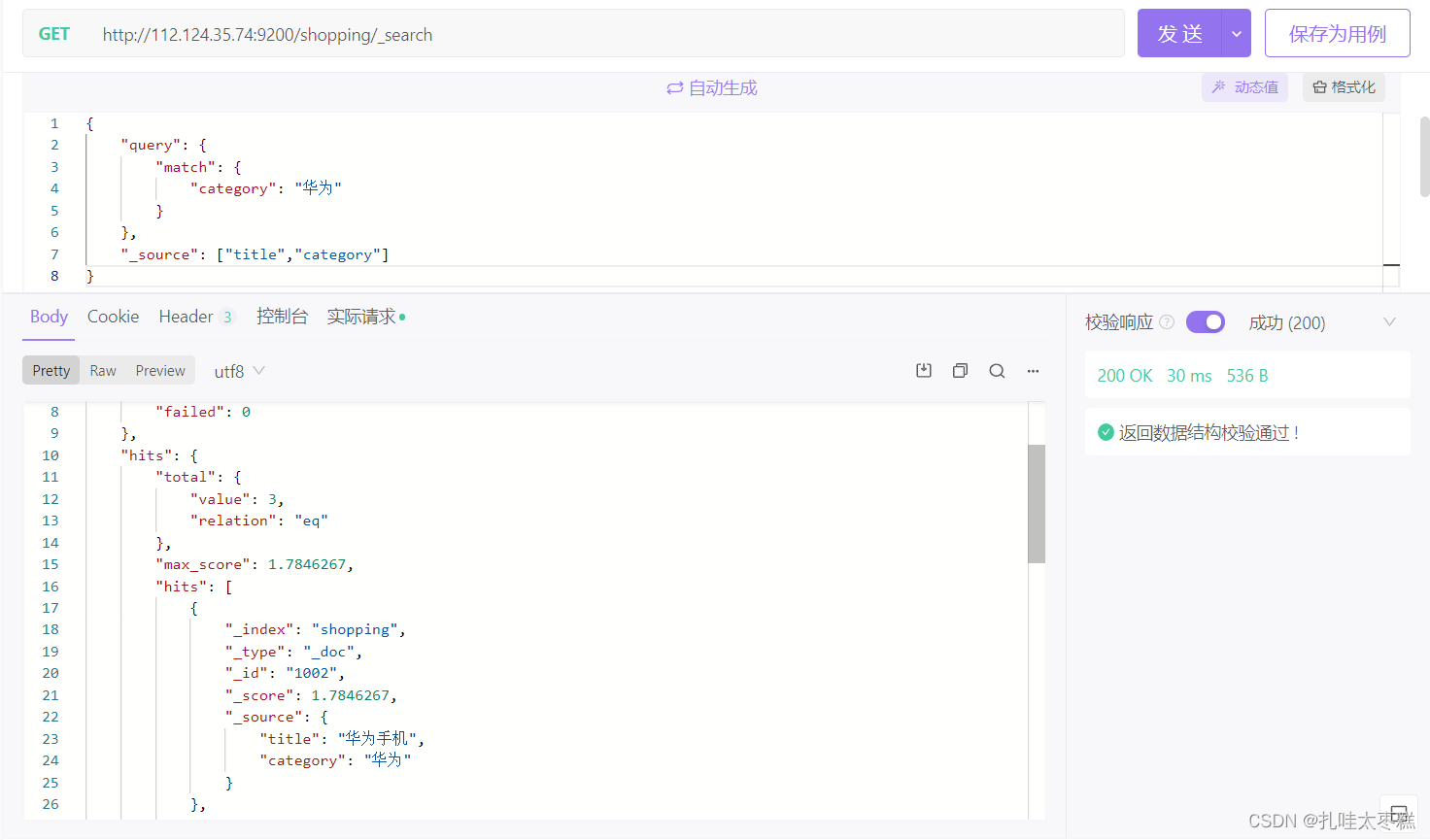
3.1.4 指定字段返回
可以通过"_source"字段指定返回结果的字段值
{
"query": {
"match": {
"category": "华为"
}
},
"_source": ["title","category"]
}
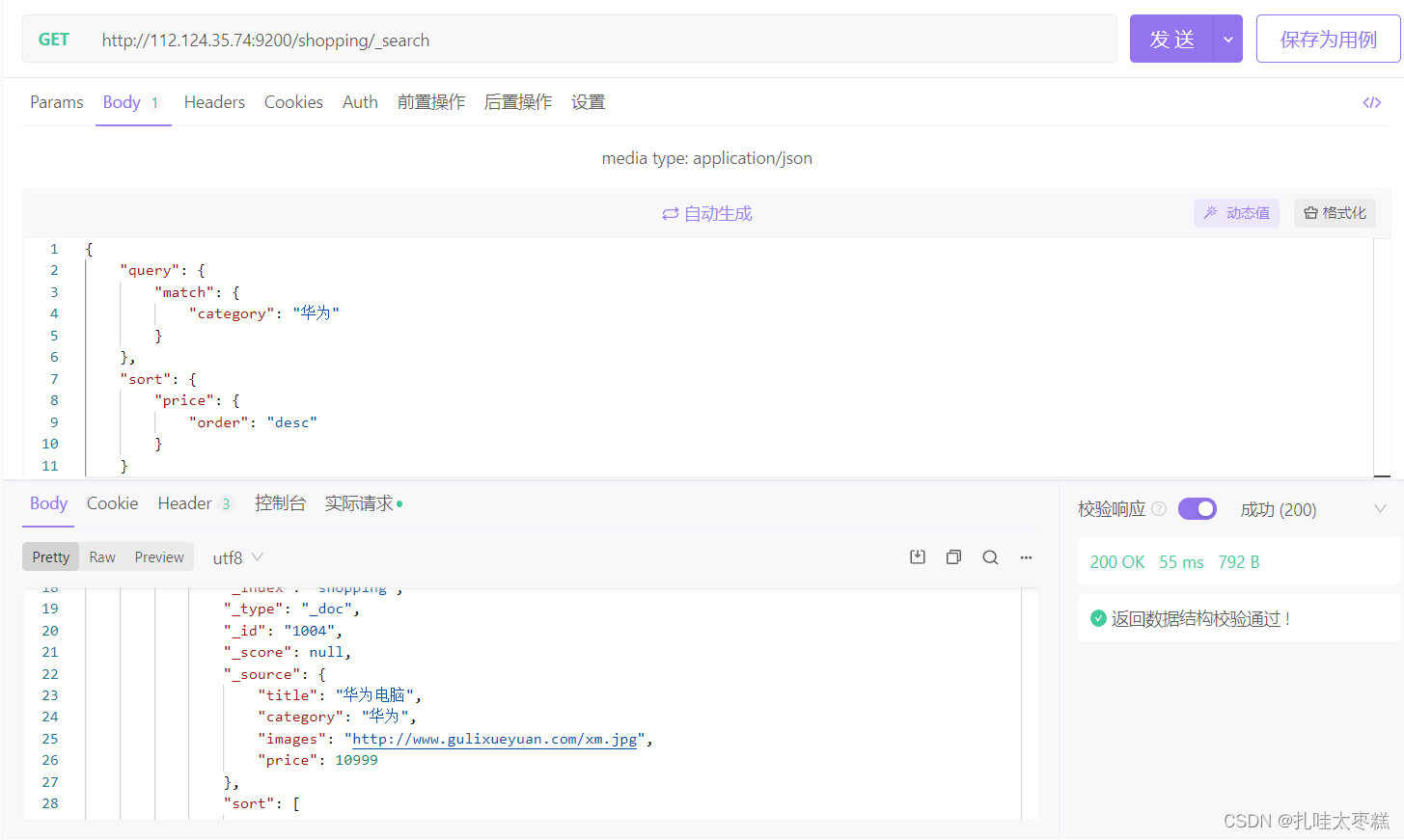
3.1.5 指定字段排序
可以通过"sort"字段指定字段进行排序及其顺序,desc降序asc升序
{
"query": {
"match": {
"category": "华为"
}
},
"sort": {
"price": {
"order": "desc"
}
}
}
3.2 多字段查询
3.2.1 and条件
must = and,转sql ——> where category = "华为" and price = 10999
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"match": {
"category": "华为"
}
},
{
"match": {
"price": 10999
}
}
]
}
}
}
3.2.2 or条件
should = or,转sql ——> where category = "华为" or category = "小米"
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"should": [
{
"match": {
"category": "华为"
}
},
{
"match": {
"category": "小米"
}
}
]
}
}
}
3.2.3 值范围查询
| es | 对应英文全拼 | sql |
|---|---|---|
| gt | greater than | > |
| gte | greater than or equal | >= |
| lt | less than | < |
| lte | less than or equal | <= |
以下es的json请求体转sql ——> where price >= 100 and price <= 4000
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"filter": {
"range": {
"price": {
"gte": 100,
"lte": 4000
}
}
}
}
}
}
3.2.4 全文检索、完全匹配
全文检索
使用“match”进行检索的话,会将条件“卡拉米”拆成单个的字,也就是说当所有数据中category字段包含以上三个字中的任何一个查出来。
于是下面的这个json,把category为小米的文档全查出来了。如果"category": "华米"的话将查出来所有的category包含“华“和”米”的文档都查出来,也就是说小米和华为
{
"query": {
"match": {
"category": "卡拉米"
}
}
}
完全匹配
如果将“match”改为“match_phrase”的话,就将是完全匹配。也就是说再使用以下json进行查询的话就会没有数据返回,除非换成“小米”或者“华为”这种全等的条件
{
"query": {
"match_phrase": {
"category": "华米"
}
}
}
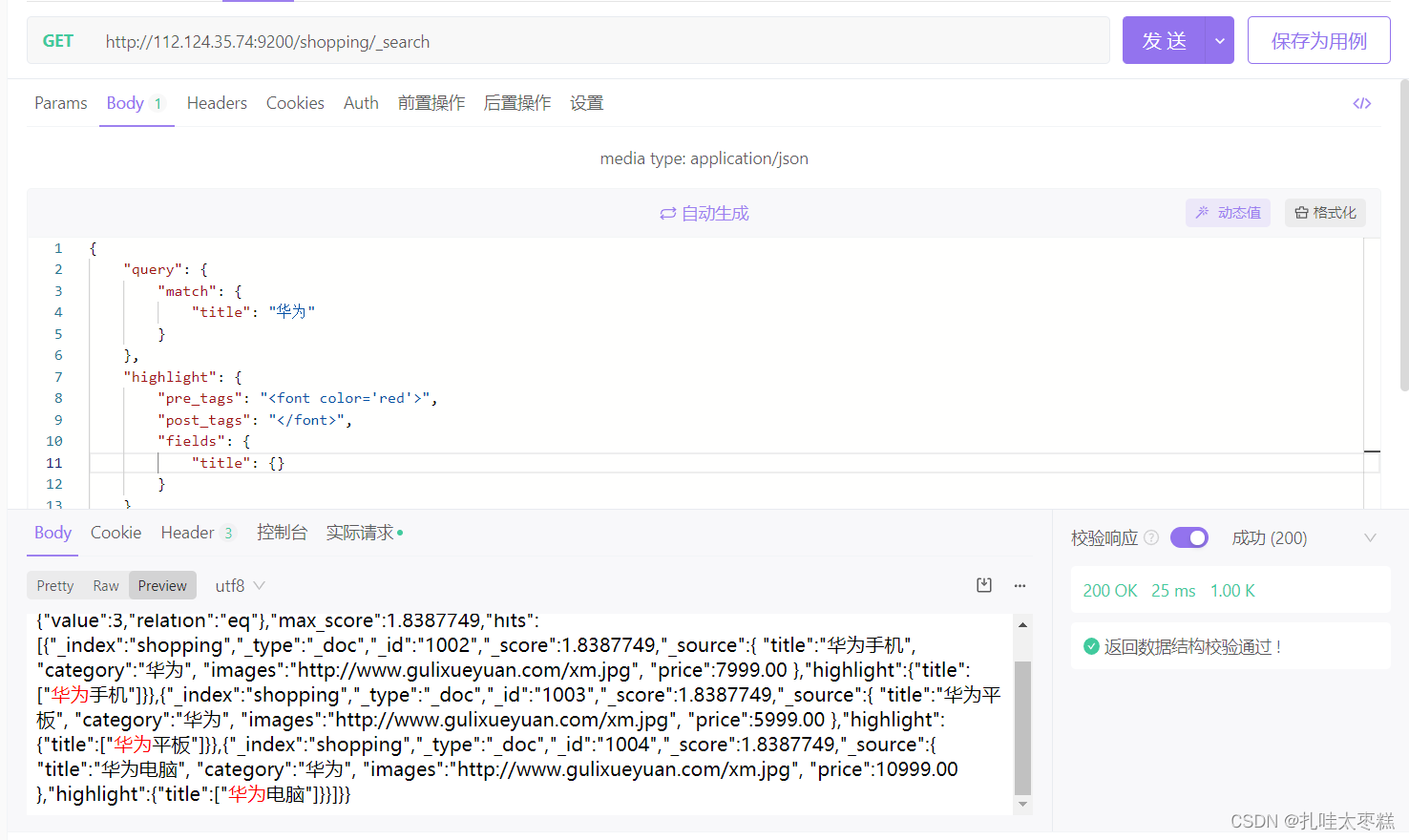
3.2.5 高亮返回
"highlight"字段,"pre_tags"和"post_tags"属性分别是高亮标签的前置标签和后置标签,将fields中指定字段的满足match的字拼接标签高亮返回
{
"query": {
"match": {
"title": "华为"
}
},
"highlight": {
"pre_tags": "<font color='red'>",
"post_tags": "</font>",
"fields": {
"title": {}
}
}
}
3.3 函数查询
下述函数查询与高亮highlight正好相反,他们只支持数字类型字段的查询
3.3.1 分组group by
terms = group by,转sql ——> group by price
{
"aggs": {
"price_groupby": { // 自定义命名
"terms": {
"field": "price"
}
}
}
}
3.3.2 求和sum
sum = sum( ),转sql ——> select sum(price)
{
"aggs": {
"sum_price": {
"sum": {
"field": "price"
}
}
},
"size": 0
}
3.3.3 求平均值avg
avg = avg( ),转sql ——> select avg(price)
{
"aggs": {
"avg_price": {
"avg": {
"field": "price"
}
}
},
"size": 0
}
3.3.4 最大值max
max = max( ),转sql ——> select max(price)
{
"aggs": {
"max_price": {
"max": {
"field": "price"
}
}
},
"size": 0
}
3.3.5 最小值min
min = min( ),转sql ——> select min(price)
{
"aggs": {
"min_price": {
"min": {
"field": "price"
}
}
},
"size": 0
}
3.3.6 一次返回count/max/min/avg/sum
{
"aggs": {
"stats_price": {
"stats": {
"field": "price"
}
}
},
"size": 0
}
3.3.7 去重后取总数
cardinality = distinct + count( ),转sql ——> select distinct count(price)
{
"aggs": {
"cardinality_price": {
"cardinality": {
"field": "price"
}
}
},
"size": 0
}

发表评论