合并两个有序链表
第一种思路
直接创建一个空链表,分别判断两个原链表的元素大小,升序插入到新链表中,但是此方法可能会超出时间限制(每一次都需要判断新链表的头节点是否为空),代码重复执行太多。
typedef struct listnode listnode;
struct listnode* mergetwolists(struct listnode* list1, struct listnode* list2) {
//判断为空链表
if(list1==null){
return list2;
}
if(list2==null){
return list1;
}
listnode* l1=list1;
listnode*l2=list2;
//创建的新链表
listnode*newhead,*newtail;
newhead=newtail=null;
while(l1&&l2)
{
if(l1->val < l2->val)
{
//l1拿下来尾插
if(newhead==null){
newhead=newtail=l2;
}
else{
newtail->next=l1;
newtail=newtail->next;
}
l1=l1->next;
}
else
{
//l2拿下来尾插
if(newhead==null){
newhead=newtail=l2;
}
else{
newtail->next=l2;
newtail=newtail->next;
}
l2=l2->next;
}
}
//跳出循环,要么l1先为空,要么l2先为空
if(l2)
{
newtail->next=l2;
}
if(l1)
{
newtail->next=l1;
}
return newhead;
}
第二种思路
优化:让新链表不为空,判断两个原链表元素大小后,直接插入到新链表中
typedef struct listnode listnode;
struct listnode* mergetwolists(struct listnode* list1, struct listnode* list2) {
//判断为空链表
if(list1==null){
return list2;
}
if(list2==null){
return list1;
}
listnode* l1=list1;
listnode*l2=list2;
//创建的新链表(链表不为空)
listnode*newhead,*newtail;
//newhead=newtail=null;
newhead=newtail=(listnode*)malloc(sizeof(listnode));
while(l1&&l2)
{
if(l1->val < l2->val)
{
//l1拿下来尾插
newtail->next=l1;
newtail=newtail->next;
l1=l1->next;
}
else
{
//l2拿下来尾插
newtail->next=l2;
newtail=newtail->next;
l2=l2->next;
}
}
//跳出循环,要么l1先为空,要么l2先为空
if(l2)
{
newtail->next=l2;
}
if(l1)
{
newtail->next=l1;
}
//动态申请的空间要手动释放掉
listnode* ret=newhead->next;
free(newhead);
newhead=null;
return ret;
}
环形链表的约瑟夫问题
环形链表的约瑟夫问题——牛客网

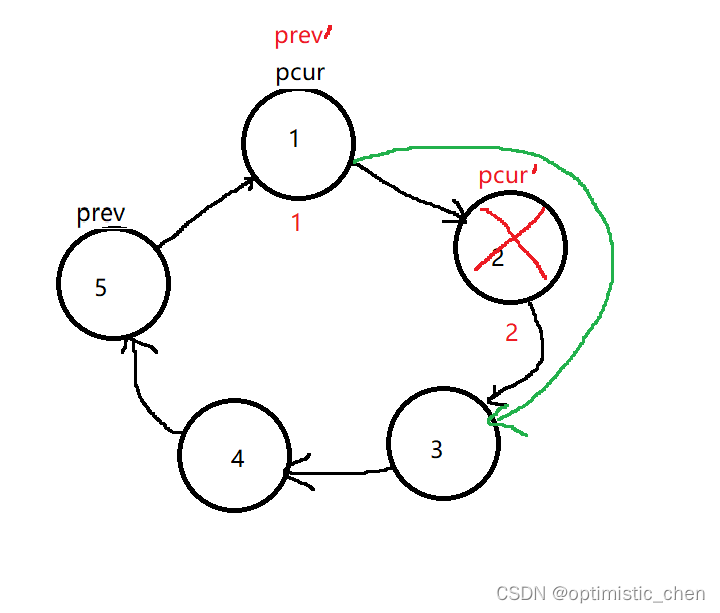
环形链表与我们平时见到的链表不同的是:他的尾节点的next指针指向头节点,而不是null。
typedef struct listnode listnode;
//创建节点
listnode*buynode(int x)
{
listnode*node=(listnode*)malloc(sizeof(listnode));
if(node==null)
{
exit(1);
}
node->val=x;
node->next=null;
return node;
}
listnode*createcircle(int n)
{
//先创建第一个节点
listnode*phead=buynode(1);
listnode*ptail=phead;
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++)
{
ptail->next=buynode(i);
ptail=ptail->next;
}
//首位相连
ptail->next=phead;
return ptail;
}
int ysf(int n, int m ) {
//第一步,根据n创建带环链表
listnode*prev=createcircle(n);
listnode*pcur=prev->next;
//第二步记数
int count=1;
while(pcur->next!=pcur)
{
if(count==m)
{
//销毁pcur节点
prev->next=pcur->next;
free(pcur);
pcur=prev->next;
count=1;
}
else
{
prev=pcur;
pcur=pcur->next;
count++;
}
}
//此时剩下的一个节点就是要返回的值
return pcur->val;
}
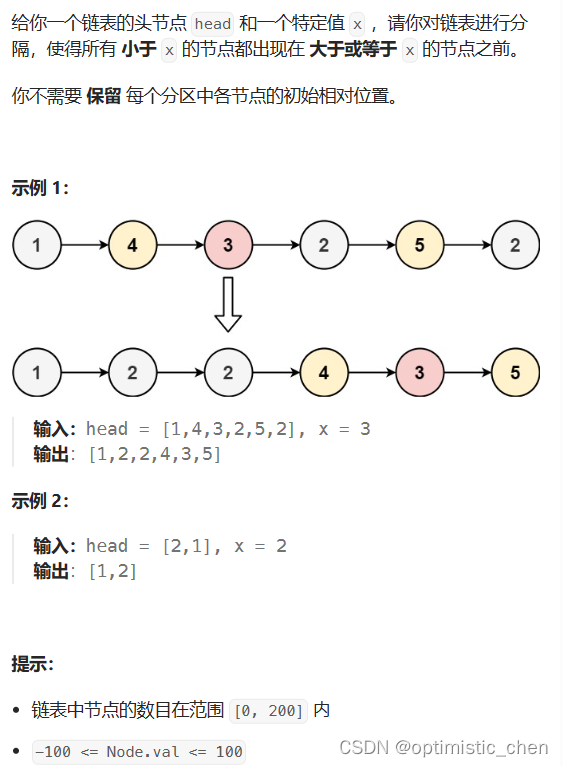
分割链表
第一种思路
双指针法:
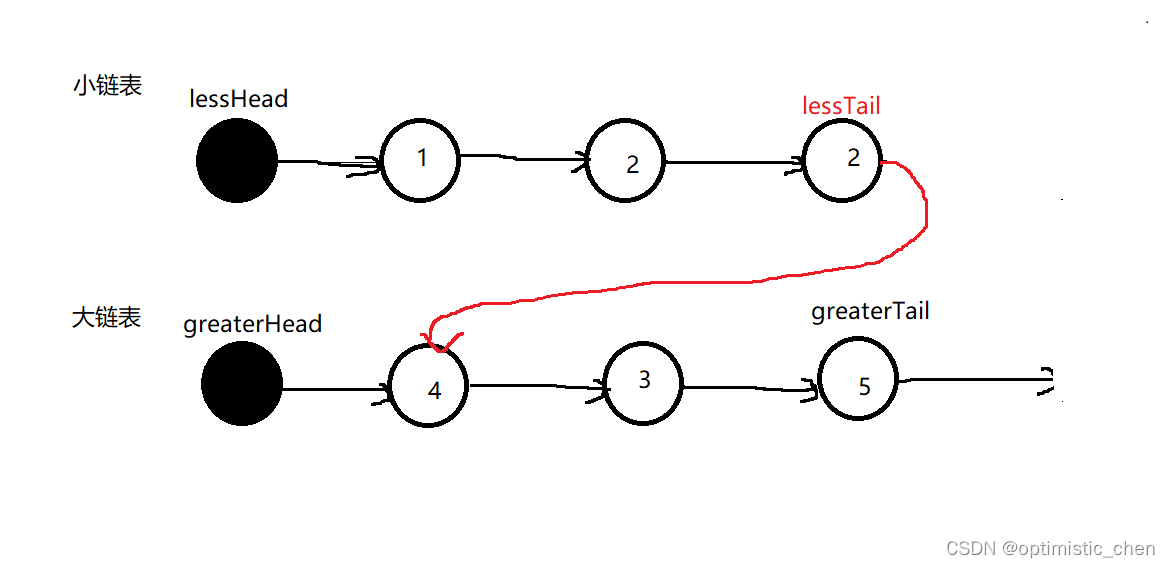
1.创建大,小两个新链表。
2.将小于特定值的节点放到小链表中,将大于等于特定值的节点放到大链表中
3.小链表的尾节点和大链表的第一个有效节点首尾相连
typedef struct listnode listnode;
struct listnode* partition(struct listnode* head, int x){
if(head==null)
{
return head;
}
//创建两个带头链表
listnode*lesshead,*lesstail;
listnode*greaterhead,*greatertail;
lesshead=lesstail=(listnode*)malloc(sizeof(listnode));
greaterhead=greatertail=(listnode*)malloc(sizeof(listnode));
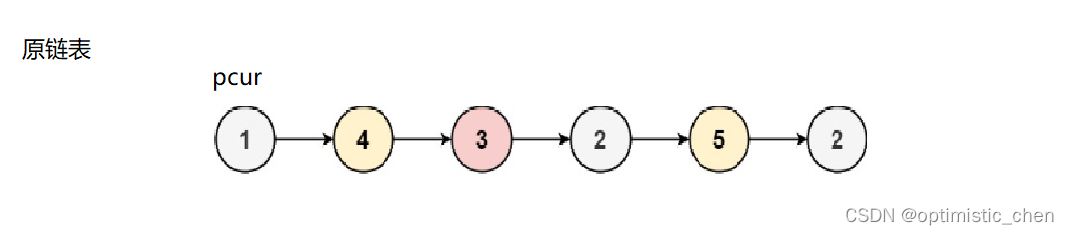
//遍历原链表,将原链表中的节点尾插到大小链表中
listnode*pcur=head;
while(pcur)
{
if(pcur->val<x)
{
//尾插到小链表中
lesstail->next=pcur;
lesstail=lesstail->next;
}
else
{
//尾插到大链表中
greatertail->next=pcur;
greatertail=greatertail->next;
}
pcur=pcur->next;
}
//修改大链表的尾节点的next指针指向
greatertail->next=null;
//小链表的尾节点和大链表的第一个有效节点首尾相连
lesstail->next=greaterhead->next;
listnode*ret=lesshead->next;
free(lesshead);
free(greaterhead);
lesshead=greaterhead=null;
return ret;
}
第二种思路
headnode哨兵结点:用于头插;tail尾指针用于尾插;cur表示当前链表结点;
遍历链表依次用链表结点元素值与x比较;小于则头插;大于则尾插;
这里有一个小细节就是头插时,如果尾指针等于哨兵headnode则需更新tail指向尾结点
struct listnode* partition(struct listnode* head, int x){
struct listnode* headnode=(struct listnode*)malloc(sizeof(struct listnode));
struct listnode* tail=headnode,*cur=head;
tail->next=null;
while(cur){
struct listnode* next=cur->next;
if(cur->val<x){
cur->next=headnode->next;
headnode->next=cur;
if(tail==headnode){
tail=cur;
}
}else{
tail->next=cur;
tail=cur;
cur->next=null;
}
cur=next;
}
return headnode->next;
}
完结
好了,这期的分享到这里就结束了~
如果这篇博客对你有帮助的话,可以点一个免费的赞并收藏起来哟~
可以点点关注,避免找不到我~
我们下期不见不散~~
这个链表题目还会继续,敬请期待~



发表评论