【数据结构——链表深度探索】从实现到应用,保姆级攻略

🍁1. 链表的介绍
链表是数据结构中一种非常重要的基础结构,它不同于数组,链表中的元素在物理存储上并不连续,而是通过指针(或引用)连接在一起。在java中,链表的应用非常广泛,尤其是在需要动态添加或删除元素的场景中。
🍁2. 链表的实现
🍁2.1 单向链表
单链表中的每个元素都称为节点(node),每个节点包含两个部分:一部分存储数据(value),另一部分存储指向列表中下一个节点的引用(next)。最后一个节点的next引用为null,表示链表的结束。
public class mysinglelist {
static class listnode {
public int value;
public listnode next;
public listnode(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
}
public listnode head;
}
还可以创建一个ilist接口,对其中的增删查改等方法进行规范,之后mysinglelist对接口进行实现
public interface ilist {
void display();
int size();
boolean contains(int key);
void addfirst(int key);
void addlast(int key);
void addindex(int key,int index);
void remove(int key);
void removeallkey(int key);
void clear();
}
接下来就是方法的实现
🍁2.1.1 size()
只需要将head依次往末尾移动,并记录移动次数进行返回就可以了,当head为null时就表示已经遍历完成
public int size() {
listnode cur = head;
int cnt = 0;
while (cur != null) {
cnt++;
cur = cur.next;
}
return cnt;
}
🍁2.1.2 display()
遍历的话需要找到头节点,接着依次往后移动,为了不该变头节点的指向,创建一个cur节点辅助遍历,同样的,结束的标志也是最后的指向不为空
public void display() {
listnode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
system.out.print(cur.value + " ");
cur = cur.next;
}
system.out.println();
}
🍁2.1.3 contains(int key)
public boolean contains(int key) {
listnode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.value == key) {
return true;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return false;
}
🍁2.1.4 addfirst(int key),addlast(int key),addindex(int key, int index)
头插比较简单,直接创建一个节点,并初始化值,指向原来的head节点,接着改为新的head节点
public void addfirst(int key) {
listnode node = new listnode(key);
node.next = head;
head = node;
}
尾插就需要判断head节点是否为null,接着找到尾节点进行插入
public void addlast(int key) {
listnode node = new listnode(key);
//头结点为null,直接插入
if (head == null) {
head = node;
return;
}
//找到尾节点进行插入
listnode cur = head;
while (cur.next != null) {
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = node;
}
在指定索引插入就更加麻烦一些,需要对传入的索引进行判断,如果是0.就调用头插的方法,如果等于链表的长度,就调用尾插的方法,如果是中间的索引,就遍历链表,找到该索引进行插入
public void addindex(int key, int index) {
listnode node = new listnode(key);
//调用头插
if (index == 0) {
addfirst(key);
return;
}
//调用尾插
if (index == this.size()) {
addlast(key);
return;
}
//传入索引不合法的情况
if (index < 0 || index > this.size()) {
throw new indexoutofboundsexception();
}
//找到目标索引进行插入
listnode cur = head;
while (index - 1 != 0) {
cur = cur.next;
index--;
}
node.next = cur.next;
cur.next = node;
}
🍁2.1.5 remove(int key),removeallkey(int key)
如果head为空,直接返回,如果head的value就是目标元素,就把head的下一个节点作为头结点,其他情况就根据value的值寻找目标索引,如果没找到就返回,也就是cur节点为null,找到的话把cur的引用指向cur的之后第二个节点
//根据元素找到目标索引
private listnode findindexofket(int key) {
listnode cur = head;
while (cur.next != null) {
if (cur.next.value == key) {
return cur;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return null;
}
public void remove(int key) {
//头结点为空
if (head == null) {
return;
}
//头结点为目标元素
if (head.value == key) {
head = head.next;
}
//其他节点为目标元素
listnode cur = findindexofket(key);
if (cur == null) {
return;
}
cur.next = cur.next.next;
}
需要有两个指针,同时往后遍历,删除cur节点所指元素需要将pre节点的next指向cur的next,循环判断,最后还要判断head节点是否为指定元素
public void removeallkey(int key) {
//头结点为null,直接返回
if (this.head == null) {
return;
}
listnode pre = head;
listnode cur = head.next;
//循环删除
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.value == key) {
pre.next = cur.next;
cur = cur.next;
} else {
pre = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
//判断头结点
if (head.value == key) {
head = head.next;
}
}
🍁2.1.6 clear()
清空链表只需要遍历链表所有节点,将每一个节点置为null即可,因为是从头结点开始,如果直接将head置为null,后续再找head.next就会报错,所以还需要用一个中间变量cur辅助遍历
public void clear() {
listnode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
//创建变量,解决空指针异常
listnode curn = cur.next;
cur = null;
cur = curn.next;
}
head = null;
}
🍁2.2 双向链表
双向链表有两个指针域,一个指向前一个节点,一个指向后一个节点
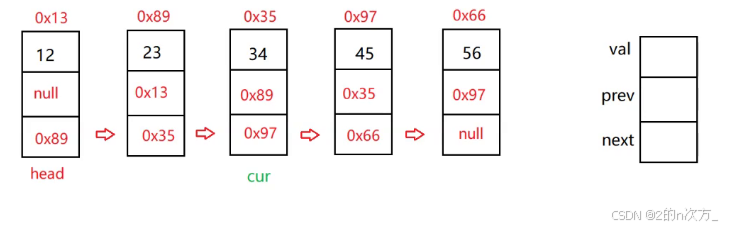
public class mylinkedlist implements ilist {
static class tlistnode {
public int value;
tlistnode pre;
tlistnode next;
public tlistnode(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
}
public tlistnode head;
public tlistnode last;
}
双向链表的size() ,display(),contains(int key)和单向链表是一样的,下面来实现其他的方法
🍁2.2.1 addfirst(int key)
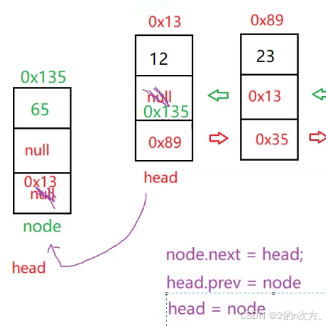
public void addfirst(int key) {
tlistnode node = new tlistnode(key);
if (head == null) {
head = last = node;
} else {
node.next = head;
head.pre = node;
head = node;
}
}
🍁2.2.2 addlast(int key)
public void addlast(int key) {
tlistnode node = new tlistnode(key);
if (head == null) {
head = last = node;
} else {
last.next = node;
node.pre = last;
last = last.next;
}
}
🍁2.2.3 addindex(int key, int index)
public void addindex(int key, int index) {
tlistnode node = new tlistnode(key);
if(index < 0 || index > size()) return;
if (index == 0) {
addfirst(key);
return;
}
if (index == size()) {
addlast(key);
}
if (index > 0 && index < size()) {
tlistnode cur = head;
//可以直接到indext的位置,因为双向链表可以找到前一个节点
while (index-- != 0) {
cur = cur.next;
}
node.next = cur;
cur.pre.next = node;
node.pre = cur.pre;
cur.pre = node;
}
}
需要修改四个位置,把要插入的节点node的next 指向cur,再把cur.pre的next指向node,此时节点的next都有了指向,接着node的pre指向cur.pre节点,cur的pre再指向node,此时就完成了插入
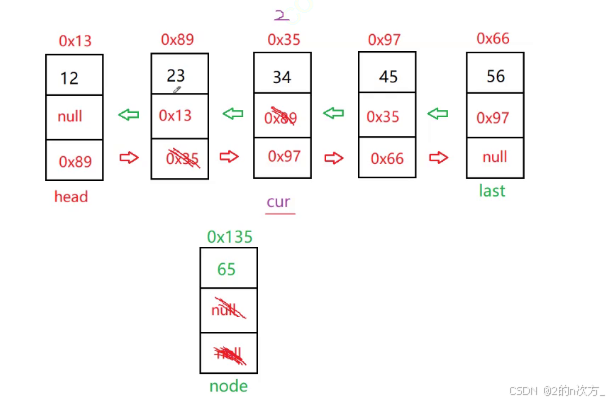
🍁2.2.4 remove(int key)和removeallkey(int key)
首先找到要删除的值的索引
private tlistnode findindexofket(int key) {
tlistnode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.value == key) {
return cur;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return null;
}
删除的时候还要考虑是否为头结点和尾节点
public void remove(int key) {
tlistnode cur = findindexofket(key);
if(cur == null){
return;
}
//头节点的情况
if(cur == head){
head = cur.next;
//只有一个节点时,指向next后head为null所以当head!=空时才能把pre置为null
if (head != null) {
head.pre = null;
}
}else{
cur.pre.next = cur.next;
//尾节点的情况
if(cur.next == null){
last = last.pre;
}else{
cur.next.pre = cur.pre;
}
}
}
相比于单向链表,双向链表的删除所有指定元素就非常简单了,只需要在原来删除一个的基础上稍加修改就可以了
public void removeallkey(int key) {
tlistnode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.value == key) {
if (cur == head) {
head = cur.next;
if (head != null) {
head.pre = null;
}
} else {
cur.pre.next = cur.next;
if (cur.next == null) {
last = last.pre;
} else {
cur.next.pre = cur.pre;
}
}
}
cur = cur.next;
}
}
🍁2.2.5 clear()
清空链表还是依次遍历每一个节点,把每一个节点都置为null,最后把head和last也置为null
public void clear() {
tlistnode cur = head;
while(cur.next!=null){
tlistnode curn = cur;
curn.pre = null;
curn.next = null;
cur = curn;
}
head = last = null;
}
🍁3. java中linkedlist的使用
🍁3.1 linkedlist的创建和使用
在上一篇数据结构arraylist的讲解中已经简单提到过👉,集合的一些基本框架,linkedlist也实现了list接口,所以也可以通过接口创建对象,也可以使用list接口中的方法
public class demo {
public static void main(string[] args) {
linkedlist<integer> list1 = new linkedlist<>();
list<integer> list2 = new linkedlist<>();
list1.add(1);
list1.add(2);
system.out.println(list1);
list2.add(1);
list2.add(3);
system.out.println(list2);
}
}
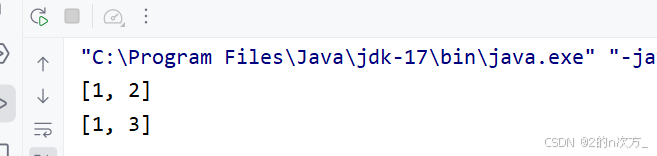
可以直接对linkedlist的对象进行打印,也就是说linkedlist重写了tosting方法

这些都是linkedlist中独有的方法,这里就不列举使用了,
🍁3.2 linkedlist的遍历
linkedlist的遍历和arraylist的遍历方式一样,在上一篇介绍了五种遍历方式,这次再简单回顾一下
public class demo {
public static void main(string[] args) {
linkedlist<integer> list1 = new linkedlist<>();
list1.add(1);
list1.add(2);
list1.add(3);
list1.add(4);
//迭代器 listiterator
listiterator<integer> lit = list1.listiterator();
while(lit.hasnext()){
system.out.print(lit.next() + " ");
}
system.out.println();
//iterator
iterator<integer> it = list1.iterator();
while(it.hasnext()){
system.out.print(it.next() + " ");
}
system.out.println();
//增强for
for(integer l : list1){
system.out.print(l + " ");
}
system.out.println();
//普通for
for(int i = 0;i < list1.size();i++){
system.out.print(list1.get(i) + " ");
}
system.out.println();
//lambda表达式
list1.foreach(e -> {
system.out.print(e + " ");
});
system.out.println();
}
}
🍁4. arraylist和linkedlist的区别
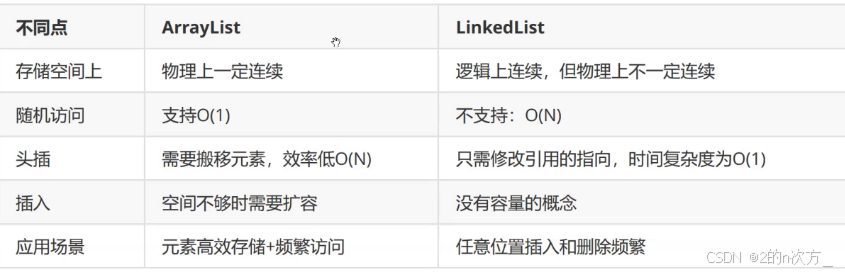
arraylist底层是一个动态数组
linkedlist底层是双向链表
arraylist:访问元素的时间复杂度为 o(1)(直接通过索引)。
linkedlist:访问元素的时间复杂度为 o(n)(需要从头或尾开始遍历到目标位置)。
arraylist:
在末尾添加元素的时间复杂度为 o(1)。
在中间插入或删除元素时,时间复杂度为 o(n),因为需要移动其他元素以保持连续的内存块。
linkedlist:
在任意位置添加或删除元素的时间复杂度为 o(1),只需改变前后节点的指针(需要先找到目标位置,时间复杂度为 o(n))。



发表评论